IB Biology - 6.3. Defense against infectious diseases
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/46
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:36 PM on 12/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
Blood clot
a semi-solid lulmp from liquid blood that is used to seal the cut in the blood vessels and prevent further entry of pathogens into the bloodstream.
2
New cards
Platelets
Are cell fragments present in blood that help create a blood clot upon injury.
3
New cards
Clotting factors
Molecules produced by damaged tissued and platelets which set off a cascade of events that lead to the formation of a blood clot.
4
New cards
Pathogen
Disease-causing organism.
5
New cards
Types of pathogens
Virus, bacteria, fungi, protozoa
6
New cards
Virus
Acellular. Need a host cell to carry out functions of life. Can have DNA or RNA. Can cause flu, HIV, measels, common cold, herpes, etc.
7
New cards
Bacteria
Prokaryotes, divide by binary fission. Can cause food poisoning, ear infections, cholera, etc.
8
New cards
Fungi
Eukaryotes, reproduce with spores. Can cause athlete's foot, ringworm, allergic reactions, etc.
9
New cards
Protozoa
Simple parasites. Can cause malaria, leishmaniasis, toxoplasmosis, etc.
10
New cards
Lines of defense against pathogens
Physical barrier: skin, mucous membranes. Blood cells: phagocytes.
11
New cards
Atherosclerosis
Degenerative disease in which areas of the artery wall become damaged. Cholesterol builds up in these damaged areas, restricting blood flow.
12
New cards
Coronary heart disease
If clots occur in myocardial tissue. Coronary muscle tissue dies as a result of a lack of blood and oxygen.
13
New cards
Phagocytes
Attaches to the pathogen's cell surface and engulfs it. White blood cells.
14
New cards
Pasogome
Vesicle that contains the pathogen.
15
New cards
Lymphocytes
Breaks down the pathogen. White blood cells, specific immunity. Can activate other lymphocytes or produce antibodies.
16
New cards
Antigen
A substance or molecule that causes antibody formation. Non-self.
17
New cards
Antibody
A globular protein that recognizes a specific antigen and binds to it as part of an immune response.
18
New cards
Clonal selection
A specific lymphocyte makes many clones of itself to produce antibodies to a specific pathogen.
19
New cards
Memory cells
Creates immunity.
20
New cards
Antibiotic
Drugs used in the treatment and prevention of prokaryotic bacteria. Designed to disrupt structures or metabolic pathways in bacteria and fungi. Ineffective against viruses
21
New cards
Antibiotic resistance
Indiscriminate use of antibiotics leads to this.
22
New cards
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
Gradually attacks the immune system. Retrovirus.
23
New cards
AIDS
A syndrome caused by HIV.
24
New cards
Specific immunity
Triggered by lymphocytes, which produce a response when in contact with a specific pathogen.
25
New cards
Mucous membrane
Parts of the skin covered in a secretion called mucous, keeps the skin moist and prevents growth of bacteria.
26
New cards
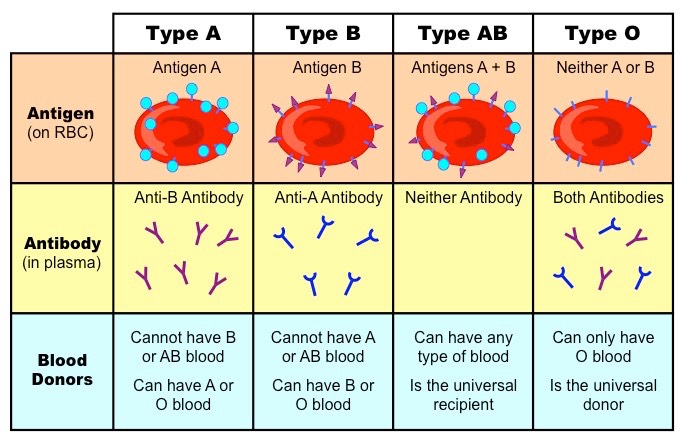
Red blood cells
Can be passed between individuals without causing immune rejection, but they do posses basic antigen markers. (ABO system).
27
New cards
Disease
Any condition that disturbs the normal functioning of the body.
28
New cards
Illness
Deterioration in the normal state of health of an organism.
29
New cards
Disease transmission
Direct contact, contamination, airborne, vectors.
30
New cards
Antibody actions
Precipitation, Agglutination, Neutralization, Inflammation, Complement activation.
31
New cards
Allergen
Environmental substance that triggers an immune response despite not being intrinsically harmful.
32
New cards
Histamine
Causes allergic reactions (such as inflammation).
33
New cards
Vaccination
Induce long-term immunity to specific pathogenic infections by stimulating the production of memory cells
34
New cards
Types of vaccines
Live attenuated, inactivated, toxoid, subunit/conjugated, RNA
35
New cards
Epidemic
Increased occurrence of a particular infection within a given region.
36
New cards
Pandemic
Epidemic that has spread across a large geographical area.
37
New cards
Herd immunity
When individuals who are not immune to a pathogen are protected from exposure by the large amounts of immune individuals within the community
38
New cards
Epidemiology
Study of patterns, causes and effects of health and disease conditions in a defined population.
39
New cards
Monoclonal antibodies
Antibodies artificially derived from a single B cell clone. Commonly used to provide immune protection for individuals who contract harmful diseases.
40
New cards
Humoral immunity
The pathway by which antibodies are produced by B lymphocytes to target exogenous antigens.
41
New cards
Cell-mediated immunity
Pathway that does not result in antigen production but instead targets endogenous antigens
42
New cards
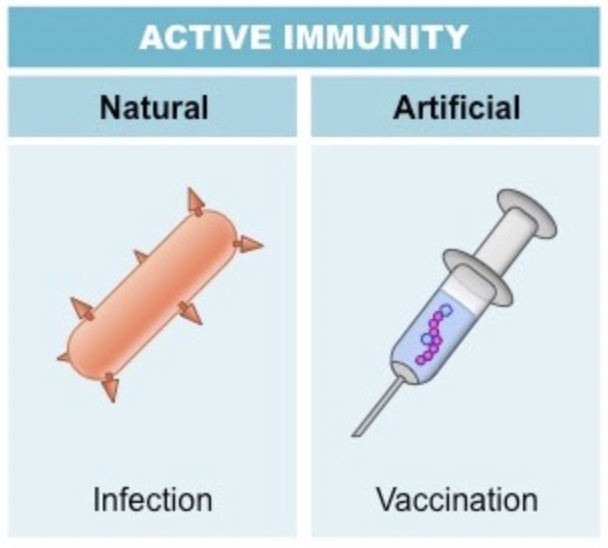
Active immunity
Production of antibodies by the body itself and the subsequent development of memory cells. Will result in long-term immunity.
43
New cards
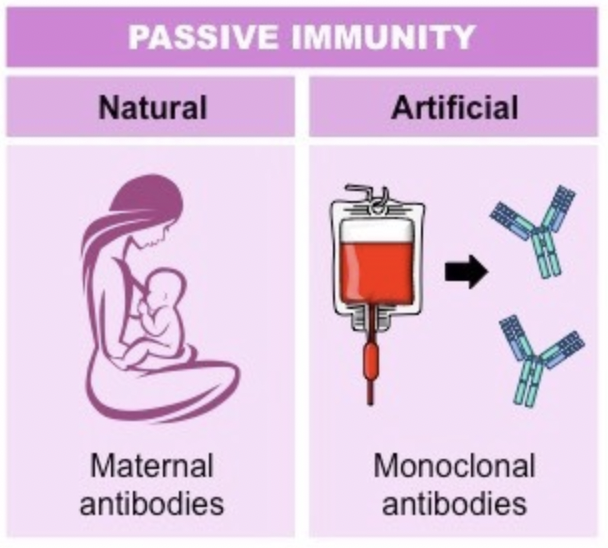
Passive immunity
Results from the acquisition of antibodies from another source and hence memory cells are not developed.
44
New cards
Hypersensitivity disorders
An excessively disproportionate immune response to a substance that is not inherently harmful (allergen).
45
New cards
Autoimmune disorders
Occurs when the immune system fails to recognize body cells as ‘self’ and begins targeting its own cells and tissues
46
New cards
Immunodeficiency disorders
Is a state in which the immune system’s capacity to fight infection is compromised or absent entirely
47
New cards
Macrophage
Large phagocyte. Finds antigens and eats them by secreting enzymes.