Chapter 28: Special Relativity
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
classical velocity addition
the method of adding velocities when 𝑣<<𝑐; velocities add like regular numbers in one-dimensional motion: 𝑢=𝑣+𝑢′, where 𝑣 is the velocity between two observers, 𝑢 is the velocity of an object relative to one observer, and 𝑢′ is the velocity relative to the other observer
first postulate of special relativity
the idea that the laws of physics are the same and can be stated in their simplest form in all inertial frames of reference
inertial frame of reference
a reference frame in which a body at rest remains at rest and a body in motion moves at a constant speed in a straight line unless acted on by an outside force
length contraction
𝐿, the shortening of the measured length of an object moving relative to the observer’s frame: L=L0√1−𝑣2𝑐2=𝐿0𝛾
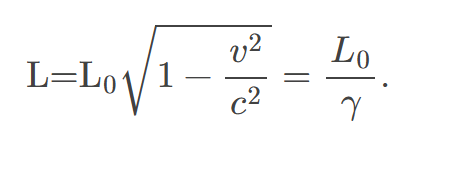
Michelson-Morley experiment
an investigation performed in 1887 that proved that the speed of light in a vacuum is the same in all frames of reference from which it is viewed
proper length
𝐿0; the distance between two points measured by an observer who is at rest relative to both of the points; Earth-bound observers measure proper length when measuring the distance between two points that are stationary relative to the Earth
proper time
Δ𝑡0. the time measured by an observer at rest relative to the event being observed: Δ𝑡=Δ𝑡0√1−𝑣2𝑐2=𝛾Δ𝑡0, where 𝛾=1√1−𝑣2𝑐2
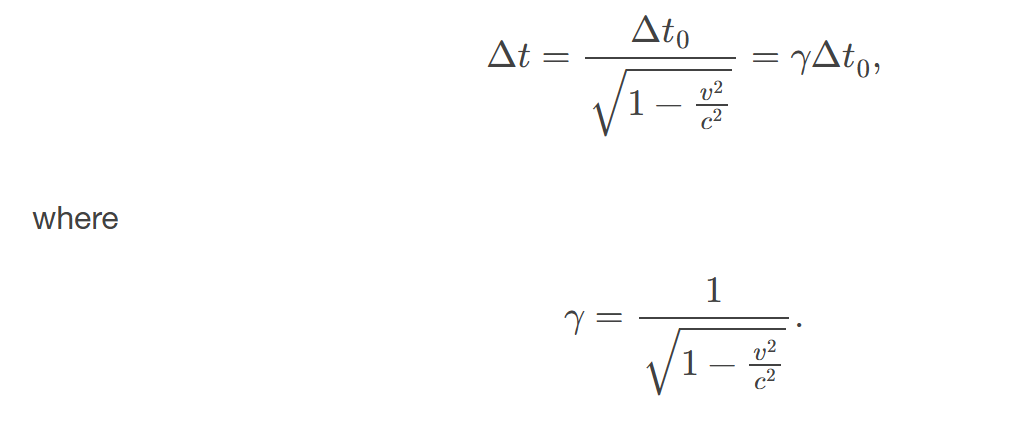
relativistic Doppler effects
a change in wavelength of radiation that is moving relative to the observer; the wavelength of the radiation is longer (called a red shift) than that emitted by the source when the source moves away from the observer and shorter (called a blue shift) when the source moves toward the observer; the shifted wavelength is described by the equation 𝜆obs=λ𝑠√1+𝑢𝑐1−𝑢𝑐 where 𝜆obs is the observed wavelength, 𝜆𝑠 is the source wavelength, and 𝑢 is the velocity of the source to the observer

relativistic kinetic energy
the kinetic energy of an object moving at relativistic speeds: KErel=(𝛾−1)𝑚𝑐2, where 𝛾=1√1−𝑣2𝑐2
relativistic momentum
𝑝, the momentum of an object moving at relativistic velocity; 𝑝=γmu, where 𝑚 is the rest mass of the object, 𝑢 is its velocity relative to an observer, and the relativistic factor 𝛾=1√1−𝑢2𝑐2

relativistic velocity addition
the method of adding velocities of an object moving at a relativistic speed: u=𝑣+𝑢′1+𝑣𝑢′𝑐2, where 𝑣 is the relative velocity between two observers, 𝑢 is the velocity of an object relative to one observer, and 𝑢′ is the velocity relative to the other observer

relativity
the study of how different observers measure the same event
rest energy
the energy stored in an object at rest: 𝐸0=𝑚𝑐2

rest mass
the mass of an object as measured by a person at rest relative to the object
second postulate of special relativity
the idea that the speed of light 𝑐 is a constant, independent of the source
special relativity
the theory that, in an inertial frame of reference, the motion of an object is relative to the frame from which it is viewed or measured
time dilation
the phenomenon of time passing slower to an observer who is moving relative to another observer
total energy
defined as 𝐸=𝛾𝑚𝑐2, where 𝛾=1√1−𝑣2𝑐2

twin paradox
this asks why a twin traveling at a relativistic speed away and then back towards the Earth ages less than the Earth-bound twin. The premise to the paradox is faulty because the traveling twin is accelerating, and special relativity does not apply to accelerating frames of reference
relativistic work-energy theorem
states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its relativistic energy, taking into account both kinetic and potential energy in relativistic contexts.
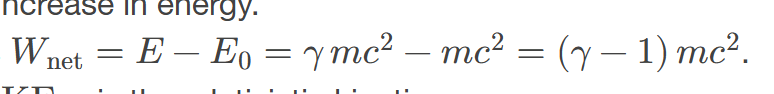
Relativistic kinetic energy
Refers to the energy an object possesses due to its motion at relativistic speeds, calculated as (E_k = \gamma mc^2 - mc^2), where (\gamma) is the Lorentz factor.
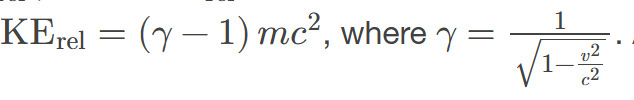
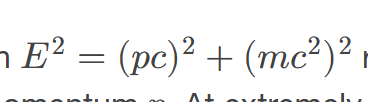
The equation 𝐸2=(𝑝𝑐)2+(𝑚𝑐2)2 relates
relates the relativistic total energy 𝐸 and the relativistic momentum 𝑝. At extremely high velocities, the rest energy 𝑚𝑐2 becomes negligible, and 𝐸=𝑝𝑐.