Fuels and Heats of Reaction (Theory)
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
Organic Chemistry (definition)
Study of the compounds of carbon
Hydrocarbons (definition)
Compounds that contain carbon and hydrogen only
Fossil Fuels (definition)
Fuels that were formed from the remains of dead plants and animals that lived millions of years ago
Homologous series (definition)
Series of compounds with similar chemical properties, a general chemical formula and with each successive member differing by CH2
What kind of compounds are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons
What kind of geometry do alkanes have?
Tetrahedral geometry
Saturated compound (definition)
A compound in which there are only single bonds between its atoms
IUPAC name of CH4
Methane
IUPAC name of C2H6
Ethane
IUPAC name of C3H8
Propane
IUPAC name of C4H10
Butane
IUPAC name of C5H12
Pentane
IUPAC name of C6H14
Hexane
IUPAC name of C7H16
Heptane
IUPAC name of C8H18
Octane
IUPAC name of C9H20
Nonane
IUPAC name of C10H22
Decane
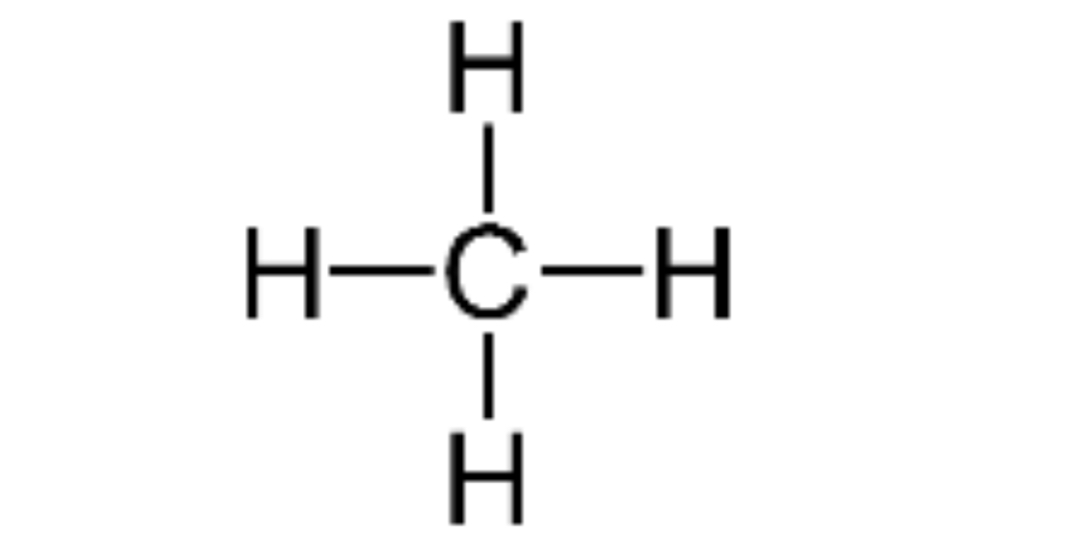
Draw methane structural formula
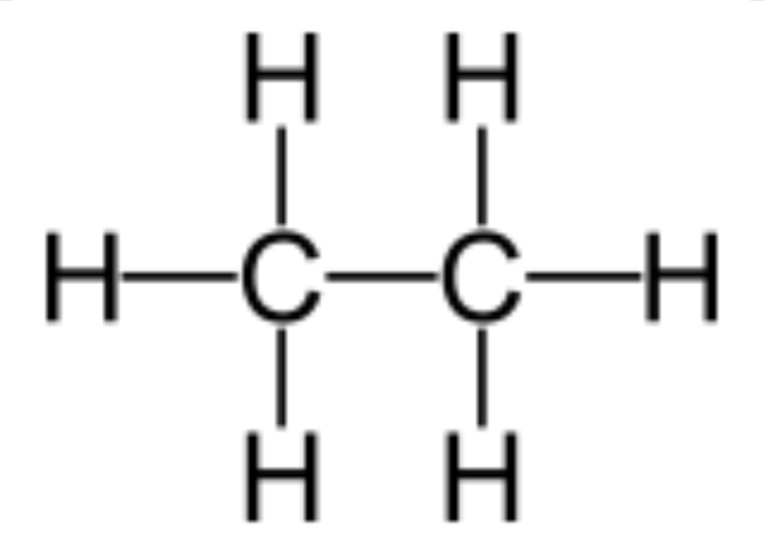
Draw ethane structural formula
What is the general formula of the alkanes?
CnH2n+2
What solvents are alkanes soluble in?
Non-polar substances e.g. cyclohexane
Why are alkanes insoluble in water?
Non-polar. Only have Van-der-Walls forces between molecules.
C1-C4 are …
Gases
C5-C16 are …
Liquids
C17 and above are …
Waxy solids
Alkanes (boiling points)
Larger molecules have stronger Van-der-Waals forces, increasing their boiling and melting points
Structural isomers (definition)
Compounds that have the same molecular formulae but different structural formulae.
Steps 1 for naming alkanes
Identify longest carbon chain, name the parent molecule
Steps 2 for naming alkanes
Number the carbon chain starting from the end that gives the branches the lowest possible numbers.
CH3 is called what when branching off of a compound?
Methyl
C2H5 is called what when branching off of a compound?
Ethyl
What kind of geometry do alkenes have?
Planar
What kind of compounds are alkenes?
Unsaturated hydrocarbons
Unsaturated compound (definition)
A compound which contains one or more double or triple bonds between its atoms.
IUPAC name for C2H4
Ethene
IUPAC name for C3H6
Propene
IUPAC name for C4H8 if the double bond is between the first and second carbon
But-1-ene
IUPAC name for C4H8 if the double bond is between the second and third carbon
But-2-ene
General formula of alkenes
CnH2n
Are alkenes polar or non-polar and give an example of a solvent?
Non-polar. E.g. cyclohexane
Why are alkenes non-polar?
Large molecules have stronger Van der Waals forces, increasing boiling and melting points
Step 1 for naming alkenes
Identify longest parent carbon chain
Step 2 for naming alkenes
Number the carbons in the molecule starting at the side closest to the double bond. Put position of double bond into name e.g. hex-2-ene
Step 3 for naming alkenes
Indicate type and positions of branching
What is a cyclic hydrocarbon?
When a hydrocarbon’s longest chain of carbon atoms forms a closed ring.
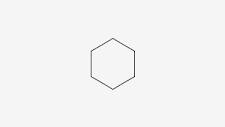
Each point is …
A carbon
Features of cyclohexane
Six carbon atoms, singly bonded in a closed ring.
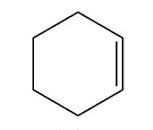
Features of cyclohexene
Six carbon atoms, with a double carbon bond in a closed ring. The double line represents the double bond
What kind of hydrocarbons are alkynes?
Unsaturated
What kind of bonds do alkynes have?
Triple bonds
What kind of geometry do alkynes have?
Planar geometry
What is the IUPAC name of C2H2 (alkyne)
Ethyne (acetylene)
General formula of alkynes
CnH2n-2
Ethyne and oxygen burn at a very … temperature
High
What compound is ethyne used in and what’s the compound used for?
Oxyacetylene. Welding and cutting metal
What kind of solubles are alkynes soluble in?
Non-polar e.g. cyclohexane
Why are alkynes non-polar?
They only have Van der Waals for es between molecules
Aromatic compounds (definition)
Compounds which contain a benzene ring
Aliphatic compounds (definition)
Open chains and closed chains with no benzene ring
Which is longer, double bonds or single bonds?
Double bonds
Are the bonds in benzene different sizes?
No
Why is there a benzene ring?
Electrons get tossed from carbon to carbon
Examples of aromatic compounds
Benzene, methylbenzene, ethylbenzene
Fractional Distillation (definition)
Used to separate different hydrocarbons into fractions, based on their boiling points
Draw a diagram of fractional distillation/ oil refining
…
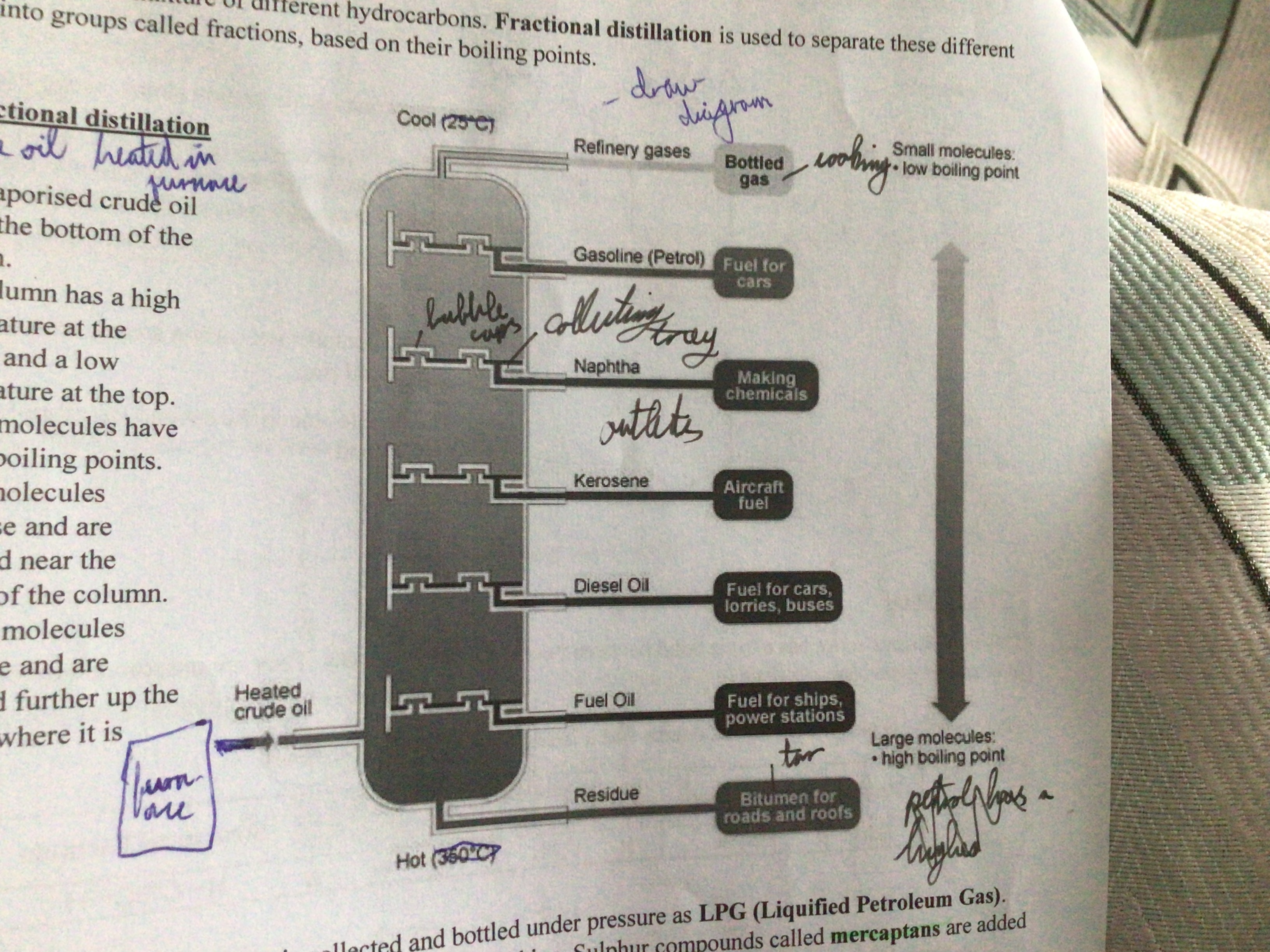
Explain fractional distillation
Crude oil heated in furnace and enters bottom of column. High temperature at bottom, low temperature at top. Larger molecules have higher boiling points. Large molecules condense and are collected near the bottom. Smaller molecules condense condense further up the column where it’s cooler.
What does LPG stand for?
Liquified Petroleum Gas
What does LPG consist of and which fraction is it collected in?
Propane and butane. Collected in refinery gases fraction
What is added to LPG?
Mercaptans
What are mercaptans and what are they used for?
Sulphur compounds which give LPG a scent
Where is natural gas found?
Porous rock underground
What does natural gas consist of and what is added to it?
Methane and ethane. Mercaptans are added for odour
Octane number (definition)
Of a fuel is a measure of its tendency to resist autoignition
Different terms for autoignition (2)
Knocking/ pinking
Autoignition (definition)
The premature ignition of a fuel-air mixture
What does a fuel with a low octane number cause?
Causes wear on the engine. Loss of power
What hydrocarbon has the lowest/ worst octane number?
Heptane
What hydrocarbon has the highest/ best octane number?
2,2,4-trimethylpentane
What does “Octane 95” mean on a fuel pump?
The fuel has the same tendency to auto ignite as a mixture of 95% 2,2,4-trimethylpentane and 5% heptane
Three factors that affect octane number
Length of chain, degree of branching, presence of rings
How does chain length affect the octane number?
Shorter carbon chains have higher octane numbers
How does degree of branching affect octane number?
The more branching a hydrocarbon has, the higher the octane number
How does the presence of rings affect octane number?
Ring structures give fuels higher octane numbers. Benzene rings have even higher octane numbers
Name the processes which raise the octane number of a fuel (5)
Isomerisation. Catalytic cracking. Dehydrocyclisation. Adding oxygenates. Addition of lead
What is isomerisation?
Changing straight chain alkanes into their branched isomers to raise octane number
What is catalytic cracking?
Uses heat and a catalyst to break down long hydrocarbons into an alkene and a shorter alkane since they have higher octane numbers
What is dehydrocyclisation?
Uses catalysts to change linear molecules into cyclic molecules or cyclic molecules into aromatic compounds. Hydrogen gas is formed
What is adding oxygenates?
The addition of oxygen-containing compounds to a fuel to raise its octane number
What is an extra benefit of adding oxygenates to fuels other than to raise octane numbers?
Makes fuel release less carbon dioxide when burnt
What is the addition of Lead
Adding lead compounds to petrol to increase octane number
Examples of oxygenates
Methanol. Ethanol. MTBE
What does MTBE stand for?
Methyl Tertiary-Butyl Ether
Name a lead compound
Tetraethyl lead
Why was lead banned in petrol?
It’s a poisonous health hazard. Poisons the metals in a car’s catalytic converter. That’s why petrol pumps say “Unleaded”
When was the addition of lead banned?
2000
What are the two ways to produce hydrogen gas for use as a fuel?
Steam reforming of natural gas. Electrolysis of water.
How does “steam reforming of natural gas” work?
Steam is reacted with natural gas using a catalyst
Steam reforming of natural gas (equation)
CH4 + H2O → 3H2 + CO
How does “Electrolysis of Water” work? What is its disadvantage?
Electric current is passed through water. This method is too expensive to be practical.
Electrolysis of Water (equation)
H2O → H2 + 1/2O2