Financial Accounting Final Exam
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
CH 1-12
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Assets
Probable furute economic benefits owned by the business as a result of past transactions
Liabilities
Probable debts or obligations of the entity that result from past transactions, which will be fufilled by providing assets or services
Stockholders’ Equity
The financing provided by the owners and the operations of the business
Balance Sheet
Reports the amount of assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity of an accounting entity at a point in time
Separate Entity Assumption
states that business transactions are seperate from and shouylf exclude the personal transactions of the owners
Financial Statement Heading Format
Who: Name of the Business
What: Title of the Statement
When: Accounting Period
Formatting of Journal Entries
Debit first, credit second. Debits and credits must equal each other.
Date Account Titles Debit Credit
Title $
Title $
Expenses
decreases in assets or increases in liabilities arising from providing goods or services during the current period
Expense Recognition Principle
Expenses are recorded when incurred in earning revenue: also called matching
Revenues
Increases in assets or settlements of liabilities arising from providing goods or services
Revenues Journal Entry
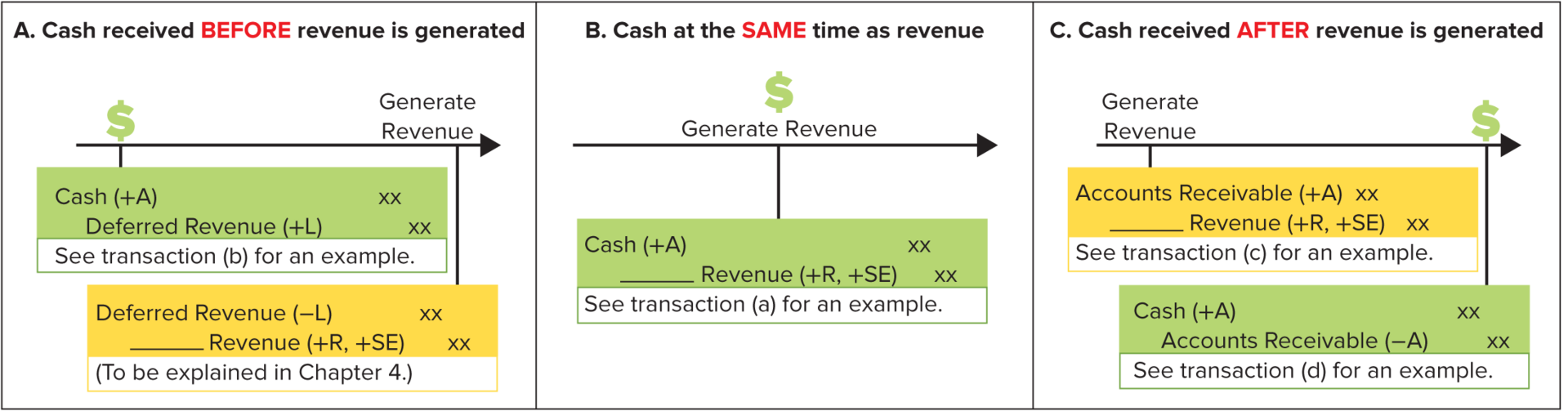
Revenue Recognition Principle
revenues are recorded when (or as) the seller provides goods or services to customers, in the amount the seller expects to be entitled to receive
Adjusting Journal Entries
Entries necessary at the end of each accounting period to report revenues and expenses in the propor period and assets and liabilities at appropriate amounts
Adjusting Journal Entries Record
1. Accruals Accrued Revenues (Revenue earned but not yet received)
Debit: Accounts Receivable
Credit: Service Revenue
Accrued Expenses (Expense incurred but not yet paid)
Debit: Expense (e.g., Salaries Expense)
Credit: Payable (e.g., Salaries Payable)
2. Deferrals Prepaid Expenses (Previously recorded asset now used)
Debit: Expense (e.g., Rent Expense)
Credit: Prepaid Asset (e.g., Prepaid Rent)
Unearned Revenues (Previously recorded liability now earned)
Debit: Unearned Revenue
Credit: Revenue (e.g., Service Revenue)
3. Depreciation To allocate cost of long-term assets over time
Debit: Depreciation Expense
Credit: Accumulated Depreciation
4. Interest Accrued Interest Expense
Formula:
Principal × Rate × TimeDebit: Interest Expense
Credit: Interest Payable
5. Supplies Used If supplies were purchased earlier and now used up:
Debit: Supplies Expense
Credit: Supplies
Adjusting entries ensure that:
Revenues are recorded when earned
Expenses are recorded when incurred
Closing Journal Entries
Temporary Accounts to Close:
Revenues
Expenses
Gains & Losses (if any)
Dividends (if declared)
1. Close Revenue Accounts to Income Summary
Debit: Each Revenue account
Credit: Income Summary
2. Close Expense Accounts to Income Summary
Debit: Income Summary
Credit: Each Expense account
3. Close Income Summary to Retained Earnings
If Net Income:
Debit: Income Summary
Credit: Retained Earnings
If Net Loss:
Debit: Retained Earnings
Credit: Income Summary
4. Close Dividends to Retained Earnings
Debit: Retained Earnings
Credit: Dividends
Order matters: Revenues → Expenses → Income Summary → Dividends
Permanent Accounts
The balance sheet accounts that carry their ending balances into the next accounting period
Temporary Accounts
Income statement accounts that are closed to retained earnings at the end of the accounting period
Reconciling Items on a Bank Reconciliation
Start with Bank Statement Balance:
Add:
Deposits in Transit (you recorded, bank hasn’t)
Subtract:
Outstanding Checks (you wrote, bank hasn’t cleared)
Start with Book Balance (Cash account):
Add:
Interest earned
EFT collections
Bank errors (if bank deducted too much)
Subtract:
NSF (bounced) checks
Bank service charges
EFT payments
Book errors (if you over-recorded deposits)
Internal Controls
control environment, risk assessment, control activities, information and communication, monitoring activities
Common Activities of Merchandising Companies
A company that sells goods that have been obtained from a supplier
Common Activities of Manufacturing Companies
A comapny that makes, not buys the prducts they sell
Common Activities of Service Companies
A company that sells services rather than physical goods
Periodic Method
A system in which ending inventory and cost of goods sold are determined only at the end of the accounting period based on a physical inventory count
Perpetual Method
A system in which a detailed inventory record is maintained by recording each purchase and sale of inventory during the accounting period
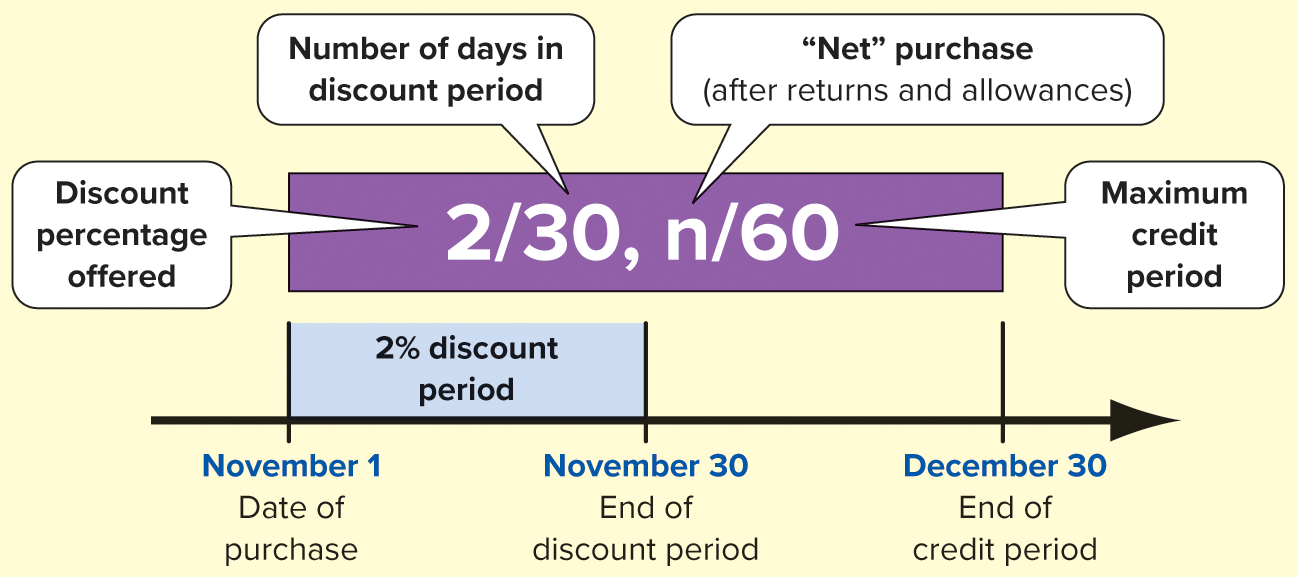
Credit Terms
Cost of Goods Sold Formula
Beginning Inventory + Purchases — Ending Inventory
COGS using FIFO
Identify units sold.
Assign cost starting from beginning inventory and oldest purchases.
Remaining units are the ending inventory, valued at the most recent purchase costs.
Ending Inventory: Composed of the most recent purchases.
COGS: Sum of the oldest costs for units sold.
COGS using LIFO
Identify units sold.
Assign cost starting from the most recent purchases backward.
Remaining units (oldest) are the ending inventory.
Ending Inventory: Composed of the oldest inventory.
COGS: Sum of the most recent purchase costs for units sold.
COGS using Weighted Average Method
Calculate total cost of goods available for sale (beginning inventory + purchases).
Calculate total units available for sale.
Weighted average cost per unit = Total cost / Total units.
Multiply by units sold for COGS and units remaining for ending inventory.
Ending Inventory: Units on hand × weighted average cost per unit.
COGS: Units sold × weighted average cost per unit.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Type:
Contra-Asset account
Paired with Accounts Receivable on the balance sheet
Normal Balance:
Credit
Purpose:
To estimate and record expected uncollectible receivables
Matches bad debt expense to the same period as related sales (per Matching Principle)
Write-Offs and recovery of bad debt
1.To Record Bad Debt Expense:
Debit: Bad Debt Expense
Credit: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
2. To Write Off an Uncollectible Account:
Debit: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Credit: Accounts Receivable
3. To Record Collection of a Previously Written-Off Account:
Step 1 Reinstate A/R: Debit: Accounts Receivable Credit: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Step 2 Record Cash Collection: Debit: Cash Credit: Accounts Receivable
Notes Recievable Journal Entry
a. Issuance of Note (Lend Money)
Debit: Notes Receivable
Credit: Cash
b. Accrue Interest Receivable:
Debit: Interest Receivable
Credit: Interest Revenue
c. Receipt of Interest at Maturity:
Debit: Cash
Credit: Interest Receivable (for accrued interest)
Credit: Interest Revenue (for remaining interest)
d. Repayment of Principal:
Debit: Cash
Credit: Notes Receivable
Interest Expense Calculation
Interest= Principal x Interest rate x Time
Interest expense Journal Entry
When interest is incurred (accrued but not yet paid):
Debit: Interest Expense
Credit: Interest Payable
When interest is paid in cash:
Debit: Interest Expense
Debit: Interest Payable (if accrued earlier)
Credit: Cash
Percentage of Credit Sales Method
Formula:
Bad Debt Expense = Credit Sales x Estimated % Uncollectible
Journal Entry:
Debit: Bad Debt Expense
Credit: Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Depreciation and Accumulated Depreciation
Depreciation and Accumulated Depreciation Classification
Straight-Line method
(Cost - Residual Value) / Useful Life = Depreciation Expense
Double Declining Method
2 / Useful Life = Rate Rate x Beginning Book Value or Cost- accumulated depreciation = Depreciation
Notes Payable Journal Entry
When you borrow (issue a note):
Debit: Cash
Credit: Notes Payable
At period-end (to accrue interest):
Debit: Interest Expense
Credit: Interest Payable
Use formula: Principal × Rate × Time
When you repay the note and interest:
Debit: Notes Payable
Debit: Interest Payable (if accrued)
Debit: Interest Expense (if not yet accrued)
Credit: Cash
Notes payable Interest Calculation
Interest = Principal × Rate × Time
Bonds Payable Journal entry
1. Issuing Bonds at Face Value:
Debit: Cash
Credit: Bonds Payable
2. Issuing Bonds at a Discount:
(Issued for less than face value)
Debit: Cash
Debit: Discount on Bonds Payable
Credit: Bonds Payable
3. Issuing Bonds at a Premium:
(Issued for more than face value)
Debit: Cash
Credit: Premium on Bonds Payable
Credit: Bonds Payable
4. Interest Payment (Face Value Example):
Debit: Interest Expense
Credit: Cash
Discount: Increase interest expense
Premium: Reduce interest expense
Bonds Payable Interest Calculation
Interest = Face Value × Stated Rate × Time
Treasury Stock
Issued shares that have been reacquired by the company
Treasury Stock Repurchase Journal Entry
Debit: Treasury Stock
Credit: Cash
Treasury stock Reissuance Journal Entry
🔹 If Reissued at More Than Cost:
Debit: Cash
Credit: Treasury Stock
Credit: Additional Paid-In Capital (APIC) – Treasury Stock
🔹 If Reissued at Less Than Cost:
If there's enough APIC–Treasury Stock:
Debit: Cash
Debit: APIC – Treasury Stock
Credit: Treasury Stock
📌 Note:
Treasury Stock is always removed at original cost
APIC–Treasury Stock is used only for gains/losses on reissuance
Never record a gain or loss on treasury stock in net income
Number of Shares Issued Calculation
Shares Issued = Shares Outstanding + Treasury Shares
Outstanding Shares and Treasury Shares
Outstanding Shares
Shares currently owned by shareholders
Used to calculate earnings per share (EPS) and dividends
Treasury Shares
Shares repurchased by the company
Not considered outstanding
No voting rights or dividends
Stock Issuance Journal Entry
1. When Stock is Issued at Par Value:
Debit: Cash (Shares issued × Par value)
Credit: Common Stock (at par value)
2. When Stock is Issued Above Par (with Additional Paid-In Capital):
Debit: Cash (Total amount received)
Credit: Common Stock (Par value × shares issued)
Credit: Additional Paid-In Capital (Difference)
Dividend Journal Entry
1. When Dividends Are Declared:
Debit: Retained Earnings
Credit: Dividends Payable
2. When Dividends Are Paid:
Debit: Dividends Payable
Credit: Cash
Notes:
Declaration creates a liability.
Payment reduces cash and clears the liability.
Par Value Per Share
The nominal (legal) value assigned to each share of stock in the corporate charter.
Usually a very small amount (e.g., $0.01 or $1 per share).
Represents the minimum legal capital that must be retained in the business and cannot be distributed as dividends.
Debit: Cash
Credit: Common Stock (Par Value × Shares Issued)
Credit: Additional Paid-In Capital (any excess over par)
Operating Actiities
Cash inflows and outflows related to the components of net income
EX: Cash received from customers (sales revenue)
Cash paid to suppliers and employees (inventory, wages)
Interest paid and received (sometimes classified as operating)
Income taxes paid
Financing Activities
Cash inflows and outflows realted to financing sources external to the company
EX: Cash received from issuing stock or bonds
Cash paid to repurchase treasury stock
Dividends paid to shareholders
Borrowing money (notes payable, loans)
Repaying borrowed funds
Investing Activities
Cash inflows and outflows related to the sale or purchase of investments and long-lived assets
EX: Purchase of property, plant, and equipment (PPE)
Sale of PPE
Purchase or sale of investments (stocks, bonds, etc.)
Loans made to others (notes receivable)
Collection of loan principal
Statement of Cash Flows
Reports inflows and outflows of cash during the accounting period in the categories of operating, investing, and financing
Direct Method
A method of presenting the operating activities section of the statement of cash flows; reports the components of cash flows from operating activities as gross receipts and gross payments
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
Cash received from customers: $XX,XXX
Cash paid to suppliers: (XX,XXX)
Cash paid to employees: (XX,XXX)
Cash paid for interest: (X,XXX)
Cash paid for income taxes: (X,XXX)
Net cash provided by operating activities: $XX,XXX
Indirect Method
Presntes the operating activities section of the cash flow statement by adjusting net income t ocompute cash flows from operating activities
Cash Flows from Operating Activities:
Net Income: $XX,XXX
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities:
Depreciation expense: +X,XXX
Decrease (increase) in accounts receivable: +/−X,XXX
Increase (decrease) in accounts payable: +/−X,XXX
Other non-cash expenses or changes: +/−X,XXX
Net cash provided by operating activities: $XX,XXX