Electrode potentials and cells PMT
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
redox reaction?
an oxidation reaction paired with a reduction reaction
reducing agent?
electron donor
oxidising agent?
electron acceptor
displacement reaction?
redox reaction where one element (stronger reducing) takes the place of another (weaker oxidising)
why can zinc displace copper but copper cant displace zinc?
zinc is a stronger reducing agent than copper, so displaces copper;
copper is a stronger oxidising agent
single displacement?
one element is displaced
double displacement?
two elements are displaced
are single displacements redox?
all single displacements are redox
are double displacements redox?
never redox
where are the strongest reducing agents in the electrochemical series?
at the top
where are the strongest oxidising agents in the electrochemcial series?
at the bottom
what will each metal act as a reducing agent for?
anything below it in the electrochemical series, elements with weaker reducing power
ions of each metal will act as an oxidising agent for?
elements above it in the series/weaker oxidising power
what makes redox reactions stronger?
elements that are further apart in the series = release more energy
what causes release of energy in redox?
transfer of electrons
what is a half cell?
a single electrode/metal dipped in a solution of its ions
what is an electrochemical cell?
Two half cells connected together using a salt bridge, wires and a voltmeter
what is a salt bridge?
liquid junction of unreactive ions that can moce between the solutions to carry flow of ions but will not interfere with the reactions
function of salt bridge?
completes the circuit, allows transfer of ions
battery?
two or more cells connected together
how can half cells reach equilibrium in a closed system?
reversible reactions
compare reducing agents equilibrium to oxidising agents equilibrium?
left of the oxidising agents, stronger = more to left
in which half cell are there more delocalised electrons?
more in the metal that acts as the reducing agent, because equilibrium lies to the left

which way do electrons flow?
away from reducing agent (more -vely charged), towards oxidising agent (more +vely charged)
what reaction occurs at the anode (+ve)?
oxidation
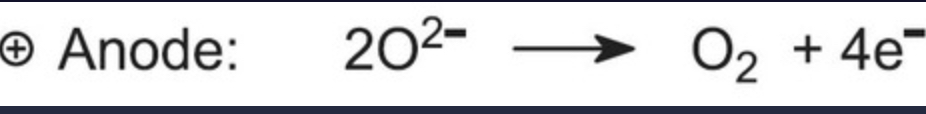
charge of anode?
Positive (attract anions)
reaction at cathode (-ve)?
reduction
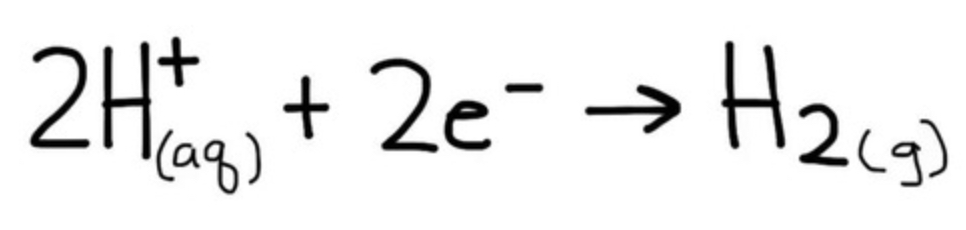
charge of cathode?
Negative (attract cations)
which way do cations (+ve) flow in a cell?
towards the cathode/negative electrode
which way do anions (-ve) flow in a cell?
towards anode
how is the equilibrium in the reducing agent half cell disrupted?
conc. of e- decreases as it goes to oxidising
shifts to left to oppose change
more electrons flow through the wire, to oxidising
how is the equilibrium in the oxidising agent half cell disrupted?
conc. of e- increases
equilibrium shifts to right to oppose change
how to measure reducing strength of a cell?
add a voltmeter -> potential difference shows reducing strength
how does resistance affect voltage/p.d?
more resistance = lower voltage
electromotive force, E?
maximum voltage possible between two electrodes, not affected by resistance
potential difference?
actual votage measured between two electrodes, is affected by resistance
conventional cell representation rules?
most negative half cell goes on the left
most oxidised species from each half cell goes next to salt bridge
salt bridge = double line ||
includes state symbols
reduced, oxidised || oxidised, reduced
draw standard hydrogen electrode/half cell
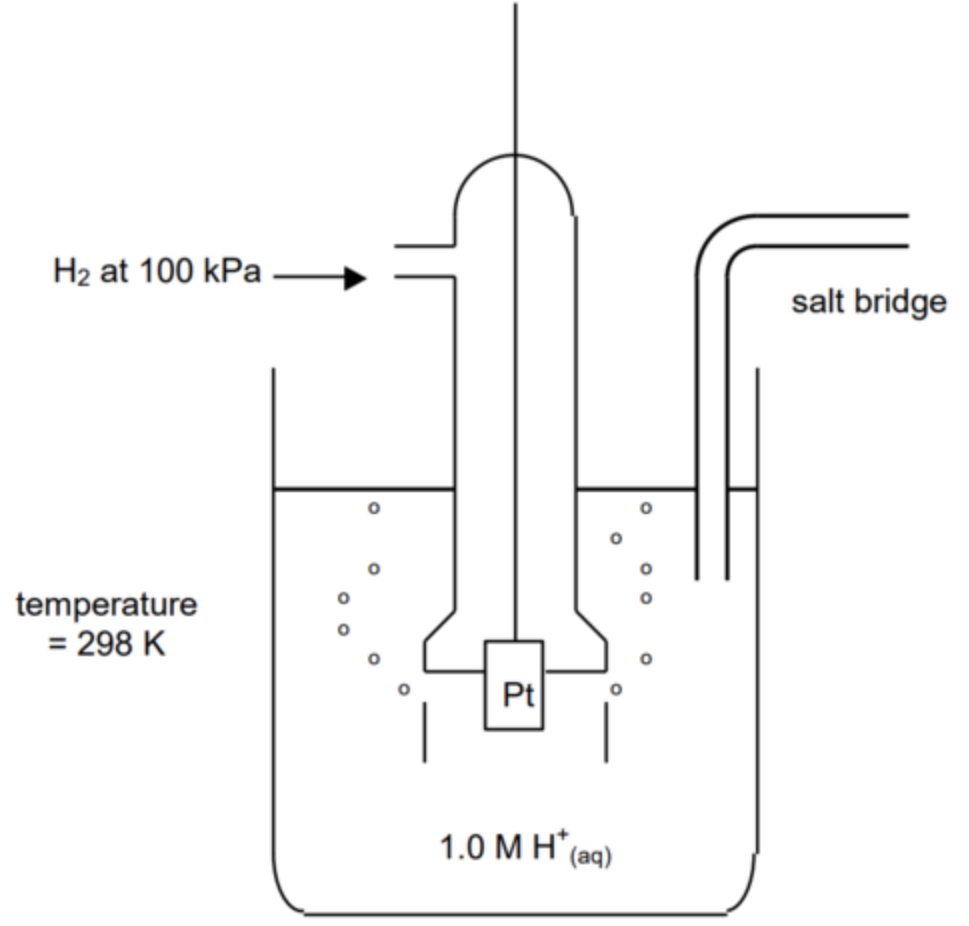
what is the SHE used for?
measuring standard for hald-cell potentials, has a cell potential of 0V, measured under standard conditions
standard conditions used for electrochemical cells?
solutions of 1.0moldm-3 concentration
298K
100kPa
if the hydrogen electrode is connected to a stronger reducing agent, which reaction happens?
hydrogen ions pick up e- from Pt and are reduced to H2 (g)
2H+ (aq) + 2e- ⇌ H2 (g)
if the hydrogen electrode is connected to a weaker reducing agent (stronger oxidising agent), which reaction happens?
H2(g) oxidised to hydrogen ions and e- flow to oxidising electrode
hydrogen electrode consists of?
strip of platinum dipped in a solution of hydrogen ions (H+, from HCl) bubbled through hydrogen gas
pros of using platinum in SHE?
metallic, so will conduct electricity, but are also inert so will not interfere with the reaction
how to calculate a half cell potential?
measure under standard conditions and compare to the SHE, which is 0V
what does a negative potential mean in terms of oxidation and reduction?
substances are more easily oxidised and will lose electrons
what does a positive potential mean in terms of oxidation and reduction?
substances are more easily reduced and will gain electrons to become more stable
cell EMF calculation?
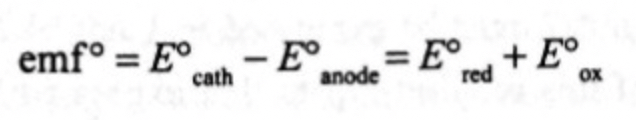
what EMF value would you get for a favourable, spontaneous reaction?
positive value, more positive = more favourable
anticlockwise rule to combine half cell reactions?
write the most negative EMF on top
draw anticlockwise arrows around reactions
balance electrons on both sides
write out the cell reaction
are positive electrode potential species better oxidisng or reducing agents?
oxidising agents, so will oxidise species more negative than it
are negative electrode potential species better oxidisng or reducing agents?
reducing, so will reduce those less negative than it
effect of increasing the concentration of solutions used in the electrochemical cell on cell EMF? why?
makes the cell EMF more positive as fewer electrons are produced in the reaction
effect of increasing pressure of the cell on EMF?
more negative, as more electrons are produced (equilibrium determined from half equations x)
3 types of uses for electrochemical cells?
produce non-rechargeable, rechargeable or fuel cells (commercial cells for energy)
reactions that take place within a rechargeble cell?
reversible reaction, meaning reactants can reform
common cells used as rechargeable batteries in phones, laptops and cars?
lithium ion cells
what do lithium ion cells/batteries consist of?
lithium cobalt anode and graphite (carbon) cathode, an electrolyte of a lithium salt in an organic solvent to carry the flow of charge
half equation for the negative electrode in a lithium ion cell?

half equation for the positive electrode in a lithium ion cell?
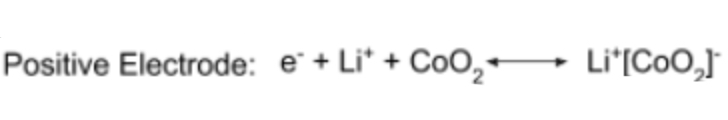
full half equation for a lithium ion cell?
Li + Li+ + CoO2
in order to be recharged, what needs to be applied?
a current over the cell, which forces the electrons to move in the opposite direction, causing reaction to reverse = recharging
why cant non-rechargeable cells recharge?
reactions used arent reversible