Terminology pertaining to the ENMT system
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Medical terms pertaining upper respiratory physical findings
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
otitis externa
inflammation of the outer ear
otitis media
inflammation of the middle ear
dysphagia
condition in which swallowing is difficult or painful
epistaxis
bleeding from the nose
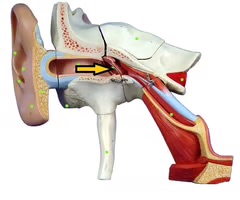
TM
tympanic membrane
Hemotympanum
The presence of blood in the tympanic membrane.
Tympanic membrane
is the membrane that separates the other ear (ear canal) with the inner ear.
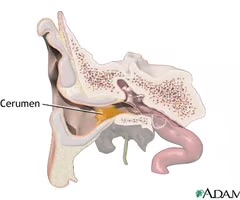
Cerumen impaction
buildup of earwax that blocks the ear canal causing decreased hearing and inability to visualize the tympanic membrane.
hemoptysis
coughing up blood
otalgia
pain in the ear
dry mucous membrane
generalized decrease in normal lubrication of the mucous membranes due to dehydration ( oral pharynx, lips, etc.)
Hoarse voice
vocalization marked by a deep, rough, harsh, or grating quality, indicating an inflammation of the throat and larynx.
Pharynx
throat; passageway for food to the esophagus and air to the larynx
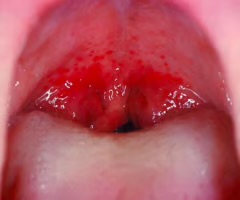
Tonsillar
related to the tonsils
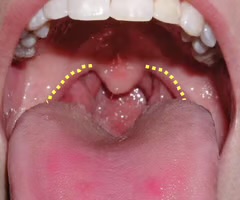
Tonsillar exudates
fluid secreted by the tonsils in response to infection or inflammation
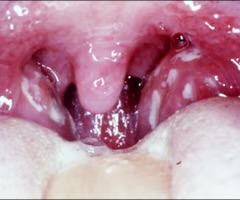
rhinorrhea
runny nose
tonsillar hypertrophy
abnormally enlarged tonsillar tissue
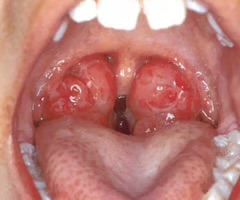
nasal turbinates
passage ways for air that goes in and out of each nostril
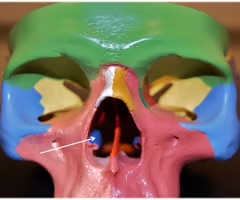
nostrils
the two external openings of the nasal cavity
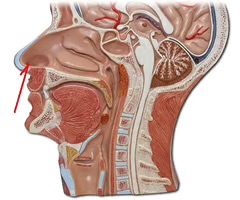
nasal mucosa
is what lines the nasal cavity. Changes in the nasal mucosa indicate bacterial infections, allergies, viral infections…
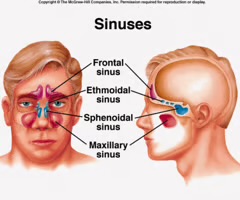
Maxillary sinuses
sinuses that are located near the nose, under the eyes, one of each side.
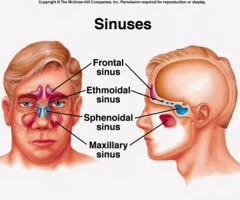
Frontal sinuses
sinuses located on the lower part of the forehead over the eye sockets and eyebrows.
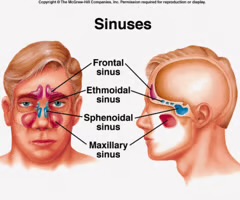
Ethmoid sinuses
sinuses located between the nasal bridge and the eyes.
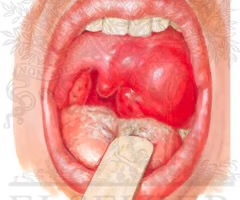
peritonsillar abscess
accumulation of pus due to an infection behind one tonsil. Usually due to complication of untreated strep throat or tonsilitis.
Uvula deviation
uvula positions more prominently to one side more than the other.
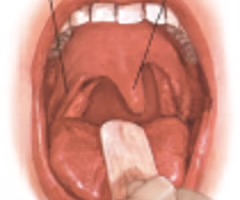
Uvula
a fleshy extension at the back of the soft palate which hangs above the throat
Patent airway
indicative that there is no airway obstruction or visible blockage in the airway. Important to assess during allergic reaction, asthma attacks…
Bulging TM
sign of otitis media. It is caused by fluid trapped behind the tympanic membrane, which causes it to bulge.
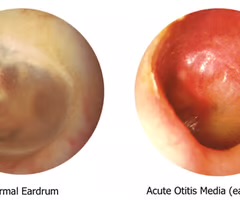
Dull TM
absent light reflex when lighting at the tympanic membrane with an otoscope
Loss of landmarks in TM
loss of ossicular landmarks which indicate otitis media
Opaque TM
a normal tympanic membrane is translucent with a pale gray color. An opaque TM lacks translucence.
Perforated TM
tear in the tympanic membrane caused by either infection, trauma, rapid changes in pressure
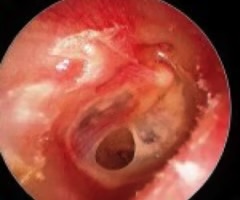
Air-fluid level behind TM
air or fluid collected behind the tympanic membrane in the middle ear which causes the tympanic membrane to bulge.
Pharyngeal erythema
redness of throat