PVCC BIO 201 Lab Exam 1
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
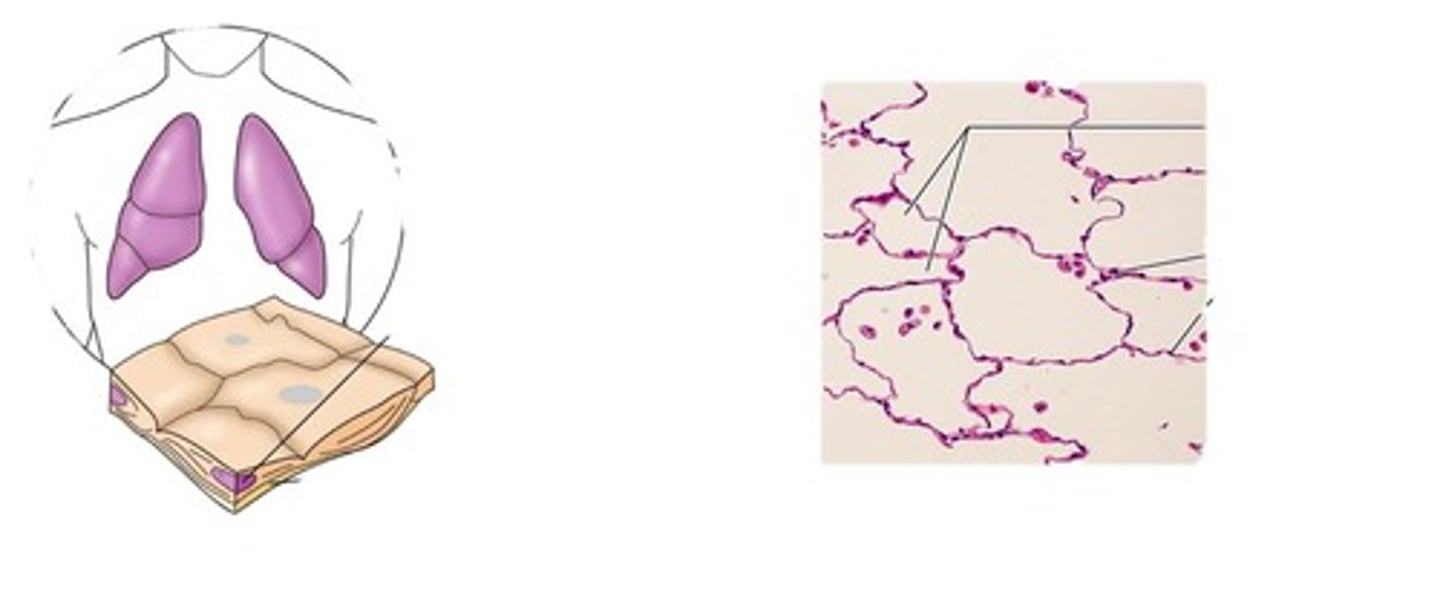
simple squamous epithelium
function: allows materials to pass by diffusion and filtration in sites where protection is not important, secretes lubricating substances in serosae
location:air sacs of lungs, kidney glomeruli, lining of hear, blood vessels
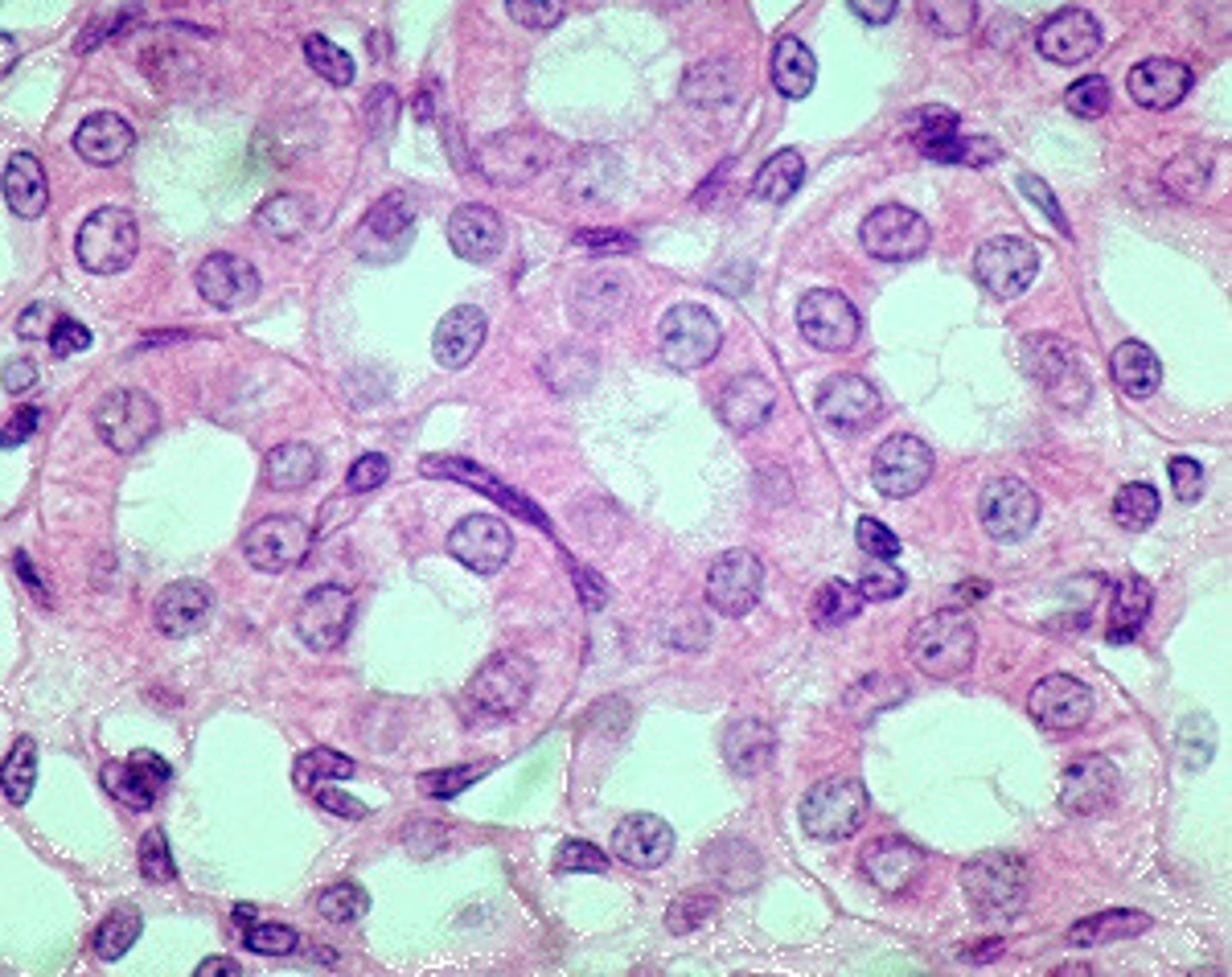
simple cuboidal epithelium
Function: secretion and absorption
Location: Kidney tubules; ducts and secretory portions of small glands, ovary surface.
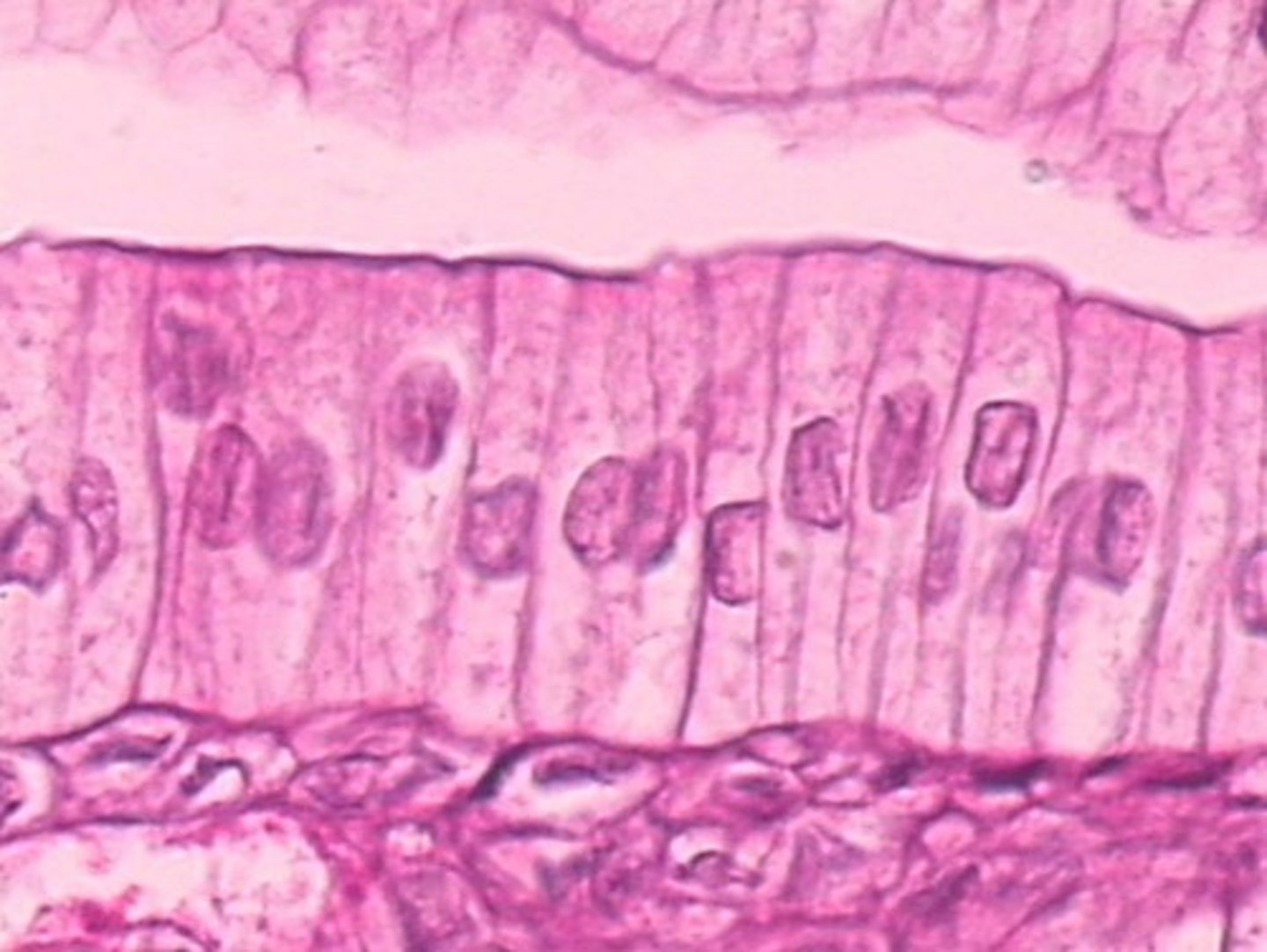
simple columnar epithelium
Function: Absorption; secretion of mucus, enzymes, and other substances; ciliated type propels mucus (or reproductive cells) by ciliated action.
Location: nonciliated type lines most of the digestive tract (stomach to anal canal), gallbladder and excretory ducts of some glands; ciliated variety lines small bronchi, uterine tubes, and some regions of the uterus.
pseudo stratified columnar epithelium
Function: Secretes substances, particularly mucus; propulsion of mucus by ciliary action.
Location: Nonciliated type in male's sperm-carrying ducts and ducts of large glands; ciliated variety lines the trachea, most of the upper respiratory tract.
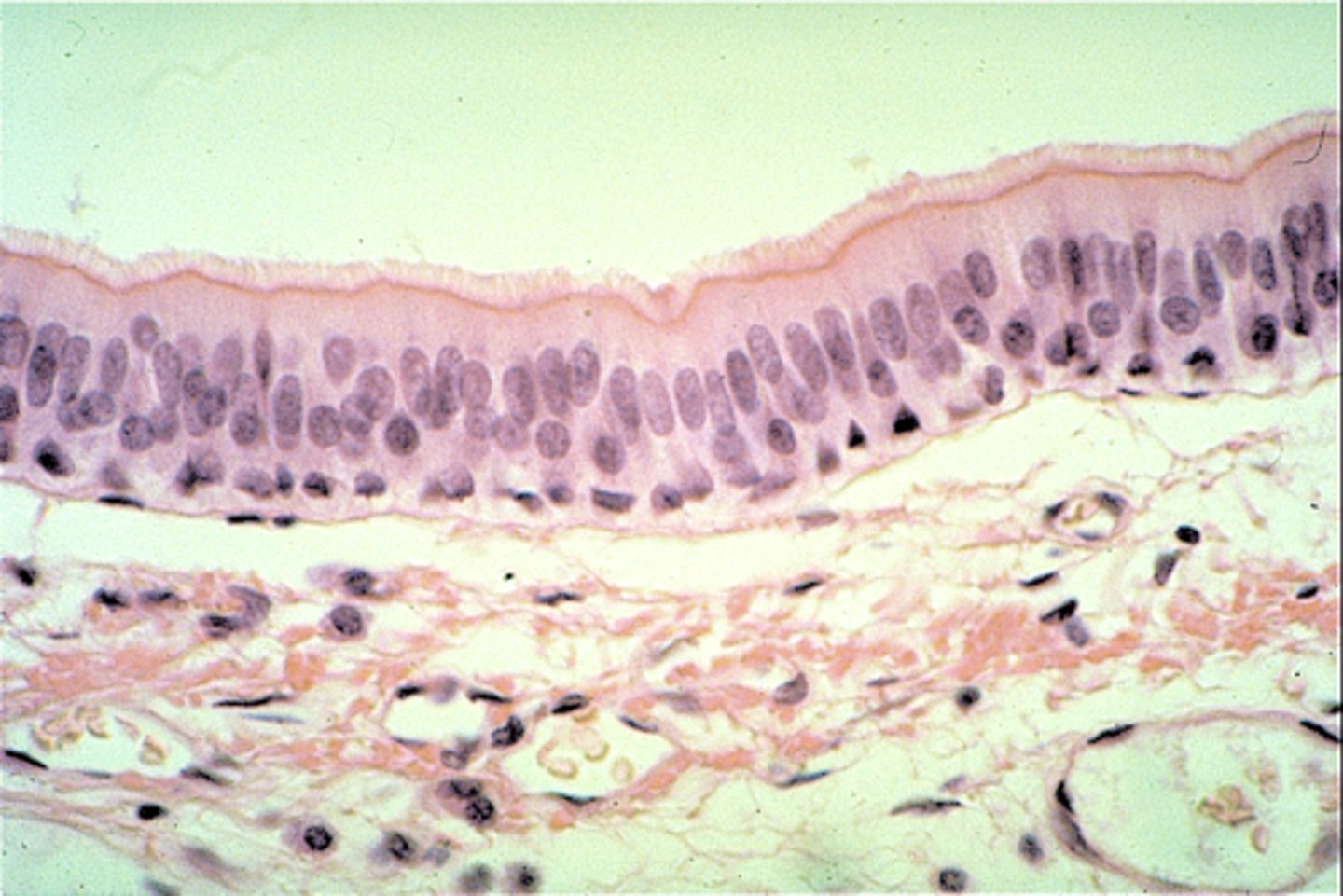
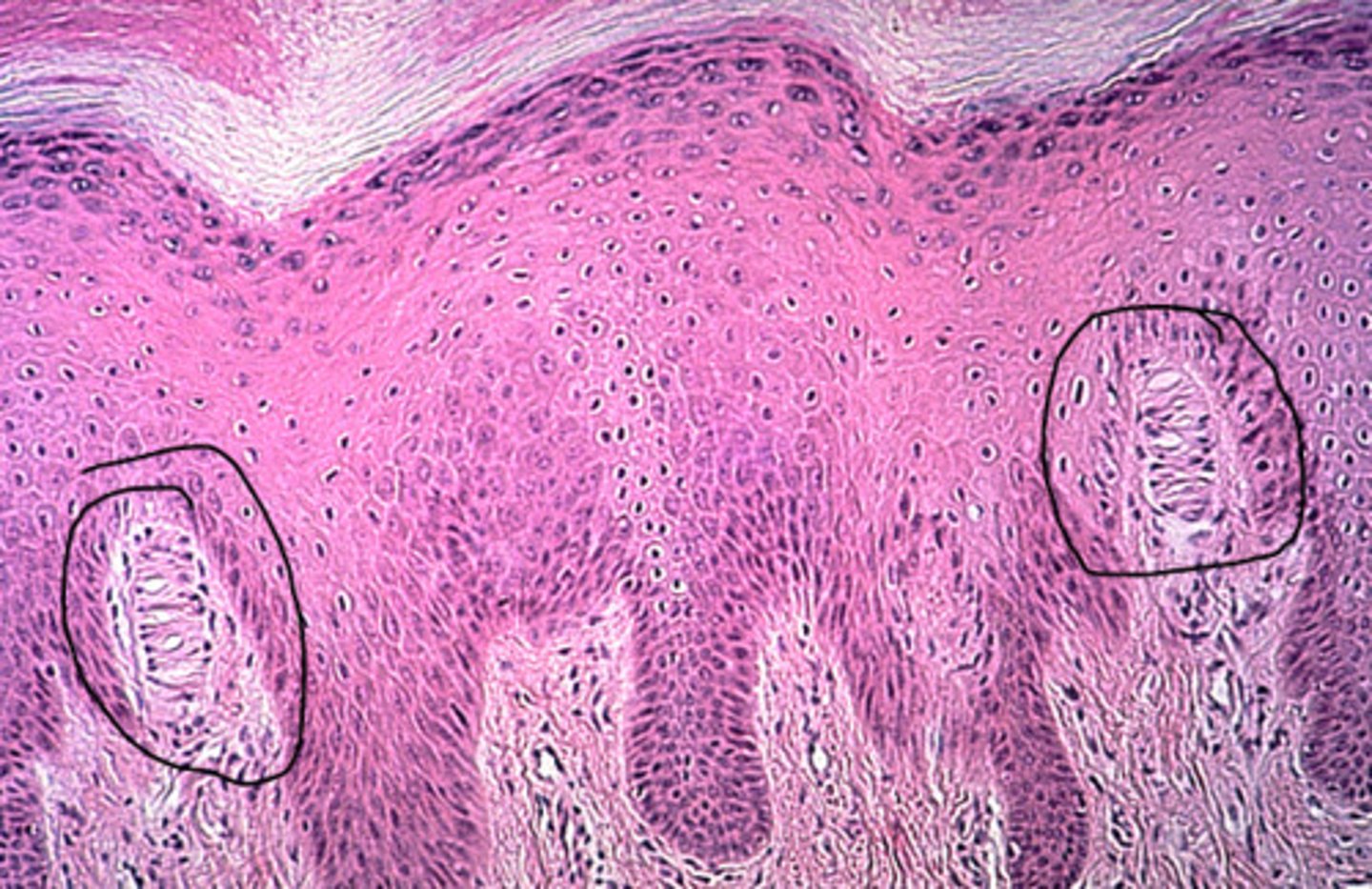
stratified squamous epithelium
Function: protects underlying tissues in areas subject to abrasion
Location: nonkeratinized type forms the moist lining of the esophagus, mouth, and vagina; keratinized type forms the epidermis of the skin, a dry membrane.
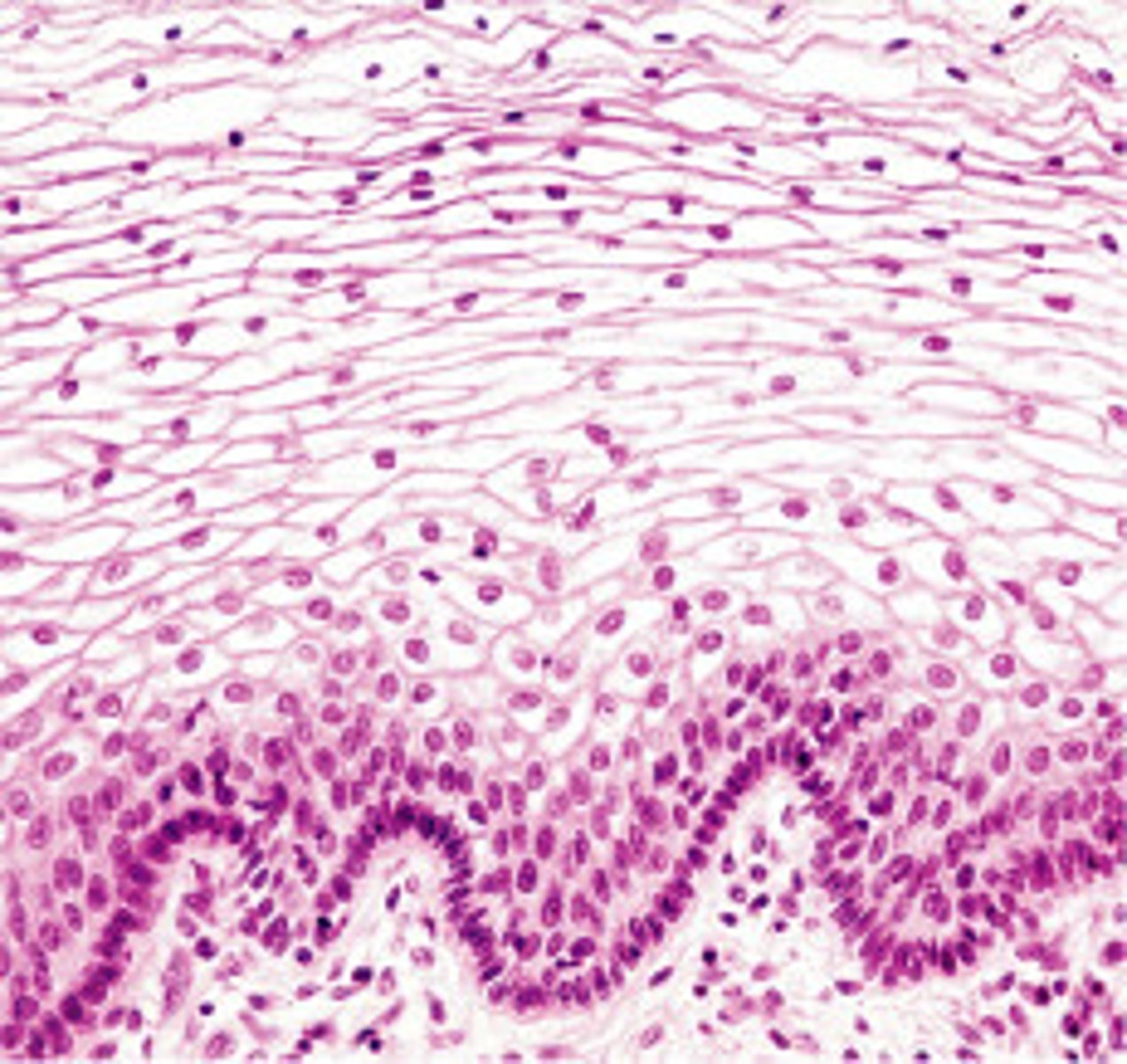
stratified cuboidal epithelium
Function: protection
Location: Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands, and salivary glands.
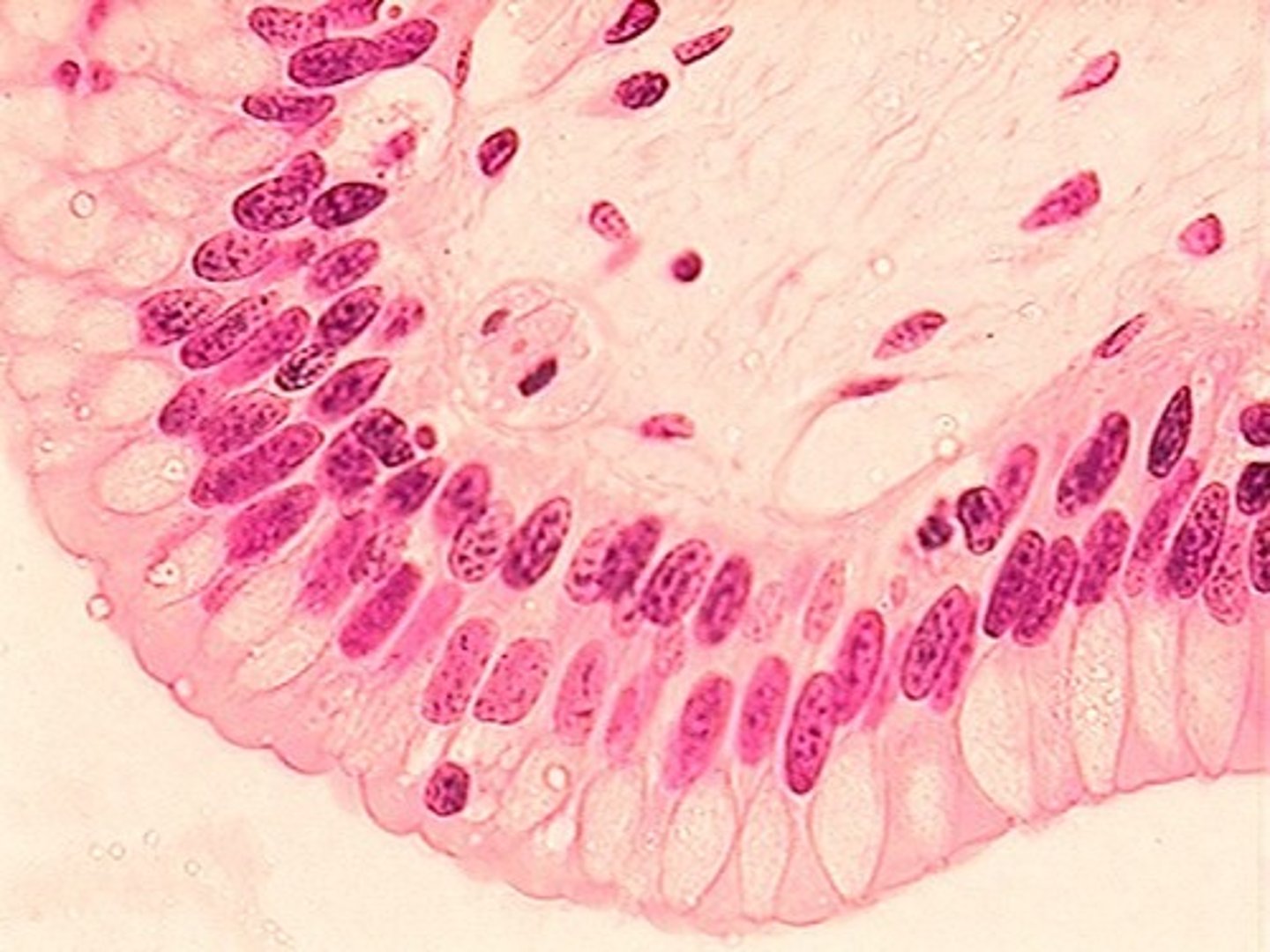
stratified columnar epithelium
Function: protection and secretion
Location: rare in the body; small amounts in male urethra and in large ducts of some glands
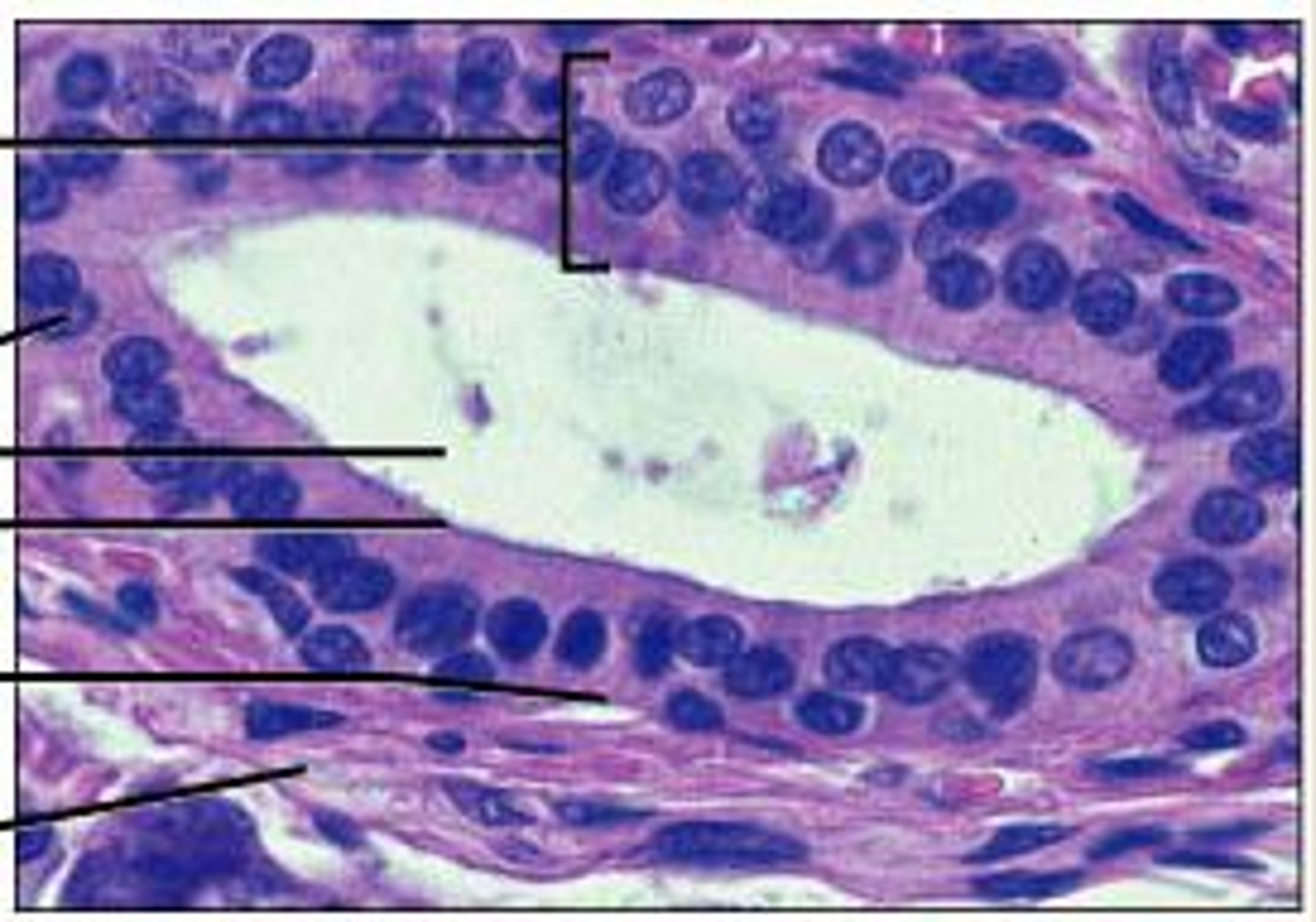
transitional epithelium
function: stretches readily and permits distension of urinary organ by contained urine
Location: lines the ureters, urinary bladder, and part of the urethra
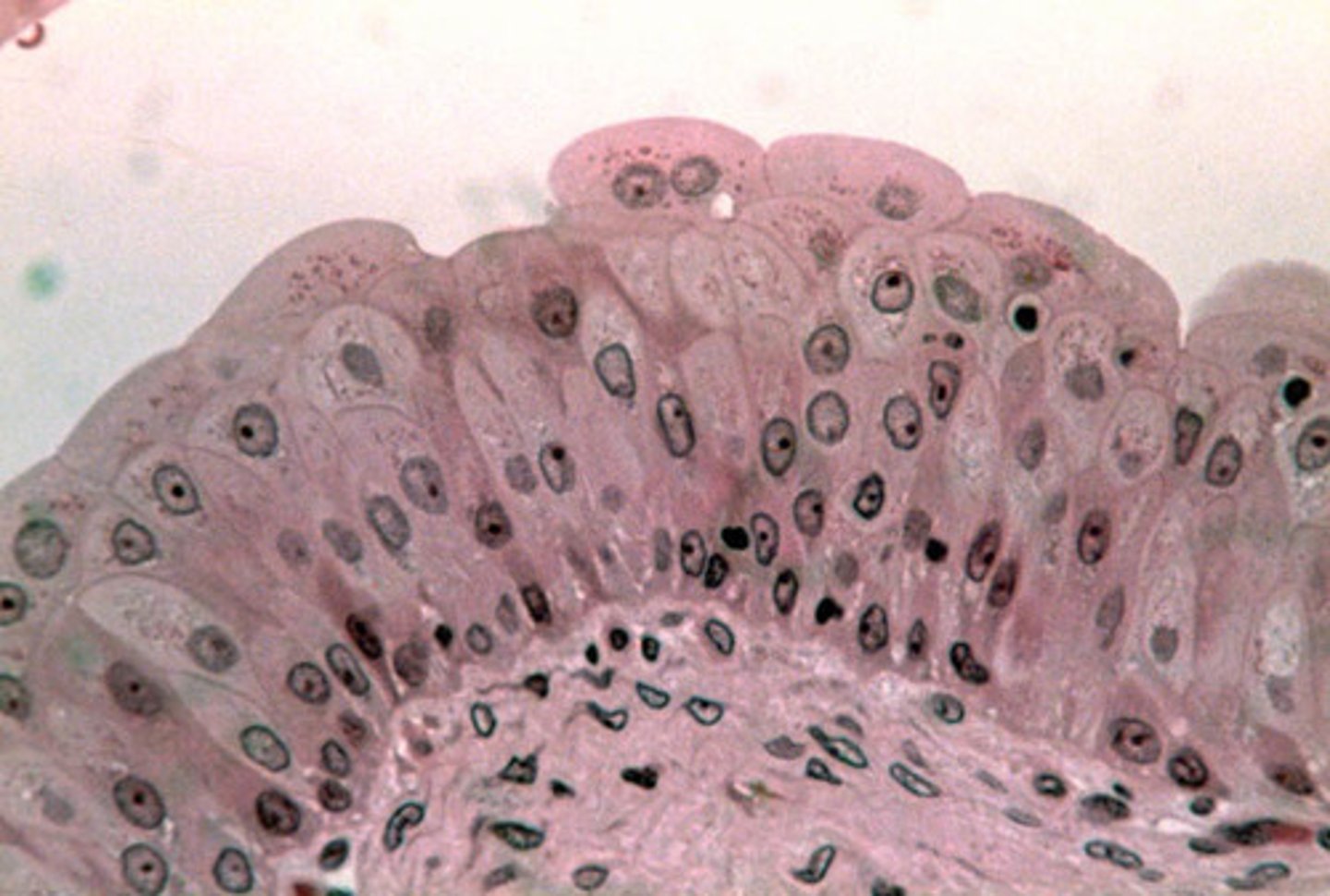
mesenchyme
Function: gives rise to all other connective tissue types
Location: primarily in embryo
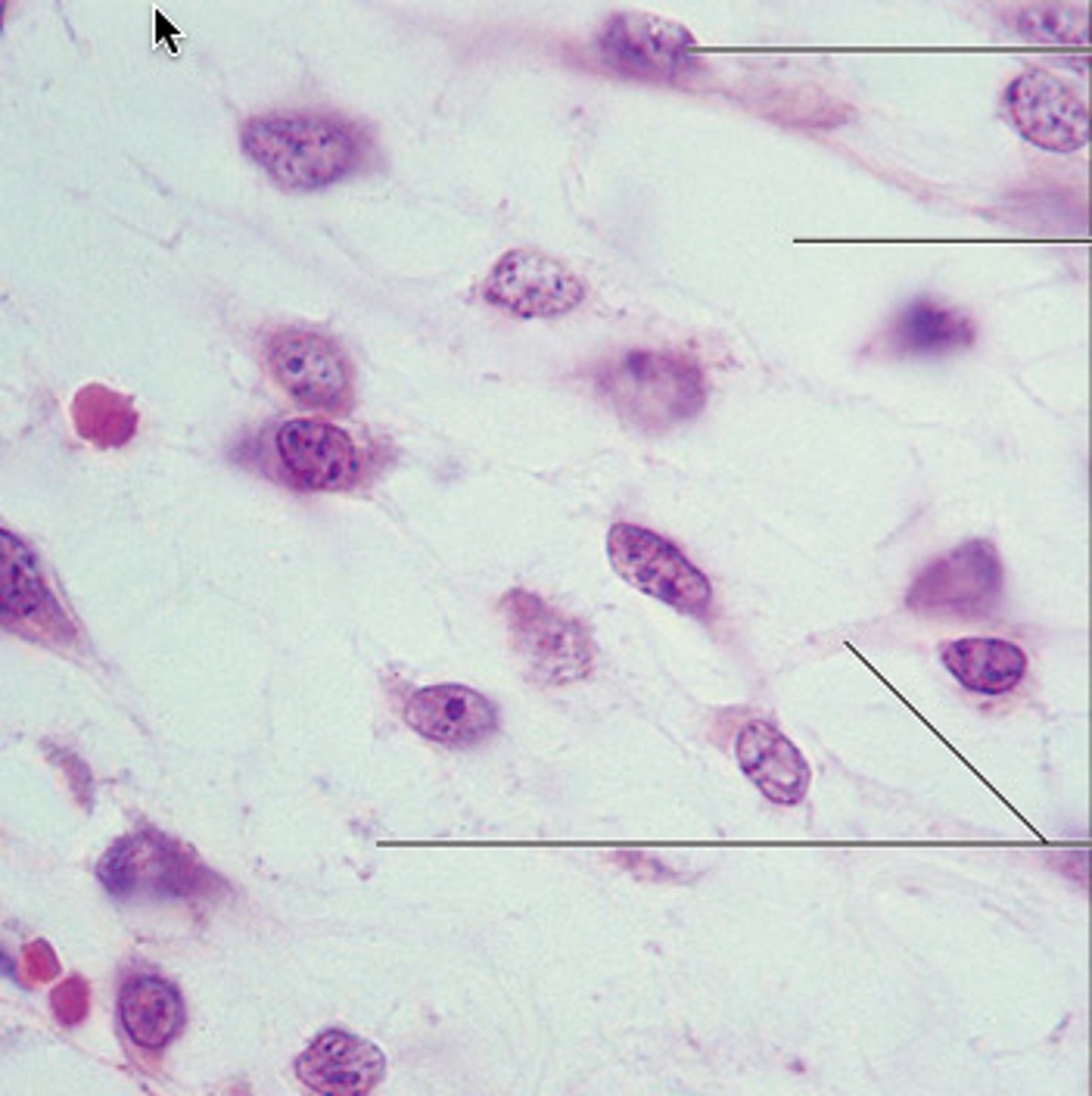
areolar connective tissue
Function: wraps and cushions organs
Location: widely distributed under epithelia of body (surrounds capillaries)
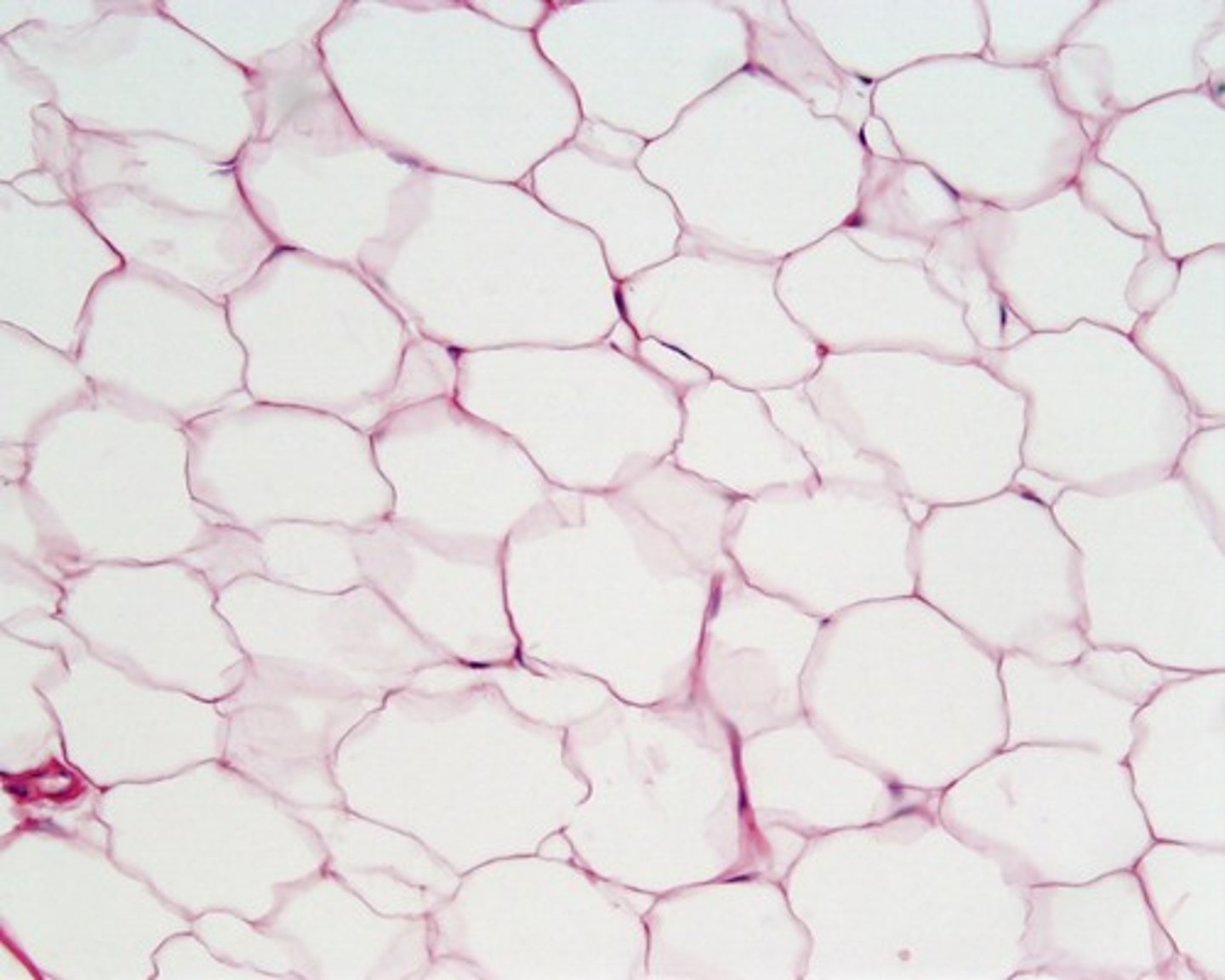
adipose connective tissue
Function: provides reserve fuel; insulates against heat loss; supports and protects organs
Location: under skin, around kidneys and eyeballs, within abdomen, in breasts.
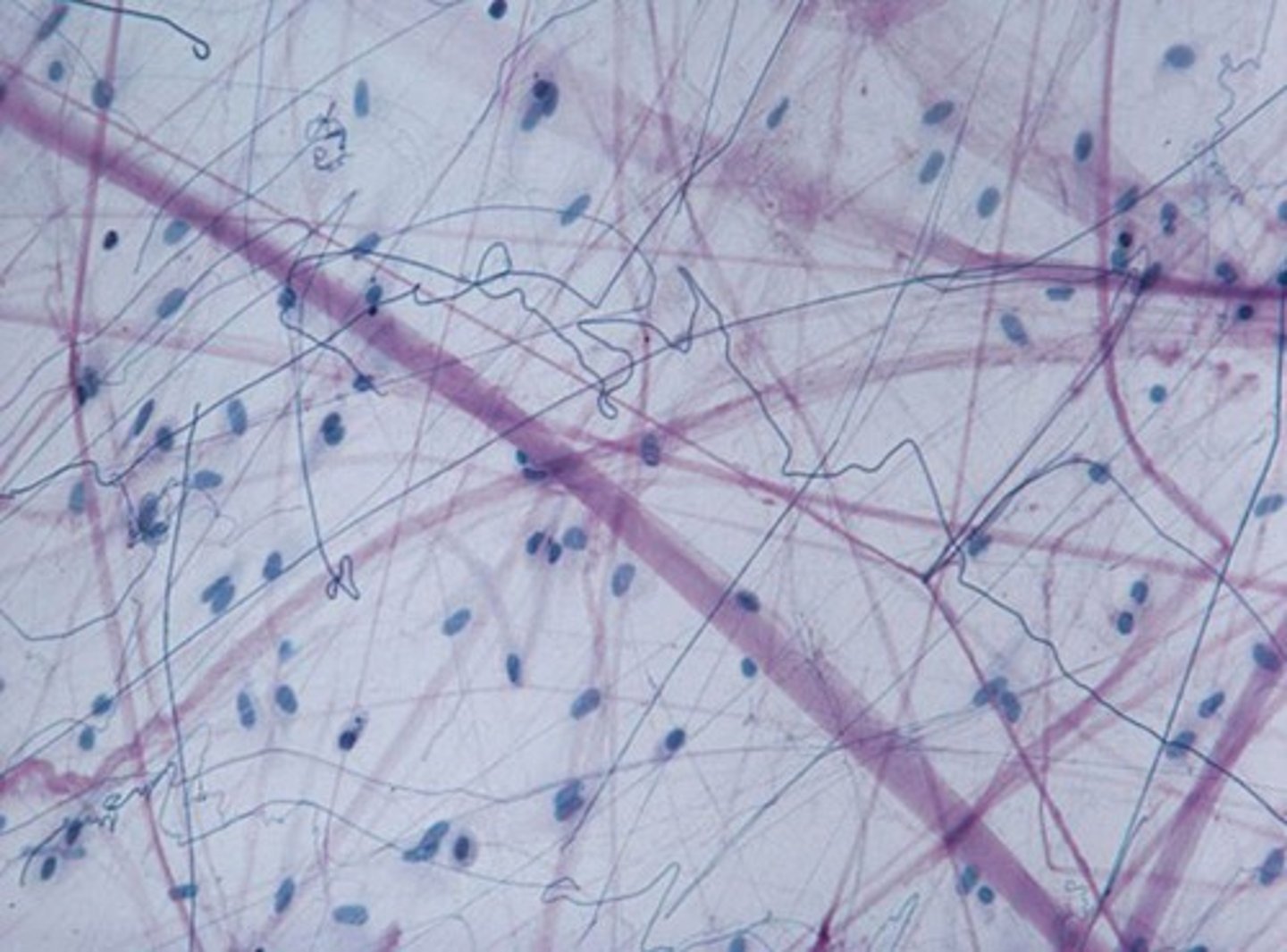
reticular connective tissue
Function: Fibers form a soft internal skeleton (stroma) that supports other cell types, including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages.
Location: Lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen).
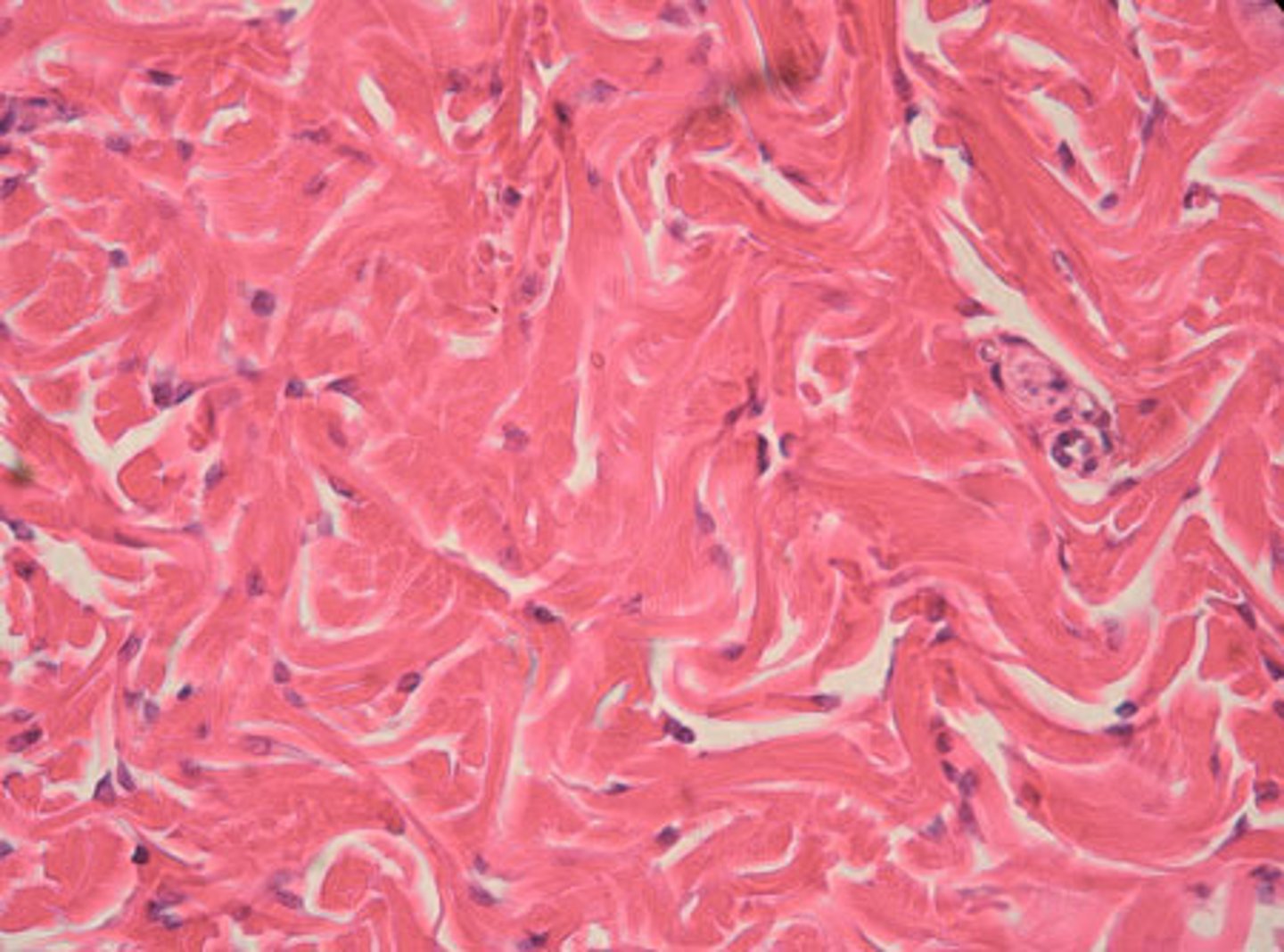
dense regular connective tissue
Function: attaches muscles to bones or to muscles; attaches bones to bones; withstands great tensile stress when pulling force is applied in one direction
Location: tendons, most ligaments, aponeuroses

dense irregular connective tissue
Function: able to withstand tension exerted in many directions; provides structural strength
Location: fibrous capsules of organs and joints; dermis of the skin; submucosa of digestive tract
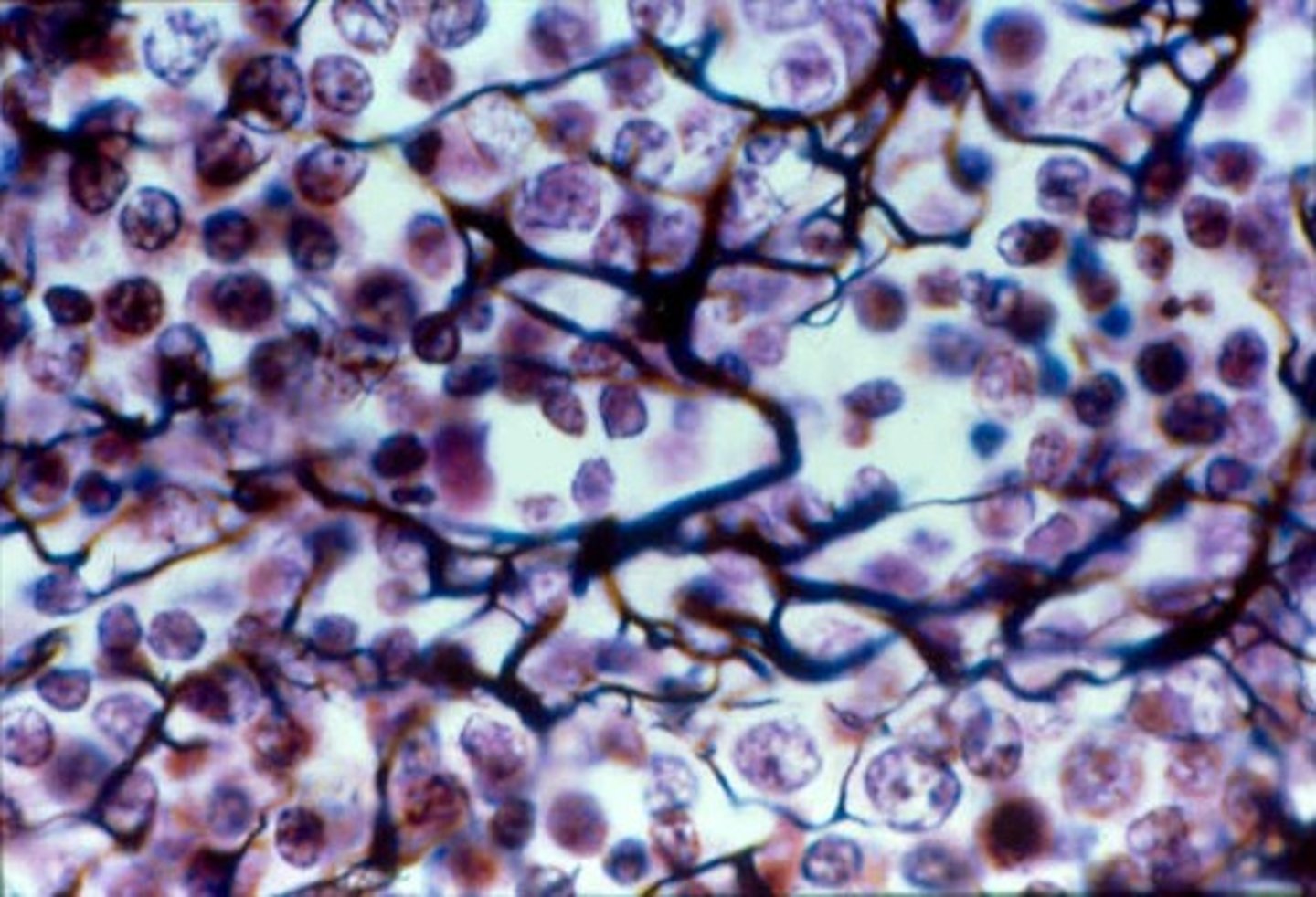
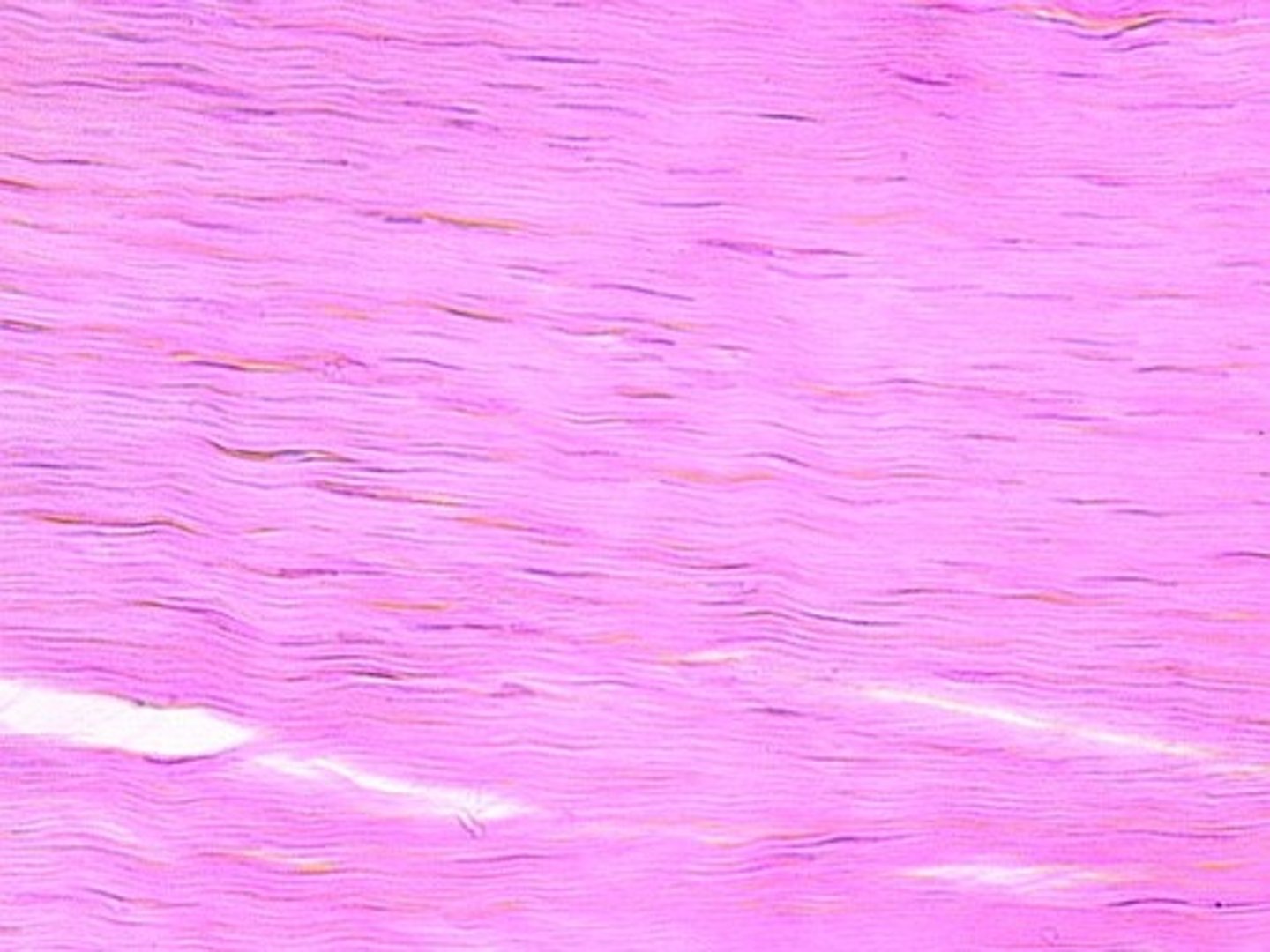
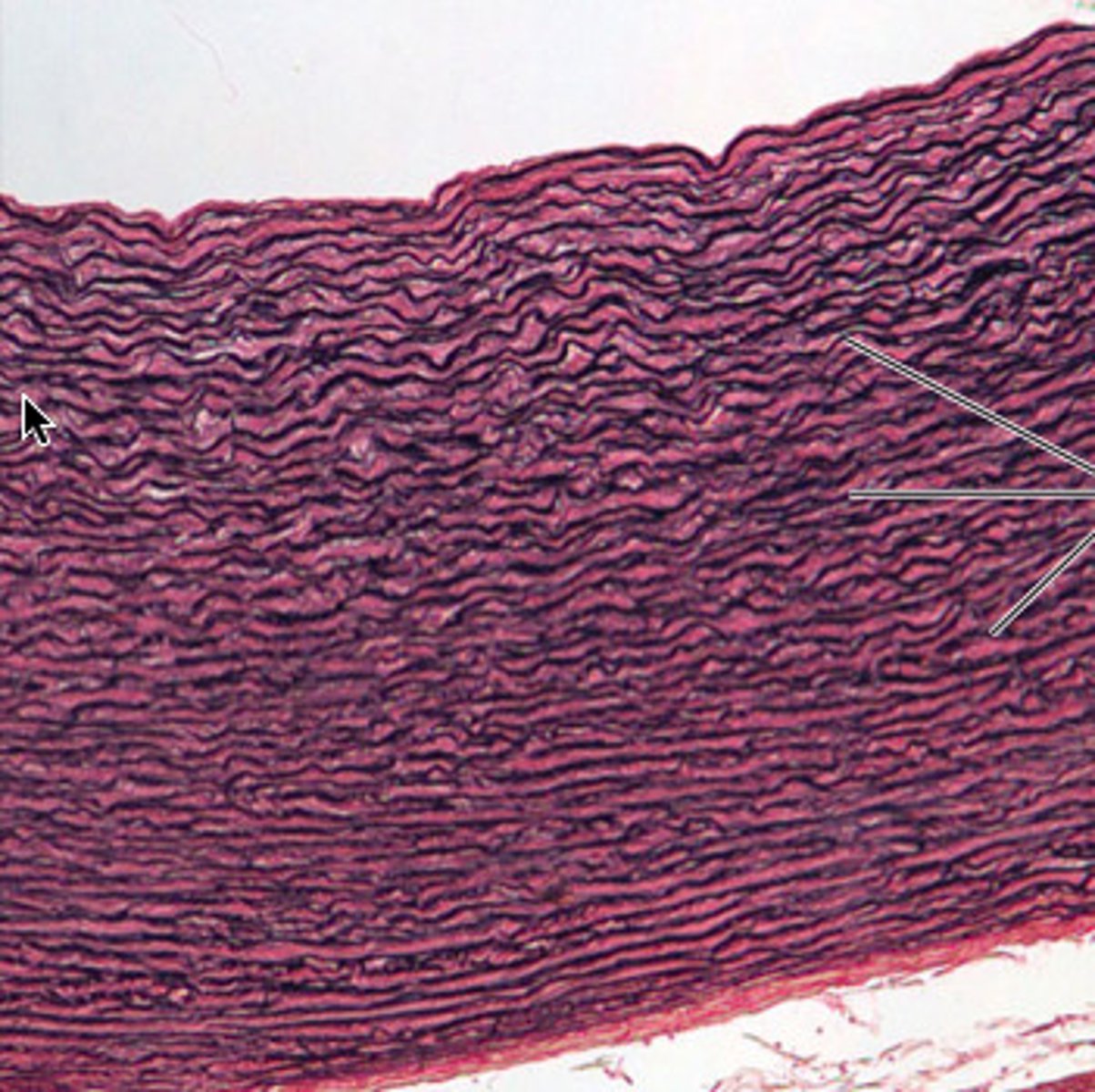
elastic connective tissue
Function: allows recoil of tissue following stretching; maintains pulsatile flow of blood through arteries; aids passive recoil of lungs following inspiration
Location: walls of large arteries; within certain ligaments associated with vertebral column, within the walls of the bronchial tubes
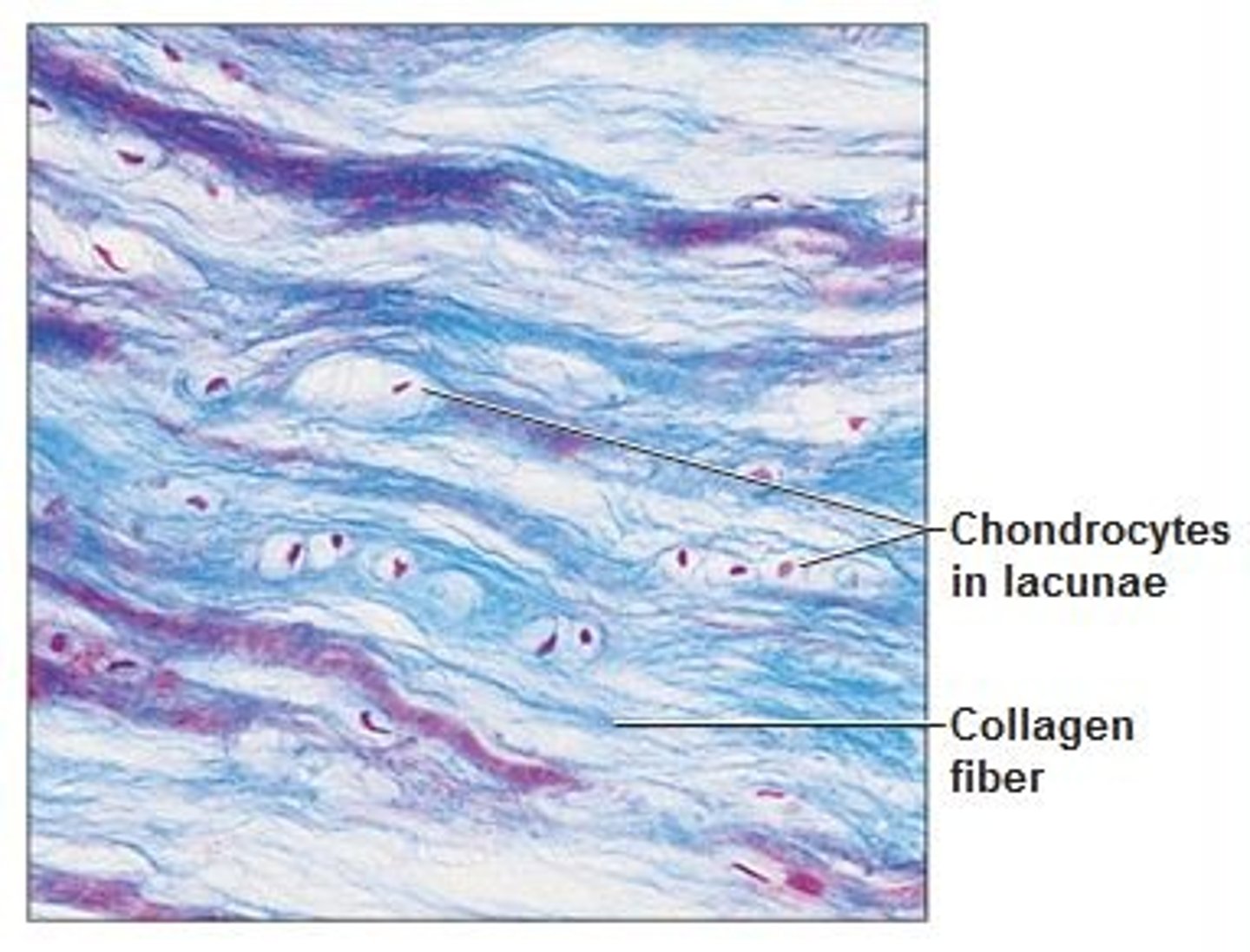
hyaline cartilage
Function: supports and reinforces; has resilient cushioning properties; resists compressive stress
Location: forms most of the embryonic skeleton; covers the ends of long bones in joint cavities; forms the costal cartilages of the ribs, cartilages of the nose, trachea, and larynx.
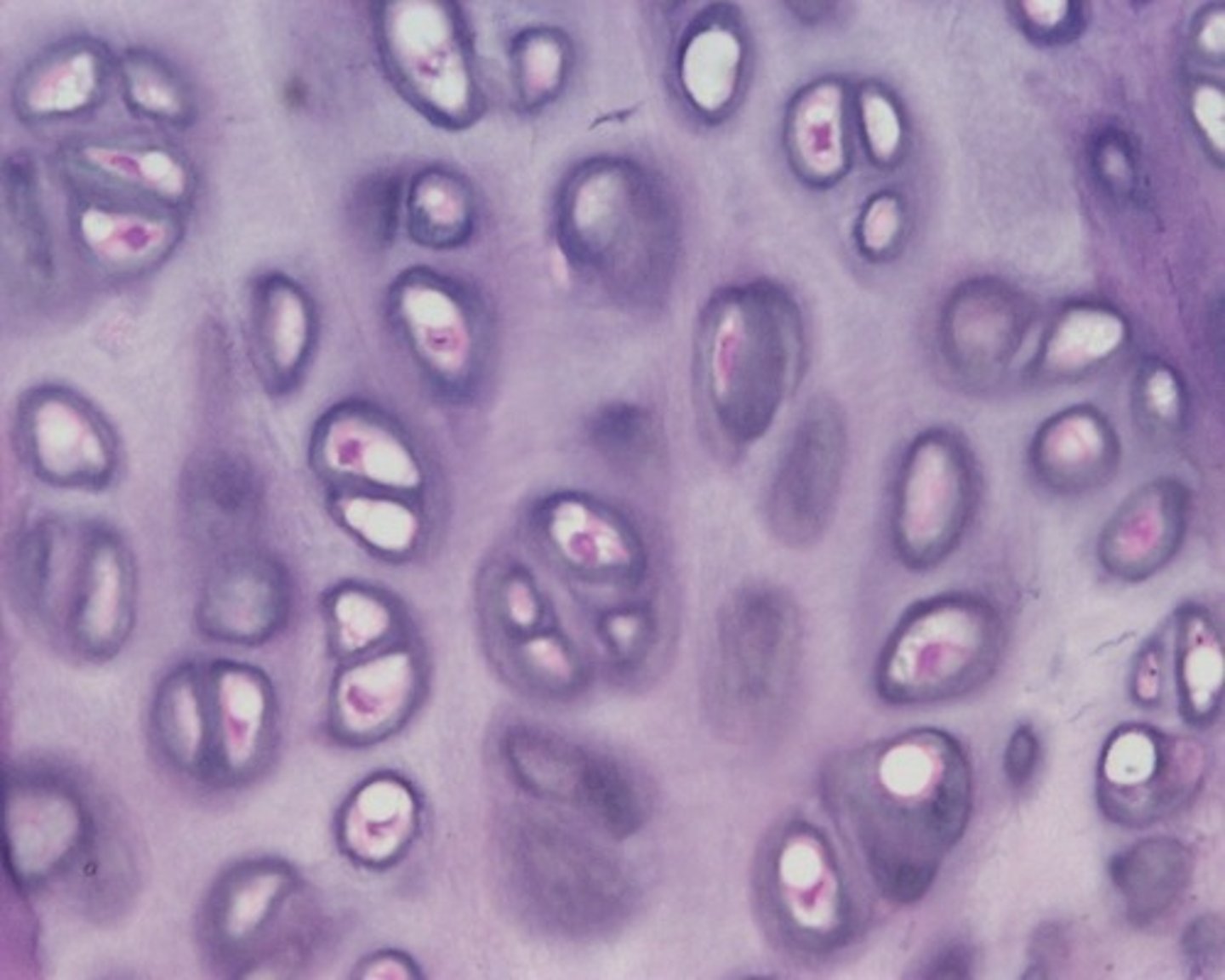
elastic cartilage
function: maintains the shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility
location: supports the external ear; epiglottis
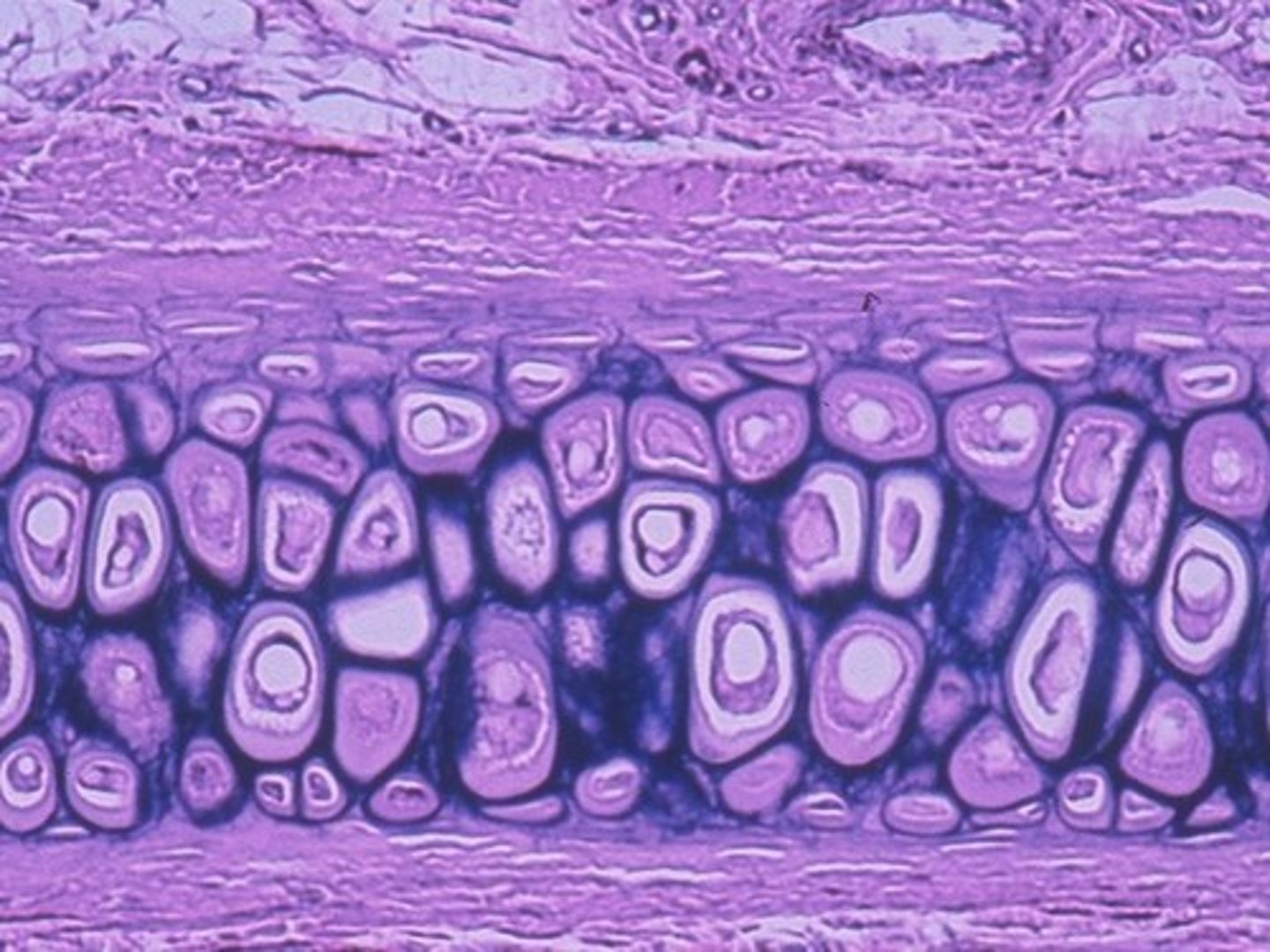
fibrocartilage
Function: Tensile Strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock
Location: Intervertebral discs; pubic symphysis; discs of knee joint
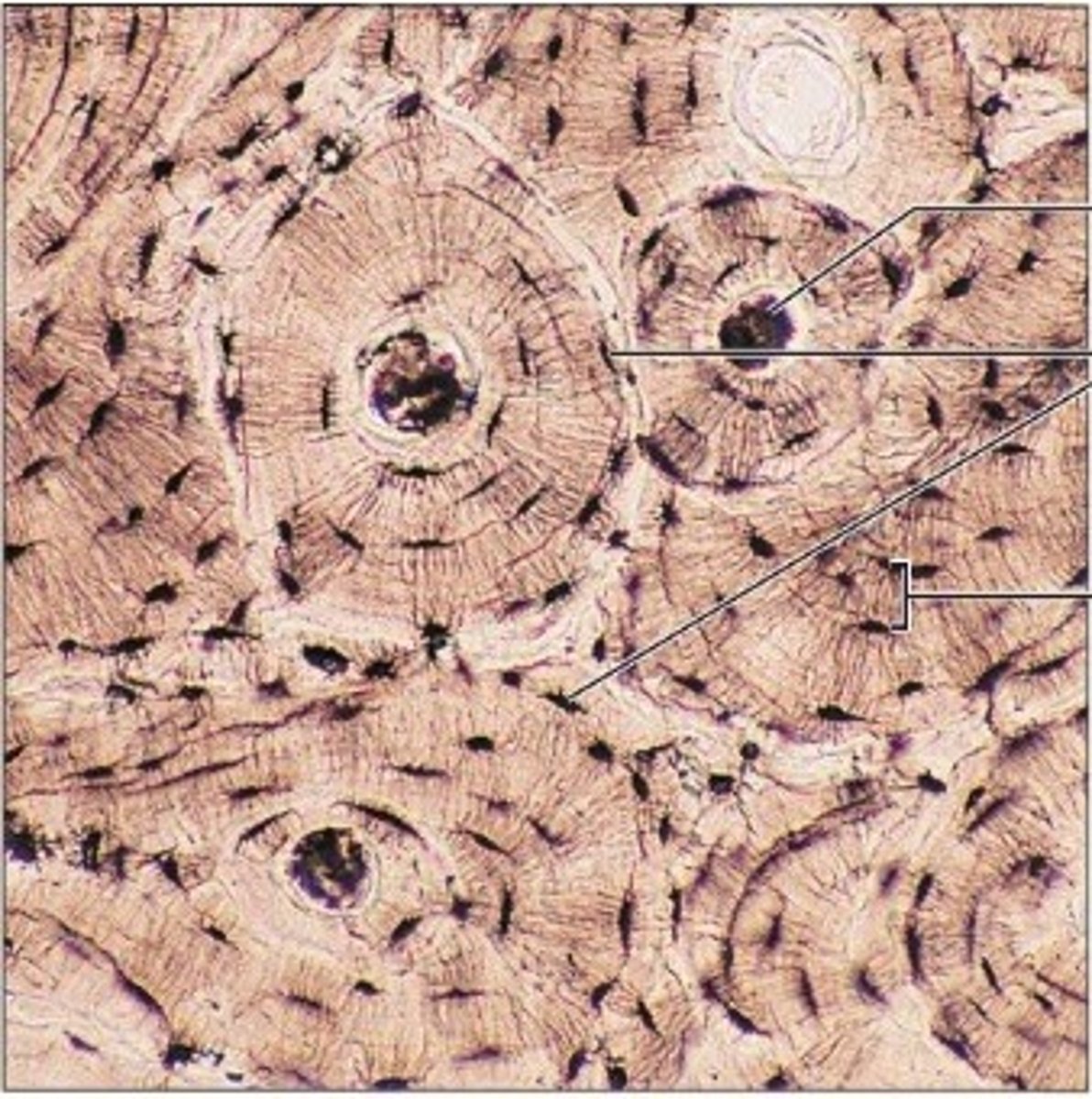
bones (osseous tissue)
Function: bone supports and protects (by enclosing); provides levers for the muscles to act on; stores calcium and other minerals and fat; marrow inside bones is site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis)
Location: Bones
bones (osseous tissue)
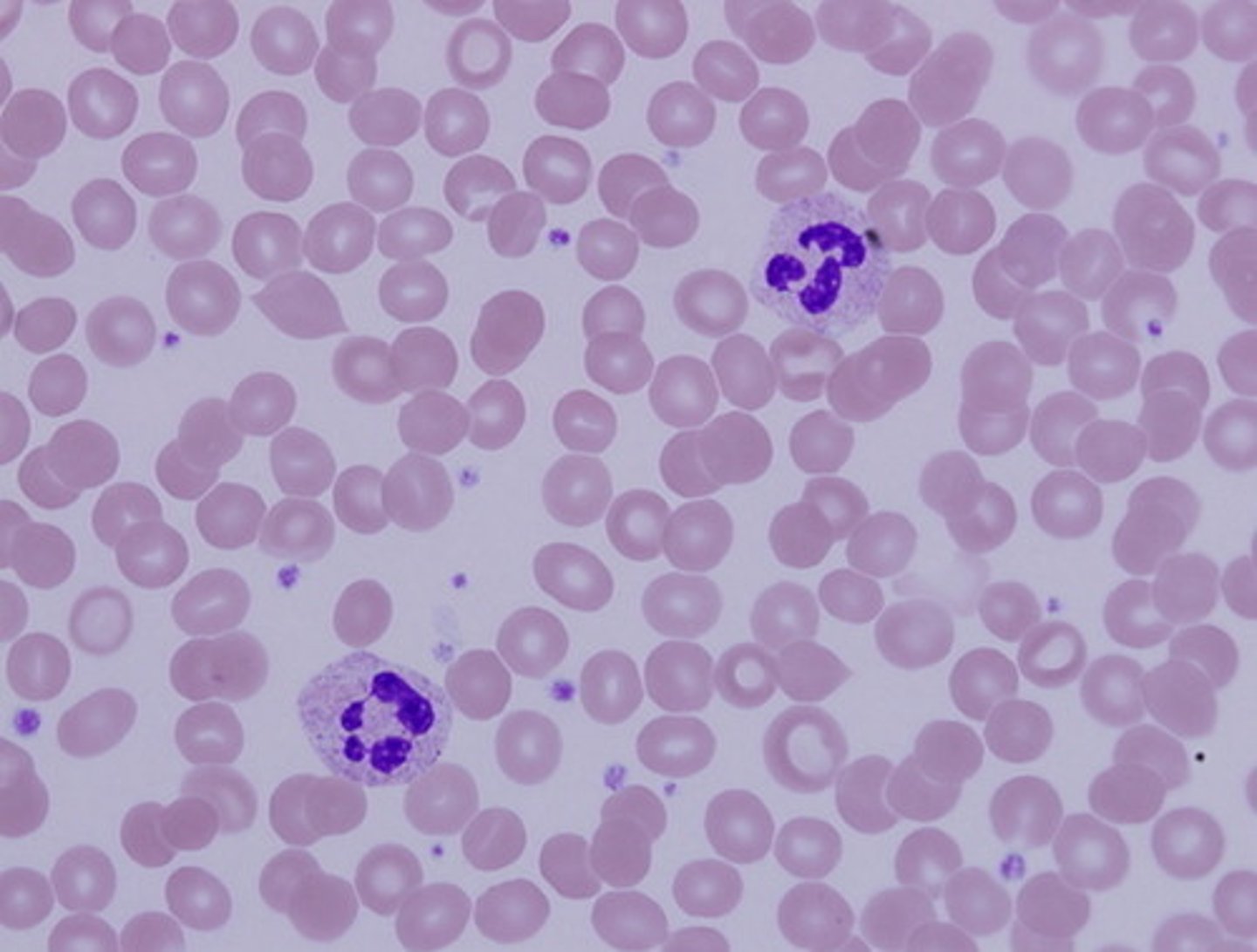
blood
Function: transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes, and other substances
Location: contained within blood vessels
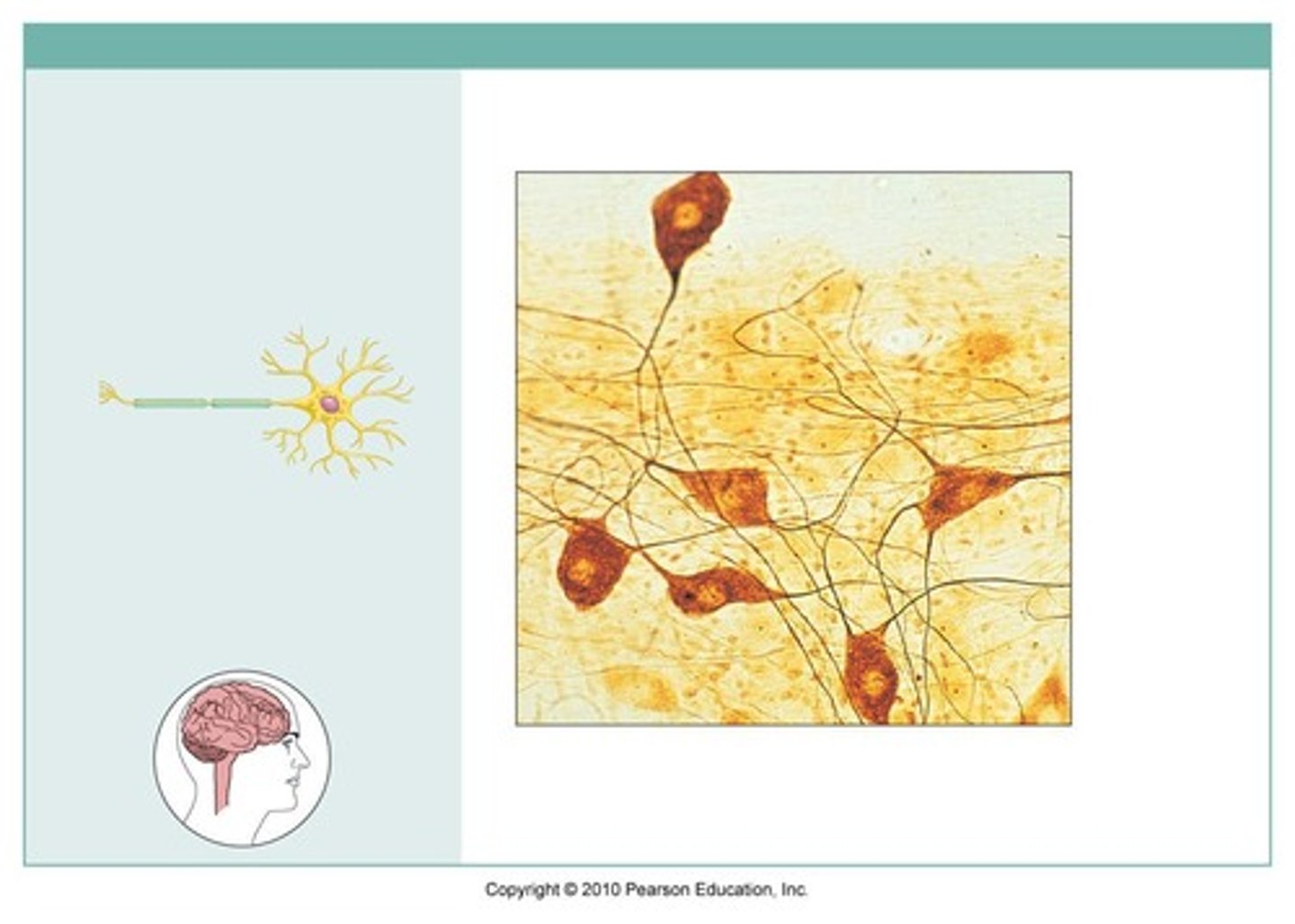
nervous tissue
function: neurons transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effects; supporting cells support and protect neurons
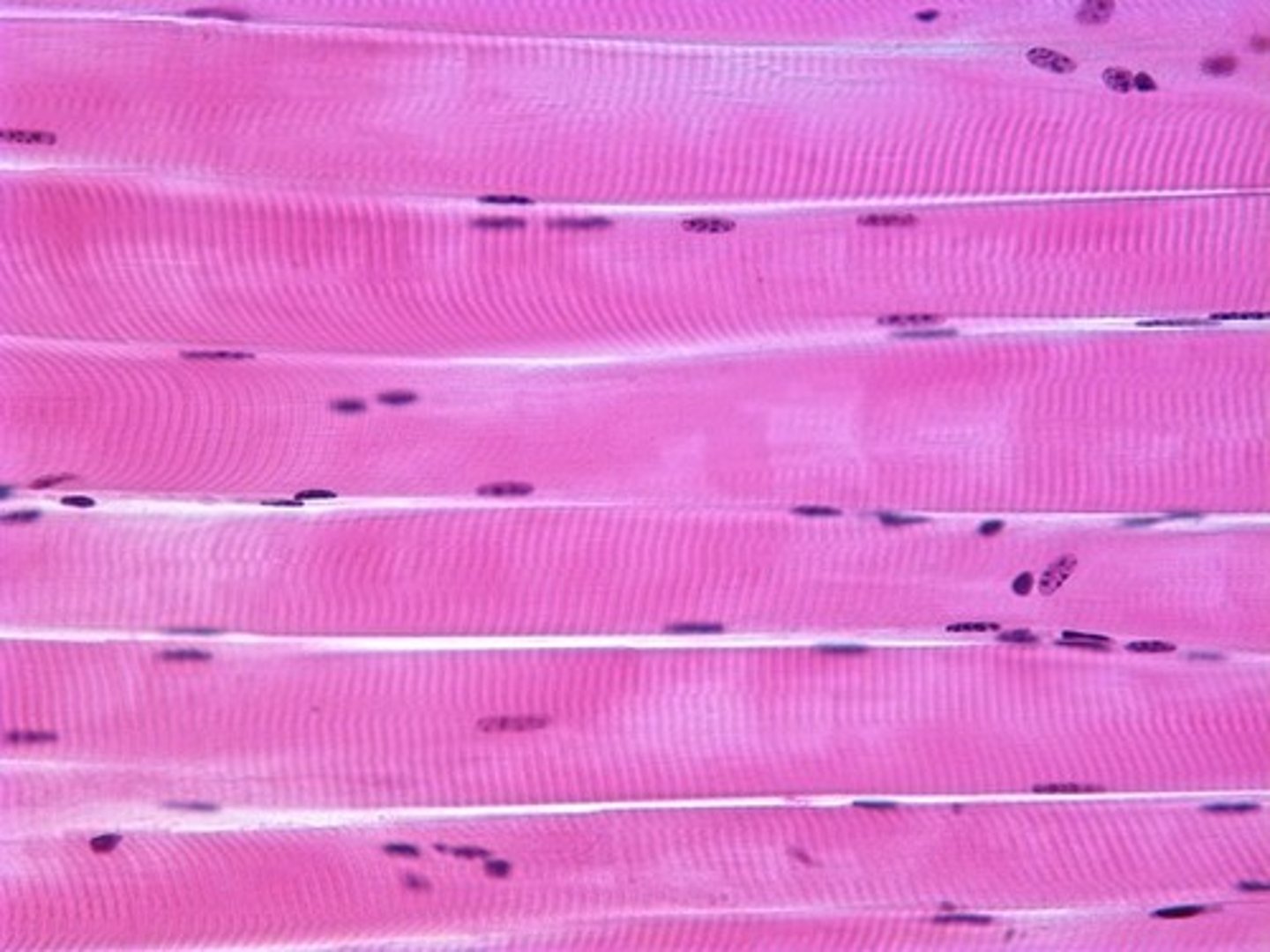
skeletal muscle
Function: Voluntary movement; locomotion; manipulation of the environment; facial expression; voluntary control.
Location: In skeletal muscles attached to bones or occasionally to skin.
cardiac muscle
Function: As it contracts, it propels blood into the circulation; involuntary control.
Location: The walls of the heart.

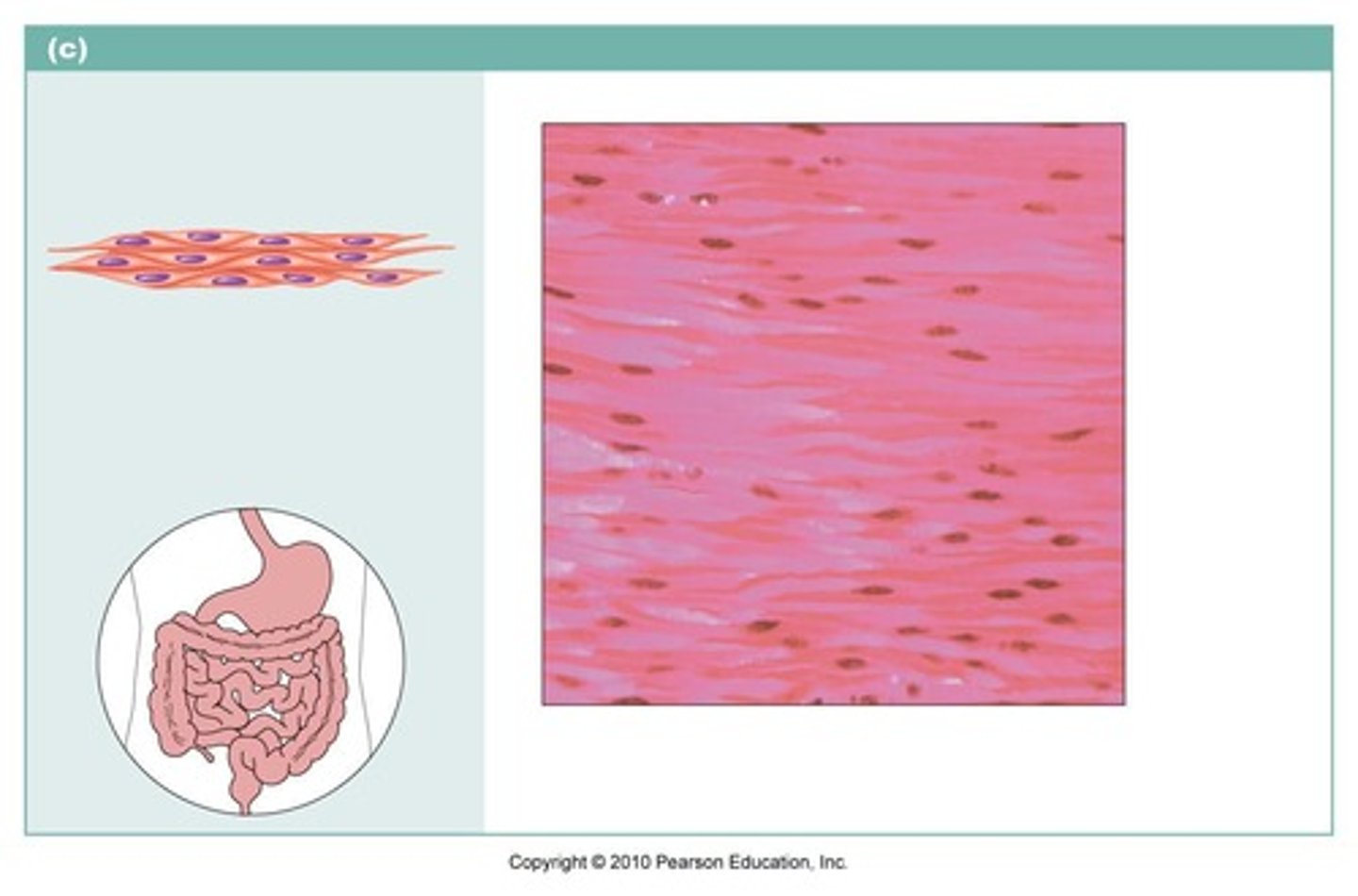
smooth muscle
function:propels substances or a baby along internal passageways; involuntary control.
location: mostly in the walls of hollow organs
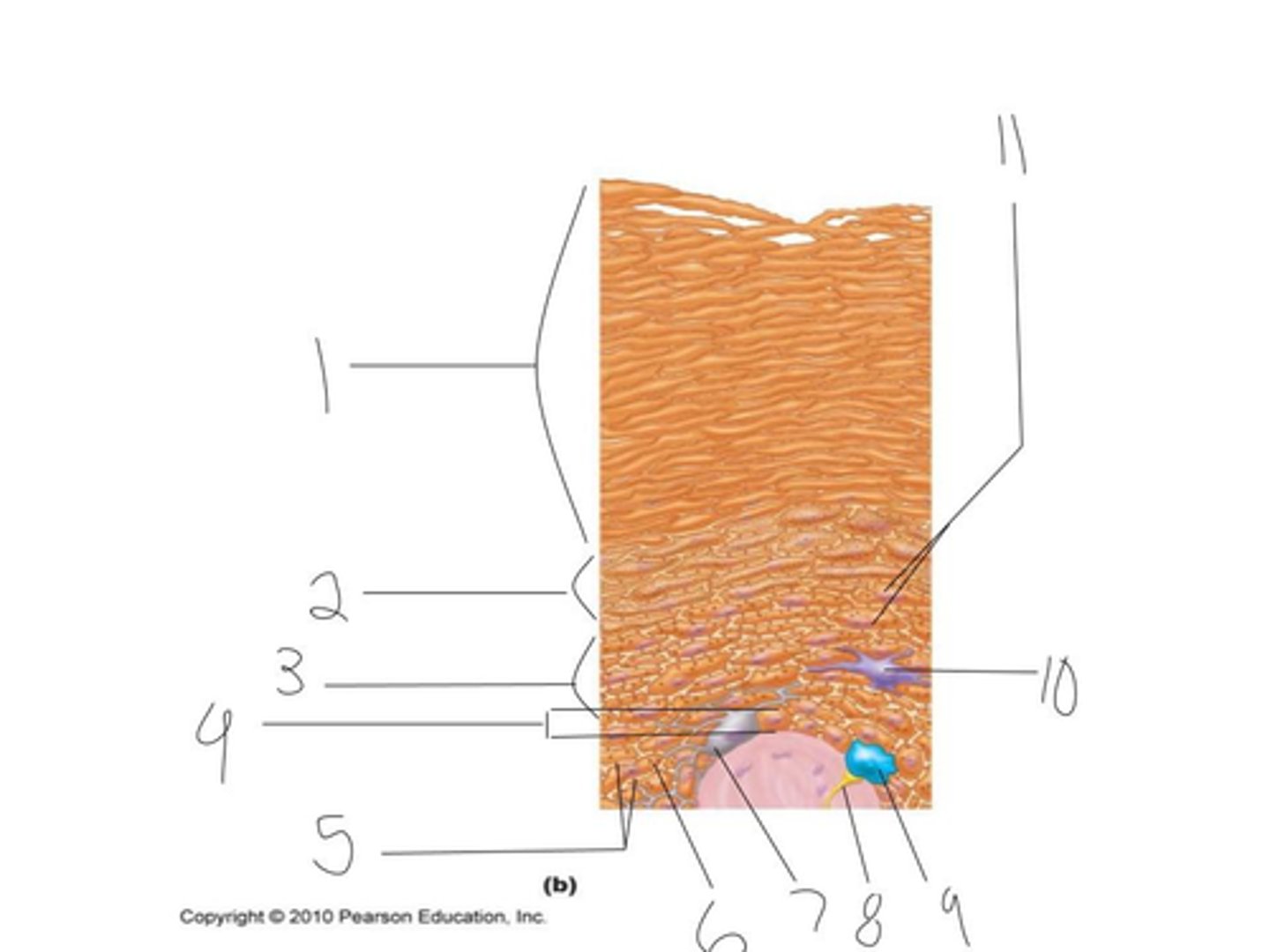
epidermis layers
stratum corneum, stratum lucidum, stratum granulosum, stratum spinosum, stratum basale

the outermost layer consisting of 20-30 layers of dead scalelike keratinocytes
stratum corneum
clear layer, present only in thick skin, a very thin transparent band of flattened dead keratinocytes
stratum lucidum
a thin layer named for abundant granules in the cell which are lamellar granules and keratohyaline granules
stratum granulosum
several layers of cells that contain thick, weblike bundles of intermediate filaments mad of pre-keratin protein. cells appear spiky
stratum spinsoum (spiny layer)
a sing row of cells immediately above the dermis that are constantly undergoing mitosis to form new cells
stratum basale
papillary dermis and reticular dermis
dermis layers
the most superficial dermal region composed of areolar connective tissue. Has dermal papillae which are fingerlike protections from its superior surface. produce fingerprints
papillary dermis
the deepest skin layer that is composed of dense irregular connective tissue and contains arteries and veins and pressure receptors knows as lamellar corpuscles
reticular dermis
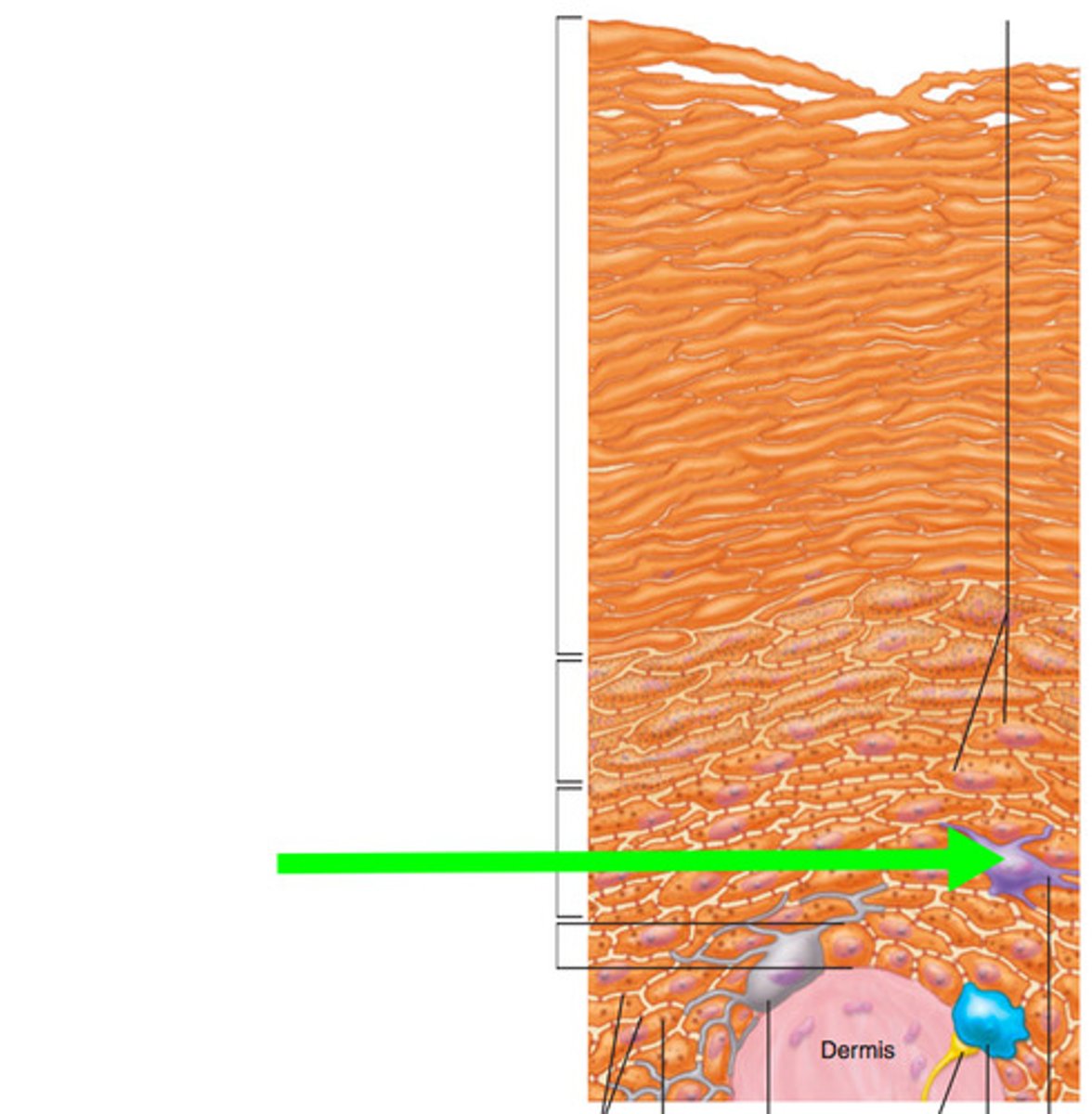
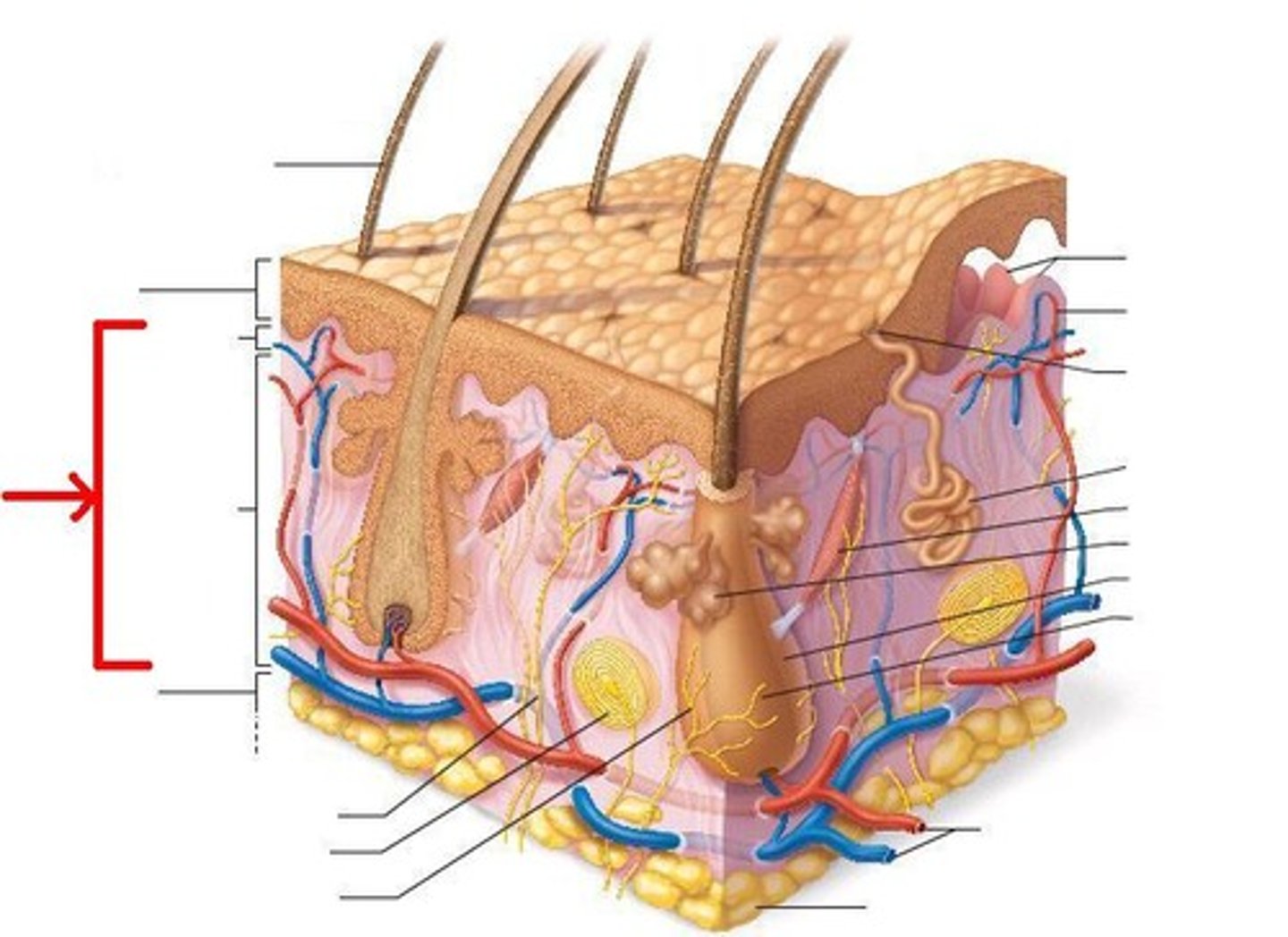
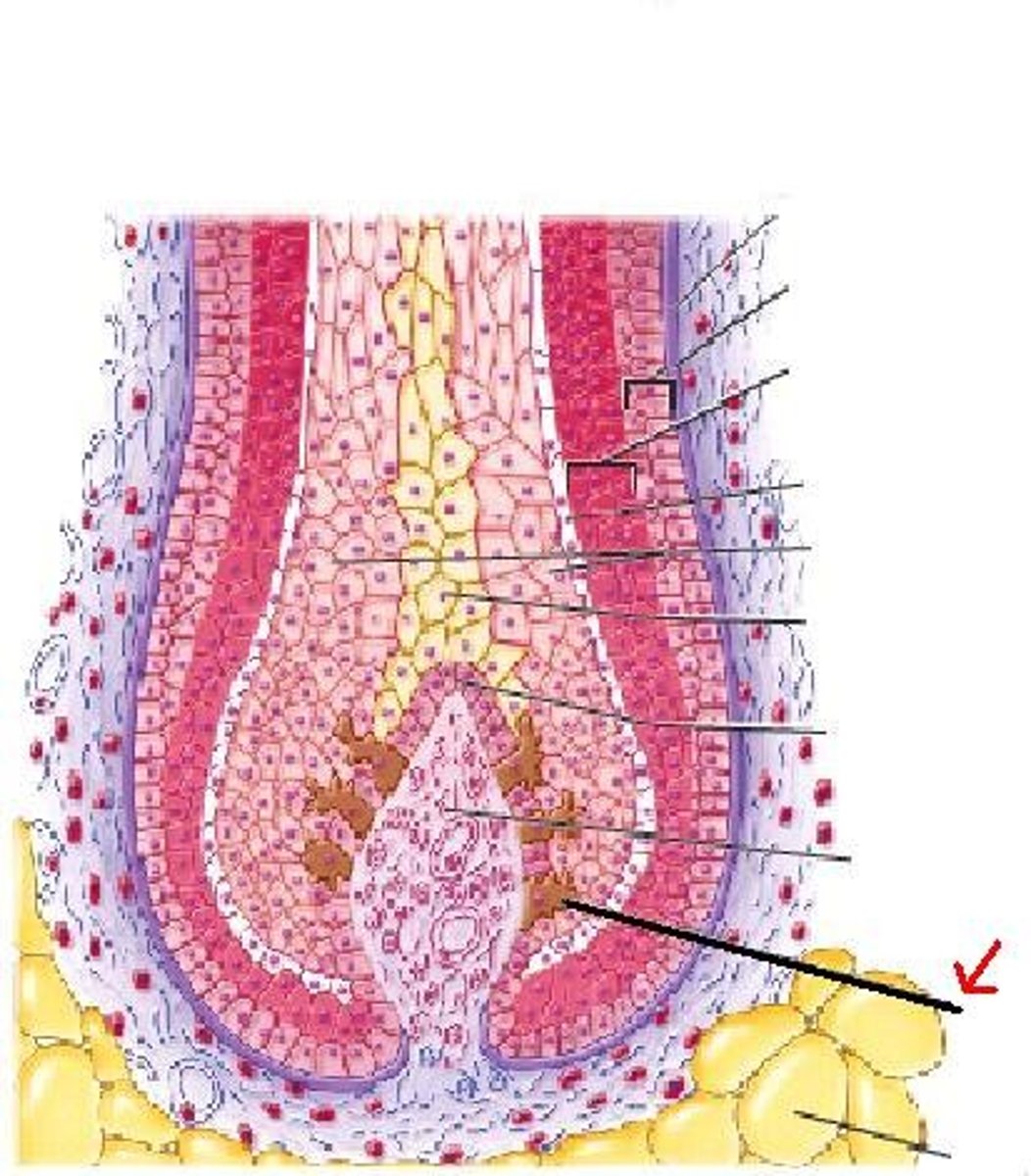
dermis
left side: hair shaft, epidermis, papillary layer, reticular layer, subcutaneous layer, sensory nerve fiber with free nerve endings, lamellar corpuscle, hair follicle receptor
right side: dermal papillae, subpapillary vascular plexus, sweat pore, eccrine sweat gland, arrestor pili muscle, sebaceous gland, hair follicle, hair root
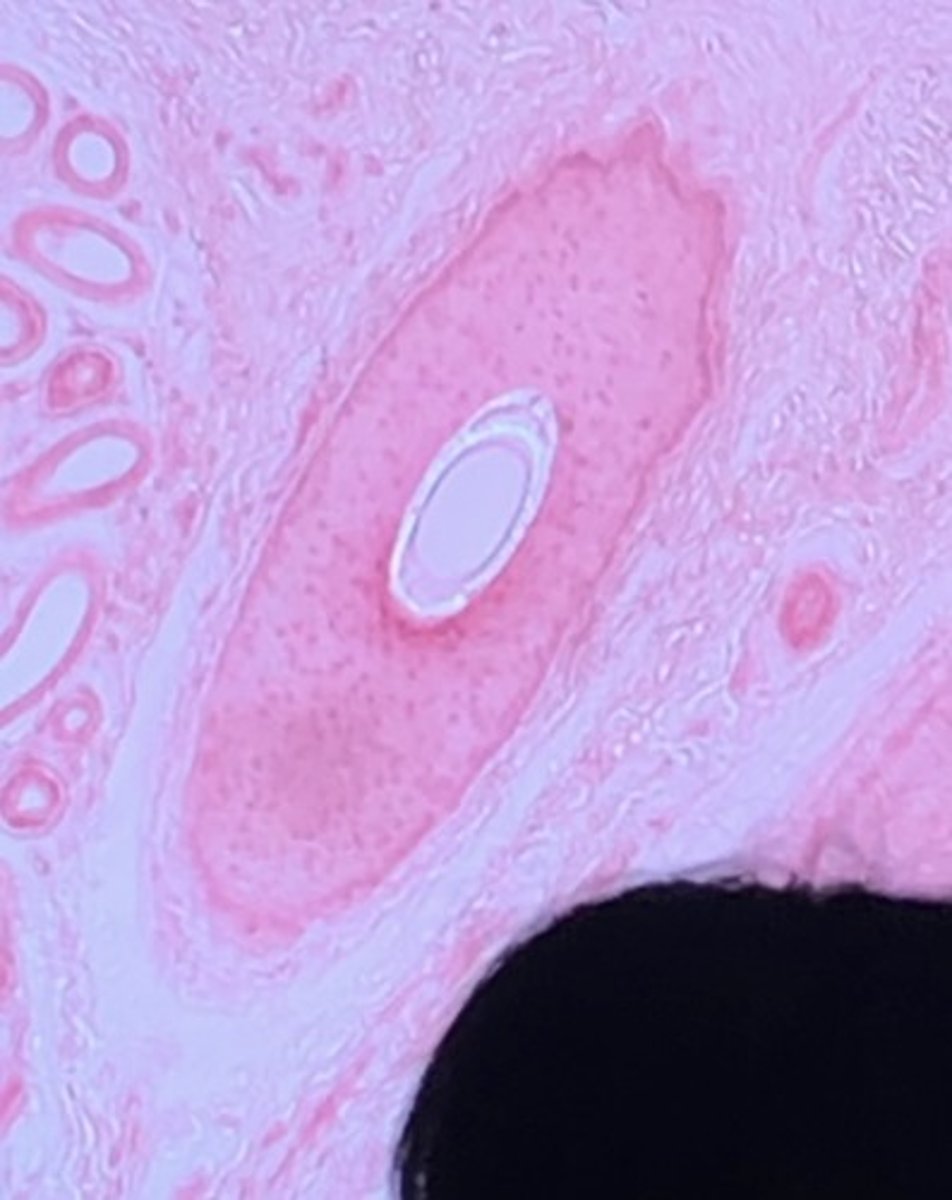
meissner's corpuscle
hair follicle
melanocyte
tactile epithelial cell
9.
dendritic cell