MCAT General Chemistry - Thermochemistry
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
system
matter that is being observed; the total amount of reactants and products in a chemical reaction
surroundings/environment
everything outside of the system
Isolated system
cannot exchange energy (heat and work) or matter with the surroundings
ex. insulated bomb calorimeter
Closed system
can exchange energy (heat and work) but not matter with the surroundings
ex. steam radiator
Open system
can exchange both energy (heat and work) and matter with the surroundings
ex. pot of boiling water
process
system experiences a change in one or more of its properties (such as concentrations of reactants or products, temperature, or pressure)
first law of thermodynamics
conservation of energy
ΔU = Q – W
where ΔU is the change in internal energy of the system, Q is the heat added to the system, and W is the work done by the system
isothermal processes
system’s temperature is constant; ΔU = 0, Q=W, hyperbolic curve on a pressure–volume graph
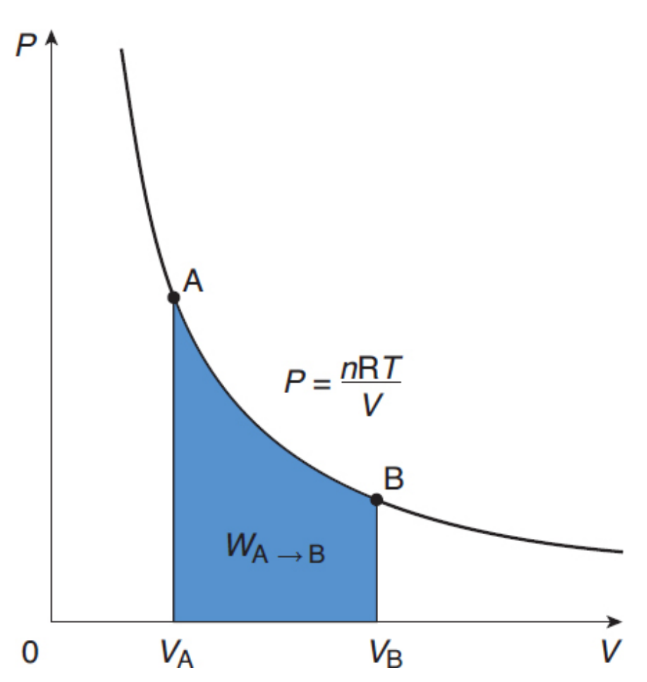
pressure–volume graph
displays changes in volume compared with changes in pressure; Work is represented by the area under such a curve
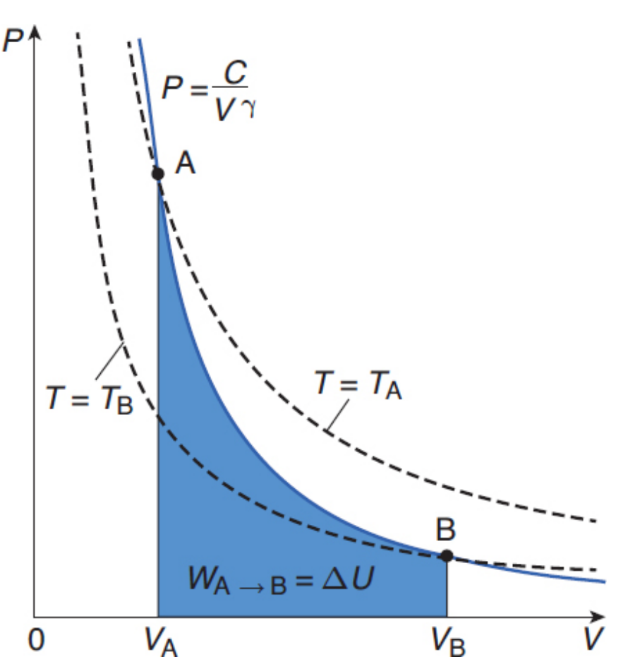
Adiabatic processes
no heat is exchanged between the system and the environment; Q = 0; ΔU = –W; appears hyperbolic on a P–V graph
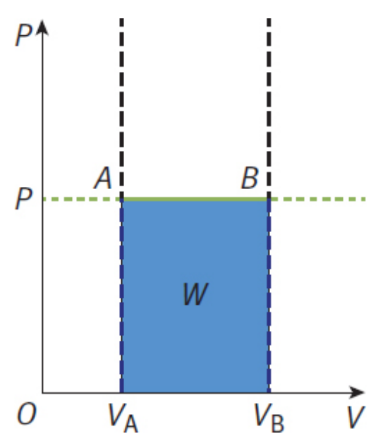
Isobaric processes
pressure of the system is constant; flat line on a P–V graph
isovolumetric (isochoric) processes
no change in volume; W=0; ΔU = Q; vertical line on a P–V graph
spontaneous process
one that can occur by itself without having to be driven by energy from an outside source; negative ΔG; will not necessarily happen quickly and may not go to completion
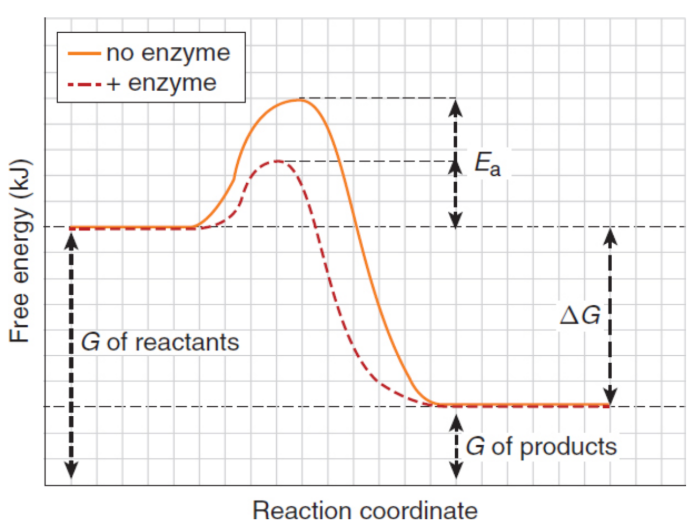
enzymes/biological catalysts
selectively enhance the rate of certain spontaneous (but slow) chemical reactions so that the biologically necessary products can be formed at a rate sufficient for sustaining life
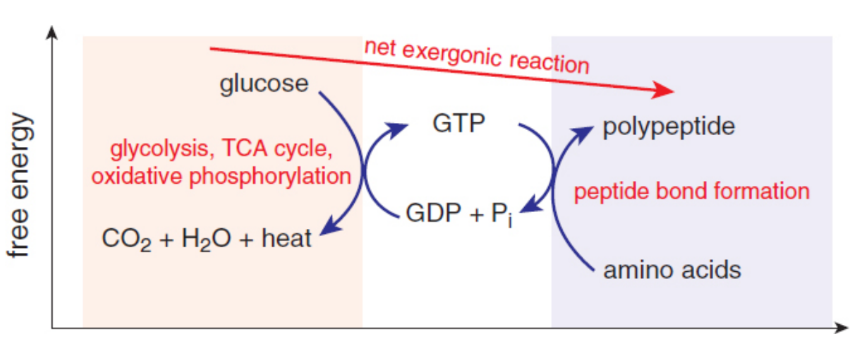
coupling
A common method for supplying energy for nonspontaneous reactions is by pairing nonspontaneous reactions to spontaneous ones that create the necessary energy
state functions
describe the system in an equilibrium state, but not how it got there
ex. pressure (P), density (ρ), temperature (T), volume (V), enthalpy (H), internal energy (U), Gibbs free energy (G), and entropy (S)
process functions
describes pathway taken from one equilibrium state to another
ex. work (W) and heat (Q)
standard conditions
defined for measuring the enthalpy, entropy, and Gibbs free energy changes of a reaction
25°C (298 K), 1 atm pressure, and 1 M concentration
kinetics, equillibrium, thermodynamics
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
temperature is 0°C (273 K) and pressure is 1 atm
ideal gas
standard state
the most stable form of a substance; “zero point” for all thermodynamic calculations
standard enthalpy - ΔH°
standard entropy - ΔS°
standard free energy changes - ΔG°
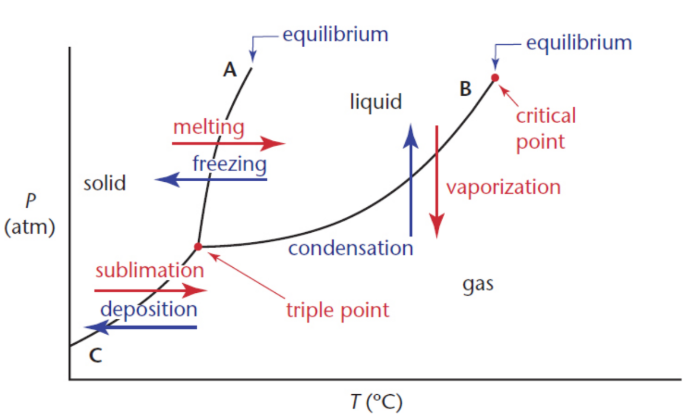
Phase diagrams
graphs that show the standard and nonstandard states of matter for a given substance in an isolated system, as determined by temperatures and pressures
Phase changes
change between states of matter; reversible, and an equilibrium of phases will eventually be reached at any given combination of temperature and pressure
evaporation/vaporization
liquid → gas; endothermic process for which the heat source is the liquid water
Boiling
specific type of vaporization; rapid bubbling of the entire liquid with rapid release of the liquid as gas particles
condensation
gas → liquid; facilitated by lower temperature or higher pressure (vapor pressure)
boiling point
liquid-gas equilibrium temperature; the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the ambient (external, applied, or incident) pressure
microstates
freedom of movement; allows energy dispersion; involved in entropy
fusion/melting
solid → liquid
solidification/crystallization/freezing
liquid → solid
melting/freezing point
solid-liquid equilibrium temperature
sublimation
solid → gas
deposition
gas → solid
cold finger
device used to purify a product that is heated under reduced pressure, causing it to sublime, then deposits onto the instrument
lines of equilibrium/phase boundaries
indicate the temperature and pressure values for the equilibria between phases; interfaces
triple point
point at which the three phase boundaries meet; temperature and pressure at which the three phases exist in equilibrium
gas phase
found at high temperatures and low pressures
solid phase
low temperatures and high pressures
liquid phase
moderate temperatures and moderate pressures
critical point
where phase boundary between the liquid and gas phases terminates; temperature and pressure above which there is no distinction between the phases; densities of ‘liquid’ and ‘vapour‘ become equal; heat of vaporization at this point and above is zero
supercritical fluids
fluids existing above the critical point
Temperature (T)
related to the average kinetic energy of the particles of a substance; how hot or cold something is
scales: Fahrenheit, Celsius, and Kelvin
thermal energy (enthalpy)
realated average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance and how much substance is present
absolute temperature scale (Kelvin)
determined via the third law of thermodynamics, which elucidated that there is a finite limit to temperature below which nothing can exist
Heat (Q)
transfer of energy from one substance to another as a result of their differences in temperature
q = mcΔT
unit of energy: joule (J) or calorie (cal) (1 cal = 4.184 J)
zeroth law of thermodynamics
objects are in thermal equilibrium only when their temperatures are equal
endothermic
Processes in which the system absorbs heat; ΔQ > 0
exothermic
processes in which the system releases heat; ΔQ < 0
Enthalpy (ΔH)
equivalent to heat under constant pressure
ΔHrxn = Hproducts – Hreactants
calorimetry
process of measuring transferred heat; constant pressure and sonstant volume
Specific heat
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius
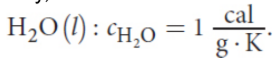
heat capacities
mass times specific heat
constant-pressure calorimeter
insulated container covered with a lid and filled with a solution in which a reaction or some physical process, such as dissolution, is occurring
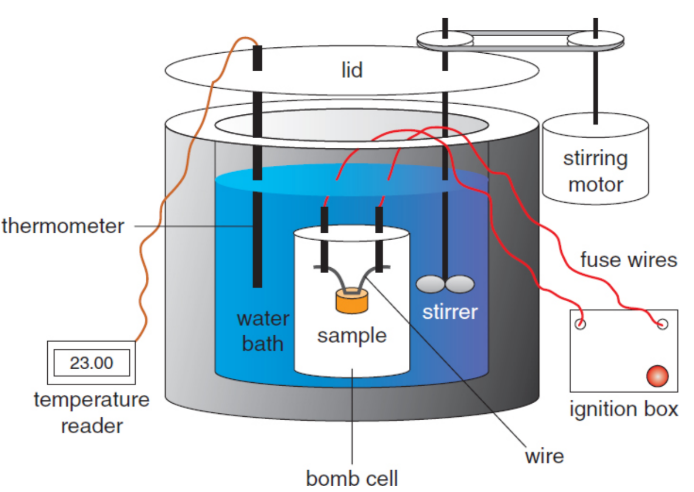
bomb calorimeter/decomposition vessel/constant pressure calorimeter
a sample of matter, typically a hydrocarbon, is placed in the steel decomposition vessel, which is filled with almost pure oxygen gas, then ignited by an electric ignition mechanism; heat that evolves is the heat of the combustion reaction; no work
Heating curves
show that phase change reactions do not undergo changes in temperature
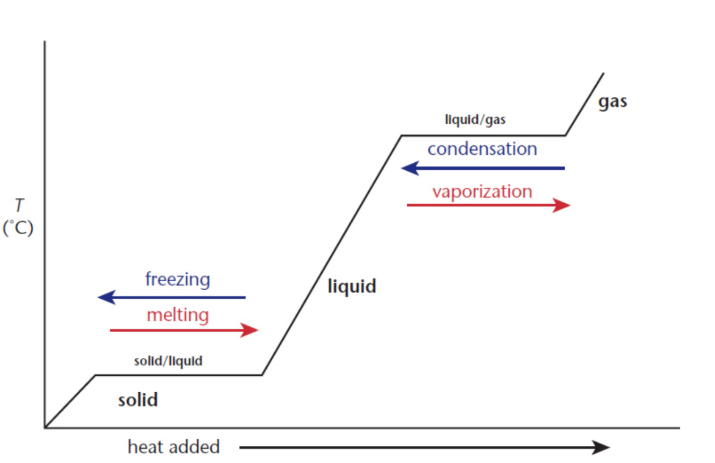
enthalpy/heat of fusion/vaporization (ΔHfus/vap)
used to determine the heat transferred during the phase change
q = mL
where m is the mass and L is the latent heat, a general term for the enthalpy of an isothermal process, given in the units cal/g
standard enthalpy of formation (ΔH°f)
enthalpy required to produce one mole of a compound from its elements in their standard states
standard enthalpy of a reaction (ΔH°rxn)
enthalpy change accompanying a reaction being carried out under standard conditions
ΔH°rxn = Σ ΔH°f,products − Σ ΔH°f,reactants
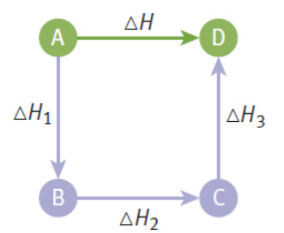
Hess’s law
enthalpy changes of reactions are additive
ΔHreactants → elements = –ΔHelements → reactants
bond enthalpies/dissociation energies
average energy that is required to break a particular type of bond between atoms
kJ/mol

standard heat of combustion (ΔH°comb)
enthalpy change associated with the combustion of a fuel
Entropy
measure of the spontaneous dispersal of energy at a specific temperature: how much energy is spread out, or how widely spread out energy becomes, in a process
where ΔS is the change in entropy, Qrev is the heat that is gained or lost in a reversible process, and T is the temperature in kelvin.
units: J/mol*K
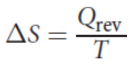
second law of thermodynamics
energy spontaneously disperses from being localized to becoming spread out if it is not hindered from doing so; time’s arrow: unidirectional limitation on the movement of energy by which we recognize before and after or new and old
ΔSuniverse = ΔSsystem + ΔSsurroundings > 0
standard entropy change for a reaction (ΔS°rxn)
ΔS°rxn = Σ ΔS°f,products − Σ ΔS°f,reactants
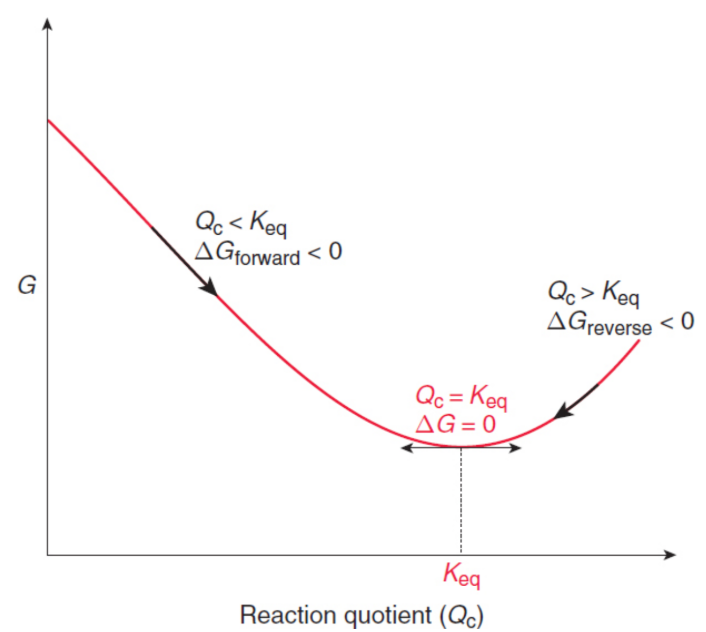
Gibbs free energy, G
measure of the change in the enthalpy and the change in entropy as a system undergoes a process; indicates whether a reaction is spontaneous or nonspontaneous; maximum amount of energy released by a process—occurring at constant temperature and pressure—that is available to perform useful work
ΔG = ΔH – TΔS
where T is the temperature in kelvin and TΔS represents the total amount of energy that is absorbed by a system when its entropy increases reversibly
exergonic
system releases energy; spontaneous
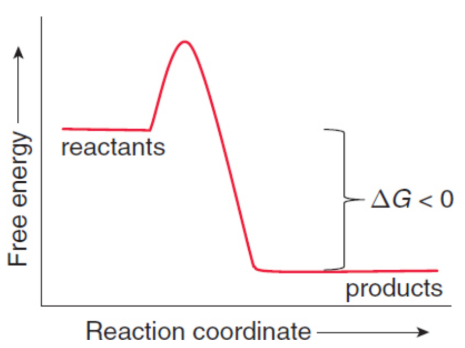
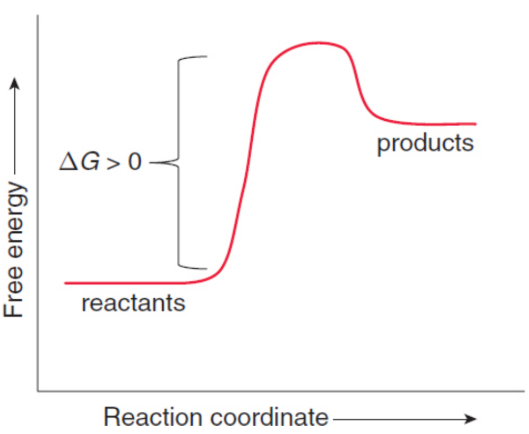
endergonic
system absorbs energy; nonspontaneous
standard free energy (ΔG°rxn)
free energy change of reactions can be measured under standard state conditions
ΔG°rxn = Σ ΔG°f,products − Σ ΔG°f,reactants
ΔG°rxn = –RT ln Keq
where R is the ideal gas constant, T is the temperature in kelvin, and Keq is the equilibrium constant
ΔGrxn = ΔG°rxn + RT ln Q = RT ln Q/Keq