Conservation Biology Exam 1
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What do we mean when we say that conservation biology must be considered a “crisis science”
nature is stochastic
we are forced to make decisions and put policy into action before all necessary data is collected
Define “background extinction rate”
expected/natural extinction rate
Stochasticity
chaos in a system, nonequilibriums exist.
demographic transition
is a model that describes the changes in birth and death rates as a country develops economically. It typically progresses from high birth and death rates to lower rates as societies advance and improve in health care and education.
[emerging economies = exponential growth]
demographic transition stage 1
pre-modern
high CBR (Crude birth rate)
high CDR (crude death rate
demographic transition stage 2
urbanizing/industrializing
high CBR
lower CDR
many developing countries get stuck in stage 2
population begins to grow exponentially
demographic transition stage 3
mature/industrial
decline in birth rate
decline in death rate
demographic transition stage 4
post industrial
may have higher death rate than birth rate
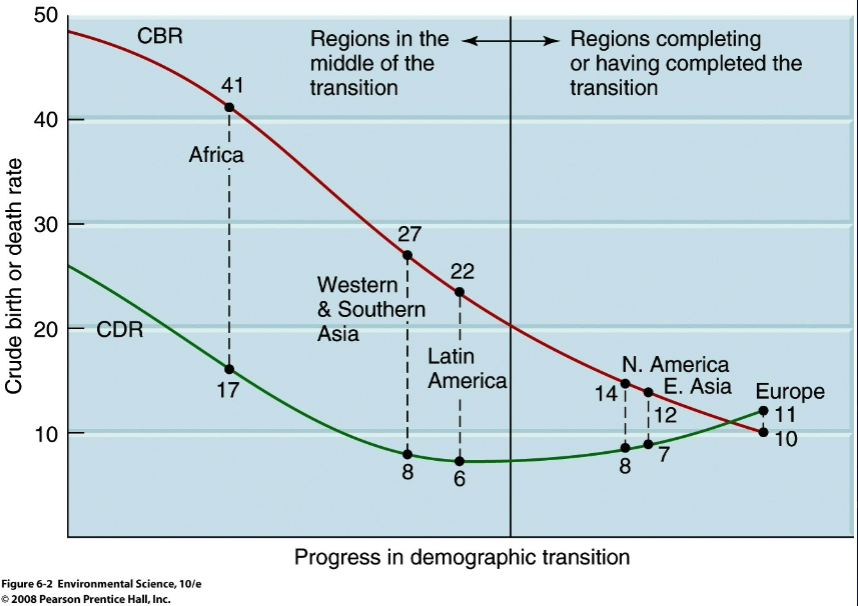
demographic transition- which continent is furthest ahead?
Europe
demographic transition- which continent is further behind?
Africa
IPAT model
Human Impact = Population x Affluence x Technology
Affluence = consumption (consumption / per person)
Technology = impact of consumption (impact / unit of consumption)
Biocentric preservation
touch nothing, destroy nothing, extract nothing
Utilitarian conservation
SUSTAINABLE use of natural resources
What do we mean when we say conservation biology must be an adaptive science?
flexible, systems always change, nothing is protected forever, policies must be maintained and changed.
Moral extensionism
moral and ethical standing beyond ourselves
How did the Ohito Declaration attempt to merge faith and religious beliefs with conservation?
10 spiritual principles and 10 courses of action that religions agreed upon
education, peacekeeping, sustainability
ahimsa
concept in Hinduism and Buddhism that stresses the importance of a nonviolent nature and kindness to all individual living beings
How did the Flint Water Crisis provide a model example for the importance of environmental justice?
impoverished area
cut corners and led to health problems
people below the poverty line
LuLu
Locally unwanted land use
toxic colonialism
developed world selling toxic waste to developing world (corrupt leaders)
impoverished people are the ones who suffer
inherent value of nature, difficulty convincing policy makers
value of existance
must be either cultural value or $$
bioprospecting
practice of going into the wilderness and finding useful products for people (primarily medicine)
issue of overharvesting
Ecosystem services (and example)
provisioning (food, medicine)
regulating (water purification, erosion control, climate change mitigation)
cultural (ecotourism)
potential way to alleviate the conflict over the conservation of the northern spotted owl and old growth forest in the pacific northwest
financial compensation
creating a mosaic of ages of trees, pay loggers to plant
no clear cutting
non-sustainable agricultural practices lead to increased conflict between humans and tigers in southern Asia
potential management solution?
habitat loss, less room for tigers
slash and burn agriculture (non sustainable), leads to desertification, which hurts the farmer and the tiger
better widespread education campaign for sustainable agriculture, how to keep the land healthy.
benefit of ecotourism to ecological systems
cultural identity around biodiversity provides a market for education
benefit of ecotourism to social systems
economic stability to the area, brings income, provides jobs, experience of viewing wildlife, connection to the land
drawback of ecotourism to ecological systems
more pollution, disturbance of wildlife
drawback of ecotourism to social systems
human injury, spread of diseases
Affluenza
Link to tragedy of the commons?
wealthy is always better
if we all have that attitude, we have the innate inclination to overharvest = nothing left for the community
5 variables that are included in the environmental model of the economy that are NOT included in the conventional view of the economy
1) Ecosystem services
2) Waste acceptance and management
3) Use of natural resources
4) Consideration of impacts on natural cycles (air and water purification)
5) Recycling the use of goods
Explain how the concept of the “Growth Paradigm” in traditional economics, may actually lead to a long-term economic and environmental decline
overuse of natural resources leads to economic loss, health impacts, social disruption
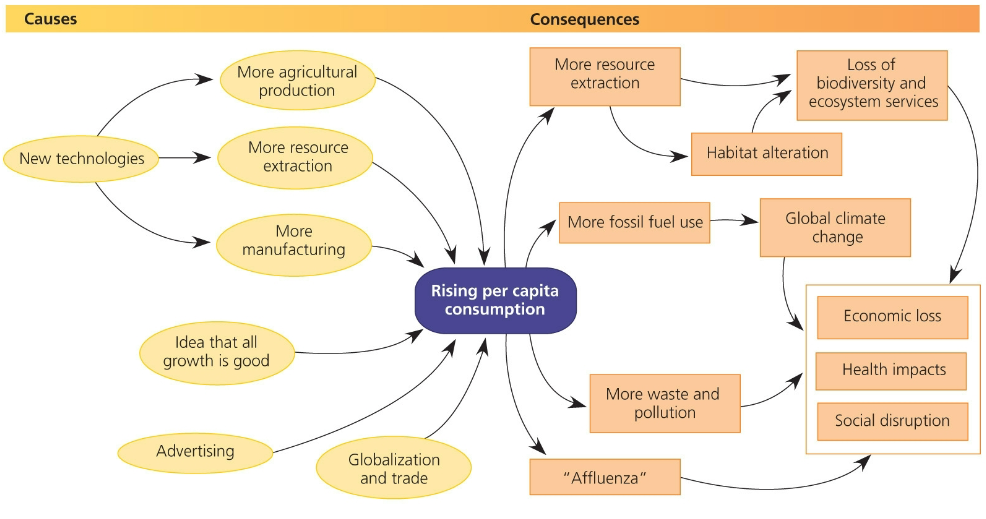
What is the correlation between a Nation’s economic growth and ecological footprint? why is it considered and ethical issue in conservation studies?
those individuals that live in the developed world have the largest ecological footprint, those in the developing world have the lowest ecological footprint.
those that live within the developing world experience the worst effects of the consequences.
PES model to sustain ecosystem services
(Payment for Ecosystem Services) rural communities provide natural resources and ecosystem services to urban communities, urban communities pay rural communities
NEPA
National Environmental Policy Act
NEPA- categorical exclusion
first step of the NEPA process
if the agency can prove that they’ve done a similar process in the past which did not hurt the environment. The NEPA process then ENDS (most end here)
NEPA- FONSI
Finding of No Significant Impact
can then continue the project
otherwise, some cases need to write an environmental impact statement (EIS)
Endangered Species Act: Critical Habitat
the habitat that an endangered species lives in
the first thing that goes into effect when a species becomes listed
Endangered Species Act: Federal Agency Consultation
other federal agencies must be in compliance with the critical habitat provision of the endangered species act with the exception of the department of defense
Endangered Species Act: Take Prohibition
taking any parts of the species (eggshells, feathers, snake molts)
no hunting, taking of endangered species
How the Trump administration is trying weaken the provisions set forth in the Endangered Species Act?
redefine “harm”
removing critical habitats
The ESA is administered by what two services?
US Fish and Wildlife Service
National Marine Fisheries Service
What authority does the “God Squad” have in regard to the provisions set by the Endangered Species Act?
congressional group that can reverse provisions of the ESA- especially of the critical habitat- if they feel it is causing enough economic damage
General weaknesses of the endangered species act?
single species
reactive, not proactive
expensive to list, takes a long time to list
How did the incident at Love Canal lead to the eventual passing of Superfund?
exposure to toxic waste, school children exposed
public outcry, mutations
Carter administration passed superfund
superfund
response to a crisis, compensation for those exposed for medical bills and relocation, liability (those who caused pollution to begin with are held liable)
AKA the Environmental response, compensation, and liability act.
Why did the Clinton Administration have to reevaluate and amend the original Superfund Act in 1994
misappropriation of funds
led to lack of funds
SLOSS debate
Single Large or Several Small
focus on single track of large lands or several smaller tracts of small land
currently= Single large is better
Y2Y
corridor project
Yellowstone to Yukon
Valorization
assigning of specific intrinsic value to nature, especially to the resources nature can provide.
enhancing the intrinsic value by emphasizing the cultural importance of those areas.
Success of The Pantanal Emas over Mesoamerican Project
PE involved local people
People were compensated
Indigenous people involved
more feasible than a larger project
Corridor-stepping stone
small areas of important habitat that are connected like stepping stones to improve gene flow and genetic diversity
what is meant by “equitability” in international environmental policy? why is it important?
following environmental policy, but being responsibly for how much you’re causing the policy to be put into place in the first place
Ramsar convention (1971)
INTERNATIONAL protection of wetlands across boarders
What are the two main pieces of Principle 21 of the Stockholm Declaration
every country has sovereign rights over their own natural resources, following international policies
no one has the right to go in and exploit others for their natural resources
Statues/principles of the Basal Convention (1982)
encouragement to reduce hazardous waste
cannot sell toxic waste to another country
if you do move hazardous waste around, it has to be regulated
CITES
Convention on the International Trade of Endangered Species
3 appendices
no trade (endangered animals)
trade allowed through permits
trade allowed
Why was it only realized in the 1970s and 1980s that CFCs were doing damage to the ozone layer (after 50 years of widely using the chemical)?
which international piece of legislation largely banned the production of CFCs?
took time for the damage to build up in the ozone layer (accumulation)
meteorology technology got better to actually view the damage to the ozone
Montreal Protocol
How many UN Sustainable Development goals are there?
17
Why did COVID interfere with progress of some of the UN sustainable goals?
Education = kids at home not getting the correct education, children still behind 5 years later (happened in both the developing and developed world)
progress toward equality, women, etc
why is the IUCN red list sometimes referred to as the “Barometer of Life”
measures the status of a species, can improve or decline, set categories
What is meant by “deep ecology”
ecocentric on crack
every single living thing on the planet has a right to life
negative- motivation for ecoterrorism
What major ecological theory/concept discussed in depth in the Song of the Dodo?
island biogeography
Briefly explain the concept of the ecology of fear
predators impact the spatial structure of prey populations
prey populations will not be found clumped in an area where they know there is a chance to be preyed upon
leads to vegetation cut back when predators are removed
What are the four processes that drive microevolutionary change in a population?
mutations
selection
gene flow
genetic drift
Why is genetic diversity in a population of a species important to the long term viability of that population?
genetic diversity is key for evolutionary change and adaptability in the future
Direct fitness, indirect fitness, inclusive fitness
the ability of an individual to survive and reproduce
fitness of genetic kin
direct plus indirect fitness
what is a bottleneck event? how does it lead to genetic drift? how can genetic drift be harmful to the long term viability of a population?
drastic decrease in a population
small population increases the chances of random sampling of the same gene, leads to gene fixation
loss of genetic diversity
polymorphism
any genes with 2 or more alleles
limitation of polymorphism calculations by chart
not enough data
small sample size
in conservation genetics, why is it useful to have both measure of polymorphism and heterozygosity in a population of a species? how does the data compliment each other?
polymorphism tells us if the gene pool has more than one allele for a locus, but not how many individuals are carrying those around
10 central characteristics of conservation biology
preserve the status quo and the potential for species to evolve
ecological systems are dynamic and non-equilibriums exist
humans are integrated into all systems in the world
focus on scarcity and abundance, and focus on rare species
“messy” inexact science, stochastic and random perturbations (disturbances)
Crisis science (Micheal Soule)
Value-laden science, the intrinsic vs the extrinsic value of nature
mission oriented and advocacy oriented science
adaptive science, nothing is protected forever (Bills are malleable, environment is changing, plans can not work forever)
legally empowered science
Major types of ecosystem services
provisioning ecosystem services (direct use)
food, fuel, timber, drinking water
regulating (indirect use)
favorable to humans. flood control, water purification, mitigation of climate change, pollination
cultural
emotional, psychological, recreation, exotourism
pay for national parks, fishing permits, etc
Social and ecological pros and cons of ecotourism
pros:
ecological: sustainable conservation through cultural identity around biodiversity, education system, protection of ecological market. Promoted sustainable agriculture
Social: experience of viewing wildlife, income from ecotourism, economy stability
cons:
ecological: increased foot traffic/trampling, reduced habitat, increased pollution, human-caused habitat conversion
social: human injury, crop damage, rising food prices/declining communities
National Environmental Policy Act of 1969
Declared national environmental policy, required Environmental
Impact Statements, created Council on Environmental Quality
Endangered Species Act of 1973
1. Establishment of critical habitat
2. Establishment of species recovery plan
3. “Take” Prohibition
4. Federal Agency Consultation
5. International Cooperation (CITES)
Comprehensive Environmental Response,
Compensation and Liability Act of 1980
Created $1.6 billion “Superfund” for emergency response, spill
prevention, and site remediation for toxic wastes. Established
liability for cleanup costs
NEPA steps
1. Government performs an action / project on private land that MAY
potentially be damaging to the natural environment – question of
categorical exclusion?
2. Government REQUIRED to conduct an Environmental
Assessment (EA); can lead to 2 conclusions:
Conclusion 1. Finding of No Significant Impact (FONSI)
Conclusion 2. A more detailed study is needed – PROCEED to
STEP 3
3. Government required to further study their actions and formulate
an Environmental Impact Statement; public can provide input (EIS);
can lead to 2 conclusions:
Conclusion 1: Government slightly alters project and proceeds
Conclusion 2: Significant environmental damage will be done –
project cannot proceed in its current state
Characteristics of Effective Environmental International Policies /
Laws
Equitability – very challenging
Small number of participants involved
Clear support of a “leader” country