Chapter 19 + 20 - Hydrocarbons + Alcohols, Carboxylic Acids and Ester
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Homologous series
Family of organic compounds with the same functional group
Characteristics
Same general formula
Similar Chemical properties as they have the same functional group
Diff by CH2
Gradual change in physical properties
Alkanes
1.Functional Group
Saturated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon-carbon single covalent bonds
CnH2n+1
As molecule increase, melting/boiling point , viscosity and flammability increases
As molecule size increases, there is a stronger intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules
Hence more energy need to overcome/flow less easily
Reaction of Alkanes
Combustion
Burning in excess oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water
Is highly exothermic
Substitution reactions
Reaction with halogens in the present of ultraviolet light
A hydrogen atom is replaced/substituted by a halogen
Alkenes
Functional Group
Hydrocarbons that contain one or more carbon-carbon double bonds
Any molecule that contains carbon-carbon double bond (or triple) is describe as unsaturated
CnH2n
As molecule increase, melting/boiling point , viscosity and flammability increases
As molecule size increases, there is a stronger intermolecular forces of attraction between molecules
Hence more energy need to overcome/flow less easily
Reaction of Alkenes
Combustion
Addition reactions
with hydrogen (heat at 150,nickel catalyst)
Used to produce margarine from vegetable oil (polyunsaturated fat)
ethene → ethane
with aqueous bromine (room temp and pressure)
test for alkane/alkene
In alkene it will decolourize reddish-brown rapidly
with steam (heat at high pressure (300, 60atm) with concentrated H3PO4 (Phosphoric acid)
Alkenes → alcohol
Addition Polymerisation
High temp, high pressure and presence of catalyst
Forms a large molecule called a polymer
Cracking
Breaking down of long-chain hydrocarbons molecules into smaller hydrocarbons molecules
High temp (600) and aluminium oxide or silicon dioxide as a catalyst
Importance of cracking
Forms shorter-chain alkenes which are important materials for important industrial processes
Shorter-chain alkanes which are high in demand
Isomerism
Compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formula
Chain Isomerism
Straight chain (unbranched)
branched
Positional Isomerism
functional group is connected to a different carbon atom
Functional group isomerism
Same molecular formular but a different functional group
Alcohols
Functional Group
Organic compounds which have the hydroxyl (OH) functional group
CnH2n+1OH
Physical Properties
Volatile Liquids
Soluble in Water
Alcohols with a short hydrocarbon chain are very soluble
Increasing melting and boiling point
Size of molecule increases becomes larger. Hence, the strength of the intermolecular forces of attraction between the molecule increases, resulting in increasing melting and boiling points down the homologous series
Chemical Reactions
Combustion
Highly exothermic
Produces water
Oxidation by atmospheric oxygen
Alcohol + Oxygen → Acid + Water
Oxidation using oxidizing agent
Acidified KMno4
Heat under reflux
Produces water
Colour change of purple to colourless
Addition reaction with ethene
Steam, heated at high pressure and concentrated phosphoric(V) acid (H3PO4)
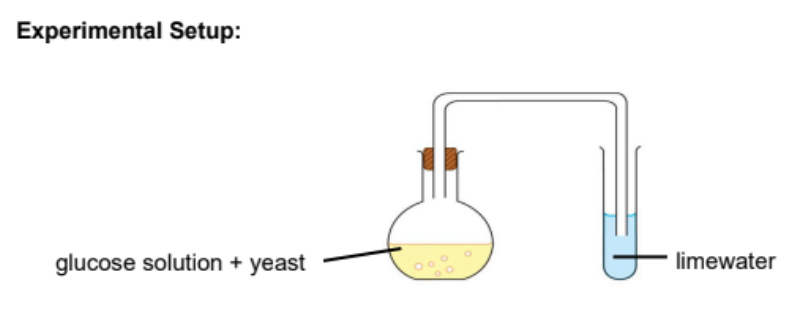
Fermentation
Yeast act on carbohydrates(glucose) in the absence of oxygen 37°C
Producing alcohol + carbon dioxide
37°C must be used as enzymes will denature and unable to catalyse the reaction
The stopper ensures the absence of oxygen in order to prevent the oxidation of ethanol into ethanoic acid by bacteria from the air
Limewater acts as an air lock to allow carbon dioxide to escape and to prevent oxygen from entering the set up
It is impossible to make pure ethanol by fermentation as yeast is killed when the mixture contains more than 15% ethanol
Ethanol can be extracted by fractional distillation allowing for higher concentration to be produced
Carboxyllic acids
Functional group
CnH2n+1COOH
Physical properties of Carboxylic acid
Very soluble in water
Melting point and boiling point increases down the group
Conducts electricity when dissolved in water due to mobile electrons
Chemical Reactions
Acid + Metal →Salt + Hydrogen
Acid + Metal Carbonate →Salt + Carbon Dioxide + Water
Acid + Base →Salt + Water
Acid + Alcohol ⇌ Ester + Water
Esters
What are they
Sweet-smelling, colourless liquid that are insoluble in water
Contains -COO- functional group
Esterification
Acid heated with alcohol in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid as a catalyst