UNIT 6 Developmental Psychology
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
prenatal period
being pregnant during 9 months, from sex → birth
conception
sex, sperm into egg, forms a zygote
zygotic period
zygote in uterine wall, rapid cell division 2 WEEKS
embryonic stage
a small blob, mitosis, some organ development, at end heart heat and vital parts develop, mother need to be careful of environment, 1 MONTH AND A HALF
fetal stage
tiny baby blob, organs fully develop, gain weight at the last 2 months, weight 7 pounds and 20in length, 7 MONTHS
zygote
fertilized egg
germinal stage
zygote and rapid cell division, sex of the baby can be determined
embryo
a small blob
placenta
food and air from mother to embryo
teratogen
harmful substance for fetus, like certain chemicals and viruses, if mother consume can have birth defects or abnormalities
FAS
fetal alcohol syndrome, physical and cognitive abnormalities, babies who have alcoholic mother, looks like down syndrome symptoms
PKU
Phenylketonuria, can’t break down protein
Tay-saches diease
can’t break down lipids, builds up in system and destorys brain and nerve cells
down syndrome
extra chromosome in zygote
longitudinal study
one group over time
cross sectional
difference age groups at once, cohort effect that culture is the same
rooting reflex
move head around to find the root of cheek touch
suckling reflex
suck anything that touches lips
startle reflex
shocked, arms fling, spread fingers, arch back
babinski reflex
toe spread when sole of foot is stroked
maturation
biological growth process, change in behavior both physical and mental
attachment
children attach to people they are close with, emotional connection (parents)
imprinting
strong attach in early years of life, goes through critical learning period
critical period
exposure to certain stimuli leads to normal development, early in life
temperment
characteristic, how one responds
easy: easy to care for, adaptive
difficult: moody and intense, react neg and strong
slow to warm up: inactive, slow to respond, mild react
stranger anxiety
scared of strangers 8 month infants
secure attachment
children without mother is in distress, when mother is back they are comforted
insecure attachment
children without mother in distress, still distressed when mother comes back (mother neglect)
ambivalent attachment
type of insecure attachment with parents, may resist comfort of parent, show mixed pos and neg feelings response to parent
avoidant attachment
avoid the mother when they come back, trust issues, caregiver emotionally unavailable
anxious attachment
hard to feel secure in relationships, cling to caregivers
mary ainsworth
strange situation behavior(attachment)
konrad lorenz
imprinting, ducks, see how attachments work and they create security
harry and marry harlow
monkey study, attachment is contact comfort or nourishment?
diana baumrind
parenting styles
authoritative (mother)
support independence, some limit, dialogue with child
authoritarian (sound of music dad)
strict obedience, strong punishment (can’t talk or negotiate)
permissive (meemaw in young sheldon)
acceptance, freedom, low expectations
neglectful (jake peralta’s dad)
not focus on kid, doesn’t limit behavior and own need over child
schema
view of the world, building block to understand and perceive the world
children form schemas thru new situations and events
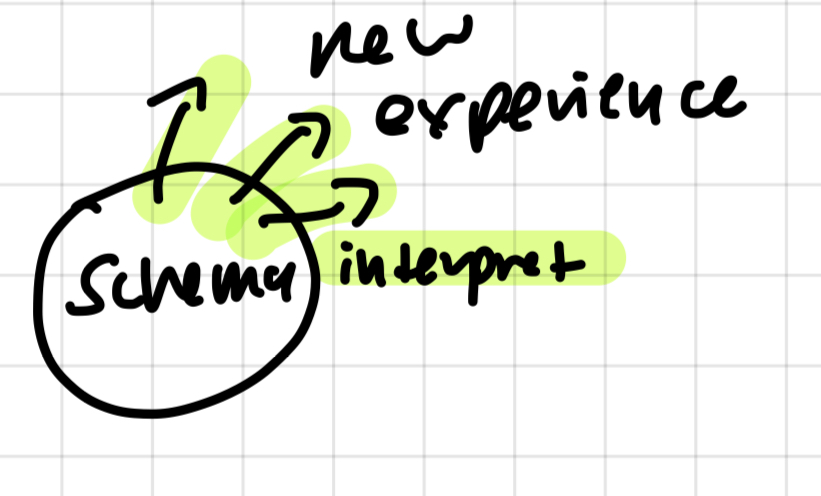
assimilation
take new info, interpret with existing schema
ex. every swimming thing is a fish
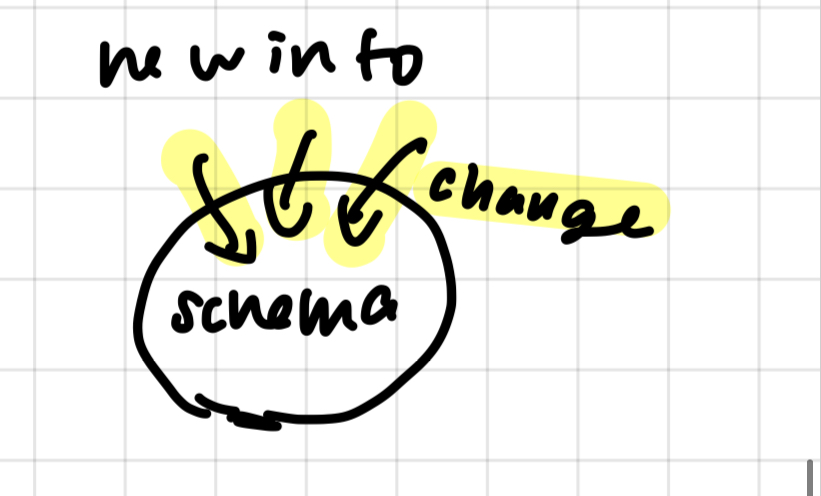
accomodation
change schema, adapting current schema with new info
sensorimotor stage
senses, motor to learn (looking, hearing, touching, mouthing, grasping)
object permanence, stranger/seperation anxiety
birth → age 2
object permanence
ability to understand objects still exist after they aren’t in sight
8-10 months
stranger/seperation anxiety
don’t leave! distressed
8 months
pre-operational stage
learn to use language, doesn’t comprehend mental ops of logic
mental representation of objects, egocentric, theory of mind, centration
2-7 age
mental representation of objects
pretend play
egocentric
can’t see any other POV than their own
theory of mind
can see others POV, sympathy
conservation
what you know, facts
ex. mass, volume, # remain the same even with changes in forms of objects
centration
what you see
focus on one aspect of situation, problem or object
ex. same number, but one looks longer
concrete operational stage
think logically, conservation, understand classification, reverse, memory improve, series of things
6-11 age
formal operational
abstract thinking, hypothetical situations, logic break down, consequence, moral reasoning
12+ age
continuous development
person’s mental, physical, emotional, social abilities gradually unfold over time
vygotsky
discontinuous development
series of stages, sudden shifts or leaps, linear and universal
piaget, erikson
Jean Piaget
child intellectual based on development stage they are in, develop of brain and cognition levels
Lev Vygotsky
learn at their own pace
zone of proximal development ZPD
stage between what child can do themselves and what they can’t do
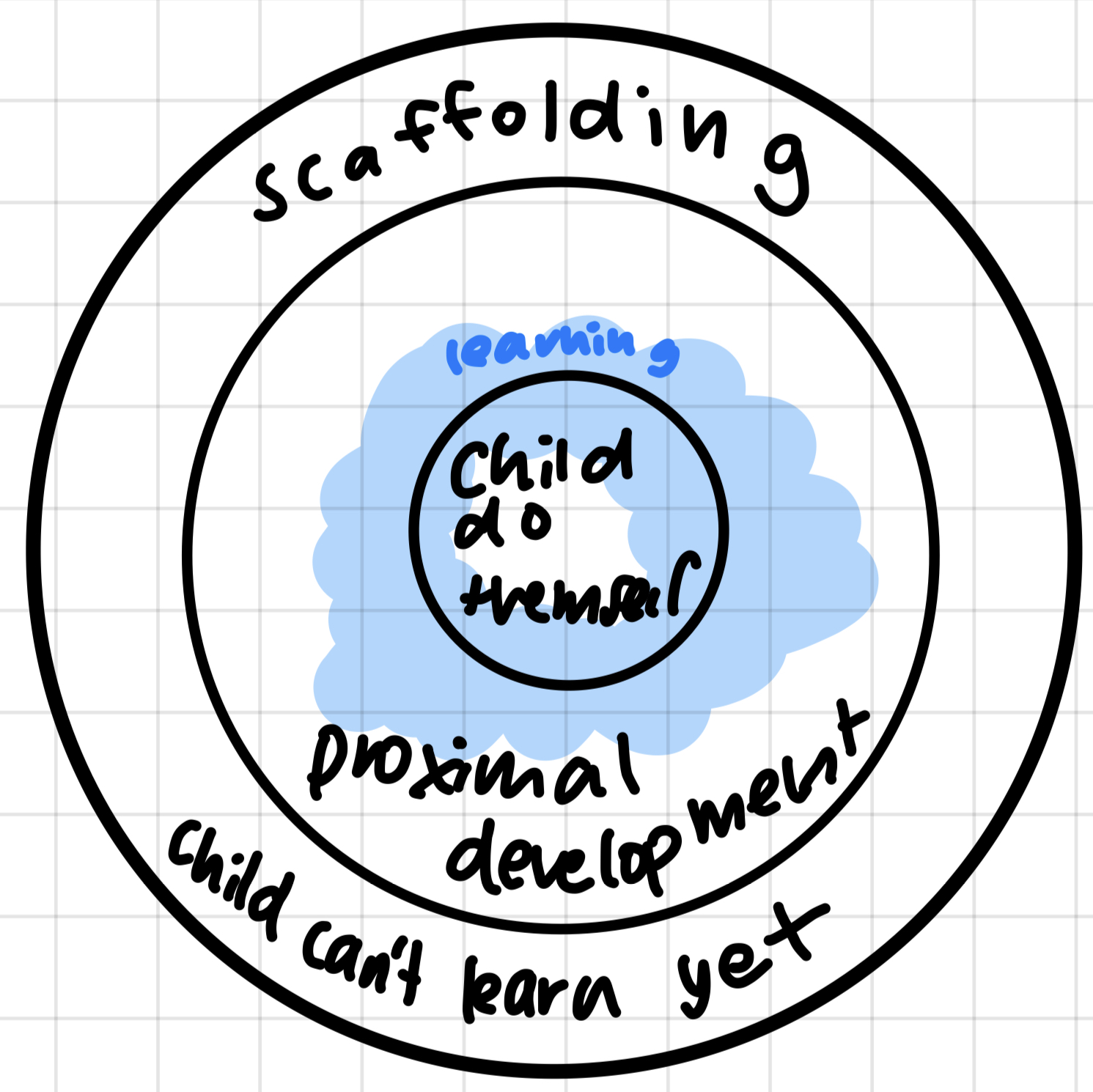
scaffolding
instructions to guide learners to learning, let them learn info
puberty
begin sexual maturity, physical changes, enviro changes
girls early mature is hard, boys late mature is hard
primary sex characteristics
organs for reproduction, ovaries and testes
secondary sex characteristics
non-reproductive (physical can see changes)
teenage conformity, frontal lobe not fully develop until 25
adolescent egocentrism
experiences are unique, no one understands
personal fables
stories made up to make teens feel invincible, special and center of attention
imaginary audience
think everyone is judging them and causes self conscious and anxiety
James Marcia
teenage identity, identity exploration, levels of finding identity
crisis
old values and choices are reexamined
commitment
dedication to role/value
foreclosure
set identity, doesn’t look at other options
high commitment and low exploration
identity diffusion
no set identity, doesn’t want to find one
low exploration low commitment
moratorium
no set identity but exploring possibilities
low commitment, high exploration
identity achievement
found identity, done exploration
high exploration high commitment
intimacy in adults
couples getting married later
after first child the couples drop in the marriage satisfaction
later people wait to get married, more divorces
having interpersonal needs lead to feelings of security
frustrated w interpersonal needs lead to anxious thoughts
social clock: when marry, when parent, when retire
aging
physical peak in 20s, faster, stronger, better coordinated, more endurance
physical decline is first symptom
decline in sperm count and decline in women fertility
menopause
no more period! around 40-50 age
fluid intelligence
to be able to solve problems, see relationships, think abstract
crystallised intelligence
intelligence gained over time, increase as you age
dementia
memory, thinking and behaviour deteriorate
alzheimer’s disease
memory loss is progressive, type of dementia
trust vs mistrust
develop sense of basic trust, 1 year old
autonomy vs shame and doubt
exercise, do things for themselves, doubt abilities, 1-2 years old
initiative vs guilt
initiate tasks, carry out plans, or feel guilty, 3-5 years old
competence vs inferiority
learn pleasure of applying themselves to tasks or else they feel inferior 6-12 years
identity vs role confusion
sense of self by testing roles and putting it into single identity, or be confused on who they are, 12-20 years old
intimacy vs isolation
struggle to form close relationships, love or socially isolated
generatively vs stagnation
discover sense of contributing to the world, thru family and work or may feel lack of purpose, 40s-60s
integrity vs despair
reflecting on his or her life, feel sense of satisfaction or failure, 60+
morality
standards that are generally accepted as right or proper
pre-conventional morality
morality to avoid punishment or gain reward (before age 9)
conventional morality
moral judgements based on society rules and values (teens)
post conventional morality
personal standards of right and wrong, abstract principles of justice
carol gillian
kohlberg theory is wrong, males and females are different bc male more logical and individual, female more care
sex
male or female biologically
gender
social and cultural differences between female and male, sterotyped
gender roles
expectations of sterotypes of men and women
different in culture and over time
gender identity
sense of being male or female (how you identify youself)
gender-typed
learning to be masculine or feminine, what you learn to be that way
self concept
overall idea of who a person thinks he or she is