4.2 - Poverty & Relative Poverty (Edexcel A-level Economics Theme 4)
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Absolute poverty w/examples
Absolute poverty is a situation where individuals cannot afford to acquire the basic necessities for a healthy and safe existence
e.g shelter, water, nutrition, clothing and healthcare
Main poverty that affects developing countries
What did the world bank define absolute poverty as?
In 2022, the World Bank defined absolute poverty as anyone who was living on less than $2.15 a day
Relative poverty
Incomes below a given average in society/ Relative poverty is a situation where household income is a certain percentage less than the median household income in the economy
Main poverty that affects developed countries
What did the UK define relative poverty as?
The UK defines relative poverty as households that are living with less than 60% of the median household income
How can absolute poverty decrease even while income inequality increases?
This means that the income of wealthier households is rising faster than the income of the poorer households
Causes of changes in absolute poverty?
Strong correlation between economic growth and a decrease in absolute poverty
Economic growth increases household incomes
Government tax and benefit policies can support the most vulnerable groups in society e.g. children, pensioners, people stuck in long-term unemployment
In developed economies, benefit policies can ensure that no household is living in absolute poverty
Causes of changes in relative poverty
Rising asset prices can decrease relative poverty in households which own their own properties
Asset prices often increase faster than wages or income
Trade liberalisation expands markets and output, boosting labour demand and wages, reducing relative poverty through a multiplier effect. However, reduced government benefits can lower incomes and increase relative poverty.
Equity
Fair distribution of income
Equality
Equal distribution of income
Causes of poverty (10)
Unemployment - structural and cyclical
Poor education/skills
Poor health/healthcare
Born into poverty
Tax cuts for the rich
Subsistence agriculture
Natural disasters
Corruption
Wars and conflict
Regressive taxes
What is income inequality?
Income inequality refers to the unequal distribution (flow) of income to households i.e rent, wages, interest and profit
What is wealth inequality?
Wealth inequality refers to differences in the amount of assets that households own
What are the 2 measurements of inequality?
Lorenz curve - visual indicator
Gini coefficient - mathematical indicator
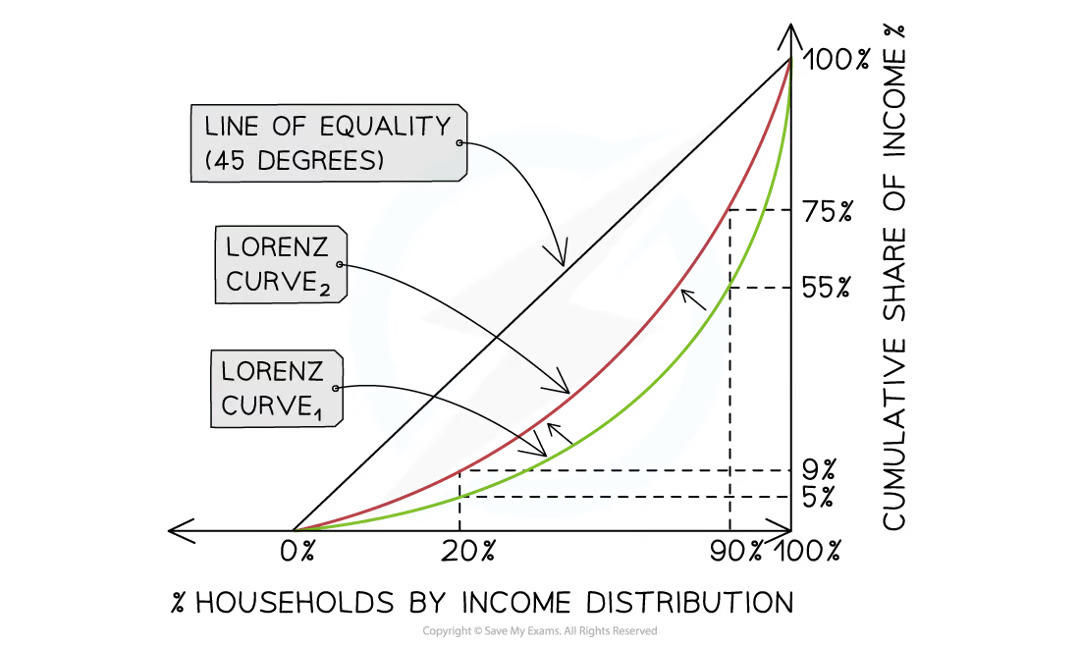
What is the analysis for this diagram?
The line of equality represents perfect income distribution (not desirable)
In the UK the bottom 20% of households receive 5% of the income flow while in Sweden they receive 9% of the income flow
In the UK the top 10% of households receive 45% of the income flow while in Sweden they receive 25%
Sweden has a more equal distribution of income than the UK (Sweden = Red line, UK = Green line)
What is the gini coefficient?
Measures the distribution of income in a population. The closer the value is to 1, the worse the income inequality
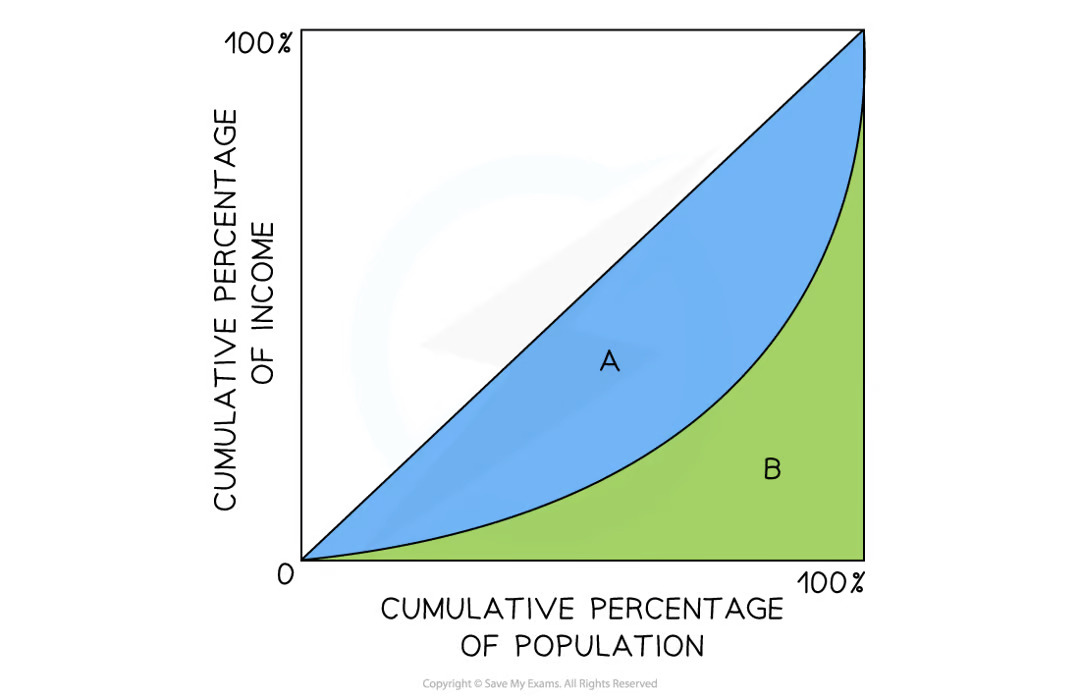
What is the analysis for the diagram?
Gini Coefficient = A/A+B
A represents the area between the line of equality and the UK Lorenz curve
B represents the area under the Lorenz curve
A value of 0 represents absolute equality (socialism) and 1 represents perfect inequality
In 2022, the USA coefficient was .41 as compared with the UK value of .35
The distribution of income in the UK was more equitable than in the USA
Causes of income and wealth inequality? (8)
Education, Training and skills
Trade unions
Benefit system
Pension payments
Wage rates
Employment Legislation
Tax structure
Asset ownership
What is meant bby education, training and labour?
Higher skill levels lead to higher incomes. Countries with poor education systems face greater income inequality compared to those with strong education systems.
What is meant by trade unions?
Countries with strong trade union membership typically have higher incomes, while low union membership makes worker exploitation through low wages more likely.
What is meant by benefit system?
Countries offering extensive benefits (e.g., unemployment, disability, and housing support) increase incomes for the lowest 20% of population, leading to a more equal income distribution.
What is meant by pension payments?
State pension payments provide a minimum standard of living for retirees, promoting more equal income distribution. Without them, a higher proportion of pensioners live in poverty.
What is meant by wage rates?
The purpose of a national minimum wage is to improve the equity in the distribution of income.
Without it, more households would be earning less and inequality would increase
What is meant by employment legislation?
Stronger worker protections, such as maternity benefits, improve income distribution by ensuring higher incomes during periods like maternity leave.
What is meant by tax structure?
Progressive tax systems ensure contributions based on ability to pay. Lowering taxes for low-income earners and raising them for high-income earners increases progressivity, promoting more equal income distribution.
What is meant by asset ownership?
Assets generate income, so more equal asset ownership reduces income inequality. The UK encouraged this by allowing council house tenants to buy properties at a discount (1980) and through current shared ownership schemes.
Why does industrialism result in inequality?
Some workers move from the lower productivity, lower paid agricultural sector into the higher productivity manufacturing sector
There is now greater income inequality with the workers left behind
Why is inequality under capitalism inevitable?
Workers with higher skills receive higher wages
Workers with little to no skills receive little to no wage
Individuals with higher income will acquire more assets leading to higher levels of income
In turn, they can keep on acquiring assets
1 Pro and 1 Con of capitalism in regards to inequality?
The incentive to acquire income raises productivity and output
The long-term cost of capitalism is that the factors of production become concentrated in ownership with relatively few individuals developing extreme wealth, at the expense of many who lose out