Lesson 58 - Introduction to the integument (part 2) - Outer ear & specialized skin structures
1/142
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
143 Terms
Why can diseases of the ears also affect the body?
ear canals are lined with skin
What can otic disease cause?
pain, discomfort, pruritis
What are some examples of diseases of the body affecting the ears?
1. Allergic skin disease can cause inflammation of the pinna & ear canals and predispose to 2˚infection
2. Endocrine disease can cause pinna to be greasy with scaling on margins
3. Auto-immune disease can cause ulcerative lesions on the pinna
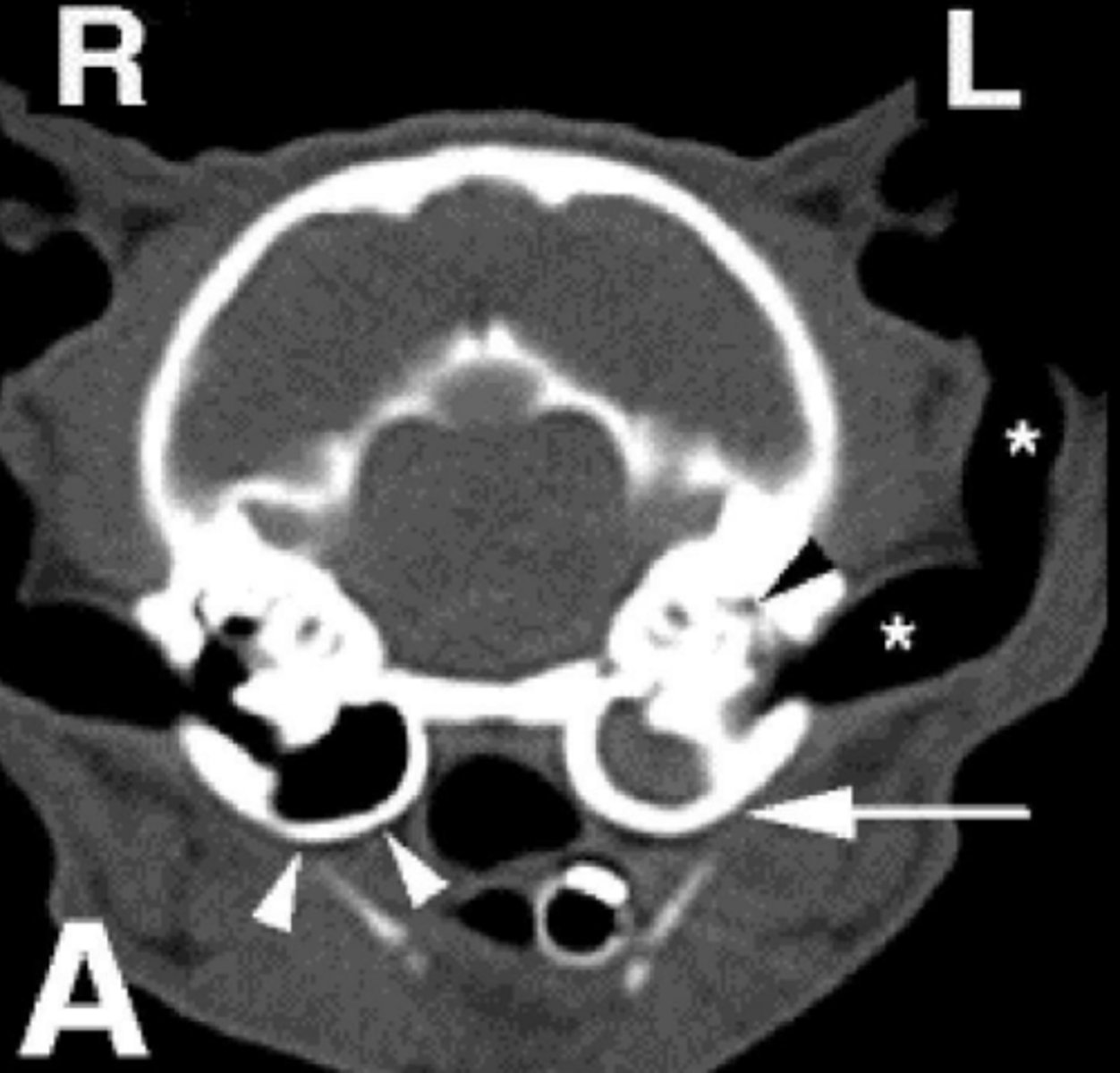
What are the top differential diagnoses for this image?
1. polyp
2. infection (otitis media)
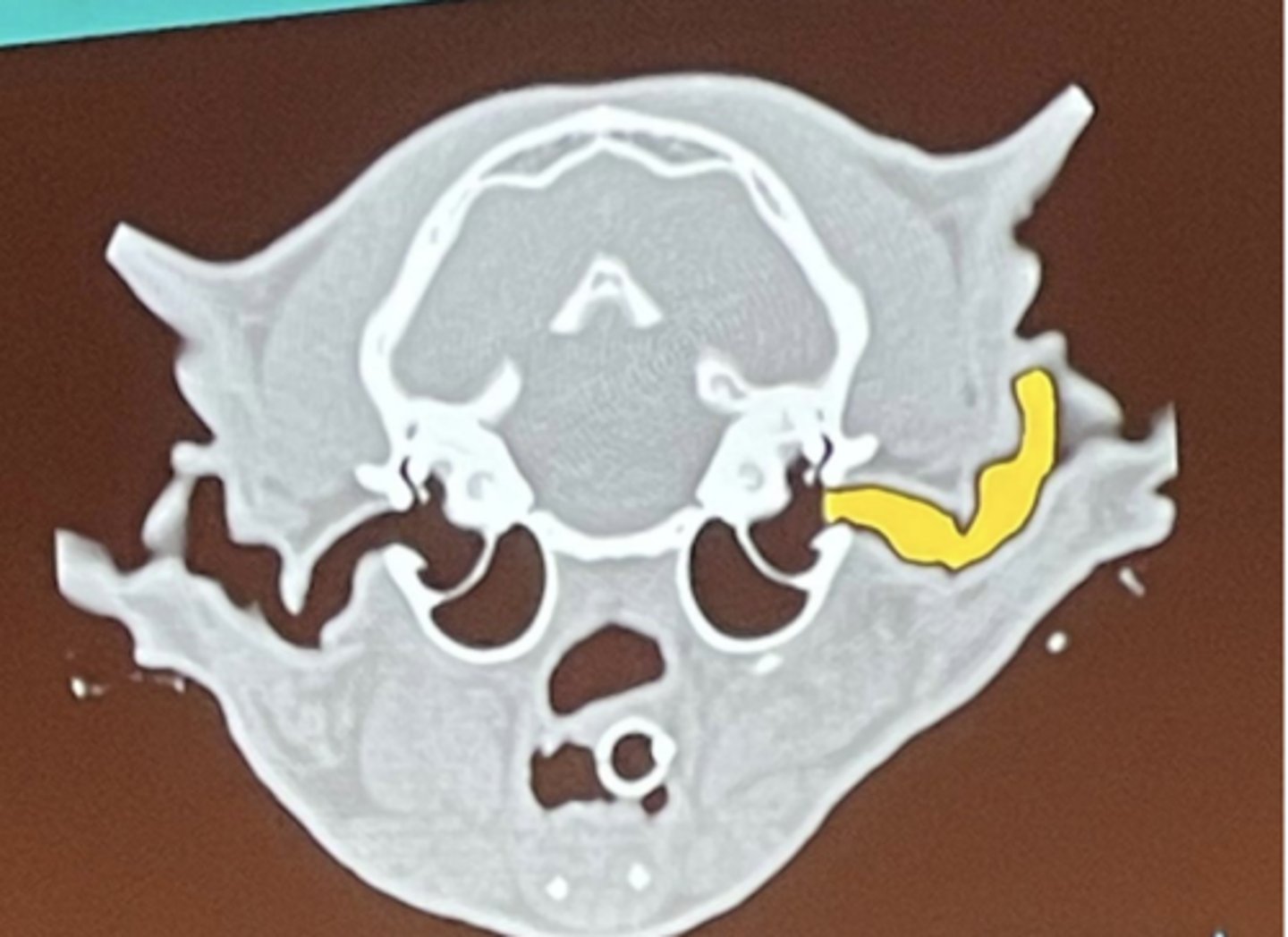
What is being highlighted in yellow?
external ear
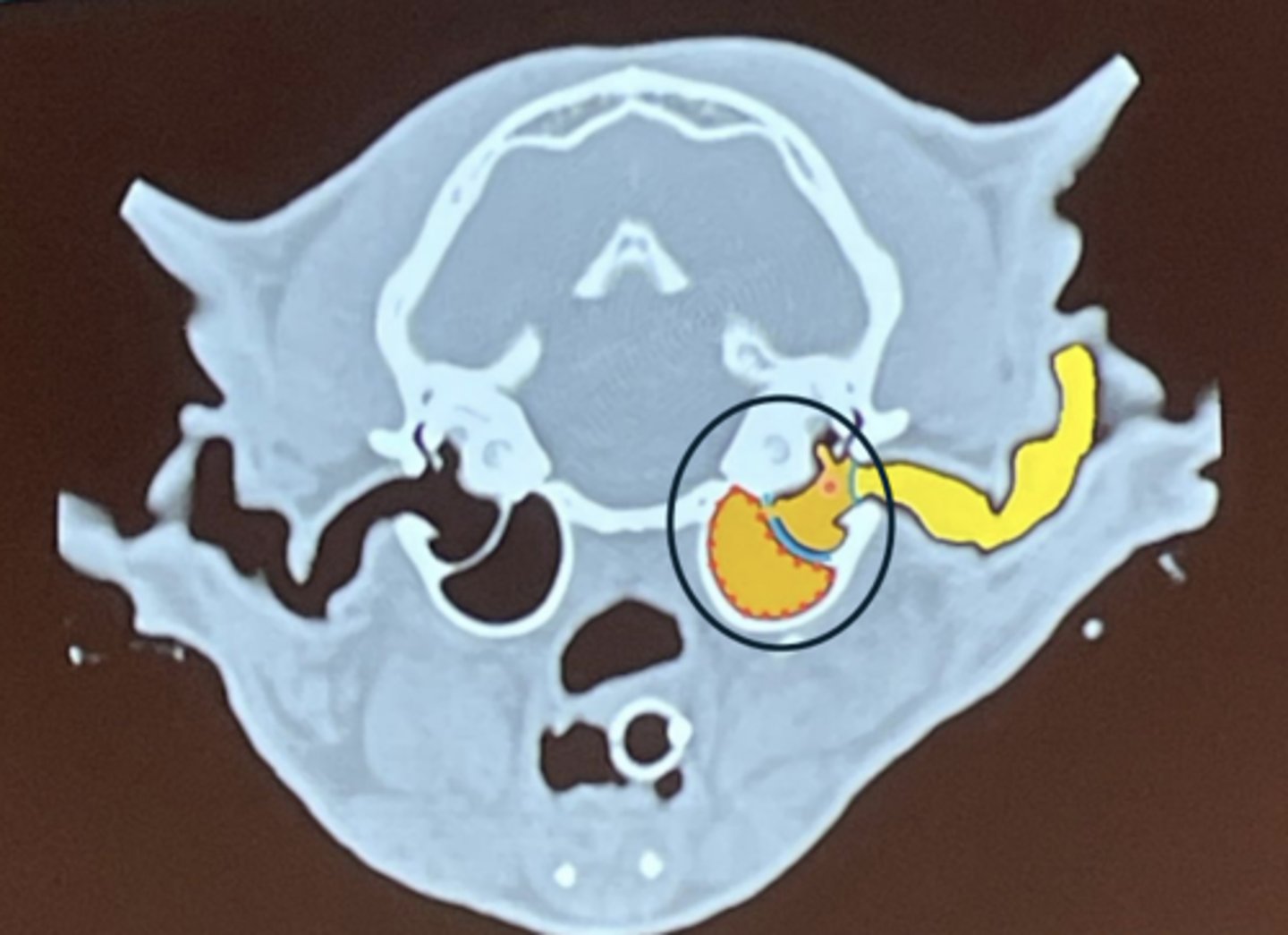
What is circled?
middle ear
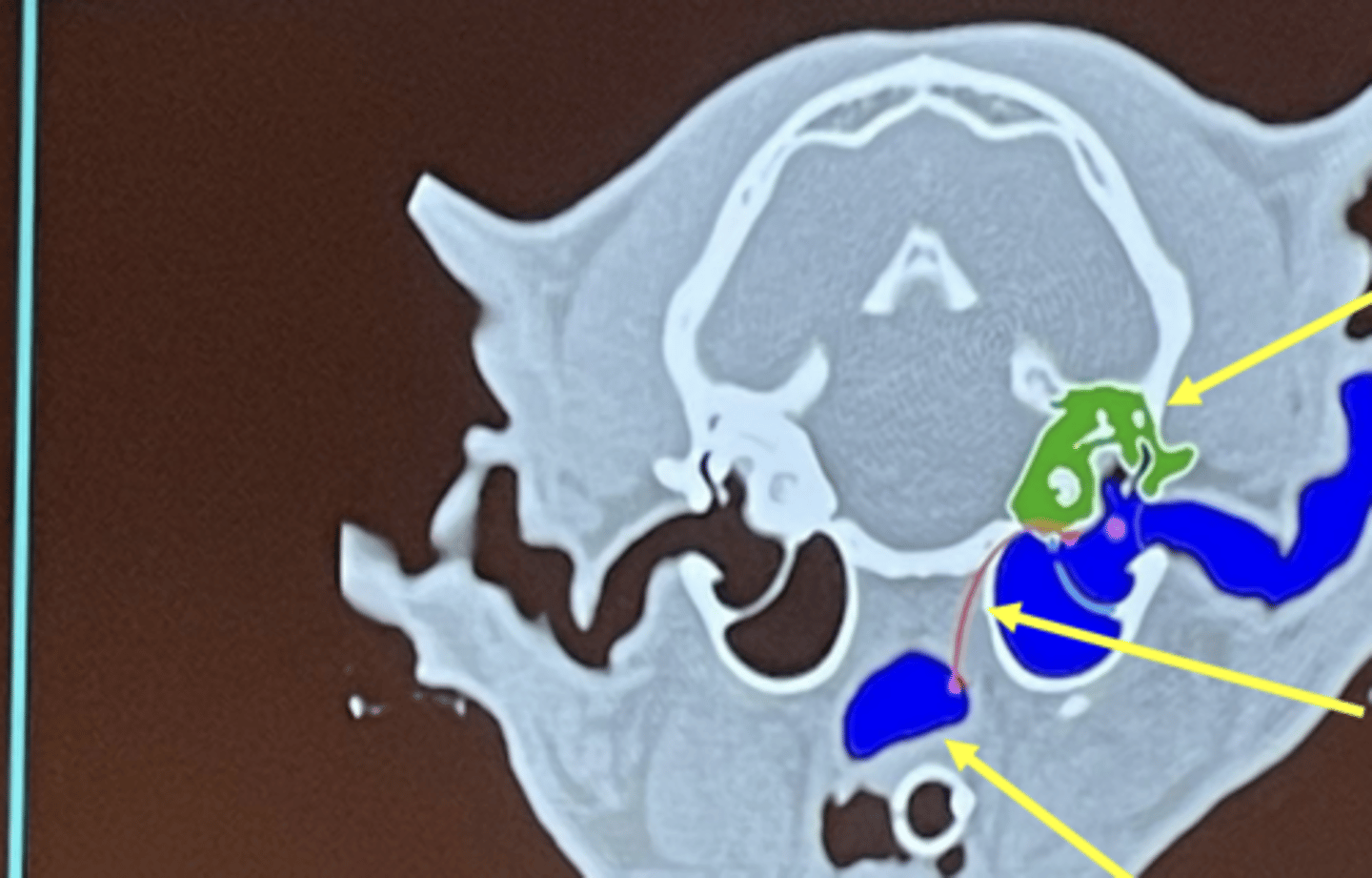
What is the top arrow pointing to (green)?
inner ear
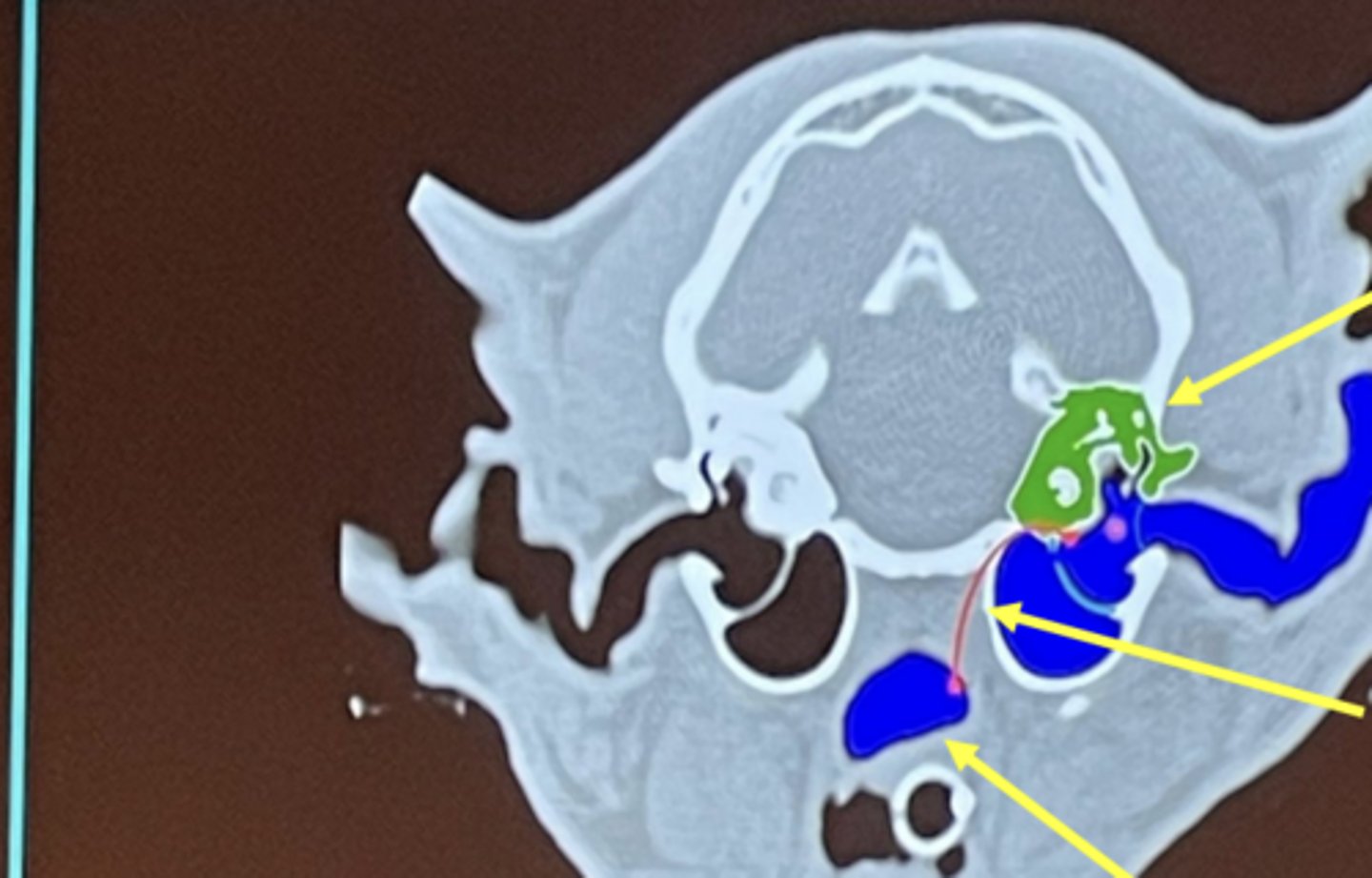
What is the middle arrow pointing to?
eustachian tube
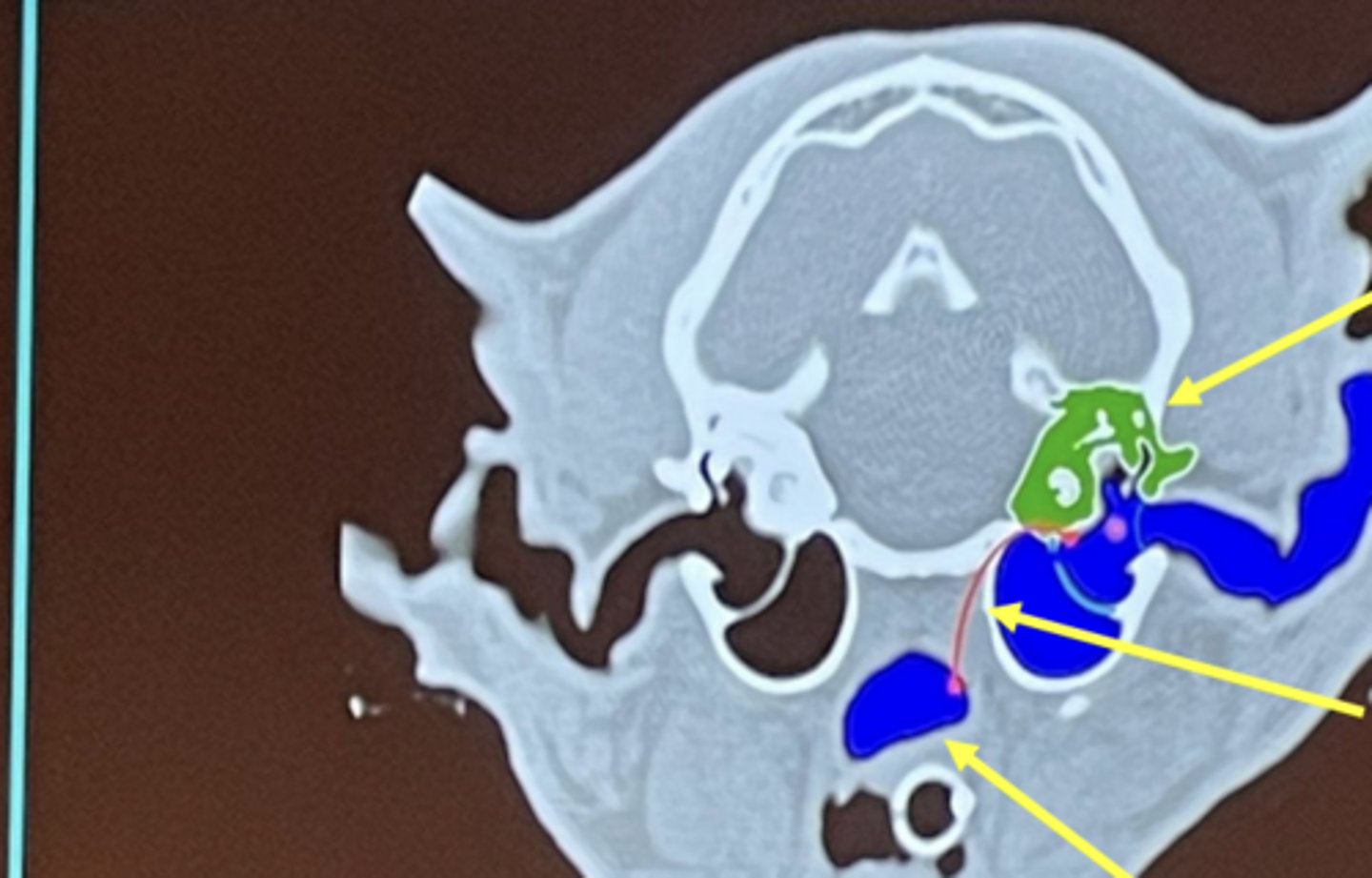
What is the bottom arrow pointing to?
nasopharynx
What is the pinna?
plate of cartilage covered with epithelium
What is the external orifice?
auricular cartilage rolls into a funnel shape and then becomes tubular to from the vertical canal
What is the ear canal?
vertical canal extends rostrally from pinna to horizontal canal then bends medially and continues as horizontal canal which ends at the tympanic membrane
What is the tympanic membrane?
thin membrane separating external and middle ear
What direction does the vertical canal slope?
rostrally
What is the auricular projection?
fold where vertical canal transitions to horizontal
What is clinically significant about the auricular projection?
can make visualization of deeper structures more difficult
What is clinically significant about the tympanic membrane?
important to assess integrity (intact vs. ruptured) on otoscopic exam
What can a ruptured tympanic membrane lead to?
otitis media
What are the functions of the ear pinna?
1. hearing
2. protection
3. thermoregulation
How can you manipulate the pinna to better visualize the horizontal canal?
pull pinna slightly up and out
What are the benefits of using video otoscopy?
1. better visualization
2. better access to deep structures
3. increased image clarity
4. can be used to clean ears
5. basic procedures like polyp removal
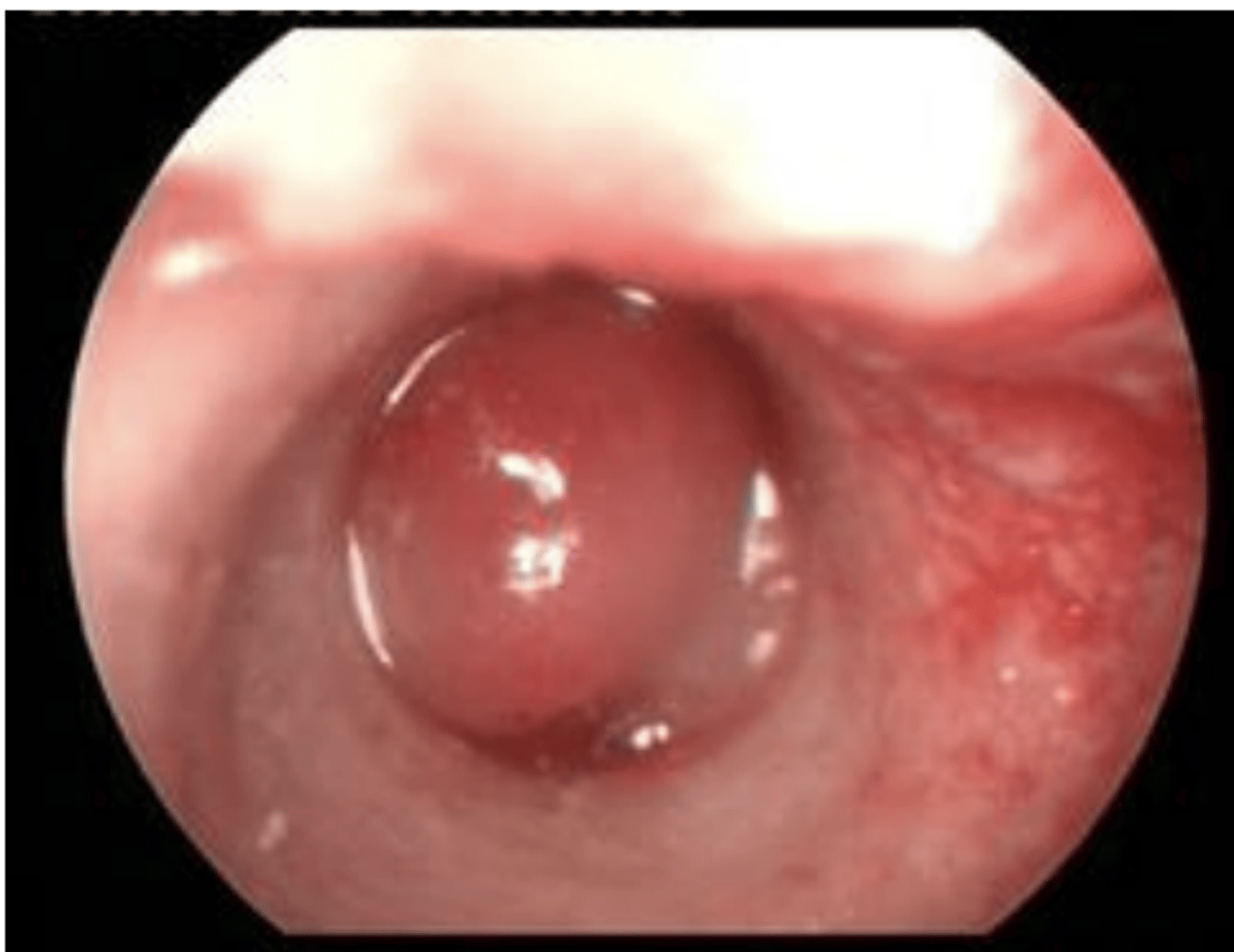
What are the differential diagnoses for this cat?
polyp, mass, or growth (most likely polyp)
What does ear pinna conformation depend on?
species (can also vary within species)
What animals have prominent external ears?
mammals
What part of the ear is often impacted by generalized skin disease?
pinna
Why do elephants have large vascular pinna?
thermoregulation (radiate heat)
Why do arctic fox have small pinna?
reduce heat loss
What are bat ears highly specialized to be used for?
echolocation
Why do jack rabbits have large, mobile ears?
to capture sounds from a wide area
Which mammals lack an external ear (pinna)?
dolphins and whales
What is the function of the external ear canal?
1. conduct and amplify sound waves
2. protect middle ear
What varies in the external ear canal in mammals?
canal length, shape, and position
What is the structure of the external ear canal in dogs?
1. L-shaped
2. vertical canal
3. horizontal canal
4. 5-10 cm long
5. width and length vary by breed
What are the characteristics of the skin of mammalian ear canals?
1. similar to body skin
2. thin epidermis
3. hair follicle size may vary
4. sebaceous glands
5. ceruminous glands
What is the role of ear wax (cerumen) in ear health and immunity?
made of exfoliated epithelial cells, glandular secretions, immunoglobulins and plays a role in protective immunity
What immunoglobulins are in cerumen?
1. IgG
2. IgA
3. IgM
When is cerumen production increased?
inflammation
What is part of the normal flora of cerumen?
small number of bacteria and yeast spp.
What is epithelial migration?
lateral (outward) movement of epithelial cells serves to expel cerumen, dirt & debris from within the external ear (self cleaning mechanism)
When is epithelial migration impaired?
when external ear is inflamed or diseased
What is the tympanic membrane also called?
ear drum
What are the functions of the tympanic membrane?
1. hearing (sound and vibration transmission)
2. divide external and middle ear
3. protects middle ear
What is the structure of tympanic membrane?
white, translucent, oval-shaped membrane
What species lack a pinna and have a tympanic membrane located close to the skin surface?
birds and reptiles
What is the advantage of birds not having an ear pinna?
they have a funnel shaped opening that makes them more aerodynamic
What is the significance of bird ears being covered by auricular feathers?
1. protection
2. reduce wind noise
3. filters debris
What does reptile ear anatomy vary among?
species
What is a columella bone?
bone that connects the tympanic membrane to the inner ear (lizards and crocs)
What structure of the outer ear do snakes lack?
tympanic membrane
What is the function of the columella in snakes?
attaches to the jawbone to allow sensing of vibrations
What are you evaluating in an otoscopic exam?
1. ear canal health
2. tympanic membrane integrity
3. presence/absence of exudate
4. presence of foreign body., nodules/polyps, parasites
What is otitis externa?
inflammation of outer ear
What are the clinical signs of otitis externa?
1. erythema
2. alopecia
3. malodor
4. edema
5. erosion/ulceration
6. abnormal ear carriage
7. excoriation
8. exudate
9. crusting/scaling
10. stenosis
What are the characteristics of acute inflammation with otitis externa?
nonspecific inflammatory changes like inflammation/erythema, edema, and increased wax
What are the characteristics of chronic inflammation with otitis externa?
1. epithelial hyperplasia
2. dilated ceruminous glands
3. hyperplasia of the sebaceous glands
4. hyperpigmentation
5. fibroplasia (fibrosis)
6. fibroproliferative nodules
What is the progression of pathological changes with otitis externa?
chronic inflammation, stenosis of the canal, fibrosis of dermis and subcutis, and calcification of cartilage
What is the etiology of otitis externa?
1. predisposing factors
2. primary factors
3. perpetuating factors
4. secondary factors
How do predisposing factors contribute to ear disease?
alter microenvironment of ear canal
What are some examples of predisposing factors?
1. breed ear conformation
2. maceration (from moisture and humidity)
3. iatrogenic (ear plucking, overcleaning, irritating topicals)
4. obstructive ear disease (benign, can be primary)
How do primary factors contribute to ear disease?
initiate and directly incite inflammation in the ear
What are some examples of primary factors?
1. allergy
2. foreign body
3. neoplasia
4. immune-mediated
5. parasites
6. keratinization disorders
7. obstructive ear disease (benign, can be primary)
How do perpetuating factors contribute to ear disease?
continues inflammation but does not initiate it and prevents successful resolution or causes relapse
What are some examples of perpetuating factors?
1. otitis media
2. treatment errors
3. biofilm
4. contact reaction to meds
5. pathologic changes
6. debris
7. owner non-compliance
How do secondary factors contribute to ear disease?
contribute to inflammation, pruritus and wax production
What are some examples of secondary factors?
1. bacteria
2. yeast
What are some common bacteria that contribute to ear inflammation?
1. Staph. Pseudintermedius
2. Pseudomonas spp.
3. Strep. spp.
4. Proteus spp
What are some common yeats that contribute to ear inflammation?
1. Malassezia spp.
2. Candida spp.
3. Aspergillus (rare)
What are specialized skin structures?
modified components of the integumentary system that vary depending on the species and serve various function
What are some examples of specialized skin structures?
1. Hair/wool
2. Feathers
3. Scales
4. Claws, nails, and hooves
5. Horns
6. Antlers
What features of hair vary by species?
1. type
2. density
3. distribution
4. main function
What is the function of the hair of cetaceans?
sensory
What are whiskers (vibrissae)?
extremely sensitive, coarse hairs usually located on the face, which are used to sense the surrounding environment
What does the white tuft of hair on baby chimp and gorilla rumps signal to other troop members?
they are youngsters
What does a darker color mane in lions indicate?
more testosterone (more appealing to females)
What do some camelids have for insulation?
wooly undercoat
What species has an insulated undercoat that can grow to 40 inches long?
muskoxen
Buddy presents with a painful right ear for the past 5 days. He has been receiving immunotherapy for atopic dermatitis (environmental allergy). He is currently on Hill’s Derm Complete diet. He is an indoor/outdoor dog. In his spare time, he loves going to the beach & playing in the waves. He is diagnosed with Pseudomonas infection of the right ear. What are the primary factors?
atopic dermatitis
Buddy presents with a painful right ear for the past 5 days. He has been receiving immunotherapy for atopic dermatitis (environmental allergy). He is currently on Hill’s Derm Complete diet. He is an indoor/outdoor dog. In his spare time, he loves going to the beach & playing in the waves. He is diagnosed with Pseudomonas infection of the right ear. What are the predisposing factors?
1. playing in waves (maceration)
2. breed (GSD)
3. indoor/outdoor lifestyle
Buddy presents with a painful right ear for the past 5 days. He has been receiving immunotherapy for atopic dermatitis (environmental allergy). He is currently on Hill’s Derm Complete diet. He is an indoor/outdoor dog. In his spare time, he loves going to the beach & playing in the waves. He is diagnosed with Pseudomonas infection of the right ear. What are the secondary factors?
Pseudomonas infection
What do all birds have?
feathers
What do all mammals have?
hair
What are feathers?
modified epidermal structures
Where do birds usually have feathers?
the entire body surface except for some small bare patches around the eyes, beak base, or legs
What do most birds have?
feather tracts (pterylae) separated by bare skin areas called apteria
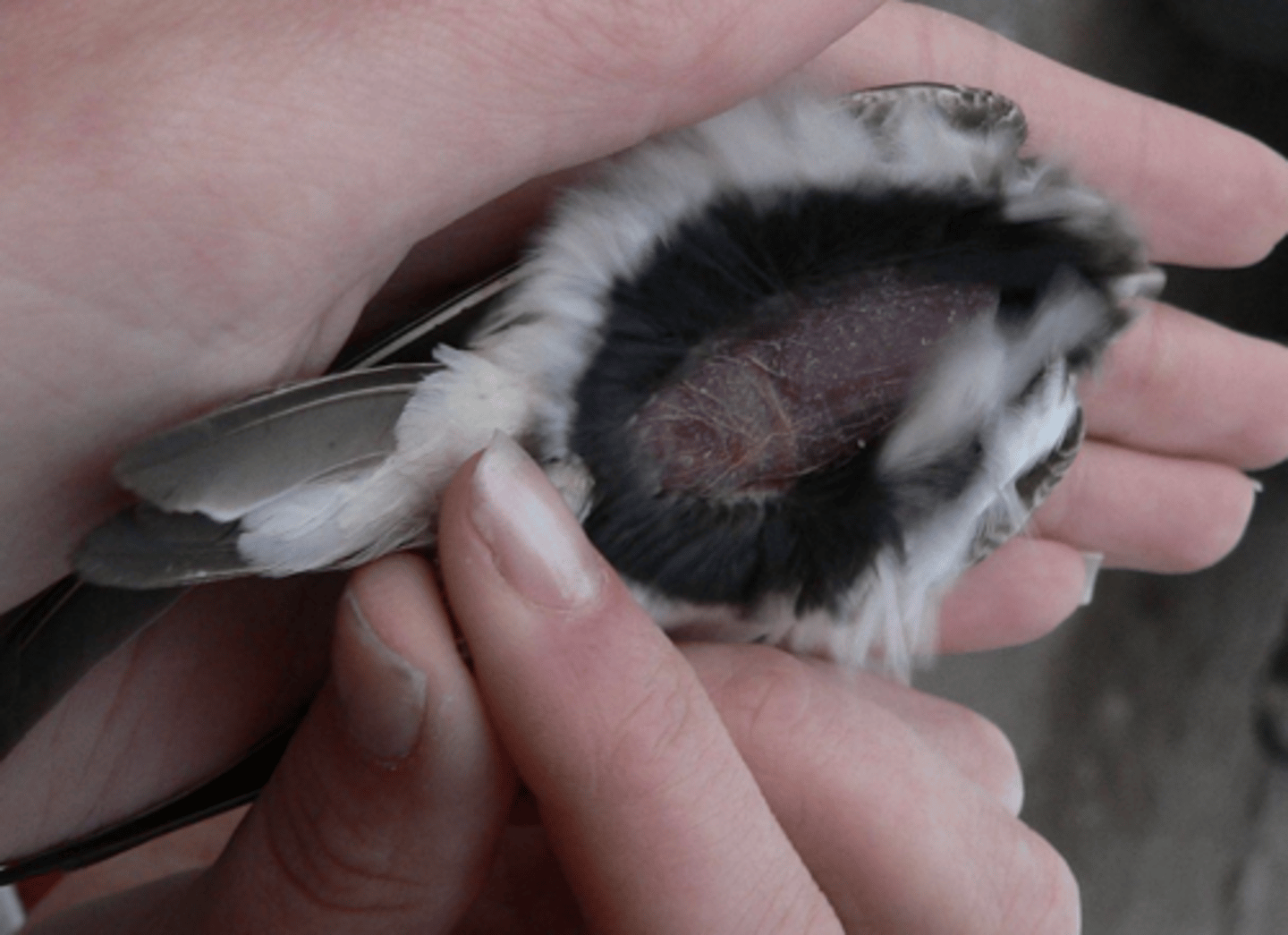

What is this an image of?
brood patch during nesting season
What can bare patches of skin in birds be advantageous for?
thermoregulation, hygiene or display of colorful skin
What do arctic owls have on their legs and feet for insulation?
feathers
Where do feathers grow from?
follicle
What signals and supports feather development?
dermal papillae
What do epidermal cells lining the follicle produce to form the hard, structural parts of the feather?
beta-keratin
What is a blood feather?
stage of feather development where it is enclosed in a keratinous sheath and contains a vascularized pulp
What is a pin feather?
stage of feather development where it matures and progresses and the blood supply recedes (sheath is eventually shed)
What is the name of the base of a bird's feather?
calamus
Which type of feathers covers the bird's body in an overlapping pattern and are specifically called coverts when located on the wings?
contour
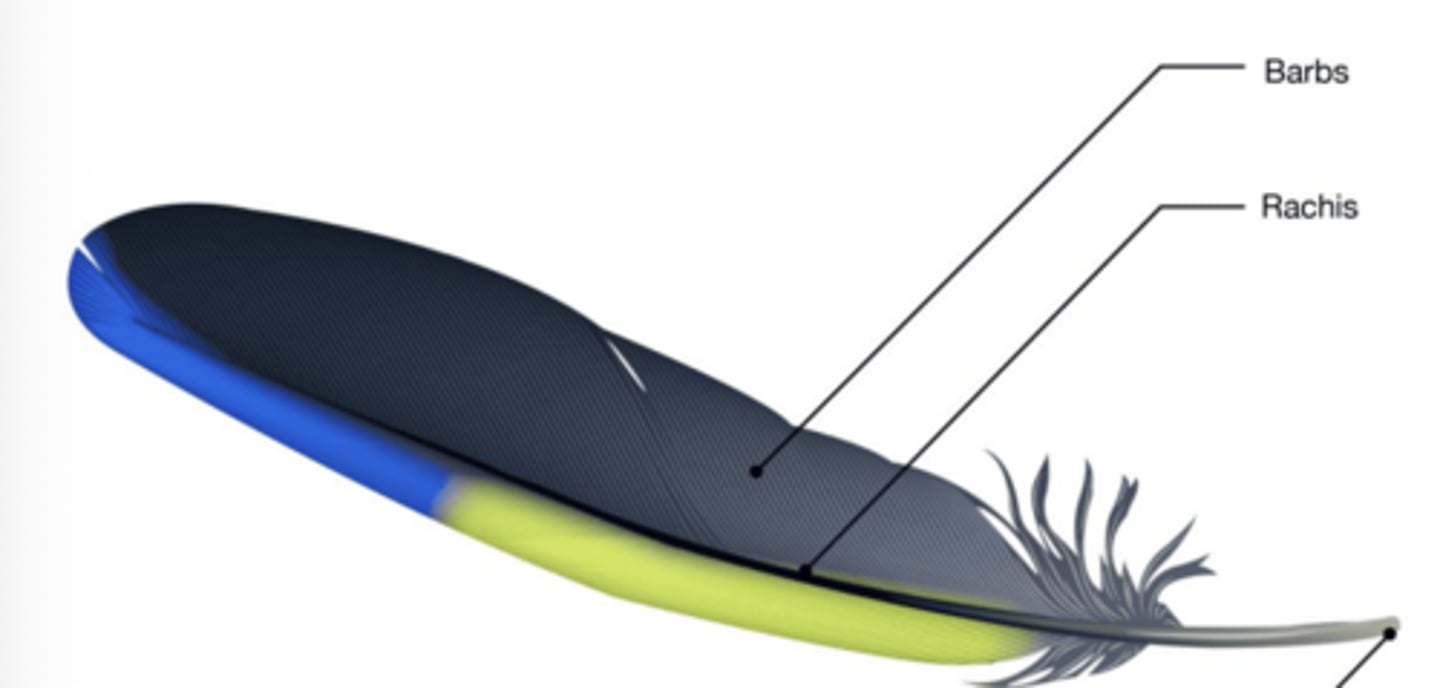

What kind of feather is this?
wing
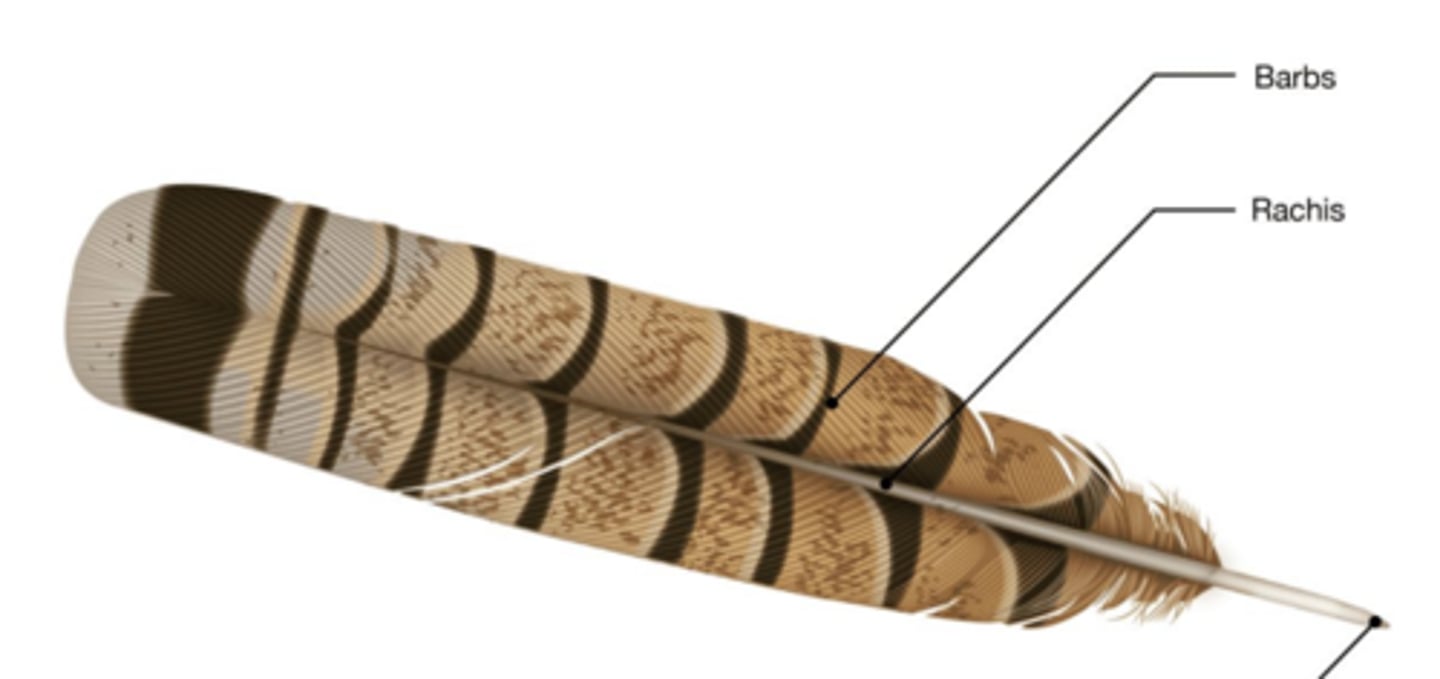
What kind of feather is this?
tail
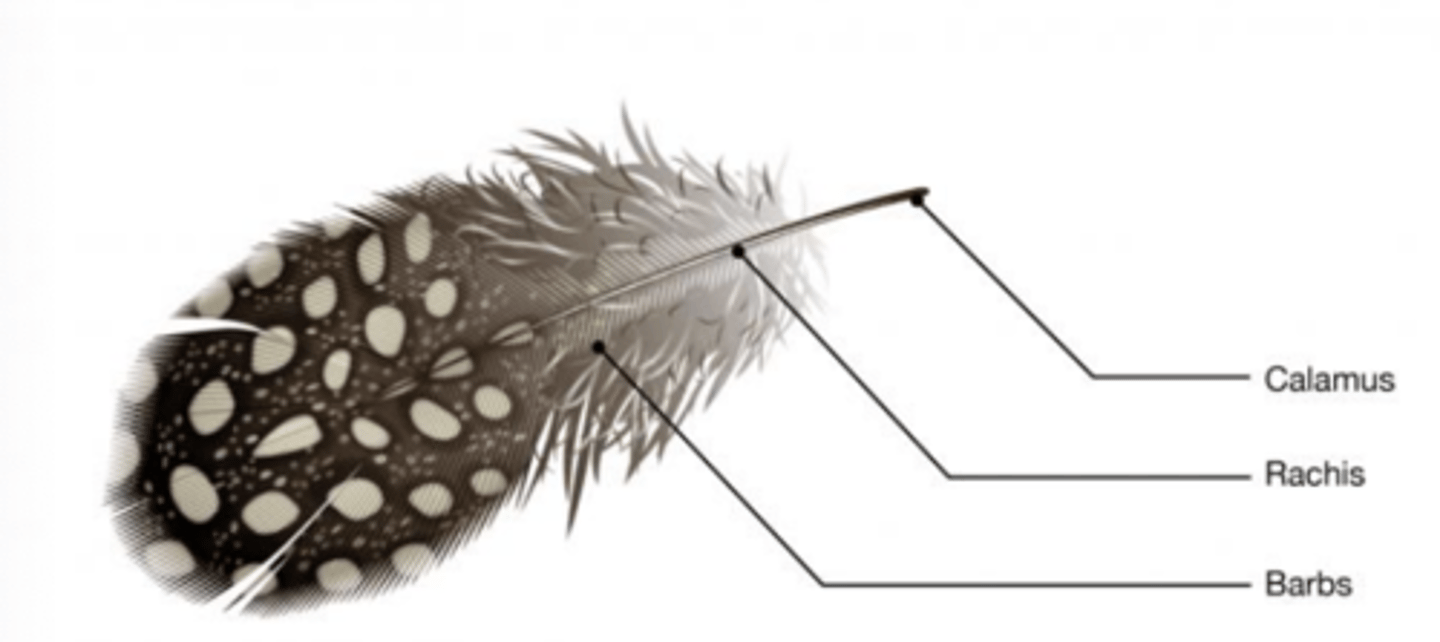

What kind of feather is this?
contour
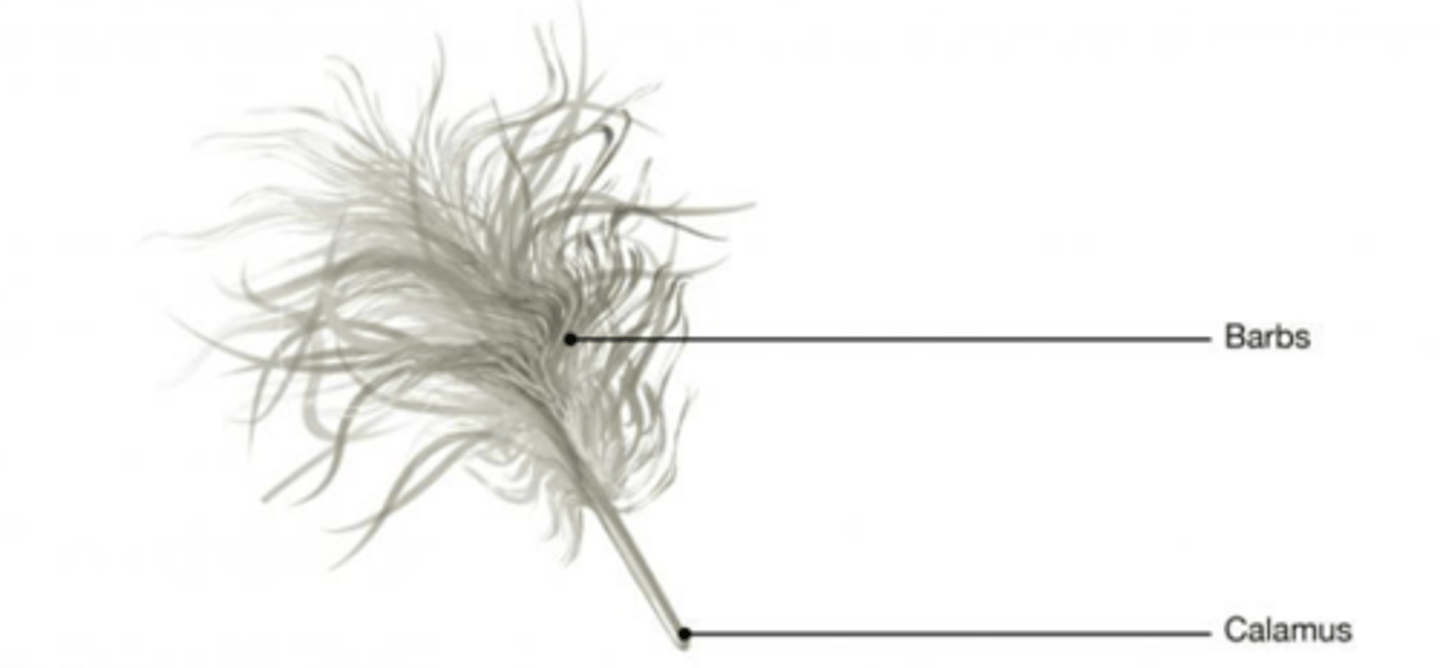

What kind of feather is this?
down
Do feathers continue to grow after the feather is fully mature?
no
What is molting?
natural shedding of old feathers to make way for new feathers