AICE INFO TECH (AS LEVEL) Theory Study Guide
1/254
Earn XP
Description and Tags
theory with everything from both Hodder and camb textbooks
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
255 Terms
data
raw numbers, letters, symbols, sounds, or images without meaning (ex. 1249430, 06/18/2009)
information
data with context and meaning
direct data source
data that is collected for the purpose for which it is used. (primary source if ur in aice psych or socio)
Questionnaires
Questionnaires
-useful when there are a large number of respondents
-statistical analysis will be used on the results.
-elicit the information required
-enable analysis of the data effectively
-gather enough information without putting people off from completing the questionnaire
Online Questionnaires
-enable quicker analysis of data
-data is entered directly into a database
-no further data entry by a third party is necessary
indirect data source
data that was collected for a different purpose (secondary source)
How do governments use electoral registers? (ex of an indirect source)
-governments keep a register of people who are registered to vote in each household
-includes names and addresses
-main purpose is to enable those people to vote in elections
-option for individual entries on an electoral register to be hidden from public view
Advantages/Disadvantages of Direct Data Sources
Advantages
-data will be relevant because what is needed has been collected
-original source is known and can be trusted
-data is likely to be up to date because it has been collected recently
-can be collected and presented in the format required
-bias can be eliminated by asking specific questions
Disadvantages
-it can take a long time to gather original data rather than use data that already exists
-a large statistical sample of data can be difficult to collect for one-off purposes
Advantages/Disadvantages of Indirect Data Sources.
Advantages
-the data is immediately available
-if statistical analysis is required, then there are more likely to be large samples available
Disadvantages
-additional data that is not required will exist, may take time to sort through, and data that is required may not exist
-original source is unknown most of the time and so it cannot be assumed that is reliable
-data may be out of date because it was collected at a different time
-original data may be biased due to its source
-data is unlikely to be in the format required, which may make extracting the data difficult
Accuracy (quality of info)
data must be accurate in order to be considered of good quality. Ex of inaccurate data include misspellings, incorrect decimal placing, incorrect dates or time.
Relevance (quality of info)
Information must be relevant to its purpose. Having additional information that is not required means that the user must search through the data to find what is actually required. Like most examples include being given the wrong data (like bus info vs train info).
Age (quality of info)
Information must be up to date to be useful. Old information is out of date and therefore no longer useful. (ALWAYS CHECK INDIRECT DATA SOURCES)
Level Of Detail (quality of info)
There needs to be the right amount of information for it to be good quality. Its possible to have either too much or too little information provided. If there is not enough information, then it is not possible to use it correctly.
Completeness (quality of info)
All information that is required must be provided in order for it to be of good quality. Not having all the information required means it cannot be used properly.
What is needed to ensure complete quality of information?
Accuracy, Relevance, age, completeness, level of detail
Encryption
A type of encoding. Encryption is the scrambling of data so it cannot be understood without a decryption key to make it unreadable if intercepted.
Why would encryption be important?
-It encrypts data when it is stored on disks or other storage media.
-It encrypts data when being sent across a network protecting data.
-It is important when sending or storing sensitive data such as personal data or a company’s sales or other data.
-Data being sent across a network or the internet can be intercepted by hackers.
-Data stored on storage media can be stolen or lost.
-The purpose of encryption is to make data difficult or impossible to read if it is accessed by an unauthorized user.
Caesar Cipher
-Julius Caesar created the Caesar Cipher
-Also known as the shift cipher
-Selects replacement letters by shifting along the alphabet
Cipher
-A secret way of writing, in other words, a code.
-Special type of algorithm which defines the set of rules to follow to encrypt a message
Two types of encryption for data
Symmetric and Asymmetric
What is symmetric encryption?
-Oldest methods of encryption
-Requires both sender and recipient to possess a secret encryption and decryption key known as a private key
-Secret key needs to be sent to the recipient.

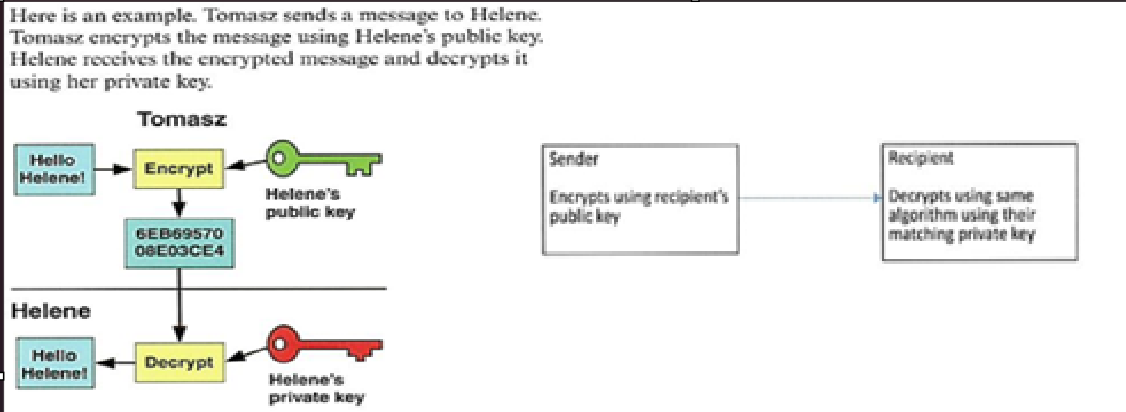
What is asymmetric encryption?
-also known as public key cryptography
-overcomes the problem of symmetric keys being intercepted by using a pair of keys
-includes a public key which is available to anybody wanting to send data
-includes a private key which is available to anybody wanting to send data and one that is only known to the recipient.
-the key is the algorithm required to encrypt and decrypt the data.
-requires a lot more processing than symmetric encryption and so it takes longer to decrypt the data.
-more secure than symmetric
-in order to find the key, digital certificates are required, which identify the user or server and provide the public key.
-digital certificates include the organization name, email, etc
SSL
Secure Socket Layer
-security method used for secure websites
-uses asymmetric encryption
-once SSL has established an authenticated session, the client and server will create symmetric keys for faster secure communication
TLS
Transport Layer Security is the same as SSL but supersedes it because it is newer. Both cam be referred to SSL.
Hard Disk (applications of encryption)
-Disk encryption will encrypt every single bit of data stored on a disk.
-encryption key will be required to access any file
-not limited to disks but backup tapes such as USB (universal serial bus) and flash memory can also use it since they are susceptible to being lost or stolen.
-data is usually accessible by entering a password or using a fingerprint to unlock the encryption.
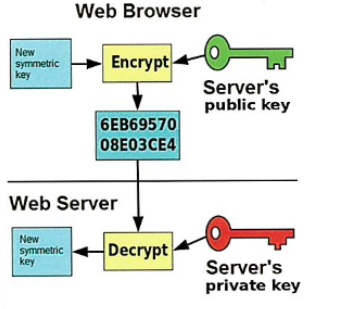
HTTPS (applications of encryption)
-Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is the encryption standard used for secure web pages.
-Uses SSL/TLS
-when a browser requests a secure page, it will check the digital certificate to ensure that it is trusted, valid and that the certificate is related to the site form which it is coming.
-the browser and web server then communicate using a symmetric encryption key which is faster than asymmetric
HTTP (applications of encryption)
-normal web pages that are not encrypted are fetched and transmitted using Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
-anybody who intercepts web pages or data being sent over HTTP would be able to read the contents of the web page or the data.
Email (applications of encryption)
-uses asymmetric encryption
-recipients of emails must have private key that matches the public key used to encrypt the original email
-both sender and recipient will need to send each other a digitally signed message that will add to the persons digital certificate
-encrypting an email will also encrypt any attachments
How encryption protects data
-Encryption scrambles the data so if it is found, it cannot be understood.
-does not stop data from being intercepted, stolen, or lost
-Strong 256-BIT AES encryption, it is almost impossible for somebody to decrypt the data
Validation (Checking the accuracy of data)
the process of checking data matches acceptable rules. When data is validated, if it conforms to the rules then it will be accepted. If it does not, then it will be rejected and a DETAILED error message will be presented.
Types of validation checks
Presence, range, format, type, lookup, consistency, and check digit.
Range Check (validation check)
range check ensures data is within a defined boundary/range. A limit check has a single boundary. A range check has 2 boundaries. Uses >(greater than), <(less than), >=(greater than or equal to), and <=(less than or equal to).
Type Check (validation check)
ensures data is of a defined data type. Ex. “Must be integer,” “Must be text,” ”must be date,” “must be numerical,” etc.
Lenght Check (validation check)
Ensures data is within a defined length or within a range of lengths. Ex. “Must be at least
Format Check (validation check)
ensures data matches a defined format, must follow a pattern.
An example of this is email addresses.
-Also known as picture check
Lookup Check (validation check)
Checks tests to see if data exists in a list.
Ex. Checking to see if a grade has been entered
Consistency Check (validation check)
Compares data in one field with data in another field to see if it already exists within a record to see if they are both consistent with each other.
Check digit (validation check)
a number or letter that is added to the end of an identification number being input. It is a form of a redundancy check because the check digit is redundant for the identification number. An algorithm is performed on it and then the result of the algorithm should match the check digit, if it matches it is valid.
Verification (Checking the accuracy of data)
ensuring data entered into the system matches the original source.
Types of verification checks
visual, double data entry, hash total, control total, parity check, and checksum.
Visual Checking (Verification Check)
for the user to check visually if the data entered matches the original source. Compares the data displayed and original data.
Double Data Entry (Verification Check)
Input data into the computer system twice. Two items of data are compared by the computer system and if they match then they are verified.
Hash Total (Verification Check)
Hash totals can be used when inputting sets of data. A hash total is calculated by adding together values from an input field for all the records that need to be input. User will manually add up the values. Once input is completed, the computer will compare the hash total it calculates automatically with the calculated one.
Control total (Verification Check)
Similar to hash totals, but control totals have some useful meaning.
Parity Check (Verification Check)
Used to find errors during data transmission. Each byte is checked individually. Only check to see if an error occurred during data transmission. With an odd parity, the total number of on bits in a byte must be an odd number.
Checksum (Verification Check)
result of a calculation on the contents of a file used to check whether a file has been transmitted or copied correctly. Useful if checking that a hacker hasn’t disguised a malicious file as a genuine one.
Batch Processing (type of data organization)
individual or transaction that need to be performed on the data are not done one by one by an operator in ‘real time’ but are collected together in a batch. Then the system automatically carries out all of the transactions and updates the data file. It needs to be stored first before it is used. Using master files or transaction files.
Master files
a table in a database containing information about one set of things, for example, employees.
Transaction file
data that is used to update a master file.
Process of updating master files with transaction files
The complete batch of records in the transaction file is processed and validated and then any invalid data is removed. The transaction file is sorted so that it is in the same order as the master file.
Batch processing advantages/disadvantages
Advantages
-single, automated process requiring little human participation which reduces costs
-can be scheduled to occur when there is little demand for computer resources, for example, at night
-as it is an automated process there will be none of the transcription and update errors that human operators would produce
-there are fewer repetitive tasks for the human operators
Disadvantages
-there is a delay as data is not processed until the specific time period
-only data of the same type can be processed since an identical, automated process is being applied to all of the data.
-errors cannot be corrected until it is complete
Online processing (type of data organization)
also known as interactive processing, data is input by the user and feedback is given in the form of outputs
Electronic funds transfer (type of data organization)
the transfer of funds electronically to or from a bank account.
online stores (type of data organization)
enables a customer to purchase a product from anywhere in the world and have it delivered to their home address. Uses an interactive system where the customer can browse or search for products using a website.
Automatic stock control (type of data organization)
Purpose of a stock control system is to ensure that a shop always has enough stocks to sell and never has too many. The main feature of a stock control system is the database which will store data about each product that the shop stocks. The product will be scanned with its barcode, the barcode number will be found in the database and the quantity recorded and automatically update.
Electronic Data Exchange (type of data organization)
EDI is the standardized format for exchanging data between organizations. For example, exchanging AP exams with college board to get scores. API (application program interfaces) are used to provide a standard interface for importing and exporting data between the different softwares.
Business-To-Business buying and selling
when a business buys in bulk from a supplier, the process can be made easier by having a common interface for sending the order and receiving the order. Some large wholesalers may insist on clients using the wholesaler’s own software, but most will provide an API for clients to link their own software to.
Real-Time processing
data is processed as soon as it has been input and outputs are generated immediately.
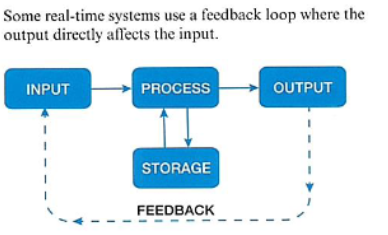
How does air traffic control use real-time processing?
data such as the location of all the airplanes currently in the air is processed immediately so it can be known by everybody using the system. this is vital so no planes have path collisions. There cannot be a delay because it can be catostrophic.
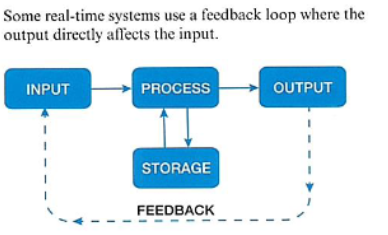
How do computer games use real-time processing?
The input from the user needs to be processed immediately so that it can take effect and the game can be controlled. Each time a user asks a game character to move forward by pressing a key or button, the character needs to do this immediately.
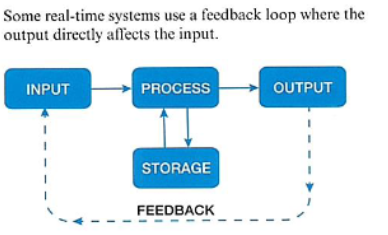
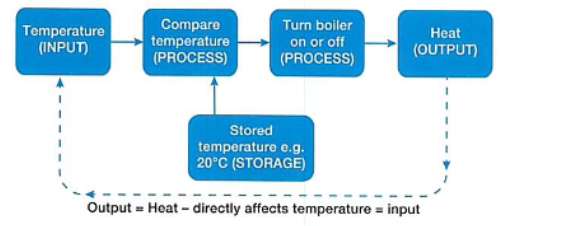
How do central heating systems use real-time processing?
Its constantly monitoring the temperature of its surroundings. The desired temperature stored it monitored in case it is too high or below the preset. Uses a controlled loop to change the temperature and turn on boiler if needed.
How do rocket guidance systems use real-time processing?
when a rocket is launched, the launch happens in real-time. If the rocket veers off the course, then any delay in receiving instructions could see the rocket continue in the wrong direction or, ultimately crash. A rocket guidance system needs to provide stability for the rocket and to control its movements. The position and rotation is constantly moving so these need to be monitored and the input changed in real-time.
Data Logging
a computer and sensor collect data. Often outputted in charts.
Devices
hardware component of a computer system consisting of electronic components.
software
programs which give instructions to the computer
operating systems
software that manages the hardware within a computer system
Mainframe computers
powerful computer serving several terminals. used for large scale transactions and business databases, also, statistical analysis such as analysis of census data. Generates a lot of heat so cooling systems are required.
Supercomputers
large computer with parallel processing to complete highly complex tasks quickly. Used in quantum mechanics since they can process things with complex equations. Used in weather forecasting and climate research. Needs to be available 100% of the time. Needs to have backup hardware components in case one fails. Generates a lot of heat so cooling systems ARE NECESSARY.
MIPs (millions of instructions per second)
Measurement of how many instructions its processors can perform every second. Not accurate measurement anymore since CISC (complex instruction set computing) processors will have a single instruction and perform many tasks at once whereas RISC (reduced instruction set computing) will have a single instruction but manage to do very little.
FLOPS and MFLOPS
floating point operations per second AND mega floating point operations per second.
FLOPS
-used for scientific computational research
MFLOPS
-more often used than FLOPS and MIPS
-more reliable than MIPS
Advantages of mainframe computers
-they are designed to be reliable, available, and serviceable (RAS)
-scalable because processors and memory can be added as required
-designed to last at least 10 years
-able to store and process extremely large amounts of data
-more than one operating system can be used at once which can improve the overall performance of the system
-hardware failures are notified immediately so that replacements can be made very quickly
-terminals only require input and output devices and can take advantage of processing power of the mainframe
Disadvantages of mainframe computers
-high cost of mainframes and supercomputers mean that they are only used by large organizations
-a lot of space is required to install them and the temperature must be maintained so that it doesn’t overheat
-specialist support staff are required for maintenance
-the interface is command driven which can be difficult to understand
-supercomputers are processing big data and so need massive external storage drives that are capable of reading and writing data quickly enough for the processing
System software
software needed to operate a computer system
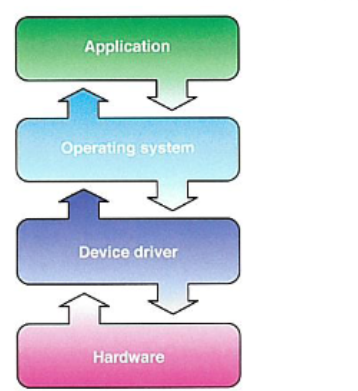
BIOS
Basic input/output system. First operating system in the piece of hardware that will load. Sits between hardware and application software’s and manages any communication between the two.
How does operating systems manage hardware?
-allocating memory to software
-sending data and instructions to output devices
-responding to input devices such as when a key is pressed
-opening and closing files on storage devices
-giving each running task a fair share of processor time
-sending error messages or status messages to application or users
-dealing with users logons and security
Device drivers
software that comes with ane xternal hardware component and sends customized instructions to that specific component. Uses generic commands
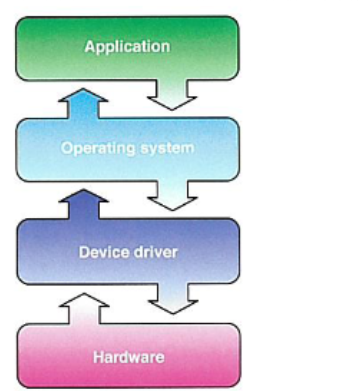
Translators
translates a program written in a high-level programming language into machine code that a computer can understand.
Compilers (type of translator)
type of translator which creates a file containing the machine code known as an executable file because it can be executed by the processor. Original file is known as the source file.
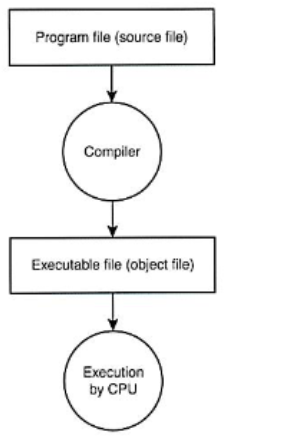
Compilation process for compilers
1st: Lexical analysis
2nd: Syntax analysis
3rd: Code generation
Lexical analysis (compilation process)
any white space or comments will be removed and the code will be broken down into tokens Token represent a keyword, constant, identifier, string, number, etc.
Syntax analysis (compilation process)
the structure of the program will be analyzed to check that it conforms to the syntax of the programming language. Dictionary will be created which is a list of variables used by the program, their data types and memory location to be used.
Code generation (compilation process)
final phase where source code is converted to machine code for the target machine type.
Interpreters (type of translator)
translate and executes a program written in high-level programming language one line at a time. Can be used with a compiler.

Compiler vs Interpreter
Compiler
-translates source code into object code all at once
-compiled object code will only work on the operating system it has been compiled for
-object code is ready to be executed without any delay
-compiling can take a long time, not appropriate for on-the-fly testing
-errors are reported after compilation has been completed
-source code is optimized to run as efficiently as possible
Interpreter
-translates source code one line at a time
-source code can be translated into object code for more than one operating system
-object code has to be generated so additional time is added to the execution time
-only the required code needs to be interpreted so this is efficient for on-the-fly testing
-errors are reported as they are found during the interpretation
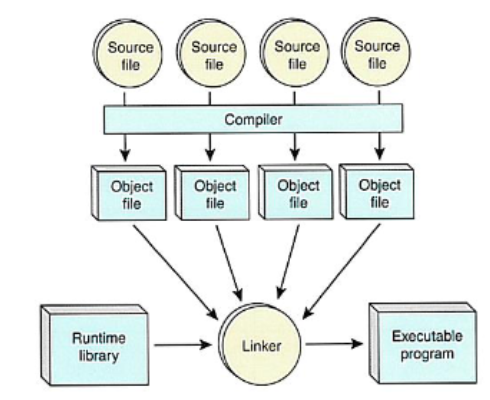
Linkers
computer programs often consist of several parts of programming code. The linkers function (also known as link editor), is to combine the object files together to form a single executable file.
Utility Software
software that performs some sort of maintenance on the computer system
Anti-Virus (type of Utility Software)
deals with other threats such as adware and spyware. It has two main functions; anti virus monitor which monitors the system for viruses, and the second function checks to see if there are ALREADY malware in the system.
Backup (type of Utility Software)
Creates a second copy of data and programs that are in storage.
Data compression (type of Utility Software)
reduces the original size of files so it uses less storage space.
Disk defragmentation (type of Utility Software) USED ONLY FOR HARD DRIVES
organizes all files so that each file is kept together. Moves fragmented parts of files that are related and makes it into one sector, and removes/moves small files to free space.
HDD (hard disk drive)
stores data onto a driver. Contains two main parts: the read/write head which sits at the end of an access arm and magnetizes sectors onto the disk (platter). Each platter will have tracks and each track will split into sectors. The tracks that are in the same position on each platter form a cylinder. When possible, a computer will attempt to store data in clusters on a single cylinder.
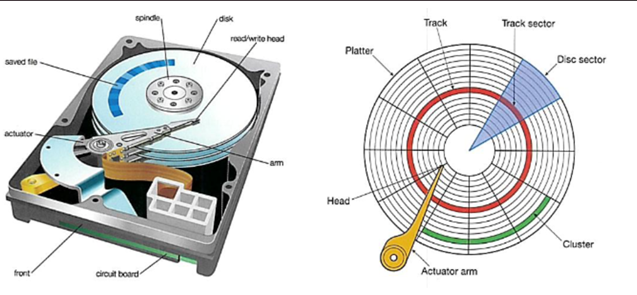
Fragmented files
as a hard disk gets used, files are kept together in storage on the same cylinder or adjacent cylinders. When files are deleted, gaps are left on the disk. As the files grow in size, they use up more space on the disk and may no longer be on the same cylinder.
Formatting HDD files
process of organizing the tracks on the disk into sectors. Each sector is where data is stored.
File management in HDD files
Files can be copied using features within an operating system’s own interface. However, this can be slow and options are limited.
Off-the-shelf-software
general purpose software available to the large market
Custom-written software
software that is written especially to meet the requirements of a client
Advantages/Disadvantages of Custom-written software
Advantages
-requirements of the client can be precisely met with no additional or unnecessary features
-developers of the software will ensure that the software is compatible with the hardware
-client will have access from the developers for support
Disadvantages
-entire development cost of custom written software is met by the client which makes it expensive
-takes a long time to develop, so client will have to wait
-may have bugs since it has never been used before
Advantages/Disadvantages of Off-the-shelf software
Advantages
-cost is spread between all the customers who purchase it at a specified price, which means the cost is much lower
-immediately available so it can be used right away
-bugs will have already been found and patches will be added as its used
-able to get a range of support from public resources such as forums
Disadvantages
-some tasks that the customer needs to carry out may not be possible and there will be unnecessary features.
-software may not be compatible with existing hardware or software used by customer
Proprietary software
owned by a single person or organization who sells it for use under an agreed license.
Open source software
source code is freely available. it can be changed or shared.
User-interface
communication between the user and the computer system