Bio 160 Exam 2 DBQ's
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
What type of mutation results in a single nucleotide change but does not alter the amino acid sequence?
Silent Mutation
A gene mutation changes a codon from UAC (tyrosine) to UAA (stop codon). What type of mutation is this?
Nonsense
A scientist mutates the template strand of a gene but leaves the coding strand unchanged. What will happen during transcription?
The mRNA will be altered
Where does transcription occur in eukaryotic cells?
Nucleus
During elongation, which enzyme synthesizes mRNA?
RNA Polymerase
A mutation prevents RNA polymerase from binding to the promoter. What will happen?
Transcription will not begin
A mutation changes a codon from GGC to GGU, yet the amino acid remains glycine. Why?
The wobble position allows different third bases to still code for the same amino acid
Alpha-amanitin is a toxin found in some poisonous mushrooms. A researcher exposes eukaryotic cells to alpha-amanitin and observes a drastic reduction in the production of mRNA but no significant effect on the production of rRNA or tRNA. Based on this observation, which RNA polymerase is most likely inhibited by alpha-amanitin?
RNA Polymerase III
Describe the role of sigma factors in bacterial transcription.
Different sigma factors regulate the expression of different sets of genes, Sigma factors help RNA polymerase recognize and bind to promoter regions
What is the function and some characteristics of alpha-amanitin?
It inhibits RNA Polymerase II, blocking mRNA synthesis, It has little to no effect on RNA Polymerase I, It moderately inhibits RNA Polymerase III
Describe transcription termination in bacteria.
Rho-dependent termination requires a Rho protein to dislodge RNA polymerase, Rho-independent termination relies on a hairpin structure followed by a poly-U sequence
Describe function and characteristics of alternative splicing.
Exon skipping is a common form of alternative splicing, Alternative splicing can be tissue-specific, leading to different protein isoforms in different cell types, Alternative splicing increases protein diversity without increasing the number of genes
Describe the role of the anticodon.
It carries amino acid to the ribosome
A tRNA with the anticodon 3'-UAC-5' binds to an mRNA codon during translation. What is the corresponding mRNA codon?
5'-AUG-3'
A researcher is investigating why liver cells and muscle cells in the same person have different structures and functions, despite having identical DNA. What is the most likely reason for these differences?
Different cell types express different sets of genes due to differential gene regulation
A biologist is engineering a synthetic tRNA with an altered anticodon that still carries the correct amino acid. What could be a possible effect of this modified tRNA during translation?
It may insert the correct amino acid at the wrong codon, leading to a misfolded protein
Which ribosomal subunit is primarily responsible for binding mRNA during translation initiation?
The small subunit (30S in prokaryotes, 40S in eukaryotes)
In eukaryotes, which synthesizes the rRNA involved in ribosome assembly (small or large subunits)?
RNA Polymerase I & III
How do proteins regulate gene expression in operons?
They interact directly through physical contact with DNA
Which genes are part of the lac operon in E. coli?
lacY, lacZ, lacA
What is the primary function of an operon in prokaryotes?
To regulate the expression of multiple related genes in response to environmental conditions
What best describes how the lac operon is regulated?
It is always off unless lactose is present to inactivate the repressor
A bacterial cell is growing in an environment with both glucose and lactose. What is most likely happening with the lac operon?
The lac operon is repressed because the cell prefers glucose as its energy source
What would most likely happen if there were a mutation in the operator region of the lac operon that prevented the repressor from binding?
The operon would be permanently on, leading to continuous production of enzymes even in the absence of lactose
What best describes the difference between inducible and repressible operons?
Inducible operons, like the lac operon, are normally off and turned on by a specific molecule, while repressible operons, like the trp operon, are normally on and turned off by a specific molecule
What is the primary purpose of chromatin remodeling in eukaryotic cells?
To regulate the accessibility of DNA to transcription machinery
What is an example of an epigenetic change?
The addition of methyl groups to DNA that silences gene expression
What would be the most likely location of cholesterol in regards to the cell membrane's fluidity modulation?
embedded within the lipid bilayer
What are two major parts of cell membranes?
phospholipids, proteins
Lets say your body starts to break down a Twinkie you have consumed. The fat that was in your Twinkie would first be broken down into...
fatty acids and glycerol
Which type of transport requires a membrane protein but NO energy for transport?
Facilitated diffusion
What happens to an animal cell placed in a hypotonic solution?
It swells and may burst
Osmosis is the diffusion of ____ from areas of ____ concentration to areas of ____ concentration.
water, high, low
Some antibiotics work by increasing the permeability of bacterial cell walls to ions. What is the most likely mode of action of these compounds?
They form channels in the membrane
Knowing about how integral membrane proteins work and are arranged into the lipid bilayer, why would "TYR-ASN-GLN-GLY-ALA-TRP-PRO-CYS-SER-THR-ASN" most likely be representative of one that spans an entire bilayer?
mane ion know
A scientist places a freshwater fish's cell into seawater. What is the most likely outcome for the cell?
The cell will shrink as water leaves
A cell is using the sodium-potassium pump to maintain ion gradients. Later, it uses the sodium gradient to transport glucose into the cell. What type of transport is the glucose-sodium movement?
Secondary Active transport
Which of the following mechanisms would be the most likely entry mechanism forSARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19...a virus) into a "Florida" party going college student?
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Which type of endocytosis is primarily used by immune cells to engulf
(eat) bacteria?
Phagocytosis
What is the correct sequence of organelles in the secretory pathway?
Rough ER to Golgi apparatus to Vesicles to Plasma membrane
What would be some likely features of a prokaryotic cell?
mitochondria and chloroplasts
What are attributes of mitochondria AND chloroplasts that suggest they were once free-living bacteria?
they have independent circular chromosomes
(DNA), they have their own ribosomes, they are similar in size to modern day equivalents in cyanobacteria and heterotrophic bacteria, and their replication is
independent of the cell division cycle
Order from SMALLEST to LARGEST - virus, bacteria cell, water molecule, glucose, carbon atom, eukaryotic cell.
carbon atom, water molecule, glucose, virus, bacteria cell, eukaryotic cell
In photosynthetic eukaryotes, DNA is found in ________.
the chloroplasts and mitochondria, and the nucleus
Which organelle if ruptured would likely cause the most physical damage to various biomolecules in the cell?
Lysosome
Photosynthesis can probably trace its earliest evolutionary origins back to what?
Prokaryotes
Which is found in eukaryotic cells but not in prokaryotic cells?
The nucleus
Which is involved in the synthesis of oils, phospholipids, and steroids in eukaryotic cells and helps to detoxify substances in the liver cells of the body?
smooth ER
Motor proteins like Kinesin help to move vesicles around as part of the
endomembrane system primarily using networks of what?
microtubules
During which phase would a cell make a copy of its genes to be equally apportioned to daughter cells?
S phase
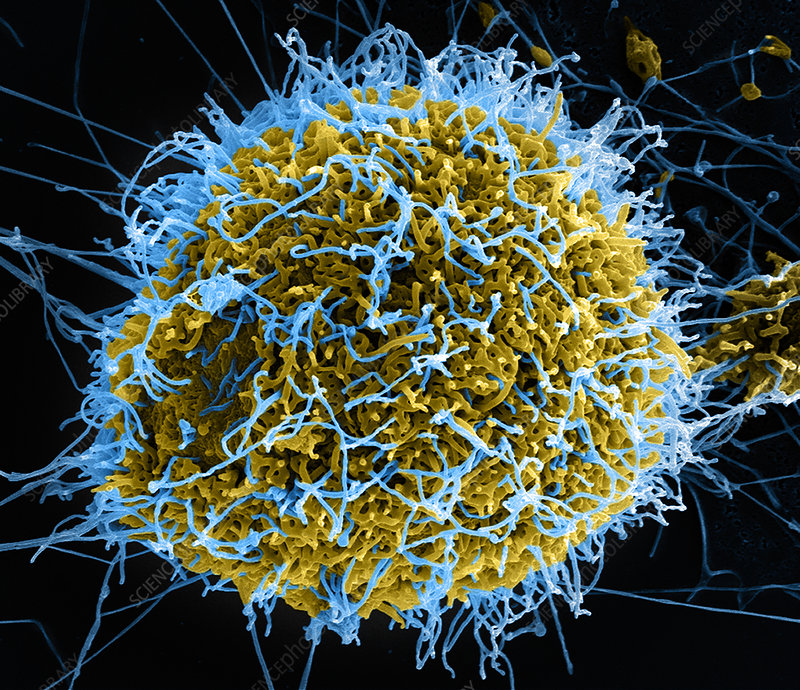
This false color image taken below of ebola virus attaching to a host cell was most likely taken with which type of microscope?
SEM (Scanning Electron Microscope)
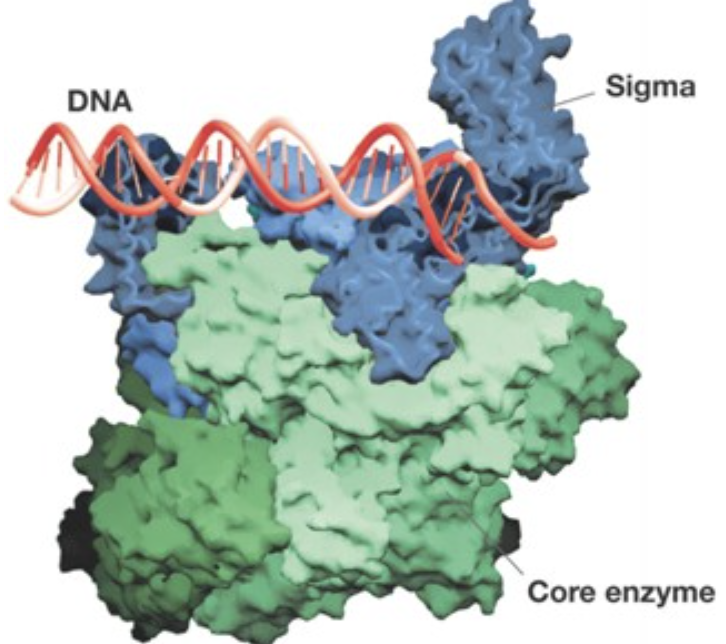
What enzymatic complex is depicted above?
RNA Polymerase
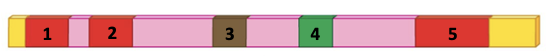
Assuming the exons are numbered in this pre mRNA above, which are valid "mature mRNAs" post alternative splicing?
12345, 12, 2345
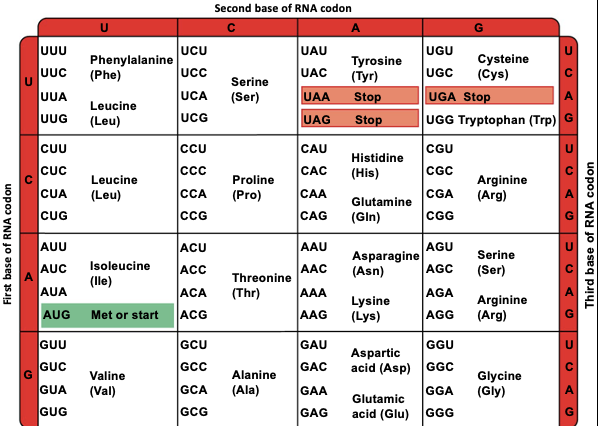
The ANTICODON 5' UGC 3' would likely lead to...
Alanine
The anticodon 5' UGA 3' would likely correlate to the sequence ______ in the NON-TEMPLATE DNA.
3’ ACT 5’
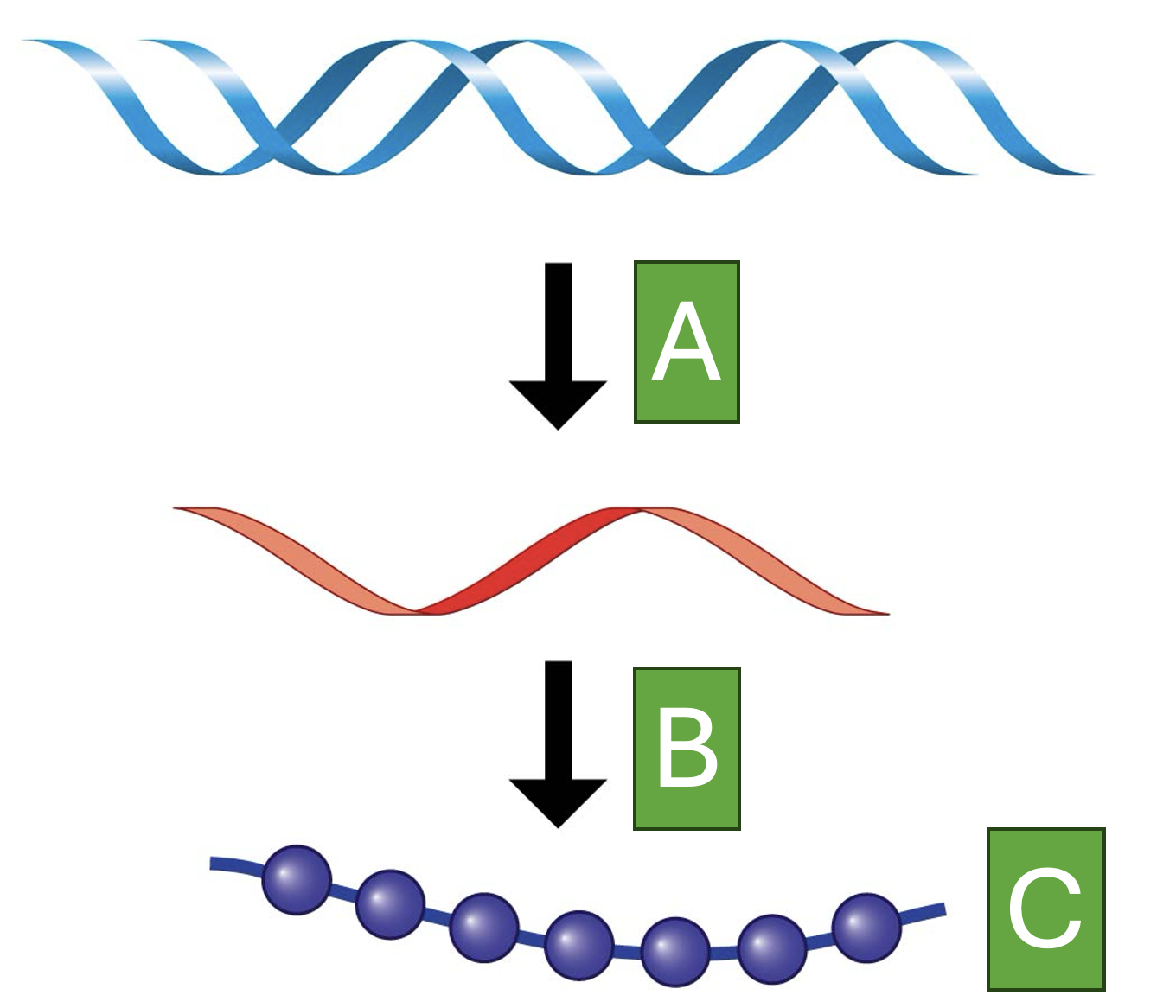
At which region would regulation of gene expression save the most energy?
Area A
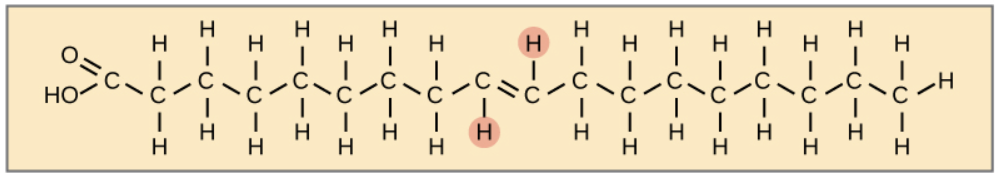
What structure below best represents what you would expect these trans fats to look like structurally?
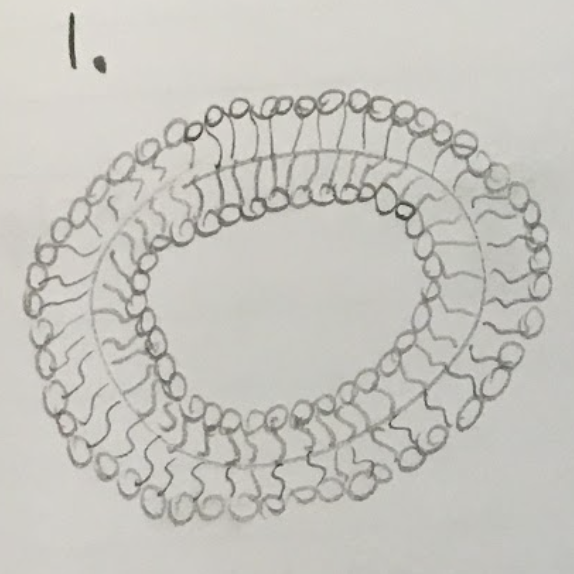
What could potentially describe the arrangement of phospholipids seen above?
liposome, vesicle
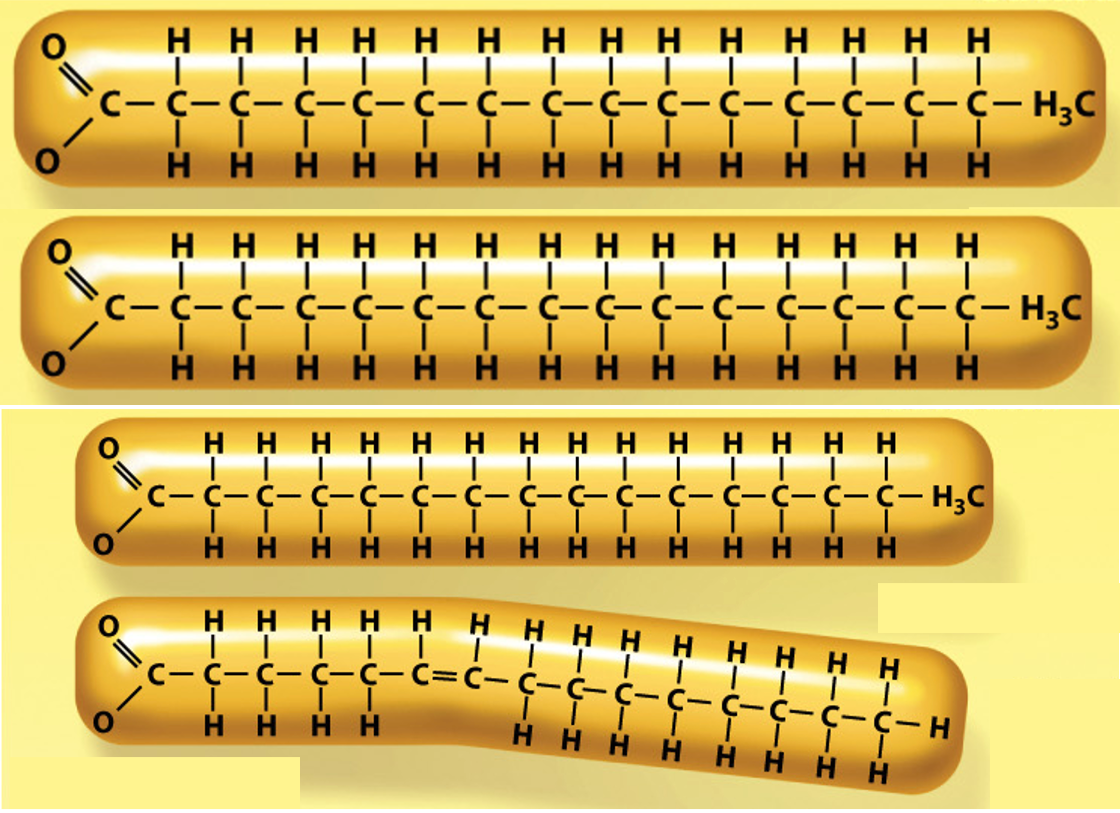
Given the membrane lipid tail structures above for membrane A & B (assume this motif is repeated throughout a given cell for each phospholipid in the membrane). Which membrane would be least permeable to glycerol?
Membrane A (two straight tails)