CH 2 Metalloids, Subatomic Particle Properties, Average Atomic Weights, Periodic Table Groups, Compound Naming Rules
1/5
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
6 Terms
List 6 metalloids
B, Boron
Si, Silicon
Ge, Germanium
As, Arsenic
Sb, Antimony
Te, Tellurium
basic properties (charge, approx. mass...) for protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Subatomic Particle | Symbol | Charge | Mass |
Proton | p or p+ | +1 | 1 AMU |
Neutron | n or n0 | 0 | 1 AMU |
Electron | e- | -1 | 0 AMU |
Equation to calculate average atomic weights.
Average Mass =
[Mass isotope #1 x (% abundance /100) ] +
[Mass isotope #2 x (% abundance /100) ]
…(continued for all isotopes)...
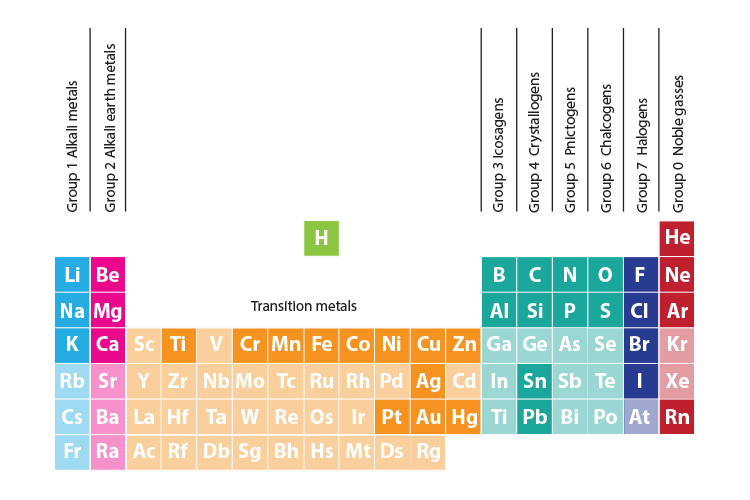
where “Alkali Metals,” “Alkaline-Earth Metals,” Transition Metals,”
“Halogens,” and “Noble Gases” are found on the periodic table.
Group 1: Alkali Metals
Group 2: Alkaline Earth Metals
Transition Metals (sunken step into p-table)
Group 7: Halogens
Last Group: Noble Gases
Ionic compound naming rules
Name the cation first
Then name the anion
If a single element (i.e. Chlorine) change suffix to -ide
If polyatomic simply state name of the polyatomic
If metal with variable charge present, include roman numerals
ex: Pb4+ is lead(IV).
Ionic compounds always based on empirical formula
Covalent compound naming rules
Write elements in the order given, changing suffix of last element to “-ide”
add appropriate prefixes to each element (mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, hepta, octa, nona, deca)
Name based on molecular, NOT EMPIRICAL formula unlike ionic compounds