Biology Semester 2 Freshman Year - Unit 8: Biotechnology and DNA
1/83
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is for the Unit 8 Biotechnology Test
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
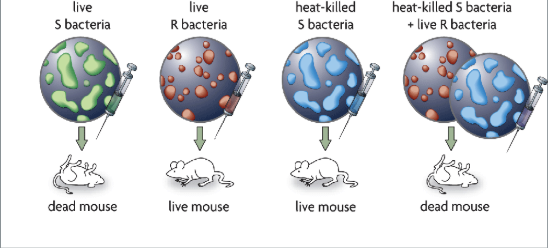
What did Fredrick Griffith discover?
found a “transforming principle)
Experimented with mice and bacteria that cause pneumonia
Used 2 forms of bacteria: the S (deadly) form and the R (non-deadly) form
A transforming material passed from dead S bacteria to live R bacteria, transformed them to be deadly
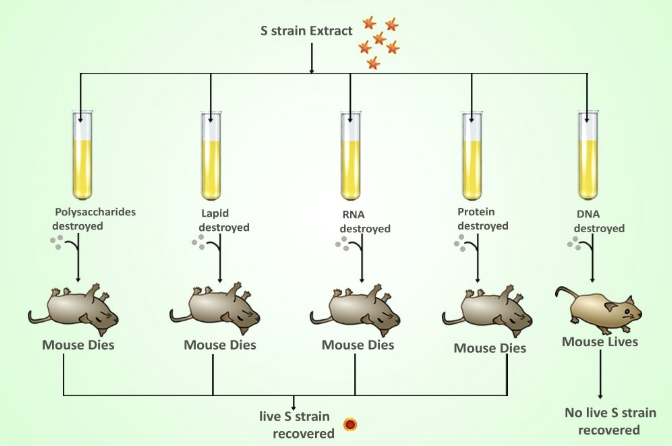
What did Avery, Macleod, & McCarthy discover?
Identified DNA as the transforming principle
Repeated Griffith’s experiment to determine what the transforming principle was
Used enzymes to destroy each type of molecule one at a time to see if transformation still occurred
What did Erwin Chargaff discover?
Discovered the base pairing rules
Found that in a DNA sample:
amount of adenine = amount of thymine
amount of guanine = amount of cytosine
Total nitrogenous bases add up to one hundred
Chargaff’s Rules: A = T, C = G
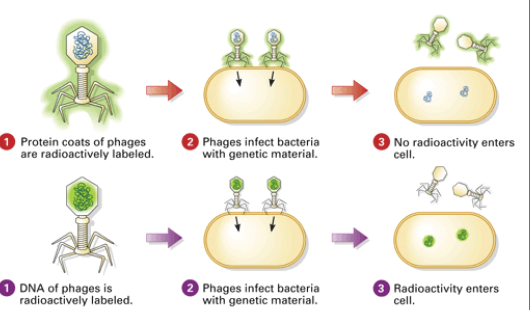
What did Hershey & Chase Discover?
Confirmed that DNA is the genetic molecule
Studied viruses that infect bacteria (called bacteriophages)
Tagged DNA with radioactive phosphorus
Tagged proteins with radioactive sulfur
Results: The tagged DNA was found inside bacteria; proteins were not
How did Franklin and Wilkins contribute to the discovery of DNA?
Took x-ray images of DNA
Suggests it was a double helix of even width
The image was necessary for Watson and Crick to build their model
How did Watson and Crick contribute to the discovery of DNA?
Build a 3D model of DNA
Double Helix
Sugar-phosphate back bone on the outside
Nitrogenous bases are on the inside
What did Venter and Collins do?
Sequenced the Human Genome
By the year 2000, they helped map the sequence of the human genome (over 3 billion base pairs!) through the Human Genome Project
What is the Central Dogma?
It is a model that describes how cells use DNA instructions to make proteins. DNA is transcribed into RNA and then, the RNA is translated to make proteins.
What are the principles of the Central Dogma?
Information flows in one direction
DNA to RNA to Proteins
What is the DNA’s role in the Central Dogma?
Store, copy and transmit genetic information
Sections of DNA called genes contain the instructions to make the proteins
What are importance of proteins?
fight disease
control/regulate cellular processes
structural
movement and support
‘transport
catalyze reactions (enzymes)
DNA is one of the 4 _____.
macromolecules
What is the full form of DNA?
Deoxyribonucleic Acid
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
nucleotide
the Polymer (set of nucleotides) forms a double helix: True or False
True
What atoms do nucleic acids consist of?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sometimes Sulfur
Acronym = CHONP
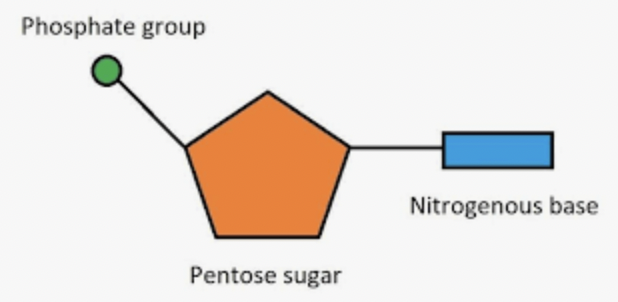
What is the structure of DNA (nucleotide)?
A nucleotide is made of 3 main parts
Phosphate group
Pentose Sugar - deoxyribose
Nitrogenous Base
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, and Guanine
Remember the base pair rule
A = T
C = G
What is the structure of DNA? (all parts)
The backbone of DNA is composed of a sugar and phosphate group, linked together with covalent bonds
The rungs of DNA consist of the bases, linked with hydrogen bonds
DNA strands run opposite of one another - this is called anti-parallel
One side runs 5’ to 3’ and the other side runs 3’ to 5’
What is the structure of DNA (shape) ?
Double Helix
What are the bonds in between the nitrogenous bases called?
hydrogen bonds
What bonds connect the backbone (phosphate group and the sugar) of DNA?
Covalent bonds
What are each of the Nitrogenous bases like?
Cytosine and Thymine (C & T) are single rings called pyrimidines
Adenine and Guanine (A & G) are double rings called purine
A pyrimidines must pair with a purine
Remember Chargaff’s Rule: A = T, G = C
What is the structure of pyrimidines (Cytosine and Thymine) ?
single rings
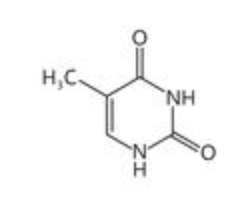
What is the structure of purines (Adenine & Guanine)?
double rings
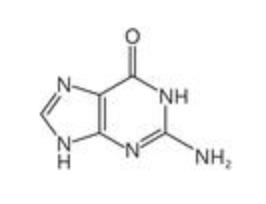
What is the function of DNA?
It stores, copies and transmits genetic info
DNA stores information in the form of what?
Genes (code for proteins)
During what phase does DNA replicate itself?
the S phase
What are enzymes?
Proteins are used to speed up biochemical reactions; they end in ase
Ex: Helicase
What is the function of Helicase in DNA Replication?
It unzips the DNA/ unwinds the DNA to make it accessible for replication
Explanation: It breaks the hydrogen bonds between base pairs, separating the two strands to create a replication fork
The replication fork allows new DNA strands to be synthesized on each of the separated strand
What is the function of the replication fork in DNA replication?
It allows new DNA strands to be synthesized on the separated strand
NOTE: the more there are, the faster replication will happen
What is the function of the DNA Polymerase in DNA Replication?
It extends new strands by attaching new nucleotides. It also proofreads (checks for errors).
What is the function of Ligase in DNA Replication?
It seals any gaps in the DNA.
What is the function of Telomerase in DNA Replication?
They add repetitive DNA sequences to the end of chromosomes called telomeres in order to prevent them from shortening with each cell division and losing important genetic information.
What are the steps involved in DNA Replication and what do the proteins do?
Helicase separates the DNA strands
Then, the replication fork is created (DNA is being synthesized on each DNA strand)
the more forks the faster the replication can happen
DNA Polymerase adds new nucleotides
Ligase fills any gaps in the DNA
Telomerase prevents genes from being lost by capping chromosomes near the end (telomeres)
Finally, the enzymes detach from DNA and the DNA is coiled back up
Is DNA considered parallel or antiparallel?
antiparallel
DNA is considered semi-conservative: True or False
True
Why is DNA considered semi-conservative?
B/c it ends with 2 new DNA molecules
each one is made up of one new strand and one original strand
Describe Prokaryotic DNA Replication
Takes place in the cytoplasm
Only one origin of replication
Describe Eukaryotic DNA Replication
Takes place in the nucleus
More DNA, therefore multiple sites of replication and replication forks to speed up the reaction
What are Mutations?
Changes in the DNA
some can have no effect on the organism
others may be beneficial
Some can cause a loss of genetic informations which causes the protein to not be made properly
What is biotechnology?
It is the use of living systems (like cells or organisms) to make technological advances and products.
Benefits the fields of medicine, agriculture, industry and criminal justice
Examples: Cloning, GMOs, DNA Fingerprinting, Genome sequencing, Brewing and fermentation, CRISPR, Stem cell therapy
What does Biotechnology rely on?
cutting DNA at specific places
Restriction enzymes cut DNA at specific sequences and manipulate other genes
different restriction site for each enzyme
Some create blunt ends and others create sticky ends
What are sticky ends when DNA is cut using a restriction enzyme?
It means that when it was cut, it left some sections of the DNA with unpaired bases
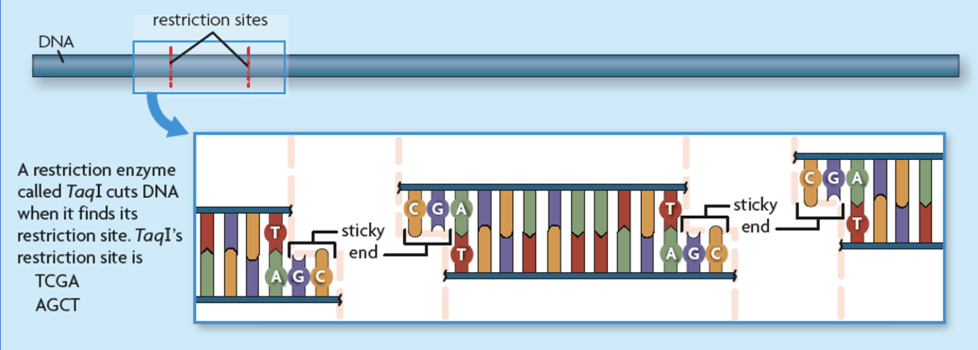
What are blunt ends when DNA is cut using a restriction enzyme?
It has no unpaired bases at the cutting site.
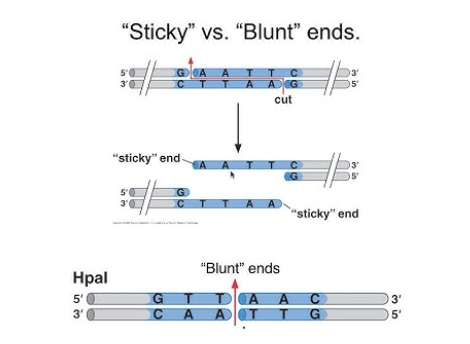
Why do we cut DNA?
Restriction enzymes allow for recombinant DNA and transgenic organisms
Possible because all organisms are based on the same genetic code
First, cut the DNA and Plasmid with the Restriction Enzyme
Lastly, use ligase to seal gaps
These biotechnologies help create medicines that save lives, improve crops, and are even
What is PCR?
Called the Polymerase Chain Reaction
Uses polymerase to copy specific DNA segments
Used in molecular biology to study DNA in greater detail
Similar to DNA replication
What are the three steps of PCR?
Heat is used to separate DNA molecules (denaturing)
Primers bind to each DNA strand to serve as a starting point for replication (annealing)
DNA Polymerase binds nucleotides together to make new strands of DNA (extension)
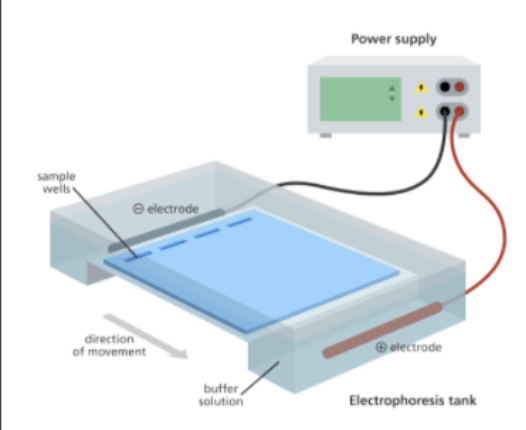
What is Gel Electrophoresis?
Its is a process that helps scientists analyze DNA in separating fragments
Uses electricity to separate DNA by size
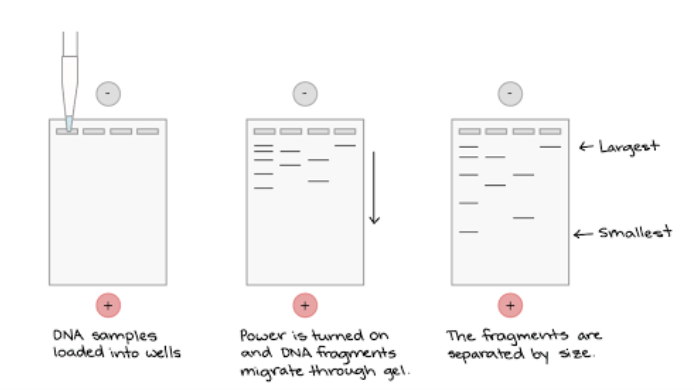
How does Gel Electrophoresis work?
the DNA fragments are loaded into the wells of the gel
DNA is negatively charged so it migrates to the positive electrode
Smaller DNA fragments travel further than DNA larger fragments
What is DNA Fingerprinting and why and how is it used?
Uses a person’s DNA for identification
Based on noncoding regions of DNA that have repetitive sequences
Number of repeats differs between people
When repeats are cut out (restriction enzymes), copied (PCR), and analyzed (gel electrophoresis) it creates a specific banding pattern on a gel known as someone’s DNA fingerprint
What are the uses of DNA fingerprinting?
Crime scene investigation
Paternity testing
Ancestry testing
Evolutionary studies
Species identification
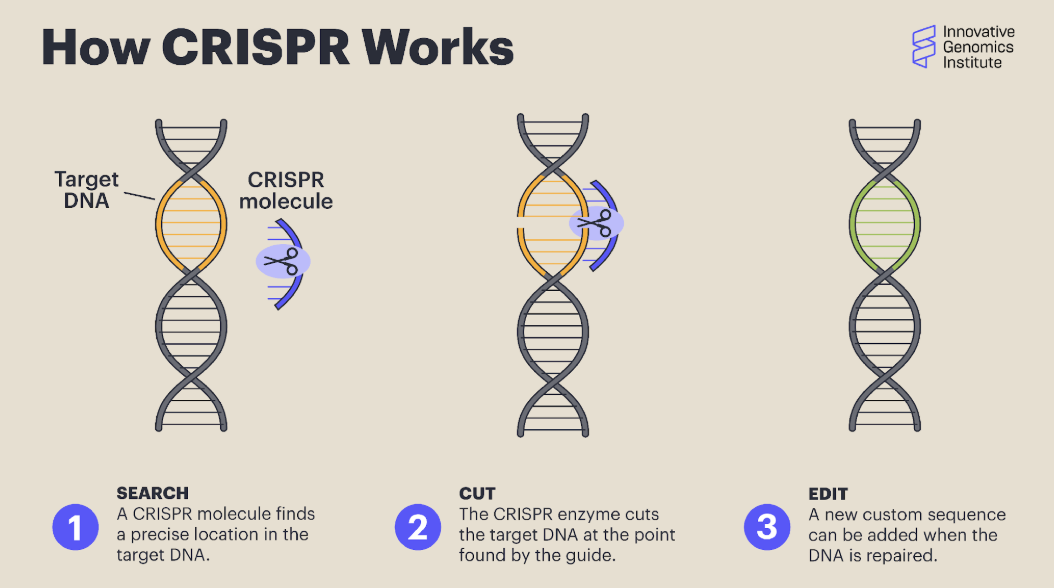
What is CRISPR used for?
Treating genetic diseases- it can be used to correct gene errors that cause diseases like sickle cell disease, cystic fibrosis, and hemophilia.
Creating disease-resistant organisms- it can be used to create mosquitos that are resistant to malaria
Agriculture- it can improve crops by modifying genes that affect yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content.
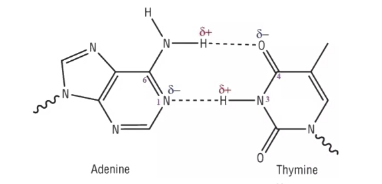
How many hydrogen bonds do Adenine and Thymine have?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds do Cytosine and Guanine have?
3 hydrogen bonds
What does PCR stand for in regards to biotechnology?
Polymerase Chain Reaction
What does semi-conservative mean?
It means the new DNA (resulting from the DNA replication) is made of one original strand and one new strand.
In eukaryotes, why does DNA create many replication forks during DNA replication?
to speed up (or increase the rate of) replication
What are genes?
sections of DNA that code for proteins
In gel electrophoresis, what causes the samples to move across the gel?
an electric charge
In gel electrophoresis, why do the samples move different distances across the gel?
Smaller segments tend to move faster and larger segments move slower
(This is because gel - electrophoresis separates the sample by size)
What are some of the ways we can use gel-electrophoresis?
ancestry testing
species identification
crime scene investigation
evolutionary studies
paternity testing
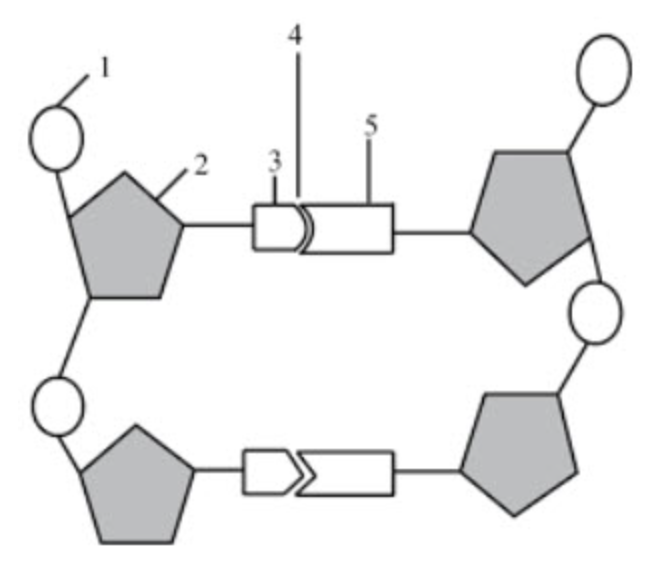
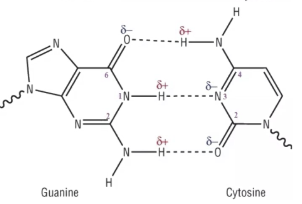
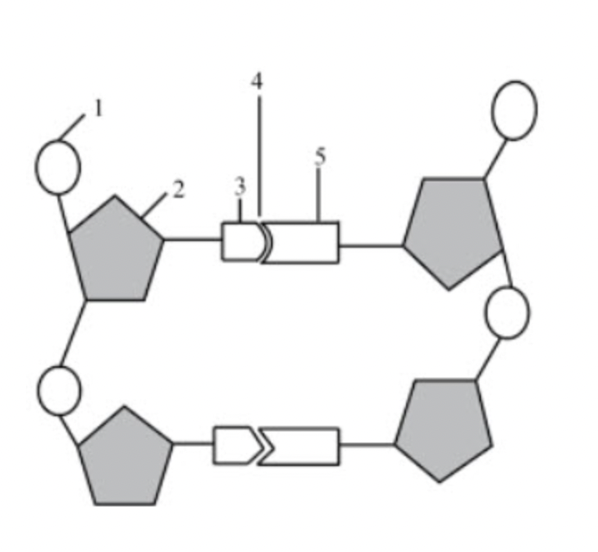
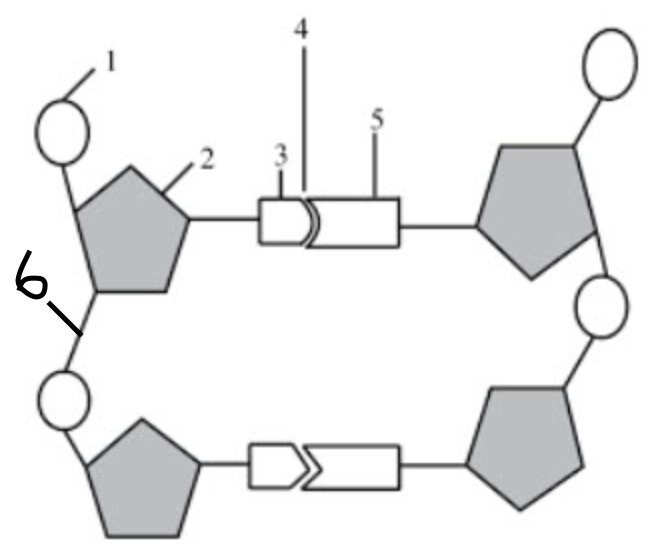
What structure is number 1 pointing to?
phosphate group
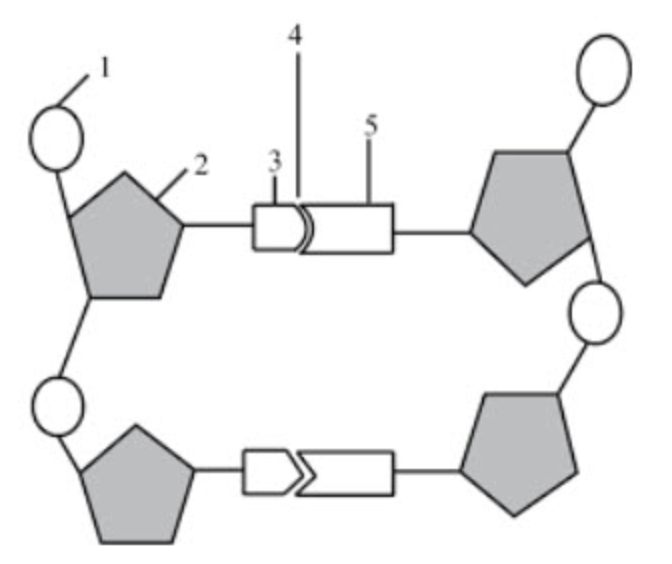
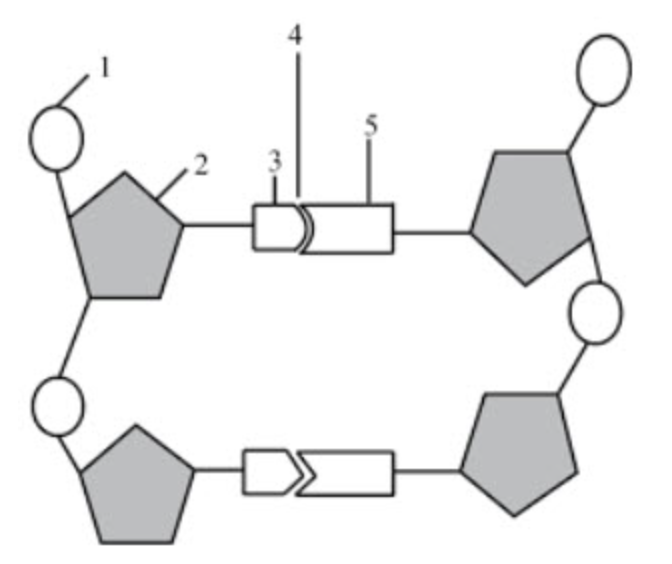
What structure is number 2 pointing to if the diagram itself shows DNA?
deoxyribose
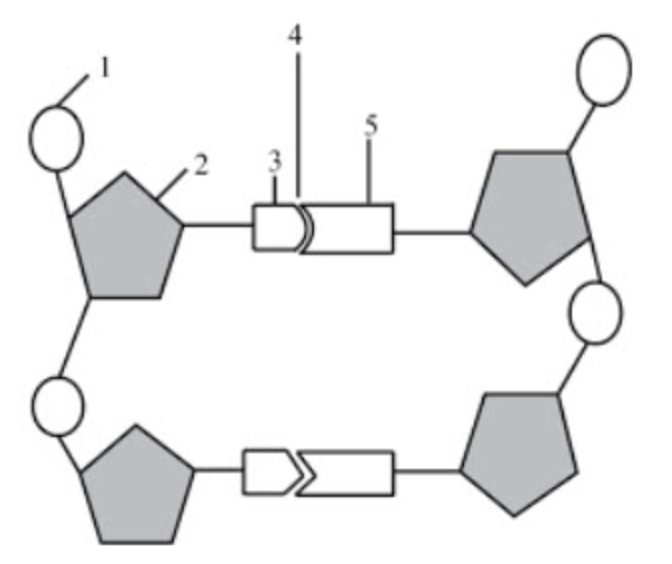
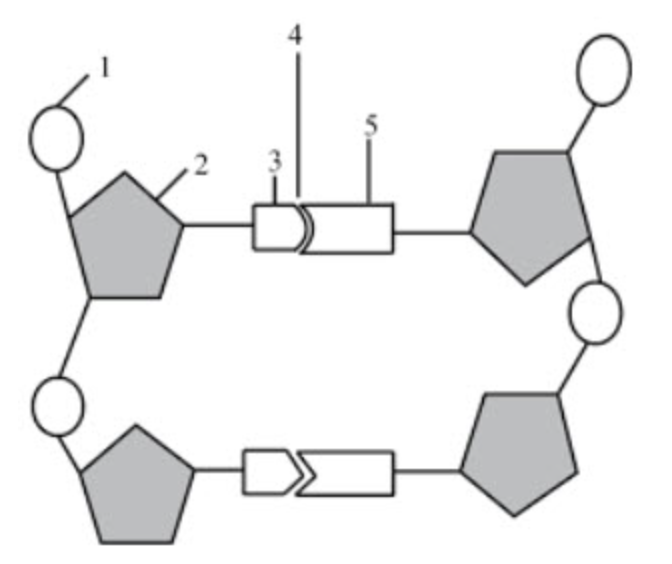
What structure is number 3 & 5 pointing to?
nitrogenous bases
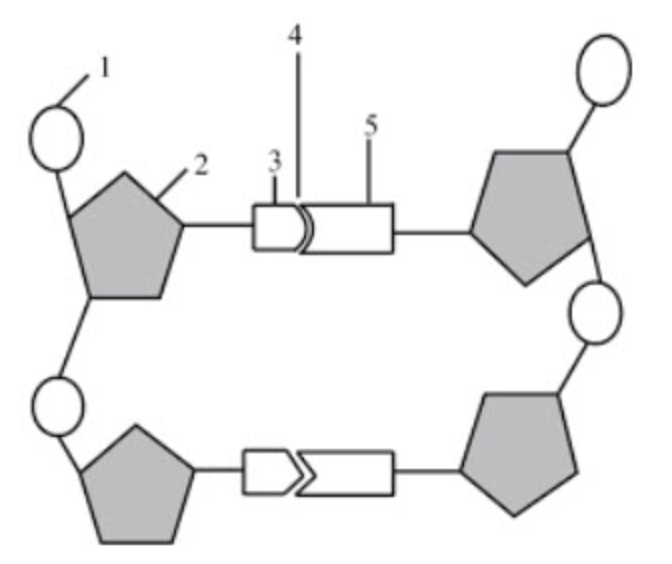
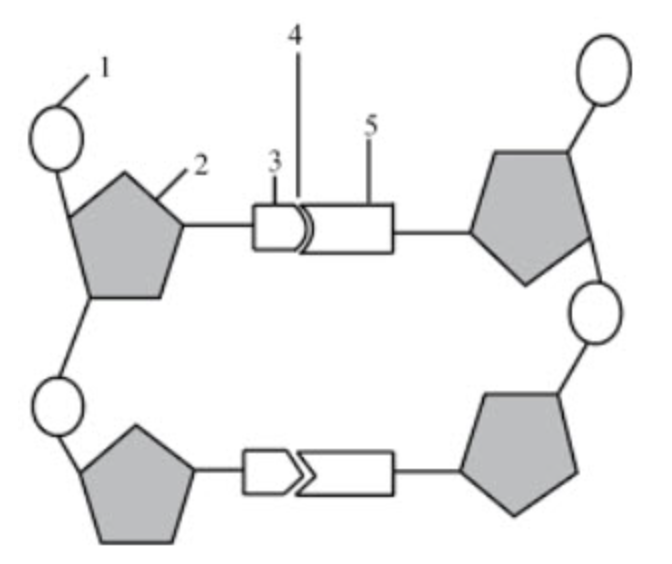
What structure is number 4 pointing to?
hydrogen bonds
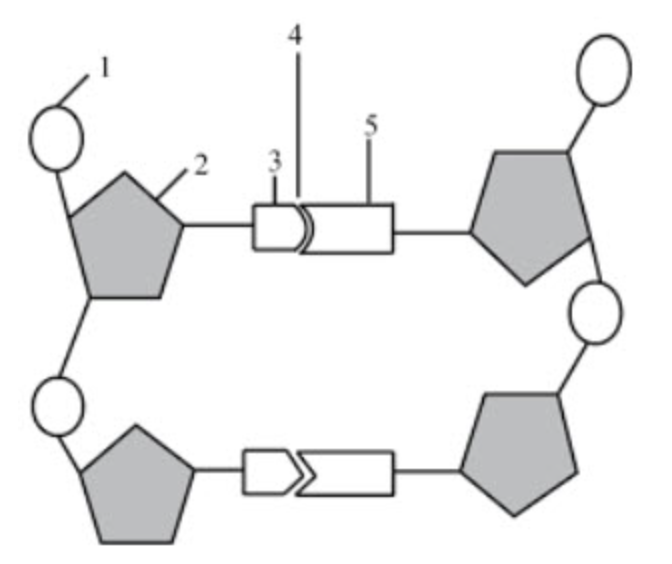
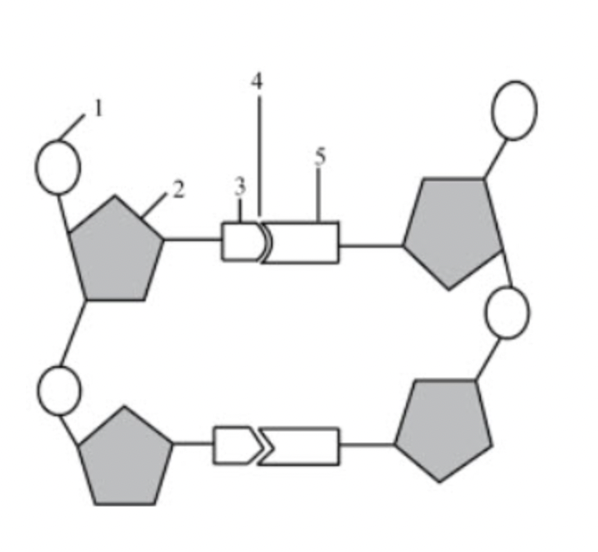
If structure three was adenine, what would structure 5 be?
thymine
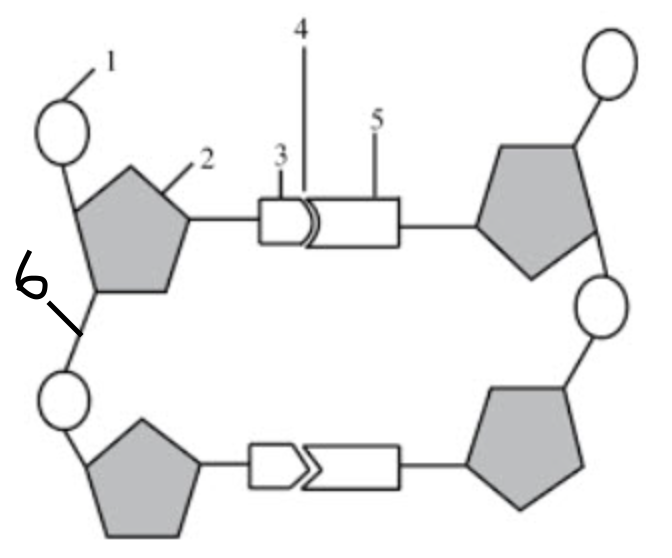
What structure is number 6 pointing to?
the covalent bonds
they connect the backbone of the nucleic acid
they connect the phosphate group and sugar
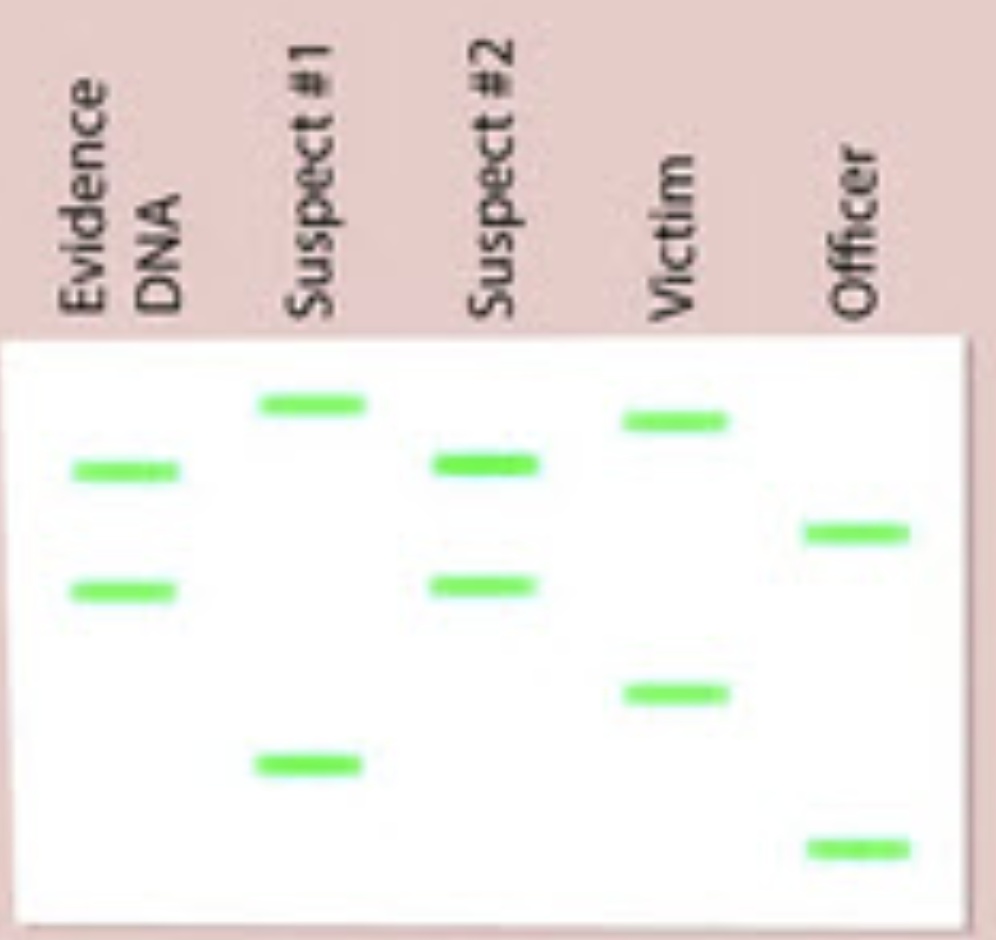
The image below shows the gel electrophoresis of DNA from a crime scene. It includes DNA from other sources. Using the image below compare the evidence DNA to the suspects' DNA samples. Which suspect matches the evidence DNA?
suspect #2
How do Eukaryotes replicate DNA?
Answer choices:
helicase starts at the beginning of the DNA molecule and starts unzipping. DNA polymerase then follows helicase from the beginning of the DNA molecule to the end.
the plasmid is copied all at once.
helicase starts in multiple locations, creating multiple replication forks
helicase starts in multiple locations, creating multiple replication forks
What goes into the sample wells in gel electrophoresis?
copied fragments of DNA from an organism
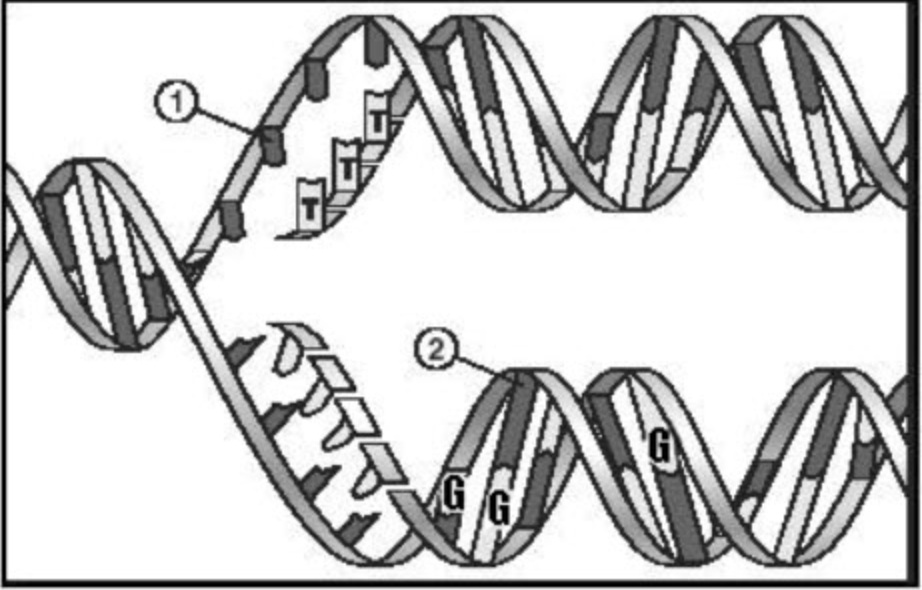
In the image, what is #2 pointing to?
And if it is a nitrogenous base, Is it a pyrimidine or purine?
cytosine, which is a pyrimidine
How do prokaryotes replicate DNA?
Answer choices:
the plasmid is copied all at once.
plasmids start copying at one spot and continue in 2 directions until the entire plasmid is copied
helicase starts copying in multiple locations
plasmids start copying at one spot and continue in 2 directions until the entire plasmid is copied
Restriction enzymes cut DNA into smaller fragments. How do restriction enzymes know where to cut?
Answer choices:
They cut where primers are located.
they cut at a specific sequence of DNA for each type of restriction enzyme
They cut randomly.
they cut at a specific sequence of DNA for each type of restriction enzyme
Why would scientists need to make lots of copies of DNA?
Answer choices:
So they can use the DNA to build one, long molecule of DNA.
Samples from organisms are too small to use for lab tests.
DNA is used as fuel for some lab equipment. They make copies so they have enought fuel.
Samples from organisms are too small to use for lab tests.
What does an “antiparallel“ structure mean?
parallel, but in opposite directions
How do you calculate the percentage of each nitrogenous base?
Guanine and Cytosine have the same percent
Adenine and Thymine have the same percent
A + T + G + C = 100%
For example, guanine is 21% and you want to find the rest of the nitrogenous base percentages
We know cytosine also has 21% because they are the same.
We add together 21 and 21 and subtract this from 100.
We get 58 and then we divide this by 2
FINAL ANSWER = 29%
Results:
Cytosine = 21%
Guanine = 21%
Adenine = 29%
Thymine = 29%
To check, add them all together, we get 100% which means we are right!
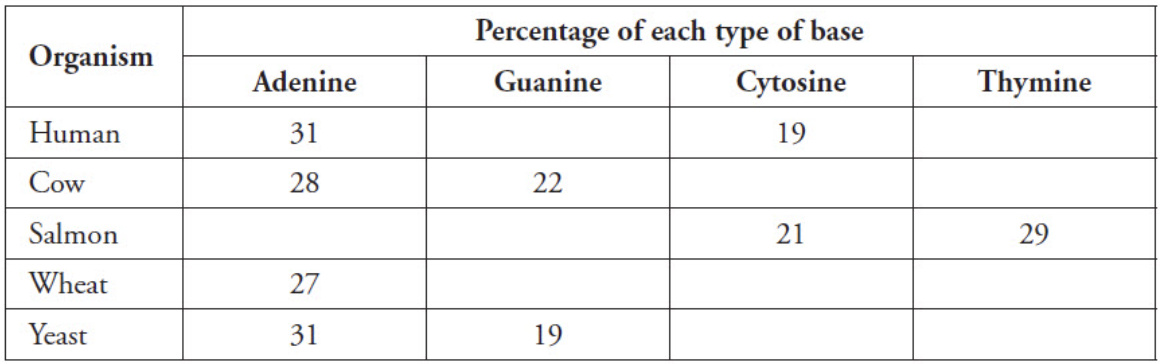
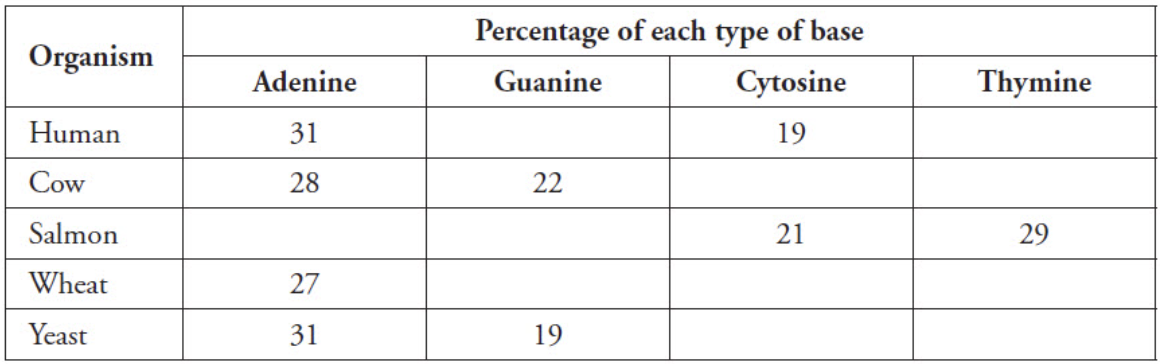
The table below shows the results of measuring the percentages of the four bases in DNA of several organisms. Based on the table below and Chargaff's rule, what percent of guanine should salmon have?
21%
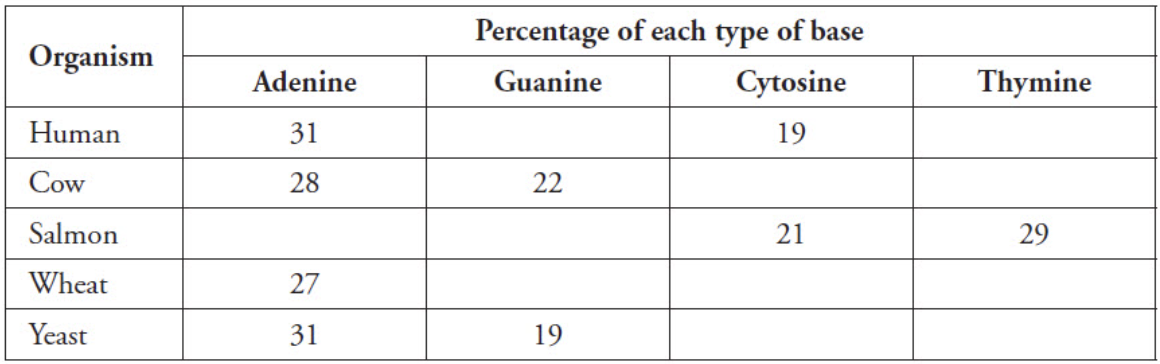
The table below shows the results of measuring the percentages of the four bases in DNA of several organisms. Based on the table below and Chargaff's rule, what percent of thymine should a human have?
31% (this is because we know that adenine is also 31% and no. of thymine = no. of adenine)
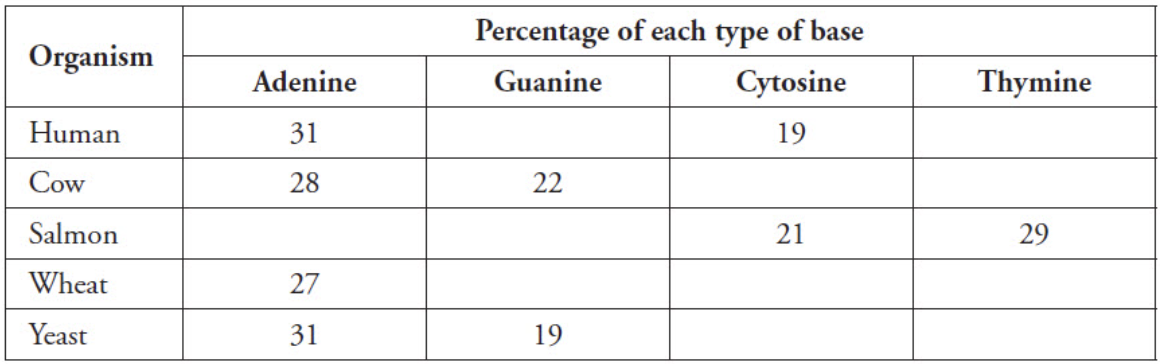
The table below shows the results of measuring the percentages of the four bases in DNA of several organisms. Based on the table below and Chargaff's rule, what percent of cytosine should wheat have?
23%
The table below shows the results of measuring the percentages of the four bases in DNA of several organisms. Based on the table below and Chargaff's rule, what percent of adenine should salmon have?
29%
What is a plasmid?
bacterial dna (prokaryote dna)
circular
How do prokaryotes replicate DNA?
plasmids (bacterial DNA) start copying at one spot and continue in 2 directions until the entire plasmid is copied
and remember, prokaryotic DNA is circular
so the DNA starts at one spot to copy and then moves in 2 directions
then when it meets at the point, the entire DNA is copied
In terms of sites of replication, is prokaryotic or eukaryotic DNA replication faster?
Eukaryotic
this is because eukaryotes have multiple sites for replication and prokaryotes only have one
this allows for replication to be quicker
Think of it this way, will a person completing a project by themselves be quicker, or a team with 5 people completing a project be quicker
because eukaryotes have more “people”/sites to do replication, its replication occurs faster
and prokaryotes have only one point of origin which means they have one person to do all the work which takes more time
this is why eukaryotic DNA replication is faster in terms of sites of replication
It terms of size, is prokaryotic or eukaryotic DNA replication faster?
prokaryotic
because their DNA is smaller and less complex than eukaryotic DNA