Price determination in a competitive market
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
Demand definition
The quantity of a good or service that a consumer is willing and able to buy at a given price at a point of time
Determinants of demand
Changes in the price of substitute goods
Changes in the price of complement good
Personal disposable income
Tastes and preferences
Population Size
Advertising
Supply definition
The quantity of a good or service that producers are willing and able to sell, at a given price, over a given period of time
Laws of Supply
'As the price of a product rises, the quantity supplied of the product will usually increase, ceteris paribus'
Supply slopes upwards -> Firms have profit max objective
Assume firms don't change size, cost of producing extra units of the good generally increases as firms produce more of the good
Supplier initially uses most efficient FOPs first, meaning first units sold cheaper however higher quantity means less efficient resources are employed which means his cost for the extra units go up and he needs a higher price for a larger quantity
Determinants of supply
Improvements in technology
Changes in the cost of productions e.g. wages or raw materials
Taxes imposed on firms e.g. VAT
Subsidies
Firms entering/leaving the market
Equilibrium Price
Price at which the quantity demanded is equal to the quantity supplied. Also known as the market-clearing price
Consumer Surplus definition
The difference between how much buyers are willing to pay for the good and for what they actually pay. It is the area above the market price and bordered by the demand curve and the price axis.
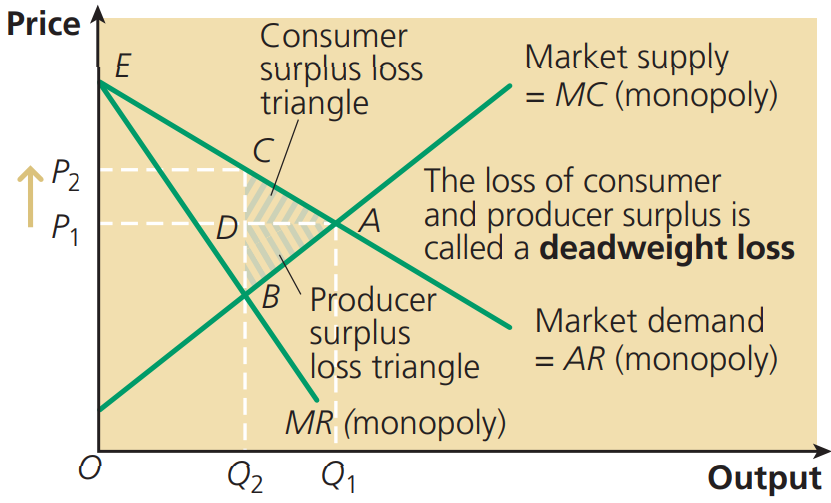
Producer Surplus
The difference between the price a firm succeeds in charging and the minimum price it would be willing to accept
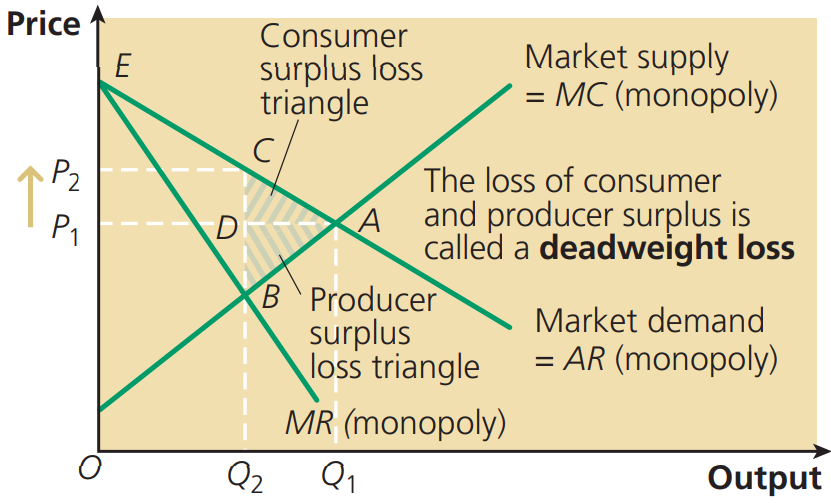
Elasticity definition
Measures the proportionate responsiveness of the second variable to the change in the first variable
Price Elasticity of Demand definition and formula
Measures the extent to which the demand for a good changes in response to a change in the price of that good. PED = %Change in q.d/ %Change in price
Factors affecting PED
Luxury or necessity
Availability of substitutes
The 'width' of the market definition
Proportion of income spent on the good
Time period
What does it mean when PED > 1?
Elastic meaning that when the price of a product increases/decreases, the quantity demanded changes significantly in the opposite direction
What does it mean when PED < 0?
Inelastic meaning that quantity demanded changes only slightly in response to a change in price
What does it mean when PED = 1?
Unitary meaning that %change in q.d. is exactly equal to %change in price
What does it mean when PED = ∞?
Perfectly elastic meaning that q.d. is infinetly responsive to any changes in price where the slighest increase in price results in q.d. dropping to 0 and any decrease leads to an infinitely large q.d.
What does it mean when PED = 0?
Perfectly inelastic meaning q.d. does not repsond at all to changes in price
Income Elasticity of Demand (YED) definition and formula
Measures how much demand for a product changes in response to a change in consumers' income. YED = % Change in q.d / % Change in income
What does it mean YED is between -1 and +1
Income inelastic (demand changes less than proportionately to income changes - demand still rises with income, but only a little)
What does it mean when YED is less than -1 or greater than +1?
Income elastic (demand changes more than proportionately to income changes - as income ↑, demand rises more significantly)
What does it mean when YED > 0?
Normal good
What does it mean when YED < 0?
Inferior good
What does it mean when YED > 1?
Luxury good
Price Elasticity of supply definition and formula
Measures the responsiveness of supply to changes in price. PES = % Change in q.s. / % Change in price
Factors affecting PES
Spare capacity - The ease of switching between alternative methods of production
Availability of FOPs (State of economy e.g. recession or boom)
Stockpiles and Perishability
Time Period
The number of firms in the market and the ease of entering the market
What does it mean when PES < 1?
Inelastic meaning that producers are not very responsive to changes in price
A significant increase/decrease in price leads to only a small change in quantity supplied
What does it mean when PES > 1?
Elastic meaning that producers can significantly increase/decrease the quantity they supply in repsonse to a change in price
Small ↑ in price leads to a relatively large increase in q.s. same as as small ↓ in price
What does it mean when PES = 1?
Unitary where %change in q.s. is exactly equal to the %change in price
What does it mean when PES = 0?
Perfectly inelastic supply meaning that the q.s. remains constant regardless of any change in price
What does it mean when PES = ∞?
Perfectly elastic means that producers can respond instantly and infinitely to any change in price
Cross Elasticity of Demand (XED) definition and formula
Measures how much demand for a product changes in response to a change in price of another good. XED = % Change in q.d. of good X / % Change in price of good Y
What does it mean when XED is between -1 and +1?
Cross inelastic
What does it mean if XED is less than -1 or greater than +1?
Cross elastic
What does it mean if XED is positive?
Substitute goods - the closer the substitute, the higher the value
What does it mean if XED is negative?
Complement goods - the stronger the complement, the lower tha value
What does it mean if XED = 0?
Unrelated goods
Complement Goods definition
When goods are in joint demand. When a consumer demands one good they are likely to demand the other e.g. printers and ink cartridges
Substitute Good definition
Alternative goods that can be used for the same purpose. e.g. PS4 & XBOX
Derived Demand definition
When demand for one good (often labour market) is as a result of demand for another good e.g. production of cars, leads to demand for factory workers
Composite Demand definition
When a good is demanded for two or more distinct uses e.g. milk for cheese or butter
Competing Supply definition
When raw materials are used to produce one good they cannot be used to produce another good e.g. wheat for flour or for biofuel
Joint Supply definition
When two or more goods are produced together e.g. beef and leather
What is a contraction in demand?
When a rise in price leads to less being demanded
What is an extension of demand?
When a fall in price results in more of the good being demanded