THE Science Biology Quiz Flashcards
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Answer with DEFINITION
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the cell theory?
The cell is the basic unit of life.
All organisms are composed of one or more cells.
All cells come from pre-existing cells.
Prokaryotic Cells
a type of cell whose organelles are not surrounded by membranes and have no nucleus (unicellular)
Eukaryotic Cells
a type of cell whose organelles are surrounded by membranes, has a nucleus, and can be multicellular or unicellular.
Unicellular Organisms
organisms made up of one cell, can be made of eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells.
Multicellular Organisms
organisms made up of more than one cell, all made up of eukaryotic cells.
Characteristics of Living Things
Living things respond to their environment.
Living things need energy.
Living things grow.
Living things reproduce.
Living things must get rid of waste.
What are organelles?
Parts of a cell that allow for it to survive.
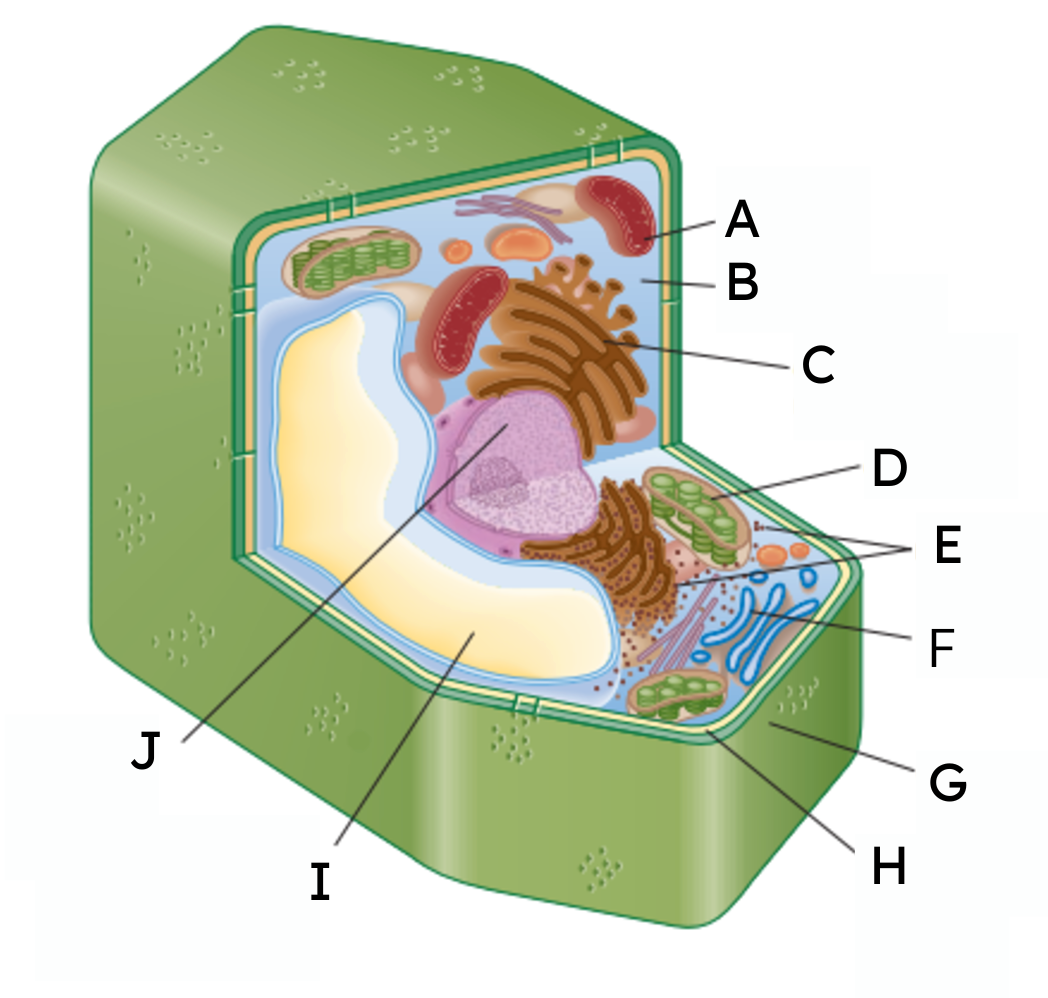
A
mitochondria
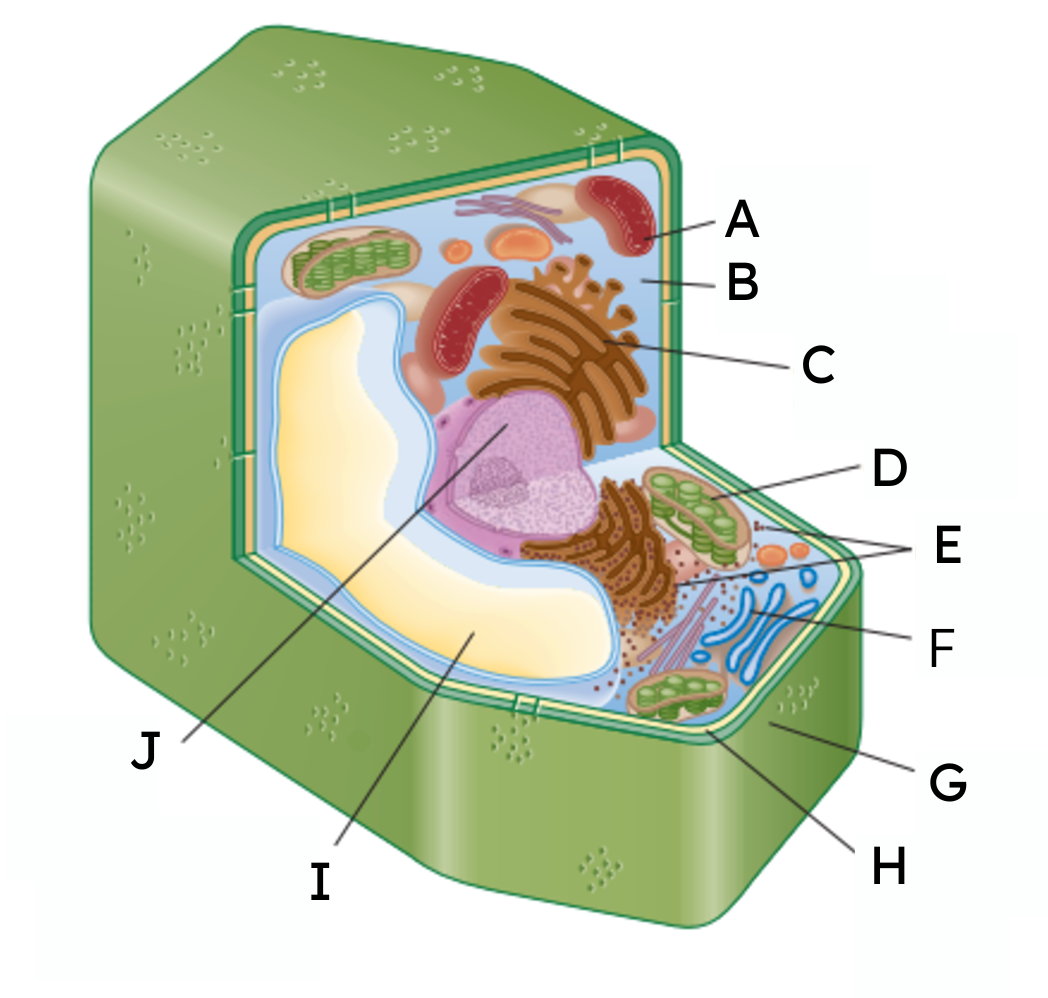
B
cytoplasm
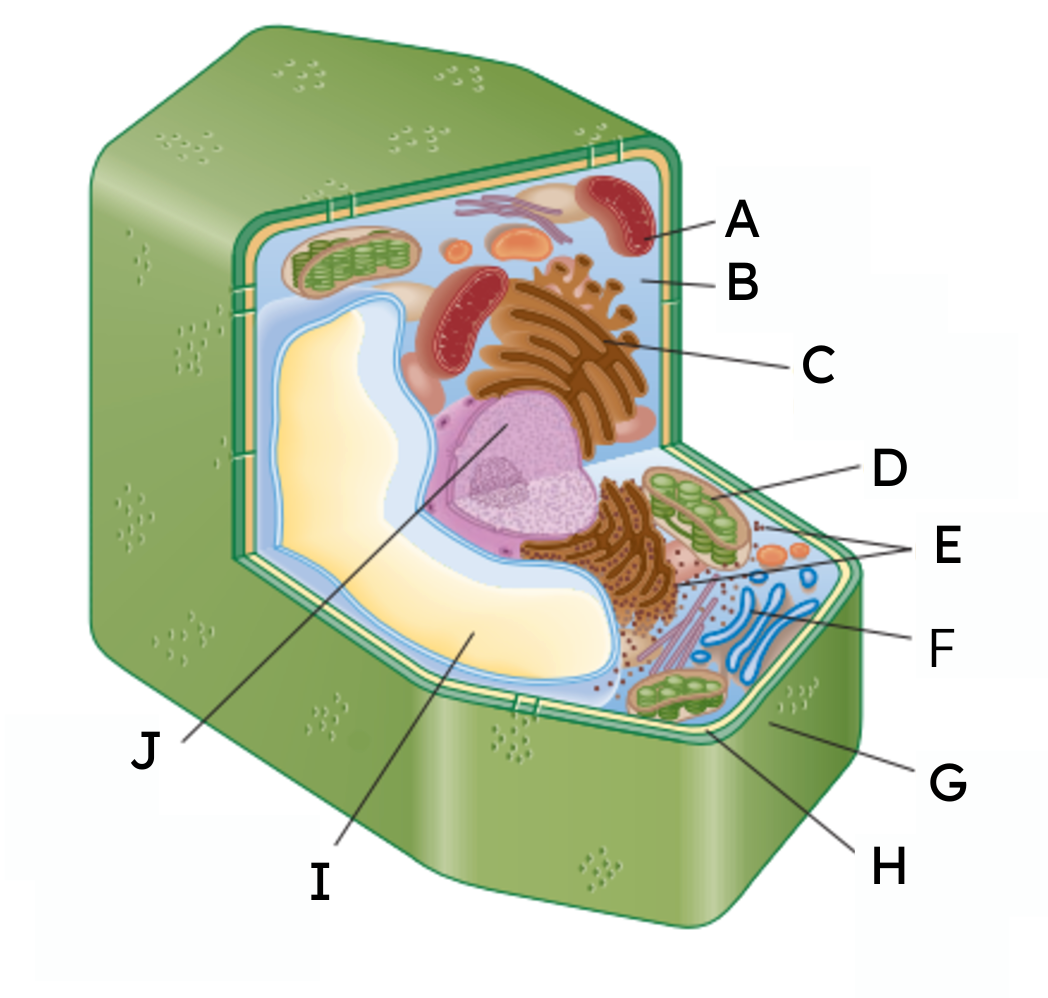
C
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
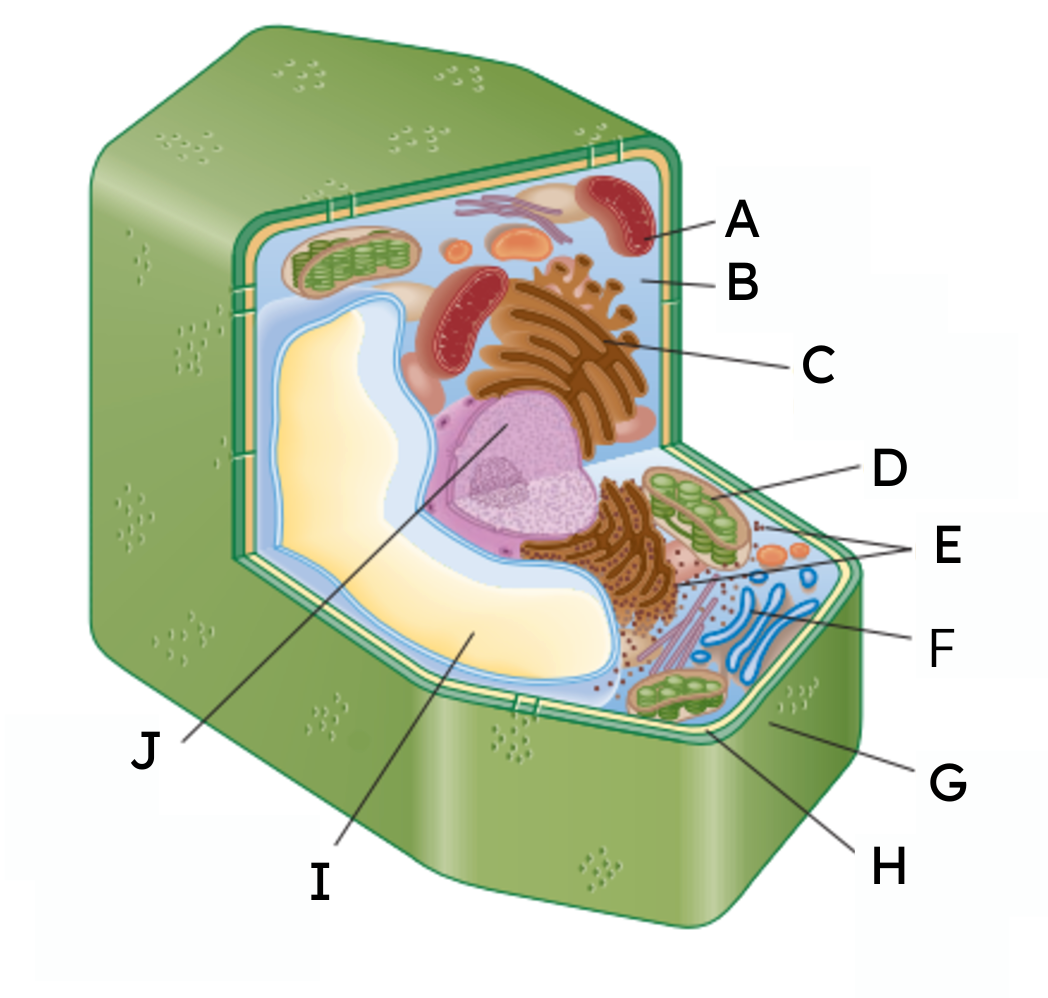
D
chloroplast
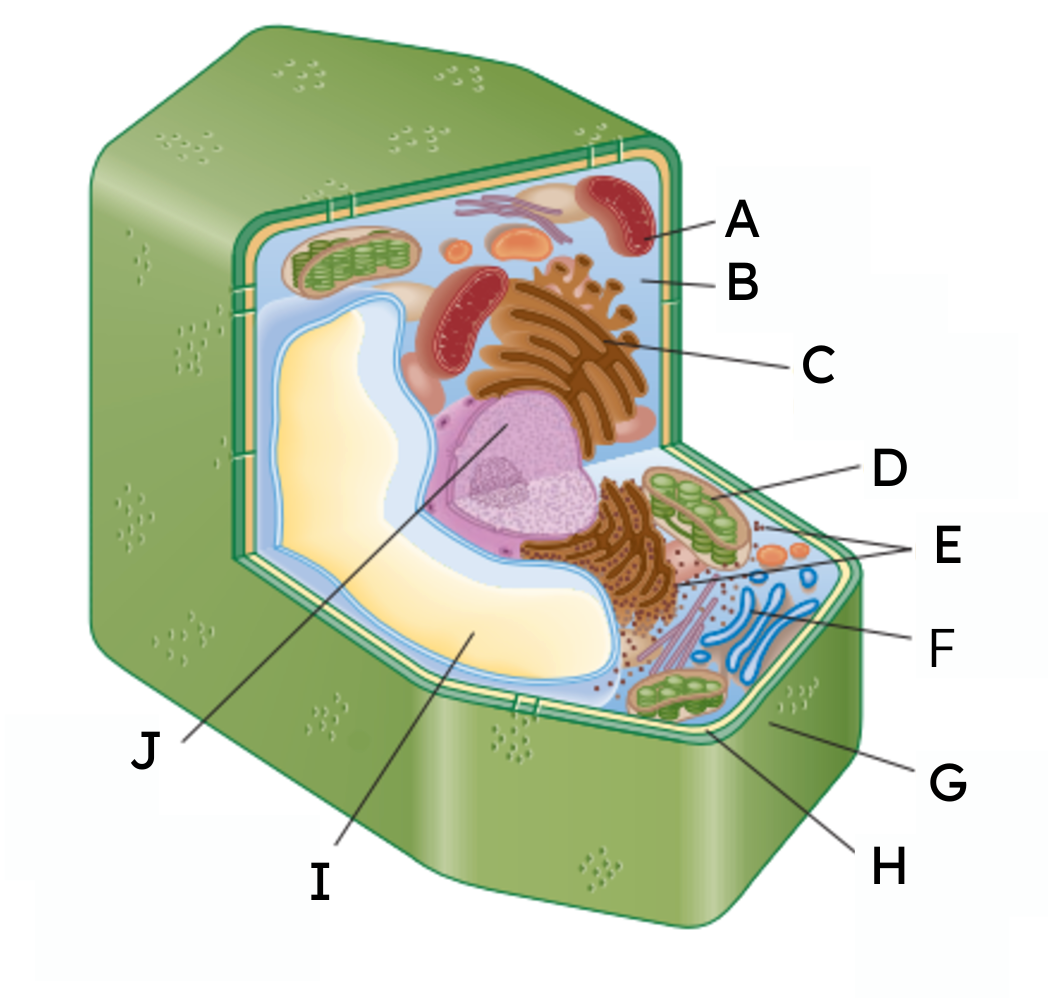
E
ribosomes
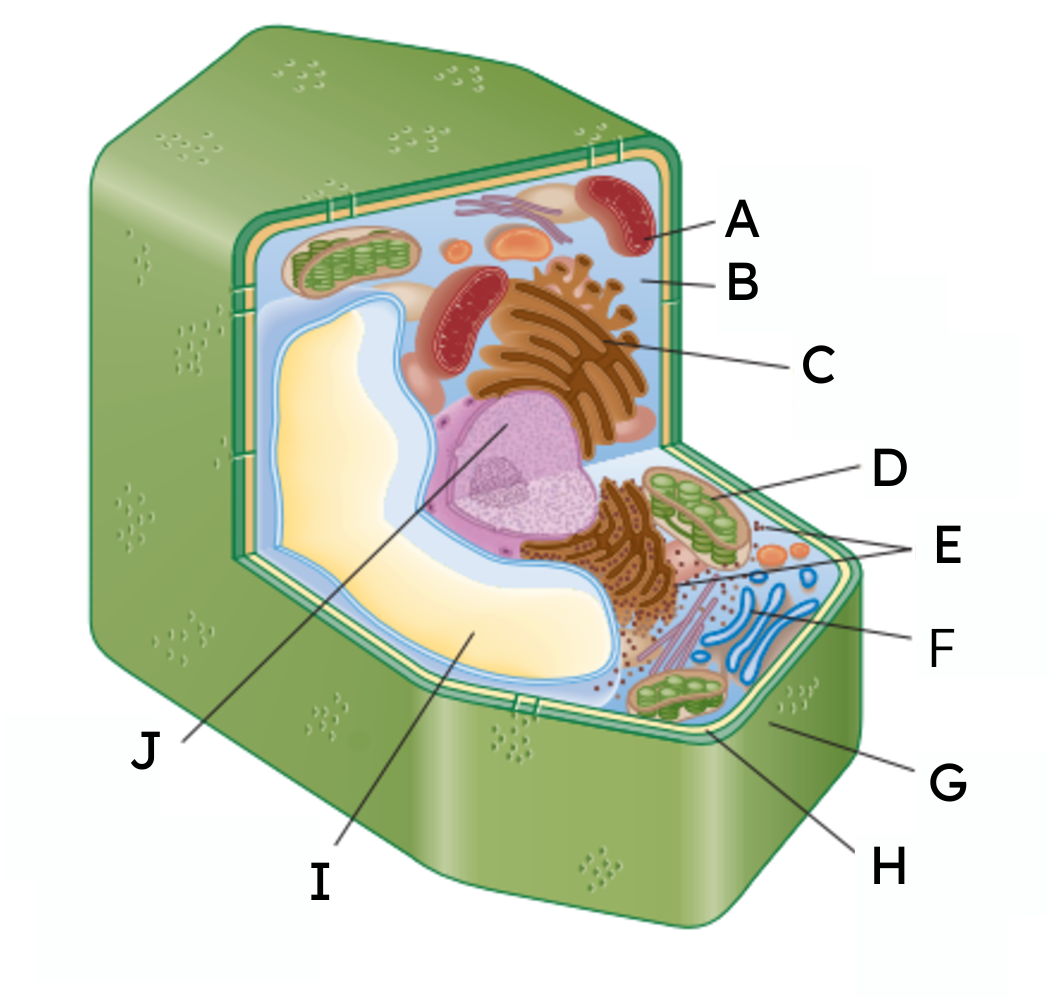
F
Golgi body
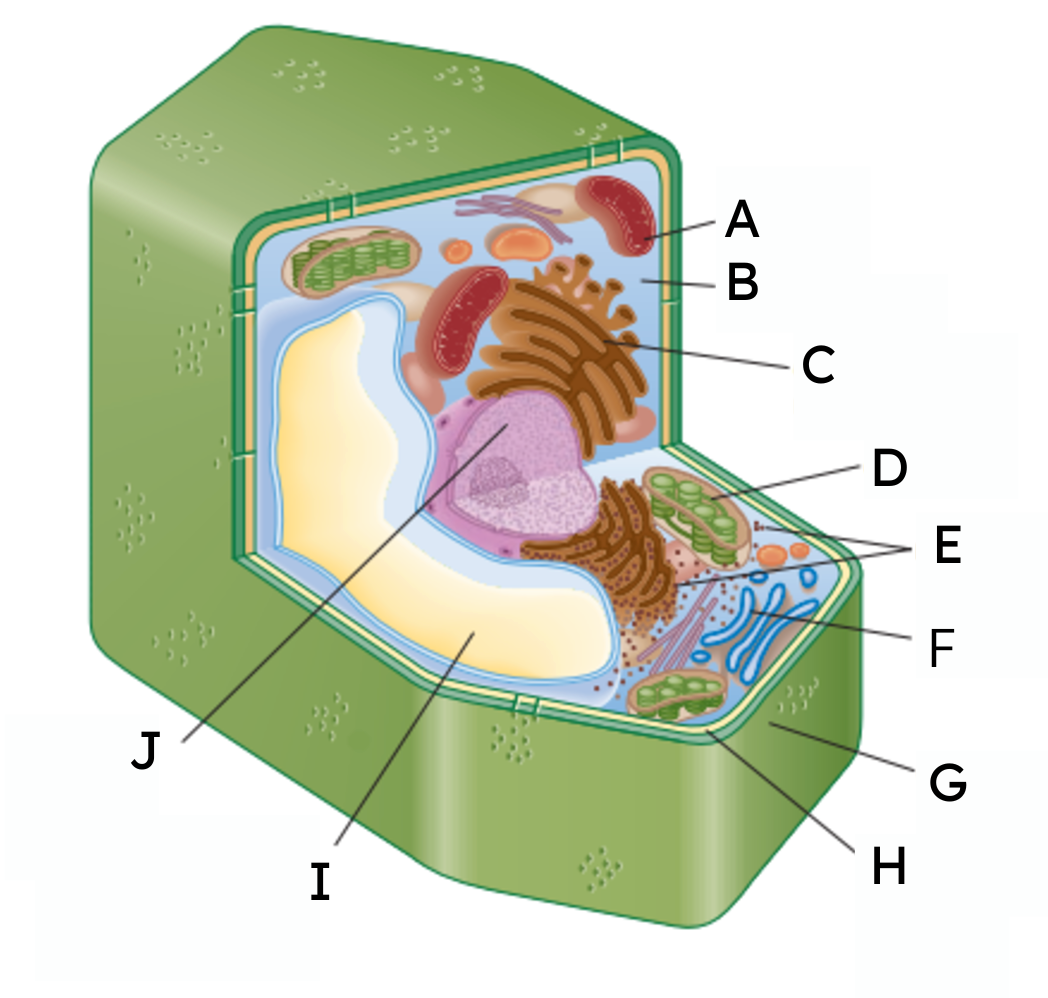
G
cell wall
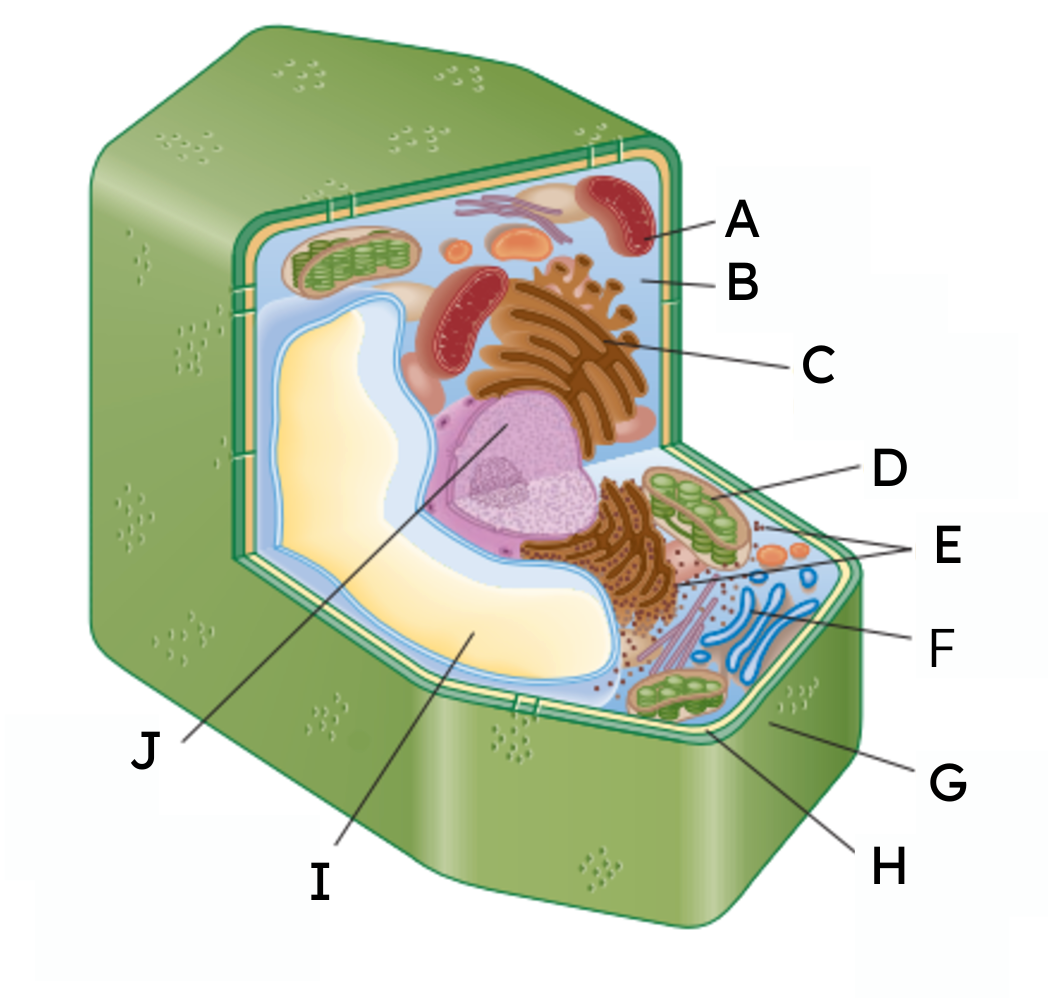
H
cell membrane
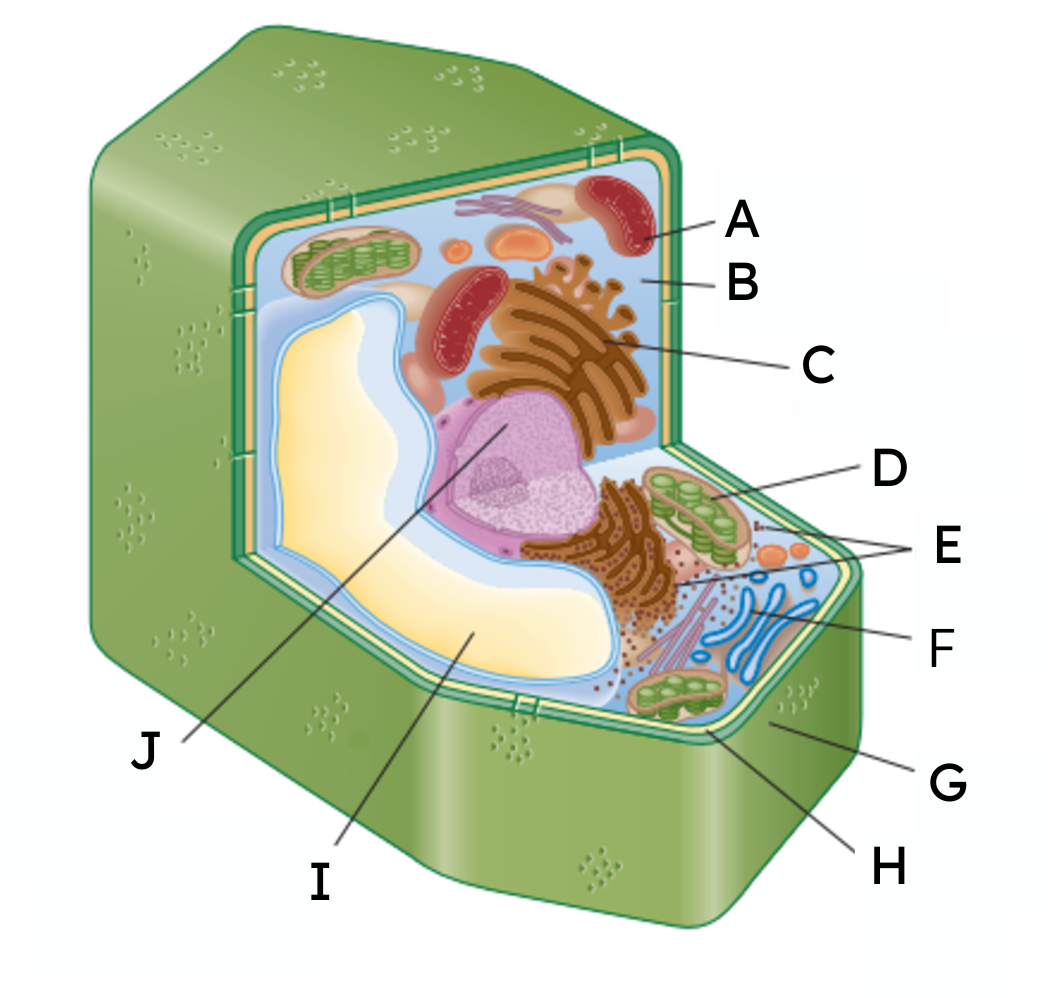
𝙸
vacuole

J
nucleus
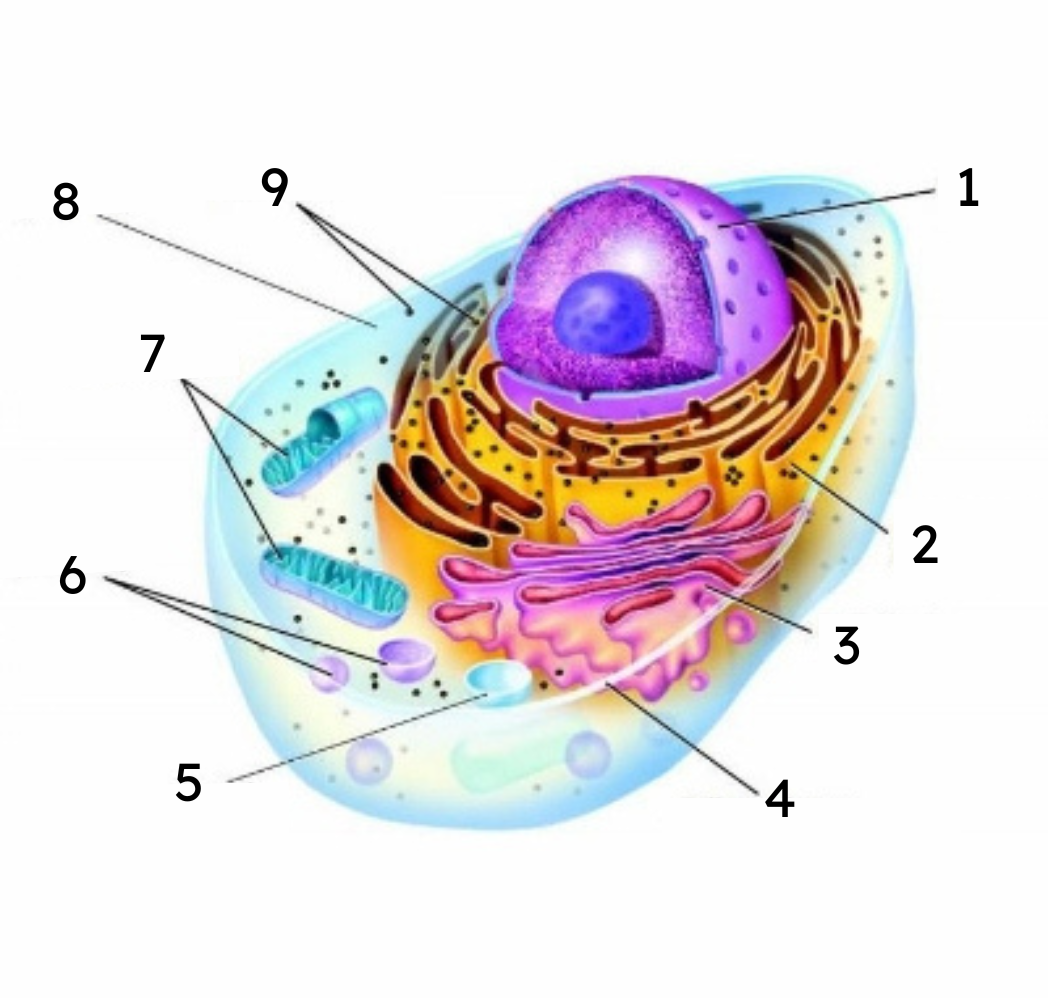
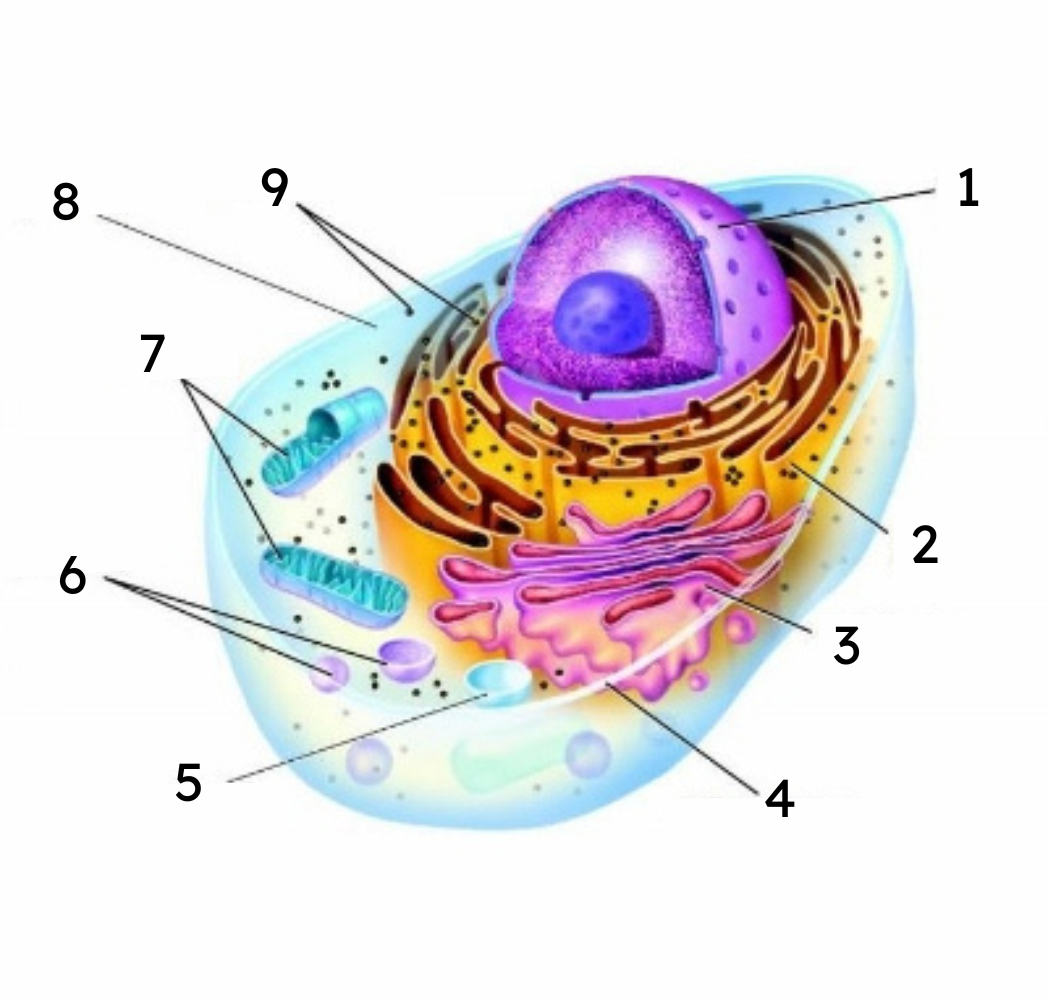
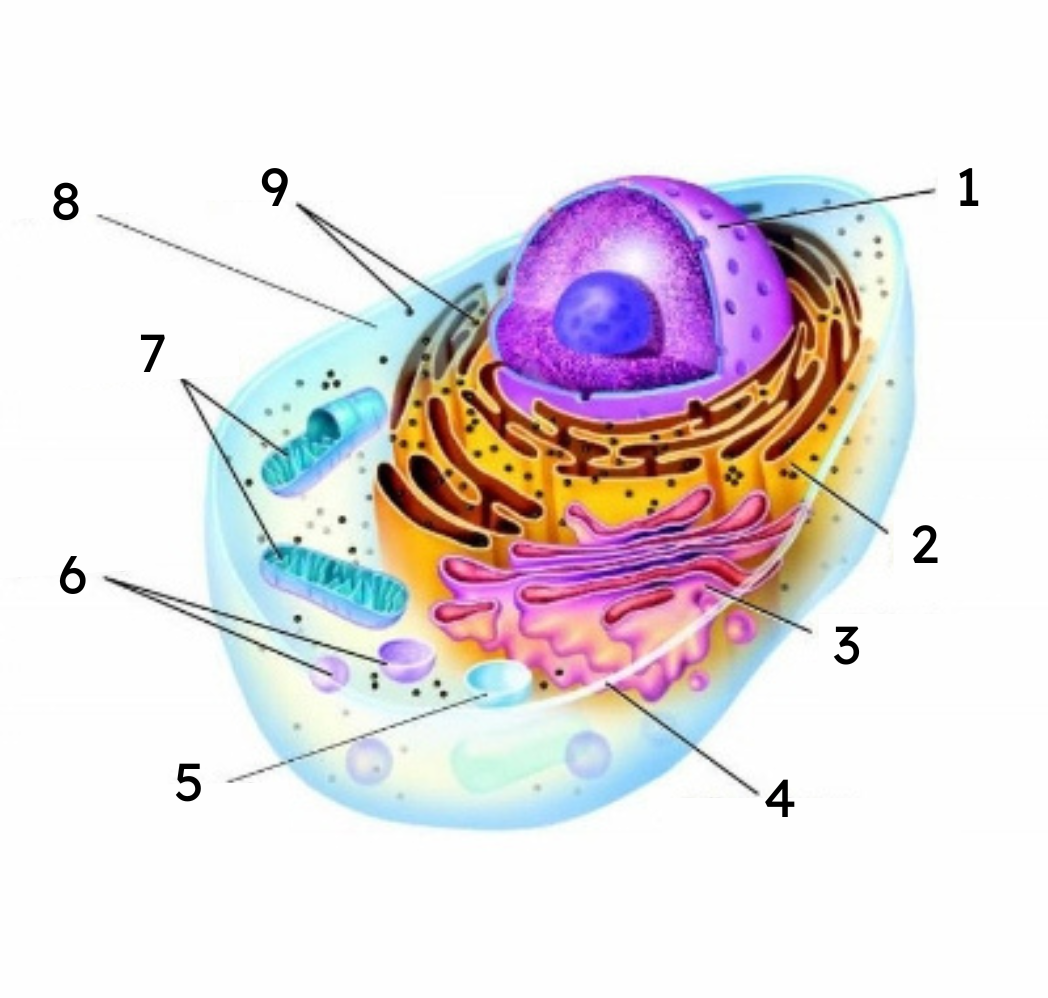
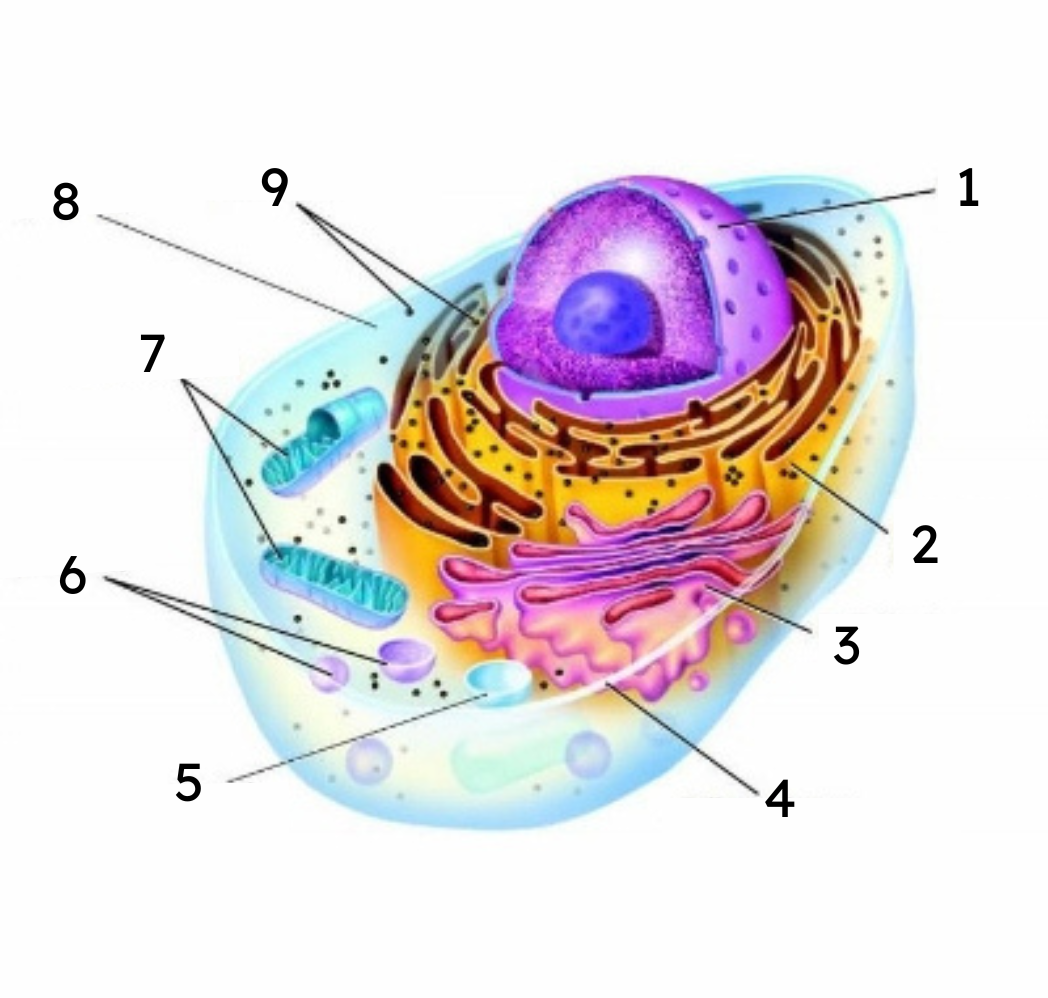
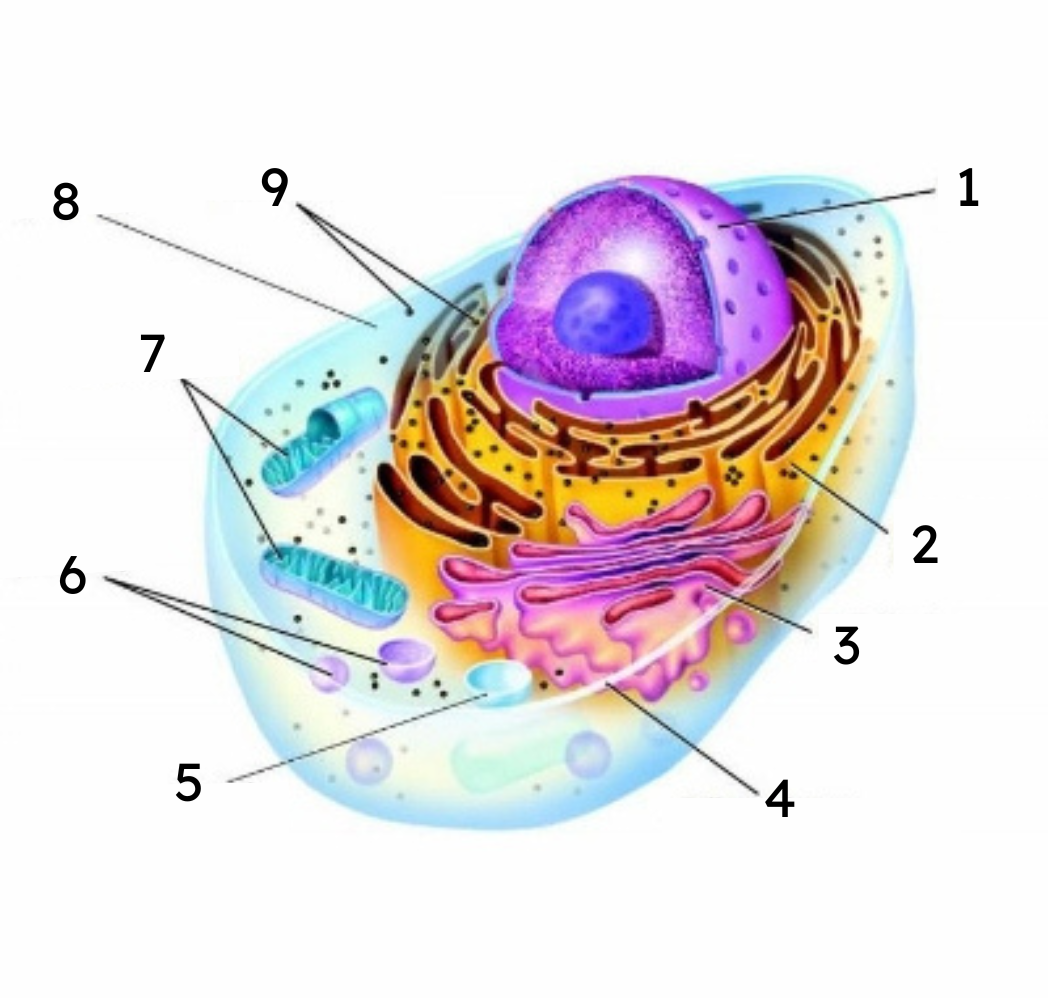
1
nucleus
2
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
3
Golgi body
4
cell membrane
5
vacuole
6
lysosomes
7
mitochondria
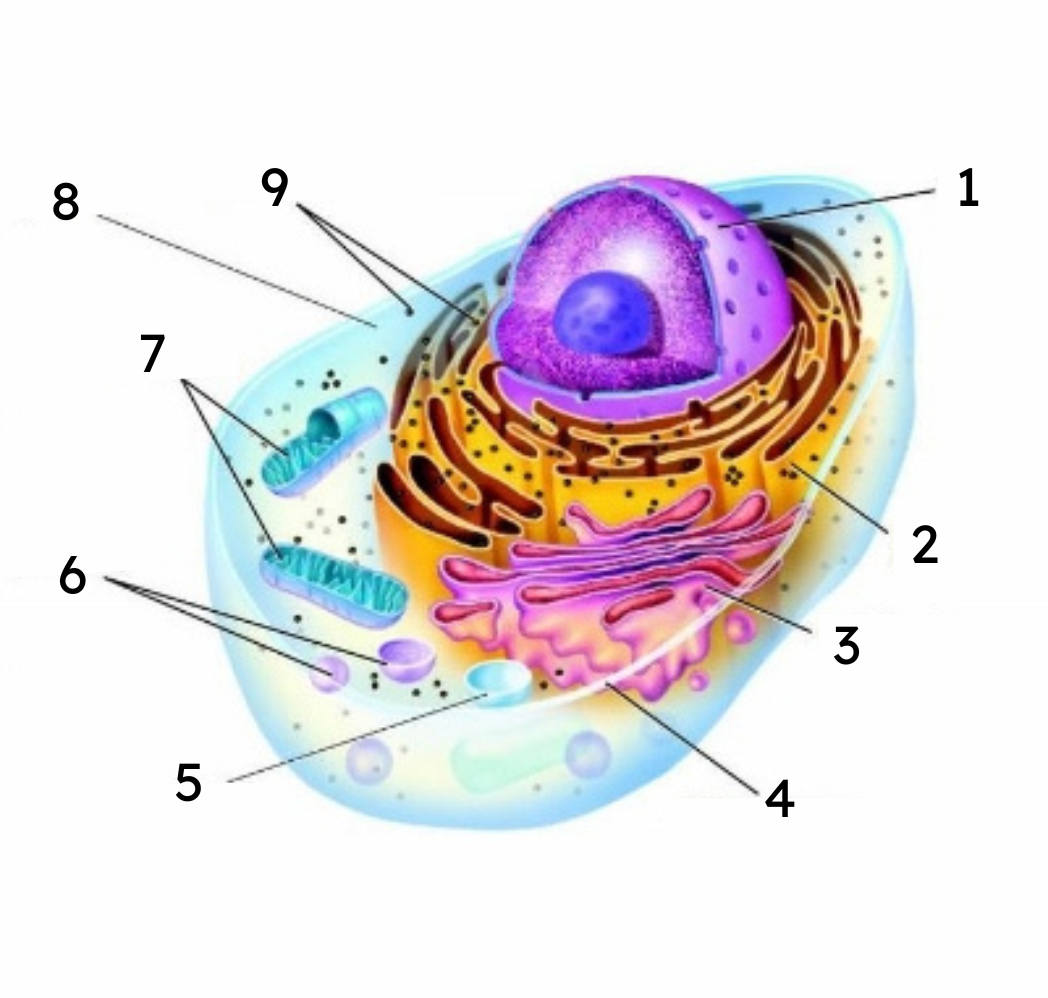
8
cytoplasm
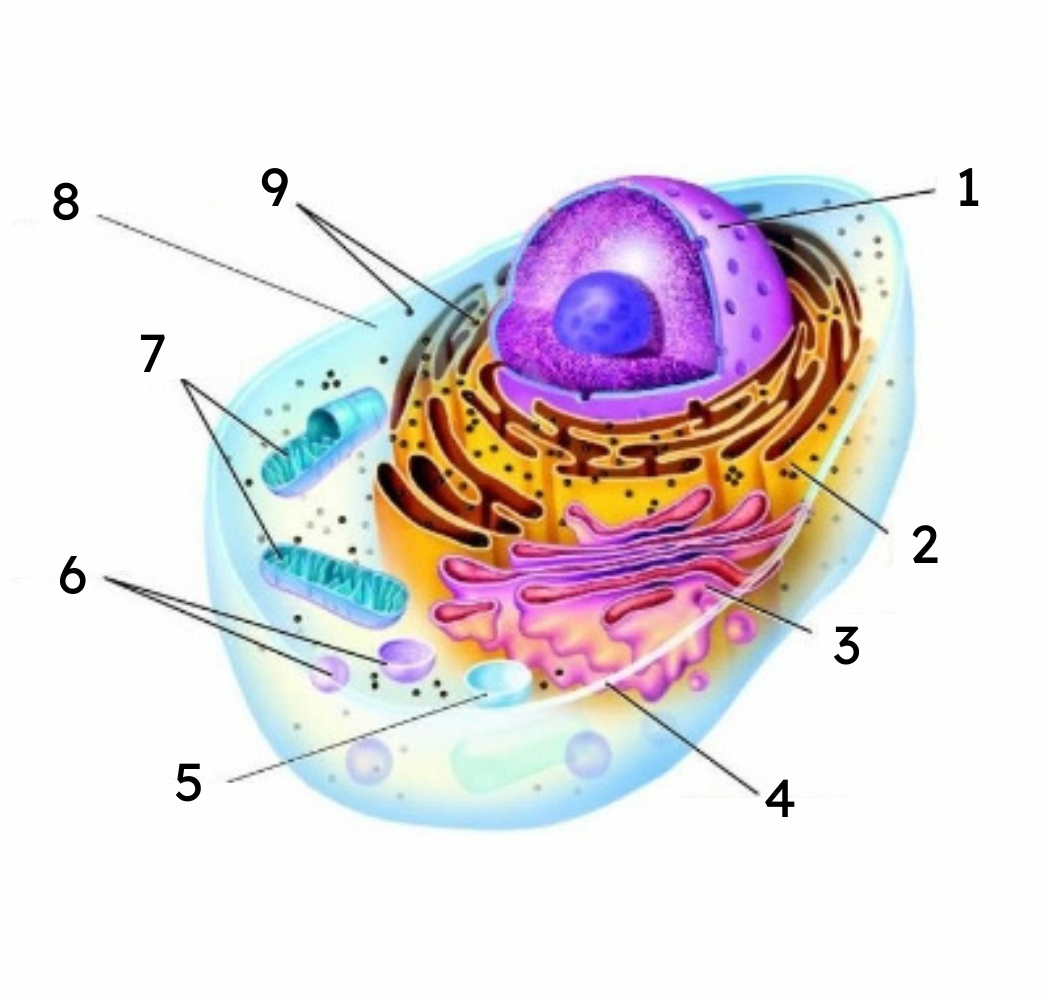
9
ribosomes
function of cell membrane
regulates movement of particles in and out of the cell
description of cell membrane
thin membrane that surrounds all the organelles
function of cytoplasm
contains organelles, H2O, and other life supporting materials
description of cytoplasm
jelly-like substance within the cell
function of nucleus
controls all activity within the cell and contains DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid)
description of nucleus
located near the centre of the cell, has its own membrane that encloses contents
function of mitochondria
energy producers in the cell, “the powerhouse”
description of mitochondria
open structure that has an inner + outer membrane, bean shaped
function of ribosomes
assembles and produces proteins
description of ribosomes
dot-like structures found scattered throughout cytoplasm or on/near the ER
function of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
assists in protein synthesis
description of endoplasmic reticulum
network of folded membrane-covered channels surrounding the nucleus, folds of a fan
function of Golgi body
sorts proteins and packs them into vesicles
description of Golgi body
stack of flattened pancakes/sacs
function of vesicles
carries proteins, nutrients, and water into and out of the cell
description of vesicles
small circular membrane bound structures
function of vacuoles
temporary storage compartments (sometimes for waste)
description of vacuoles
membrane bound structure that is larger in plant cells than animals
function of lysosomes
breaks down food particles, cell wastes, and worn out organelles
description of lysosomes
sphere like, membrane bound organelle only found in animal cells
function of cell wall
protects the cell and gives cells shape (only in plant cells)
description of cell wall
tough rigid structure, gives plant cell a box-like shape
function of chloroplasts
change’s sun energy into chemical energy, in charge of photo-synthesis
description of chloroplasts
membrane bound organelle with stack of green “coins” (only found in plant cells)
What are the organelles that only appear in the plant cell?
cell wall and chloroplasts
What are the organelles that only appear in the animal cell?
lysosomes
What is the equation for the process of cellular respiration?
food (glucose) + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy that can be used by living things
What is the equation for the process of photosynthesis?
light energy (sun energy) + carbon dioxide + water → food (glucose) + oxygen
What is diffusion?
the movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
What is concentration?
the amount of substance in a given space
How can substances pass through the cell membrane?
They can pass through because the cell membrane is a selectively permeable membrane.
What is one way substances move through the cell membrane?
By diffusion
What is it called when the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same?
Equilibrium
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
When does osmosis occur?
When water particles move from a high water concentration to a lower water concentration.
How do cells gain and lose its needed water?
osmosis
Which way will water flow when equilibrium is reached?
The water will flow back and forth.
Is osmosis a type of diffusion?
Yes