Hardware
1/161
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
Rough Hardware
Hardware meant to be concealed.
Finish Hardware
Hardware that has finished appearance as well as a function. May be considered part of the decorative treatment of a room or building.
Rough Hardware
Bolts, nails, screws, spikes, and other metal fittings.
Finish Hardware
Hinges, locks, catches, etc.
Nails
Straight, slender pieces of metal having one end pointed and the other enlarged and flattened for hammering into wood or other building materials as a fastener.
Penny (d)
Term for nail lengths
2 ; 60
Nails range in length from ___d, about 1" (25) long, to ___d, about 6" (150) long.
three
Nail length should be about ______ times thickness of the material being secured.
Large Diameter Nails
these nails are used for heavy work
Lighter Nails
these nails are used for finished work
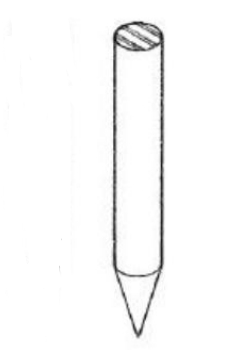
diamond-pointed nails
Most nails have this kind of point
sharp-pointed nails
These kind of nails have greater holding strength but may tend to split some woods
blunt-pointed nails
These kind of nails should be used for easily split woods
sharp-pointed nails
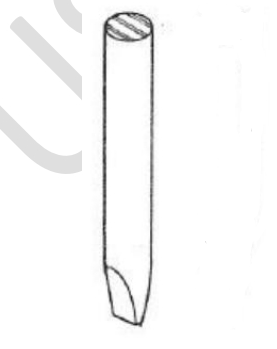
diamond-pointed nails
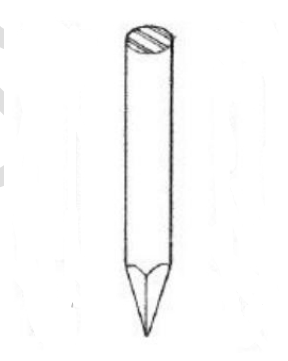
blunt-pointed nails
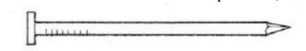
Common Nail
A cut or wire low-carbon steel nail, having a slender plain shank and a medium diamond point
Common Nail
Nail used in work where finish is unimportant, as in framing.
Finishing Nail
Slender nail made from finer wire than the common nail; has a brad-type head which permits it to be set below the surface of the wood, leaving only a small hole which can be puttied easily, used in finishing work.
Brad Nail
A small finishing nail, usually of the same thickness throughout, with a head that is almost flush with the sides or a head that projects slightly to one side.
Box Nail
Similar to a common nail but thinner; has a long shank which may be smooth or barbed.
Casing Nail
A slender nail with a small, slightly flared head used for finishing work.
Ring-Shank Nail
A nail having a number of ring-like grooves around the shank to increase its holding power.
Clinch/Clench Nail
Any nail designed for clinching, after driving.
Clinching
Process used in securing a nail, staple, screw or bolt, by hammering the protruding point so that it is bent over.
Roofing Nail
A short nail having a barbed or ring shank and a comparatively large flat head; may be galvanized or bright; often provided with a neoprene, lead, or plastic washer; used to secure roofing felt or shingles to a roof-deck or roof boards.
Metal Lath Nail
A a nail designed for securing a metal lath (a base for plaster)
Electrician’s Staple Nail
A u-shaped piece of metal or heavy wire, with pointed ends, driven into a surface to secure a sheet material, hold a hasp, etc.
Concrete Nail
A hardened steel nail having a flat countersunk head and a diamond point; used for nailing to concrete or masonry.
Masonry Nail
A hardened steel nail with a knurled or fluted shank; esp. used for fastening to masonry.
Common Nail
Type of Nails
Finishing Nail
Type of Nails

Brad Nail
Type of Nails

Box Nail
Type of Nails

Casing Nail
Type of Nails

Ring-Shank Nail
Type of Nails

Clinch/Clench Nail
Type of Nails
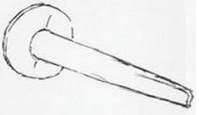
Roofing Nail
Type of Nails

Metal Lath Nail
Type of Nails

Electrician’s Staple Nail
Type of Nails

Concrete Nail
Type of Nails

Masonry Nail
Type of Nails

Flooring Nail
Type of Nails

Cut Nail
Type of Nails

Double-headed Nails
Type of Nails

Spikes
Type of Nails

Power-driven Studs
Type of Nails

Flooring Nail
Used for fastening floor boards.
Cut Nail
Used for wood flooring.
Double-headed Nails
Used for temporary structures.
Spikes
Used for fastening heavy timbers.
Power-driven Studs
Used for driving into concrete or steel
Face-nailing, Blind-nailing, Toe-nailing
Types of nail construction
Face-nailing
Nailing in which the nails are driven perpendicular to the face of the material.
Blind-nailing
Also called concealed or secret nailing. Nailing in such a way that the nail heads are not visible on the face of the work. In finished roofing, the use of nails that are not exposed to the weather.
Toe-nailing
Also called skew or tusk nailing. Nailing obliquely to the surfaces being joined.
Screws
These are externally threaded fasteners. They have greater holding power than nails, and are more easily removable because of their threaded shafts.
1/8” ; 1/2 ; 2/3
The length of a wood screw should be about ____" (3) less than the combined thickness of the boards being joined, with ___ to ___ of the screw’s length penetrating the base material.
Hardwoods
Fine-threaded screws are generally used for _________.
Softwoods
coarse-threaded ones are used for __________.
Fine-threaded Screws
Screws that are generally used for hardwoods
Coarse-threaded Screws
Screws that are generally used for softwoods
Use, Type of Head, Material, Lengths, Diameters
Screws are classified by:
steel, brass, aluminum, bronze, stainless steel
Materials for screws
1/2" to 6" (13 to 150)
Lengths for screws
up to 24 gauge
Diameters for screws.
Wood Screw
A helically threaded metal fastener having a pointed end; forms its own mating thread when driven into wood or other resilient material.
Metal Screw
Fastened by screwing into metal.
Lag Screw, Lag Bolt, Coach Screw
A bolt having a square head and a thin, coarse-pitched thread.
Screw Anchors
An anchor (similar to an expansion bolt) having a metal shell with a screw along its central axis; when the shell is placed in a hole and the screw is driven in, the shell expands, tightly securing the anchor in the hole.
Screw Anchors
Locally called a tux screw with a plastic shell.
Tekscrew
A screw used to fasten metal roofing sheets to the purlins
Wood Screw
Type of Screw
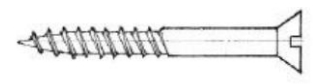
Drywall Screw
Type of Screw

Machine Screw
Type of Screw

Self-tapping Screw
Type of Screw

Sheet Metal Screw
Type of Screw
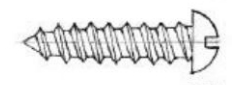
Cap Screw
Type of Screw
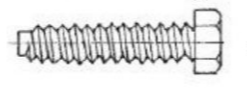
Set Screw
Type of Screw

Flat head
Type of Screw

Oval Head
Type of Screw

Round head
Type of Screw

Truss head
Type of Screw

Pan head
Type of Screw
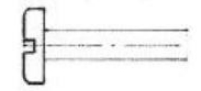
Fillister head
Type of Screw
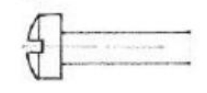
Bugle head
Type of Screw

Security head
Type of Screw
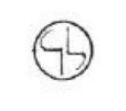
Slotted head
Type of Screw
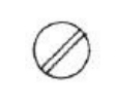
Phillips head
Type of Screw
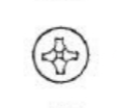
Allen head
Type of Screw
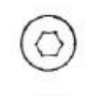
Square drive
Type of Screw

Bolts
A metallic pin or rod having a head on one end and an external thread on the other for screwing up a nut; used for holding members or parts of members together.
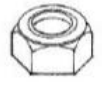
Nut
A short metal block having a central hole which is threaded to receive a bolt, screw, or other threaded part.
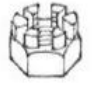
Lock Nut
Castellated Nut
Cap Nut
Spring-lock Washer
External-tooth Lock Washer
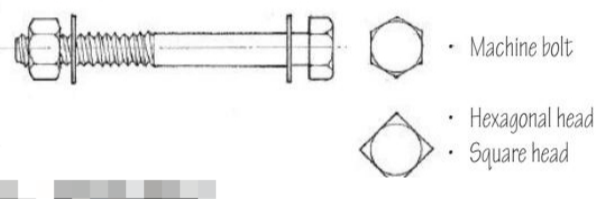
Machine Bolt
A threaded bolt having a straight shank and a conventional head such as a square, hexagonal, button, or countersunk type.
Stove bolt
A bolt with a slotted head, used in the assembly of wood-burning stoves constructed from sheet metal.