Ecology 2220 USU
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
First three exam keys
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
The only thing constant is
Change
A ____ is the collection of species population living in a given area and interacting with each other
Community
We use ___ to determine probability, or likelihood, that a measured difference is real or due only to chance or some other source of error
Statistics
A(n) ___ states that there is no real difference between observed and expected results
null hypothesis
The three sources of error in measurements and counts that we discussed in class are ______ ____, ___________ _____, and _____ ______ ______.
sampling error, measurement error, other chance events
A(n) ______ is a hypothesis supported by a large body of observations and experiments. These are the things we are most certain of in science
Theory
True or False: An enzyme, which is a lipid, catalyzes, or speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
False; protiens speeds up chemical reactions
True or False In science we learn more when we accept a hypothesis than we do when we reject a hypothesis
False; We learn more when we reject than when we accept
True or False. An compound is a substance that cannot be broken down by ordinary processes into other kinds of substances
False; an element is a substance that cannot be broken down
True or False. In our approach to Ecology, we are particularly interested in three issues: 1) where organisms are found, 2) how many occur there, and 3) why? With respect to the “why” we focus on interactions of organisms with a constantly changing abiotic environment and a constantly changing biotic environment that determine distribution (issue 1) and abundance (issue 2)
True
True or False. An ionic bond forms when atoms share one of more elections so that each has a filled outer shell and is stable
False; a covalent bond forms
True or False. Atoms are uncharged because the number of positvely-charged neutrons equals the number of negatively-charged elections
False; the number of positvely-charged protons
True or False. In general, change events will have greater effects or impacts in small populations that in large populations
True
True or False. The diversity of habitats holds one key to the diversity of life on earth. No organism can live under all conditions because adapataions for living under one set of conditions make life under other conditions impossible. Therefore, with more types of habitats we can have more species.
True
One Scentence Answer. Science differs from “other ways of knowing” in that it is self-correcting. In a single sentence, what two “rules” does science follow in order to be self-correcting?
Science exposes new ideas and results to independent testing and replication by other scientists, and abonds or modifies accepted facts or theories in light of more complete or reliable evidence
Chi-Square
Practice yourself
____ is the angle of the land’s surface and _____ is the direction the slope faces, and thus the exposure of the land’s surface to the sun
Slope, aspect
_______ is the combination of evaporation from the earth’s surface and ______ or evaporation from plant leaves
Evapotranspiration, transpiration
The ______, or the physical expression of the organism, is due to the interaction between the genotype and the enviornment.
Phenotype
______ are different variants of a gene — differ in base sequence
Alleles
True or False. The mineral compoent of soils comes from the underlying bedrock, or parent materials. The parent material is broken down by weathering, the physical, chemical, and biological alteration of rock and soil on or near the earth’s surface.
True
True or False. In Australia, unlike in Utah, north facing slopes are cooler and have more moisture than south facing slopes
False; south facing slopes are cooler than north facing slopes
T or F. A mixture of pore sizes in soils tends to be best for plant growth because the macropores hold water well and the micropores provide air pockets and therefore
oxygen
False; micropores then macropores
T or F. An individual cannot evolve, only populations can evolve
True
T or F. A recessive allele is expressed only in the heterozygous condition
False; in the homozygous condition
T or F. Differential survival and reporduction of individuals based on the traits they bear is Natural Selection. To the extent that those phenotypic traits are genetically determined, Evolution, or a change in allele frequencies in the population, occurs
True
T or F. Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) is the number of negative charges, or “exchange sites,” available in the soil. The larger the CEC, the more cations can be held.
True
T or F. Our Atlantic killifish discussion showed that evolution can occur very rapidly under the right
conditions. In particular, all else being equal, evolution occurs more rapidly when: 1) populations are large (tend to have more genetic variation and thus more likely to have suitable alleles for the new environment),
2) selection is weak (because it rapidly eliminates alleles that do not fit the new environment), and
3) generations are short (new round of selection each generation)
False; selection is strong
T or F. Compared to contiental interiors, coastal regions tend to be wetter and more variable in temperature
False; they are less variable
One sentence answer: In a web posting about the Peppered Moth story by Jordan P. Niednagel called “Moth Mayhem. The Case That's Long Been Closed” (http://www.trueauthority.com/cvse/moth.htm) we find the following
concluding statement: “The conclusion is this: We began our story with genetic information present for dark and light moths (i.e., before industrial pollution). We continued our story with genetic information present for dark and light moths (i.e., during massive industrial pollution). Lastly, we ended our story with genetic information present for dark and light moths (i.e., following environmental cleanup). The moths remained moths, whether light or dark. In other words, the only thing that happened was that the relative numbers of each went up or down. Evolution was and is not a factor, nor does it need to be mentioned. The Peppered Moth mayhem raises clouds of smoke that need not be disturbed, so that we
may see clearly in order to move on to more significant issues. The case has been closed, and hopefully will remain that way for a long, long time.” (Parenthetical comments are mine). Discuss the comment about evolution in one sentence. Do not tell me what Mr. Niednagel is saying – I know that – rather, critique his statement.
The changes in the relative numbers of the color morphs was evolution since color is genetically based and a change in the frequence of a color means a change in allele frequencies, which is evolution.
A 5‐6 February 2010 North American Blizzard, referred to variously as “Snowmageddon,” “Snowpocalypse,” and "snOMG," dumped 20‐35 inches of snow across a wide swath of the mid‐Atlantic
region. This storm shut down air, rail, and highway traffic across the region.
In response, we got a number of interesting comments:
Washington Times Op‐Ed: “Those who value freedom should thank Mother Nature for her sense of humor, undermining the case for global warming one flake at a time. So although we're quite tired of shoveling, we say, ‘Bring on the blizzard.’"
Sean Hannity: “It’s the most severe winter storm in years, which would seem to contradict Al Gore’s hysterical global warming theories.”
Newt Gingrich: “Historic snow storm in Washington – third this year – where is Al Gore to explain it snows this heavily as a sign global warming is imminent.”
Steve Doocy (Fox & Friends): "It's interesting, though, given the fact that the weather is so rotten right now that people are going, 'how can there be global warming if it's snowing and it's fairly cold?’"
Donald Trump: “With the coldest winter ever recorded, with snow setting record levels up and down the coast, the Nobel committee should take the Nobel Prize back from Al Gore.”
Clearly, a lot of folks were using this extreme snowstorm to suggest that climate change/global warming
is not real. But why might we actually expect extreme snow storms to come with a warming world?
In a warming world we woule expect more extreme snowfall events because a warming world will have more thermal energy for evaporting water and a warmer atmosphere that will hold more water vapor, so if precipitation starts, and it is cold enough, more snow is likely to fall.
Heavy rains can be associated (1) with the windward side of mountains near oceans (such as the western side of the Sierra Nevada of California), (2) with the meeting of a cold and a warm air mass
(such as a cold front coming through Utah), and (3) with Hadley Cells. Compare and contrast these three
processes leading to precipitation – that is, tell us what is the same about these processes and what is
different. (10 pts.) Make sure you describe the details of the differences.
(2 pts) What is the same?
(2 pts) What is different?
Air is physically pushed up by mountains
The colder, denser mass slides under the warmer, less dense mass, pushing it up
The intense solar radiation near the solar equator heats the air near the Earth so that it becomes dense and rises
What is the same: In all three cases relatively warm, moist air rises, cools, and releases its moisture as
rain.Different: The difference among the three is in what causes the warm moist air to rise.
The action of external forces that stabilize population size at (or at least near) the Carrying Capacity (the equilibruim) is referred to as _________ __________.
Population Regulation
During nutrient regeneration, __________ is the process where microorganisms (microbes) convert unusable organic forms of nutrients into useable inorganic (ionic) forms taken up by plants and by microbes
mineralization
______________ factors are those that increase mortality of decrease births as population size increases.
Density-Dependent
A __________ is the collection of organisms of the same kind or species living in a given area and potentailly interbreeding
population
T or F. During respiration, plants convert solar energy into energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates
False; photosynthensis not respiration
The major difference between how energy and elements move through ecosystems is that energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction, ultimately coming in as sunlight and leaving as heat, while elements are cycled, or regenerated and used over and over
True
T or F Immigration is when an individual moves out of a popualtion. Is is demographically equivalent to death.
False; Emigration
Productivity of most ecosystems is not limited energy, but by water or nitrogen or photsphorous
True
The impact of a population on its environment is not simply a function of population size, but also depends on per capita consumption and on the environmental damage caused by supplying the consumption
True
The logistic equation is dN/dt = r 0N (1 – N/K). The (1 – N/K) term is there to effectively increase the per capita rate of increase as population size increases.
False; decreases
More developed countries, like the U.S. and France, are characterized by low infanct mortality rates, low birth rates, low population growth rates, and high per capita income.
True
One sentence answers. Thinking about human populations, contrast Biological Carrying Capacity and Cultural Carrying Capacity
Biological Carrying Capacity is the maximum number of individuals that can survive in the environment, [no matter how meager the existence], while Cultural Carrying Capacity is a socially acceptable population size capable of providing a high quality of life for all. What is in blue is not required, but adds more detail.]
If you have read the notes and paid attention in class you know that high latitude regions have low annual NPP. Nonetheless, every summer millions of birds make long migrations from more southern regions including the South Pacific and Asia, the southern and eastern US, Mexico, Central America, and
South America to the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge on the North Slope of Alaska in order to breed. And then they fly home again. For example, the Pectoral Sandpiper winters in northern and Central South America and breeds along the coastal plains of northern Alaska and Canada. These migrations are energetically expensive – it takes a lot of energy to fly – and dangerous – they have to find suitable feeding sites on the way, they are more vulnerable to predation, Spring weather can be unpredictable, and more.
So why do you think a Pectoral Sandpiper would leave a tropical forest in Colombia and make this
expensive and dangerous journey all the way to the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge to breed? Why not
stay home? Let us know in one sentence – and your answer should be in terms of productivity
During the growing season day lenth is very long so plants an photosynthesize most of teh day resulting in very high seasonal primary production which supports high secondary production which provides plenty of food for birds wheether they are herbivores or carnivores.
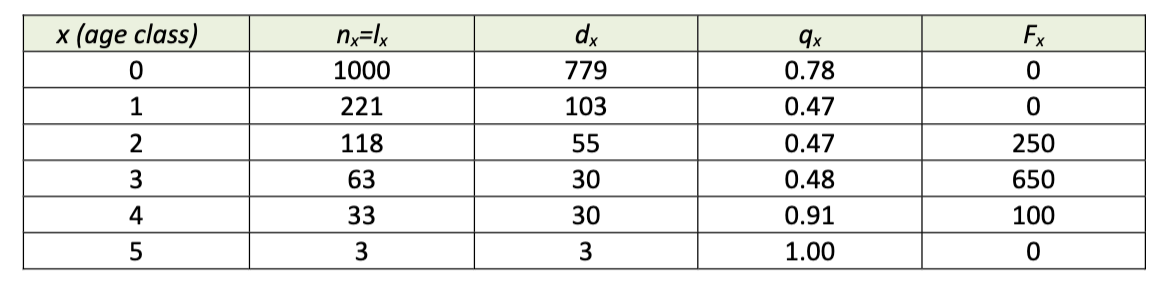
a) What does this table tell us about age-specific mortality and age-specific reproduction
b) Based on this data, is the population increasing, decreasing, or staying the same? Show how you determined this.
a )
Age‐specific mortality rate starts high, drops to a relatively constant lower rate for classes 1–3, and then rapidly rises again later in life. The highest mortality is for the young and the old.
Age-specific reproduction is pretty much the opposite. It peaks in age class 3
reproduction–I made sure the numbers worked) with less reproduction in classes 2 and 4 and no reproduction in the young and very old
b)
The population is staying the same.
∑F x /n0 = (250 + 650 + 100)/1000 = 1000/1000 = 1.0 – Or in words, the population produced a
total of 1000 offspring for starting the next generation, which is the same size as this present generation, so the size of the population has not changed
The amount of energy being added to the herbivore trophic level depends on Net Primary Production and the ecological efficiency of the herbivore trophic level; that is, on how much of the energy consumed by herbivores becomes incorported into energy stored in herbivores. Ecological effiencies depend on two parts: (1) assimilation efficiency and (2) net production efficiency
a) Define these efficiencies
b) Now apply them by comparing two animals
A fairly sedentary, slow moving iguana (a lizard) that eats old leaves and does not maintain a high body temperature
A very active mouse that eats seeds and maintains a high body temperature
Which should have the higher assimilation efficiency and why?
Which should have the highest net production efficiency and why?
Which should have the higher ecological efficiency?
a) Assimilation Efficiency- the proportion of consumed energy that is assimilated into the organism- Assimilation / Ingestion
Net Production Efficiency- The proportion of assimilated energy incorporated into the organism as new energy- Net production / gross production
b) The mouse should have a higher assimilation efficiency because seeds, which contain relatively little structural fibers, are easily digested and assimilated. In contrast, old leaves have lots of structural fibers and are poorly digested so a lot passes through undigested and unassimilated
The iguana should have the highest net production efficiency because relatively little assimilated energy is lost through respiration (has low activity and does not maintain a high body temperature). In contrast, the mouse uses a lot of energy in respiration and has relatively little energy left over to build new biomass
You cannot tell. The mouse has higher assimilation efficiency and the iguana has higher net production efficiency. Both of these improve overall ecological efficiency.