Geriatrics exam 1
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
What percent of people over 65 will have chronic disease?
80%
Medicare will only pay for the first ____ days of admission
100
Medicaid pays ~ ___% of SNF costs
80%
What is the definition of elderly?
older american act of 1965 states 60** years and older
maximum survival of a species
life span
The length a particular group can be expected to live (average)
life expectancy
what is likely the most influential influence on life expectancy?
genetic
fibroblasts divide about ___ times before removed from the population
All cells have the ability to remember how many times they divide through ______
30 times
Telomeres
What is Werner syndrome?
features of premature aging
What are the 3 theories on aging?
1. neuroendocrine pacemakers
2. Free Radical Theory products of metabolism
3. Errors in protein synthesis
What are the 2 neuroendocrine pacemakers?
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Gonadal axis
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Adrenocortical axis
What type of neuroendocrine pacemaker is this?
Menopause, Dopamine , Human Growth Hormone
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Gonadal axis
What type of neuroendocrine pacemaker is this?
Truncal obesity, glucose intolerance, osteopenia, cataracts
- Hypothalamic-Pituitary Adrenocortical axis
In the Free Radical Theory products of metabolism, there is damage of _______ antioxidants (Vit C and E)
______: may also induce DNA mutations
DNA/RNA antioxidants (Vit C and E)
UV light
Errors in protein synthesis are usually caused by
amino acid sequence errors
Aging is a _____ process, NOT accumulation of disease
developmental
_____ are conceived more and ______ live longer
males
females
Individuals born in America between 1946 and 1964 are referred to as _______ as a result of the significant increase of births that occurred during that 22-year period
'baby boomers'
Occurs independently of disease, yet is associated with increased disease prevalence and susceptibility. As we age, we lose this ability - what is this known as?
loss of homeostasis
Why do elderly people tend to weigh less?
they lose muscle and gain of fat
Why does GI motility decrease?
lower fiber
reduced fluid
reduced exercise
What occurs witht he GU/ as we age? (males and females)
impotence
What are the effects on the skin as we age?
1. lower subQ fat
2. lower vascular supply
3. dryness due to atrophy of sweat glands
4. Loss of elasticity and skin thickness
What are the visual diseases that occur as we age?
Glaucoma
macular degen
Cataracts
presbyopia
What are 2 visual disturbances that are not normal processes of aging?
glaucoma
macular degeneration
How is the lens affected as we age?
Increased ______ of lens and ciliary muscle lead to _______
rigidity; presbyopia
How is the iris affected as we age?
Decreased adaptability to changes in light, secondary to _______ of the iris
stiffness
What are the sxs of macular degen?
no pain
drusen
blurred central vision

how to tx macular degeneration?
Healthy diet
Smoking
Maintain BP and healthy weight
Excercise
What are the sxs of glaucoma
loss of side vision
- no early signs

How to tx glaucoma
Medications, usually eye drops
Laser or conventional surgery
What are the sxs of cataracts?
cloudy lens
Colors that may not appear as bright as they once did.
glare
poor night vision

What are the RF for cataracts?
smoking
DM
sunlight
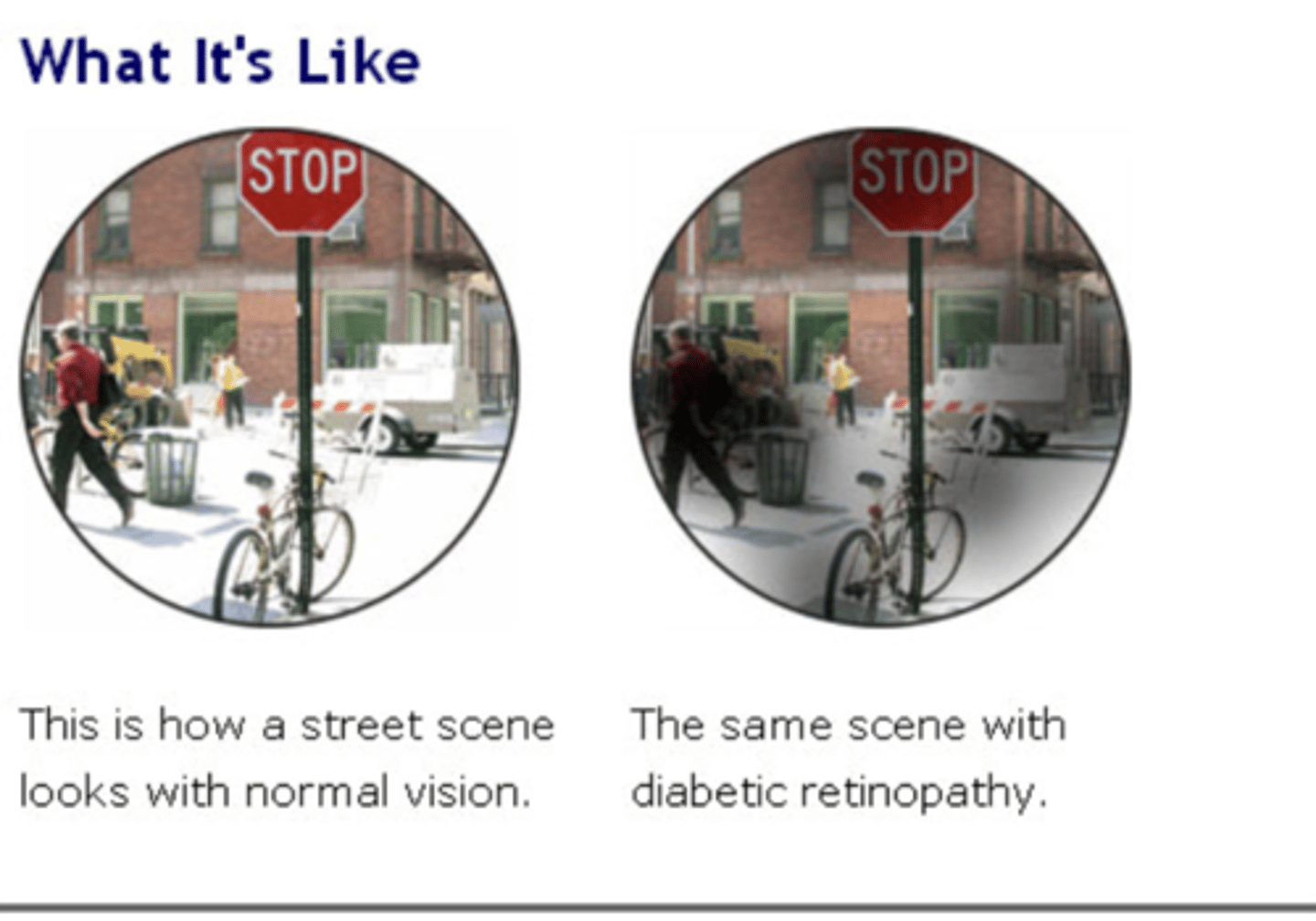
What is the tx option for diabetic retinopathy?
laser tx
sx
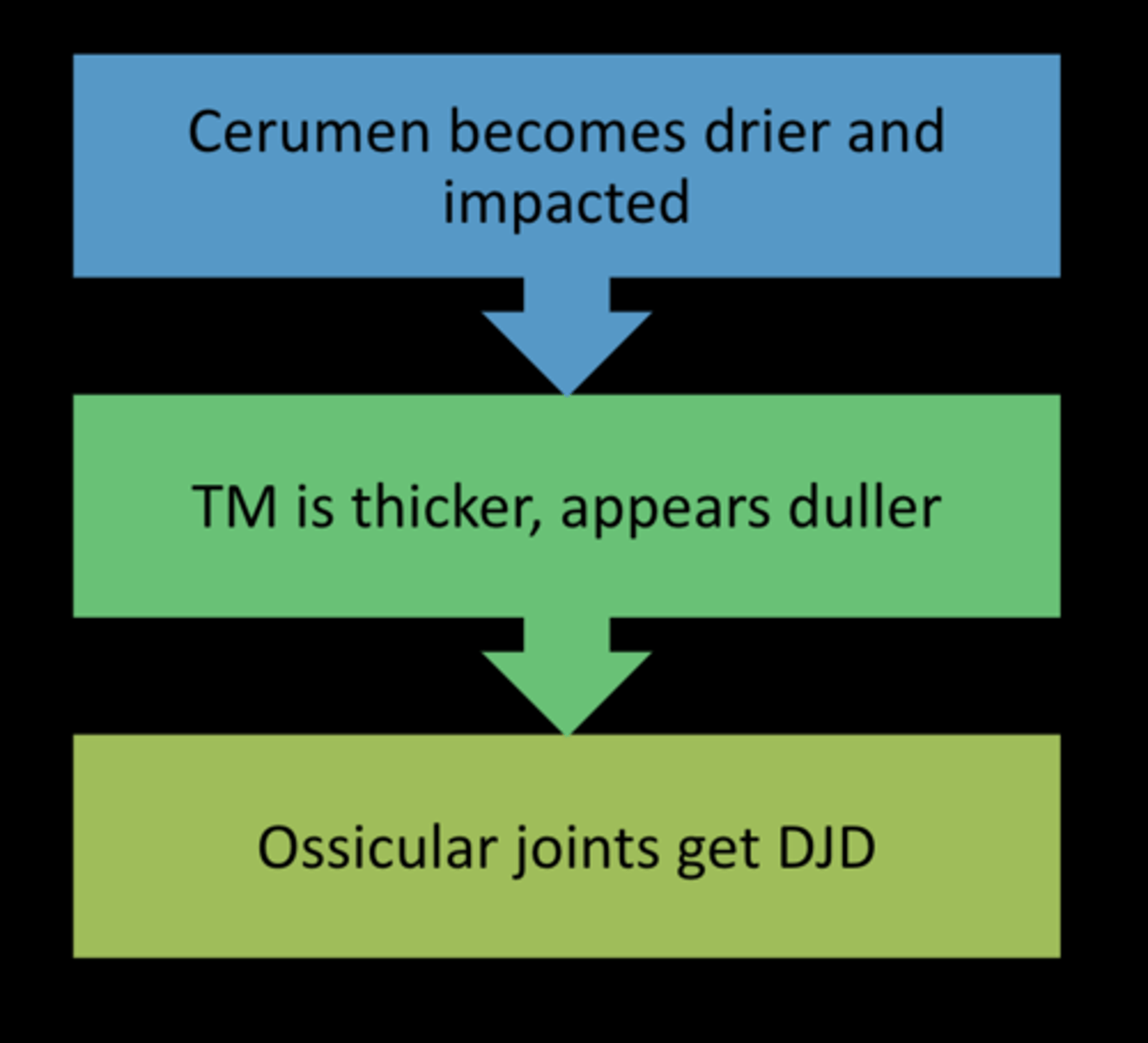
What is presbycusis? mc in who?
age related hearing loss
males
at what age does presbycussis occur?
~30y/o
how does presbycussis develop (3 steps)
What are some RF for hearing loss? what do they have in common?
HTN
Heart disease
Alcohol
Noise
DM
Smoking
all have to do with arteries
________ can cause dementia
Hearing loss
What is the cause for sensorineural hearing loss?
loss of hairs of corti
loss of cochlear neuron
inner ear problems
What is the mc cause of Conductive Hearing Loss
Auditory Canal Atrophy
5 types of conductive hearing loss
Infections in the skin lining the ear canal
Fluid in the middle ear,
Arthritis that affects the bones of the ear
A Hole in the ear drum, not very common in older people.
Paget’s disease of bone
What is a Schwannoma?
CN VIII tumor, retrocochlear hearing loss
What happens to the GI system as we age?
Tension in the upper esophageal sphincter _______ (presbyesophagus)
Stomach lining's capacity to resist damage _______
decreases
decreases
How is the nervous system affected as we age?
Brain Size _______ along with ________
Diminished Amounts Of ________ in localized areas
How to help the elderly with their sleep?
Decreases; blood flow as we age
Neurotransmitters
avoid sedatives and give afternoon sunlight
Why do we get PUD as we age?
Stomach lining's capacity to resist damage decreases
defined as age-related increased vulnerability to adverse outcomes when exposed to stressors (either intrinsic or extrinsic)
frailty
involuntary loss of urine
urinary incontinence
Who is urinary incontinence most common in?
women
what is the MC cause of urinary incontinance in women?** (TQ)
childbirth
URINARY INCONTINENCE IS NOT CAUSED BY _____ ALONE
AGE
Urination is under what control?
Central and peripheral
Bladder comfortably holds _______cc of urine before the urge to void
150-300
What occurs when the intra vesicular pressure rises above urethral phicter spressure
Leakage
intravesicular pressure can rise from increased intra-abdominal pressure
valsalva
**What is the bladder capacity in the elderly (normal is 300-600)?
250-300
- urge at 150
Why do women have incont and males have retention?
-decline in outlet resistance, from childbirth and deconditioned muscled
- enlarged prostate, increased residual urine
What is stress incontinence?
Involuntary loss of small amounts of urine due to increased intra-abdominal pressure, cough, laugh, ect
These are causes of what kind of incontinence?
Laxity of pelvic floor, causing hypermobility of bladder base and urethra or outlet or urethral sphincter weakness due to surgery or trauma
stress
What is the tx for stress incontinence?
kegels
alpha agonists
sx
What is urge incontinence?
inability to delay voiding after sensation of bladder fullness
- feel it then go
what are the causes for urge incontience?
detrusor hyperactivity caused by UTI, dementia, parkisons...
What is the tx for urge incontience?
treat infection
bladder relaxants
vladder training
What is overflow incontinence?
Leakage due to overdistended bladder
sx of overflow incontinence
Dribbling, weak stream, hesitancy, nocturia
What is the cause for overflow incontinence
obstruction (prostate)
detrusor underactivity
What is the tx for overflow incontinence?
Remove obstruction
Catheterization
What is functional incontinence?
Leakage of urine due to cognitive, functional, or environmental factors.
What are the causes for functional incontinence
dementia
restraints
inaccessible toilets
depression
catheters
What is the tx for functional incontinence
behavioral therapy
external collection
What is mixed incontinence?
combination of stress and urge incontinence
What is the tx for mixed incontinence?
bladder retraining
pelvic exercise
pharmacologic drugs
What are the complications of incontenece?
Where do you do a post void residual?** (TQ)
at the urologist!!! *
What are some reversible causes of incontinence
delirium
UTI
impaction
atrophic vaginitis
metabolic disorders
What are some Meds that cause incontience?
Diuretics
Lithium
psychotropics
anticholinergic
Alpha adrenergic
What type of incontinence does each cause:
Sedatives
Loop
Alcohol
Caffeine
Cholinergics
urge/obstructive
urge/obstructive
urge/functional
Urge
Urge
How do anticholinergics work for incontinence? - they ______ bladder capacity and ______ involuntary contractions
inc bladder capacity and decrease involuntary contractions
What type of incontinence are anticholinergics/musc used for?
Urge
stress
What are the AE of anticholinergics?
dry mouth
>IOP
delirium
visual changes
constipation
what kind of drugs are these Darifenacin (Enablex), Oxybutynin, Mirabegron (Myrbetriq ) - New
anticholinergics
what do alpha adrenergic agonists do for incontinence
increases smooth muscle contraction
What type of incontinence are alpha adrenergic agonists used for?
Stress incontinence due to sphincter weakness
What are the AE of alpha adrenergic agonists?
HA
Tachycardia
>BP
what kind of drugs are these
phenylefedrine
pseudoephedrine
alpha adrenergic agonists
What type of incontinence are Estrogen used for?
stress/urge due to atrophic vaginitis
What are the AE of Estrogens?
> BP
Endometrial CA
What type of incontinence are cholinergic used for?
Overflow incontinence 2/2 atonic bladder
What are the AE of cholinergic agents?
Bradycardia
hypotension
bronchospasm
> gastric acid secretion
What type of incontinence are alpha adrenergic blcokers used for?
overflow and urge from > prostate size
What are the AE of alpha adrenergic blcokers?
Orthostaic hypotension
Who is this surgery common in?
Repair of pelvic prolapse, bladder neck procedures
women with stress incontinence
Who is this surgery common in?
Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
men with Outlet obstruction secondary to BPH
Which catheter is this?
Males mostly, some available for females> risk of skin irritation and UTI'sMay promote dependenc
External Catheters condom with a drain
Which catheter is this?
Must be physically able
Usually seen in community setting
Less infection risk than indwelling
Intermittent Catheterization performed by caregiver or patient
Which catheter is this?
> infection risk, bladder stones, ? Ca
Only valid use chronic retention, non healing pressure
ulcers secondary incontinence
Crazy long term effects
indwelling Cath generally overused, generally seen in men
What is the only indication of an indwelling cath?
chronic retention
non healing pressure ulcer
How long does an indwelling cath remain?
30 days MAX (4 weeks)
Renal effect of old age:
EPO
Renal mass
Concentration power
Cr clearance
- increase
- decreased by 30%
- worse --> excess water
- decrease 7.5-10% per decade after 50*** (TQ)
Why do older people typically have edema?
Poor Na excretion