NS 3410 Cellular Organelles
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
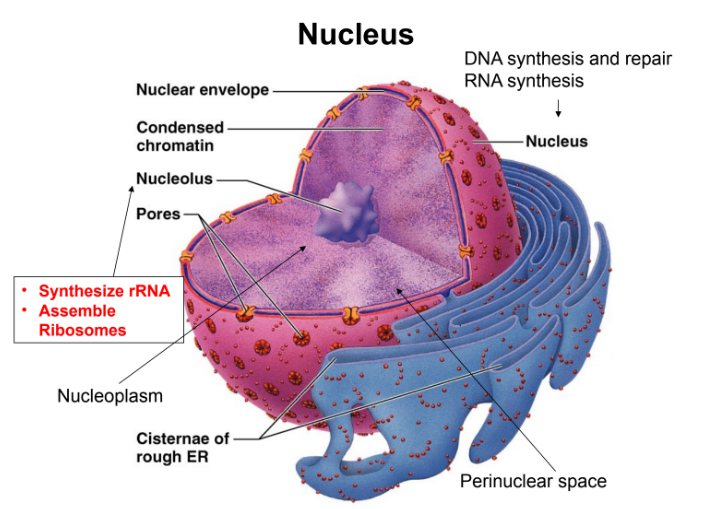
The Nucleus is comprised of what 4 things?
Nuclear envelope
Chromatin
Nucleoli
Distinct compartments rich in specific proteins
The nucleus contains ____ and its the ____ center of the cell
genes; control
The nucleus dictates the kinds and amounts of ____ to be synthesized
proteins
Cells and be either?
anucleate or multinucleate
mRNA’s (made in the nucleus) are directed to certain locations before proteins are made. Why?
it helps save energy and help prevent interactions as proteins trafficked
RNA’s may have ___ to position them within cell
“zip codes”
What two functions do Nucleolus’ serve?
Synthesize rRNA
Assemble Ribosomes
What are the 5 functions for the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)?
Synthesize lipids and steroids
Detoxify drugs
Metabolize carbohydrates
Metabolize steroids
Regulate Ca concentrations
What does the prefix sarco mean?
muscles
What is the Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum of muscles? What does it do?
Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR); Regulates Ca concentrations which is integral to muscle contraction
What are the 3 main functions of the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Protein Folding
Quality Control- Identify misfolded proteins so they are degraded in cytoplasm (ERAD= ER- associated protein degradation)
Can regulate pace of protein folding via process called UPR= unfolded protein response
Polypeptides translated from ____ into the ER
ribosome
What two things do ER do to achieve correct confirmation?
Glycosylates
Modifies
Where are proteins exocytosed out to?
cis side of Golgi apparatus
What is the main function of ribosomes?
synthesize proteins
What are the two subunits of ribosomes
Small ribosomal subunit
Large ribosomal subunit
each subunit contains ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
For protein synthesis to begin what needs to happen?
Small and large subunits join together with a strand of
messenger RNA (mRNA; made in the nucleus)
What are the two types of ribosomes?
Free floating→ scattered throughout cytoplasm
Fixed → attached to Endoplasmic Reticulum ER
What is the main function of golgi apparatus?
packaging proteins into vesicles
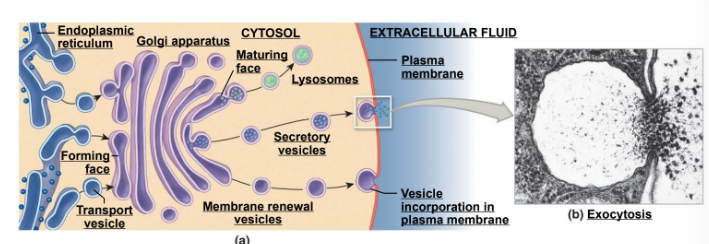
What is exocytosis?
proteins destined for release outside of the cell
What is the function of secretory vesicles?
proteins stored in vesicle within the cell until signal given for their release
What are lysosomal enzymes?
proteins targeted for lysosome; hydrolases, digestive enzymes, membrane proteins
What are lyosomes “cellular stomach”?
Spherical membranous bags containing powerful digestive enzymes – cleanup and recycling within the cell
Lysosomes digest ingested?
Bacteria, viruses, and toxins
Lysosomes degrade what?
nonfunctional organelles and macromolecules
What is autolysis?
to destroy cells, proteins, and organelles
Products of digestion can be _____ by the cell or removed by _____
reutilized; exocytosis
The interal pH of lysosomes is ~5; How is this maintained?
through proton pumps and chloride ion channels
Many lysosomal enzymes exist what are some examples?
– Polysaccharide hydrolyzing enzymes
– Protein hydrolyzing enzymes
– Nucleic acid hydrolyzing enzymes
– Lipid hydrolyzing enzymes
– Phosphatases / Sulfatases
What do peroxisomes do?
Detoxify harmful or toxic substances
Peroxisomes function in the breakdown of what?
fatty acid (beta oxidation of very long chain FA; those too long to be broken down in mitochondria)
Peroxisomes produce what?
hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Peroxisomes contain enzymes (catalase) that do what?
breakdown H2O2 into water and oxygen; and enzymes that utilize peroxide in same compartment to help prevent toxicity of H2O2
Peroxisomes contain over 50 enzymes depending on tissues; they are numerous peroxisomes in what two organs?
liver and kidney (detoxification)
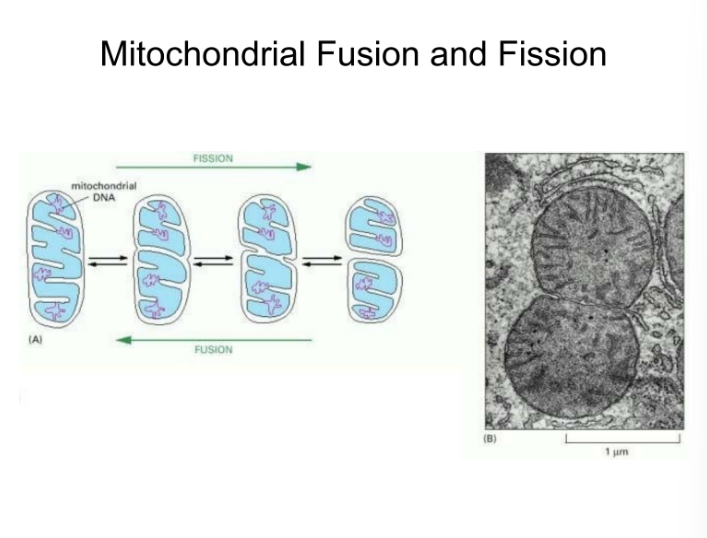
Mitochondria converts organic material into cellular energy ATP; it is the powerhouse of the cell; It what type of metabolism?
aerobic metabolism; requires oxygen
The Mitochondria produces 95% of ATP needed to keep cell alive; Urea/heme synthesis; Mitochondiral DNA is unique from ______
nuclear DNA
What are the two cytoplasmic organelles that are non-membraneous?
1) Ribosomes
2) Cytoskeleton (microtubules, microfilaments, intermediate filaments)
The cytoskeleton is the “skeleton” of the cell; it is dyanmic, elaborate series of rods running through the cytosol; It consists of what 3 things?
1) Microtubules
2) microfilaments
3) intermediate filaments

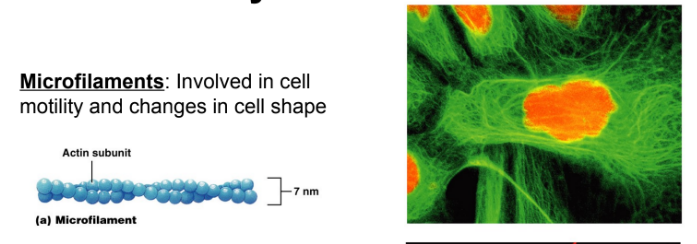
What are microfilaments?
involved in cell motility and changes in cell shape

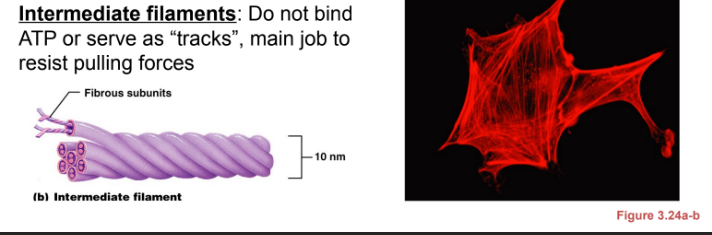
What are intermediate filaments?
do not bind ATP or serve as “tracks” main job to resist pulling forces

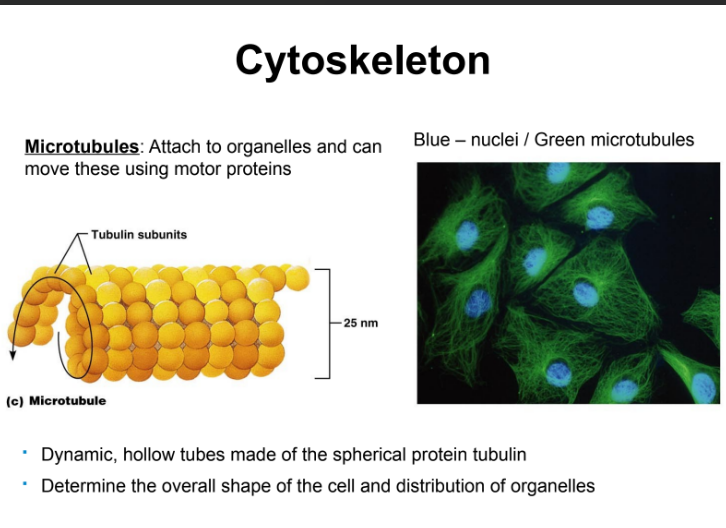
What are microtubules?
attach to organelles and can move these using motor proteins
Determine the overall shape of the cell and distribution of organelles
Take home messages: Plasma membrane
dynamic structure to all cells
Take home messages: Nucleus
control center, double membrane; a or multinucleate
Take home messages: ER
continuous with nuclear membrane, site of protein synthesis, protein folding, UPR, ERAD, Ca storage (SER), RER
Take home messages: Golgi apparatus
responsible for modifying, packaging and sorting proteins for subsequent cellular use or exocytosis
Take home messages: Lysosomes
responsible for enzymatic degradation of many cellular products
Take home messages: Proteosome
degragde mis-folded proteins
Take home messages: Peroxisomes
oxidation of very long chain fatty acid
Take home messages: Mitochondria
double membrane, ATP production, ETC, oxidative phosphorylation
Take home messages: Cytoskeleton
microfilament, intermediate, microtubule
Take home messages: Cellular organelle composition facilities?
tissue/organ function