Biology 12 Lab Practical: Fetal Pig Dissection – Vocabulary Flashcards
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Vocabulary flashcards covering major organs, vessels, anatomical planes, and structures discussed in the fetal pig dissection lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Diaphragm
Thin, dome-shaped muscle that separates thoracic and abdominal cavities and drives breathing (inhale/exhale)
Small Intestine
Digestive organ where most chemical digestion and nutrient absorption occur.
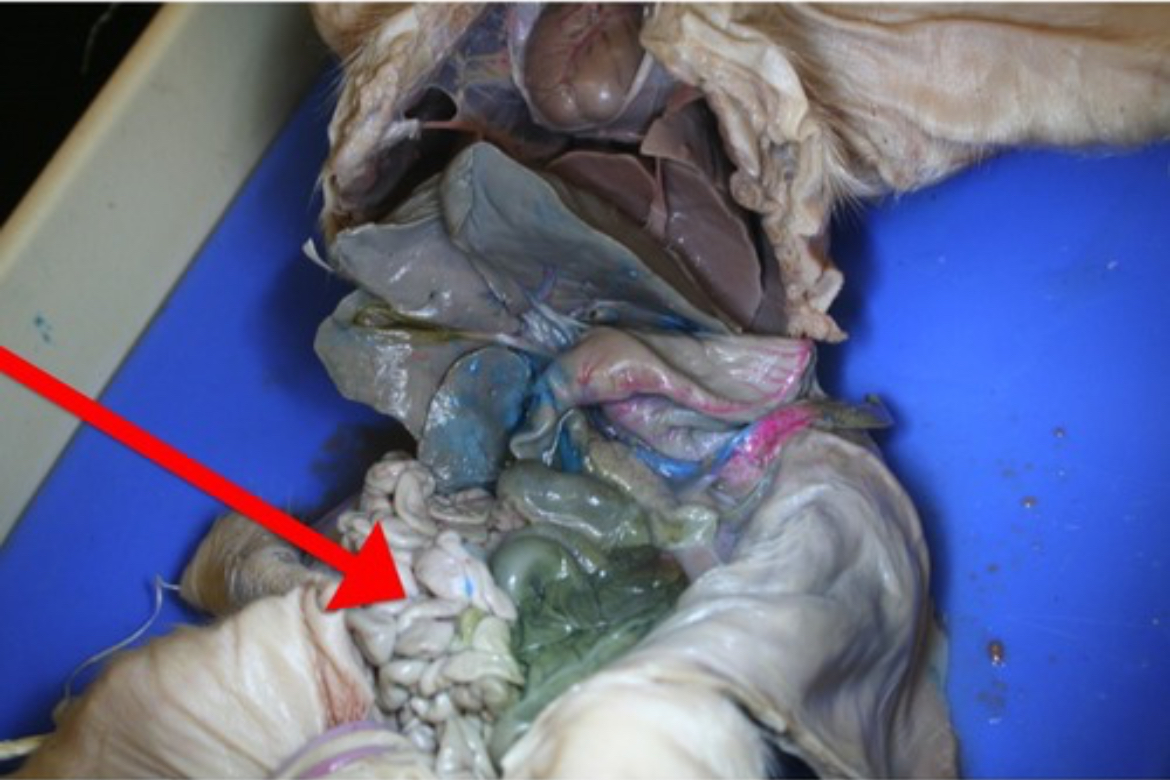
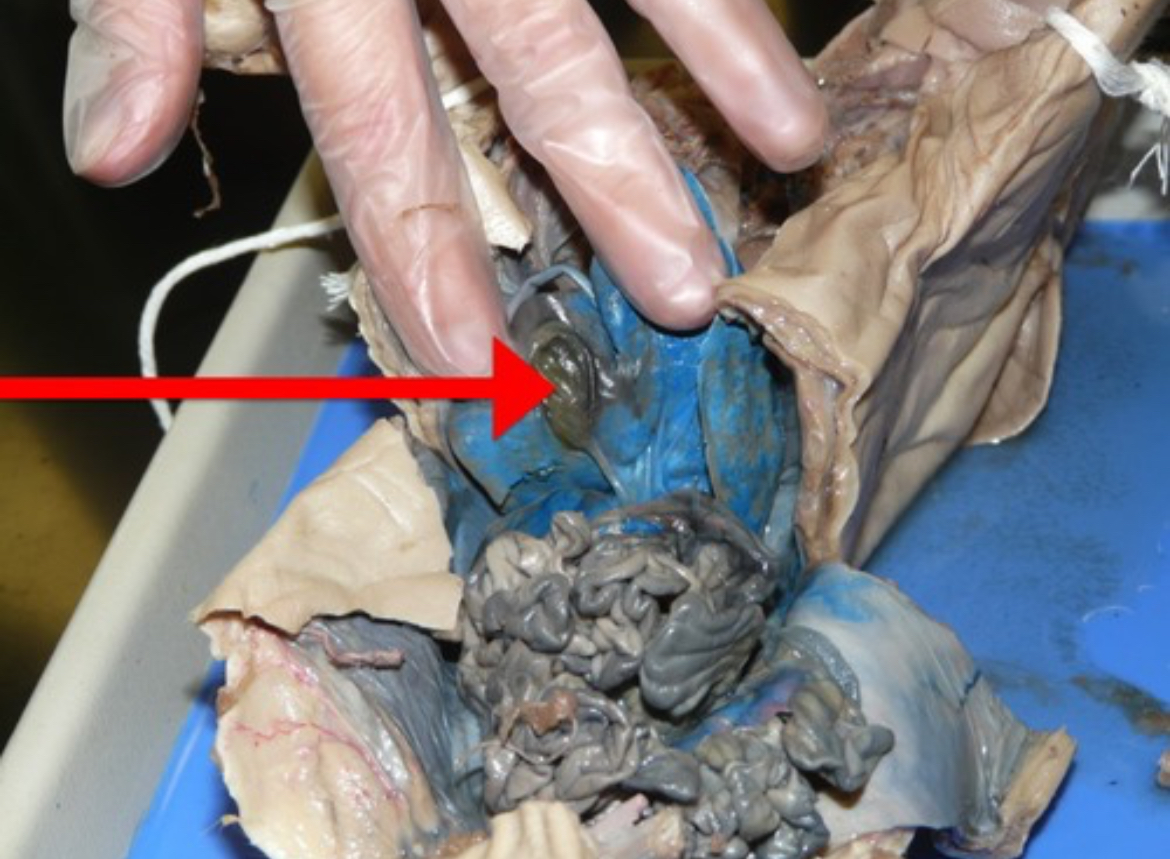
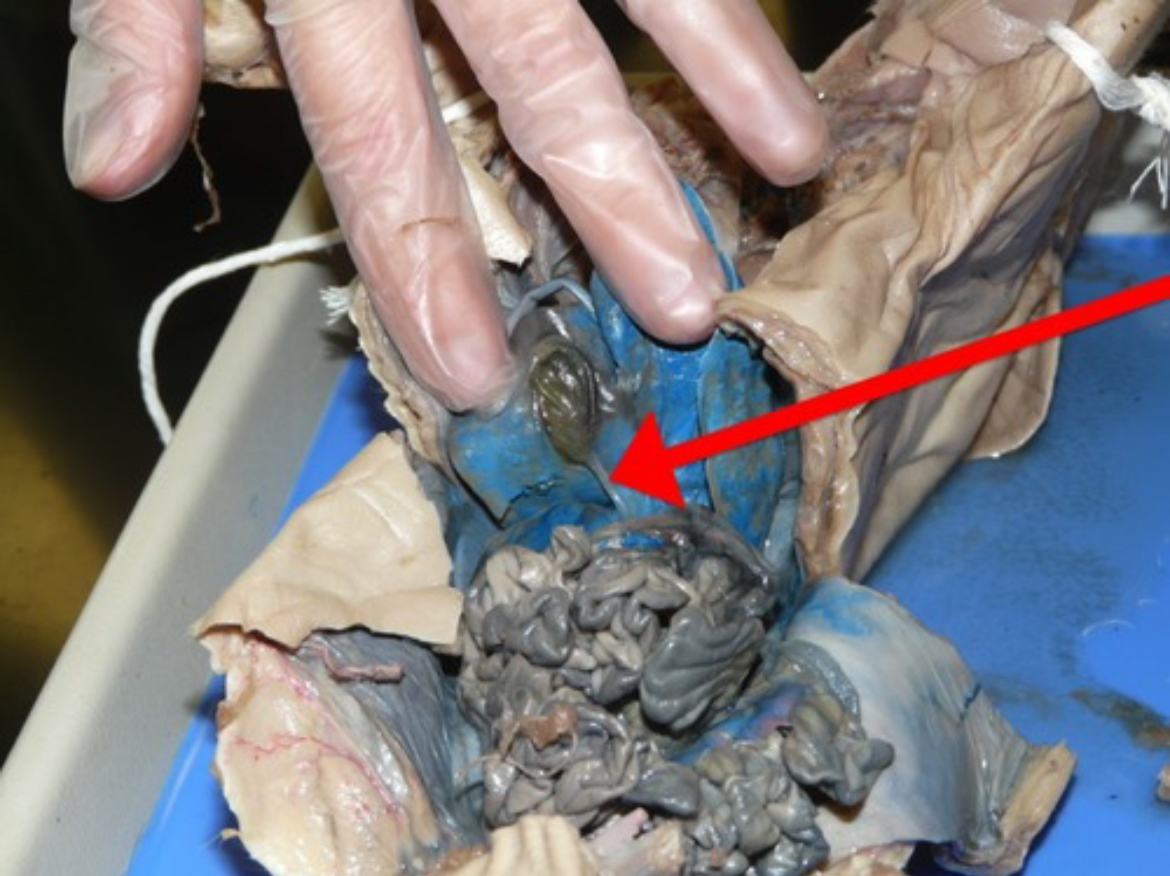
Gall Bladder
Sac-like organ that stores bile produced by the liver.
Duodenum
First section of the small intestine; receives bile and pancreatic enzymes to emulsify fats and continue digestion.
Spleen
Lymphatic organ that filters blood, removing old red blood cells and pathogens.
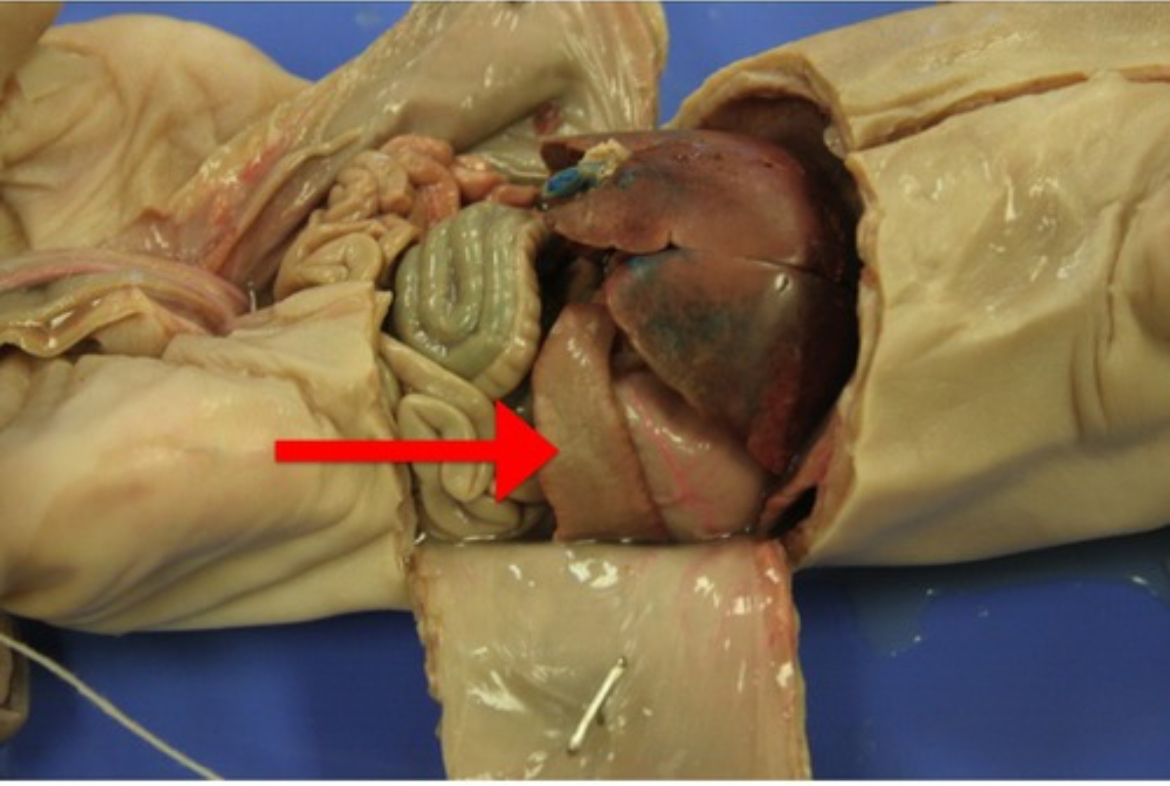
Liver
Large organ that detoxifies chemicals, metabolizes proteins, produces bile, and stores glycogen.
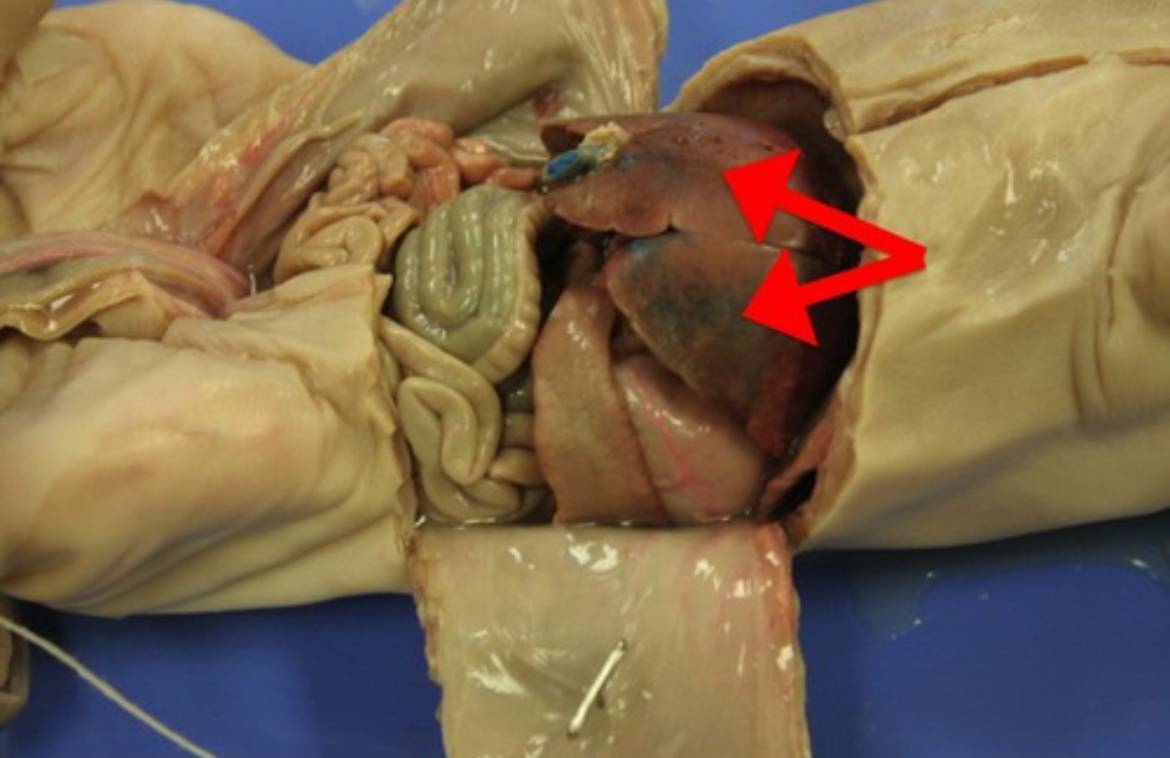
Stomach
Muscular sac that stores food, performs mechanical breakdown, and begins protein digestion with acid and enzymes.
Pancreas
Makes hormones (Insulin/Glucagon) and digestive enzymes
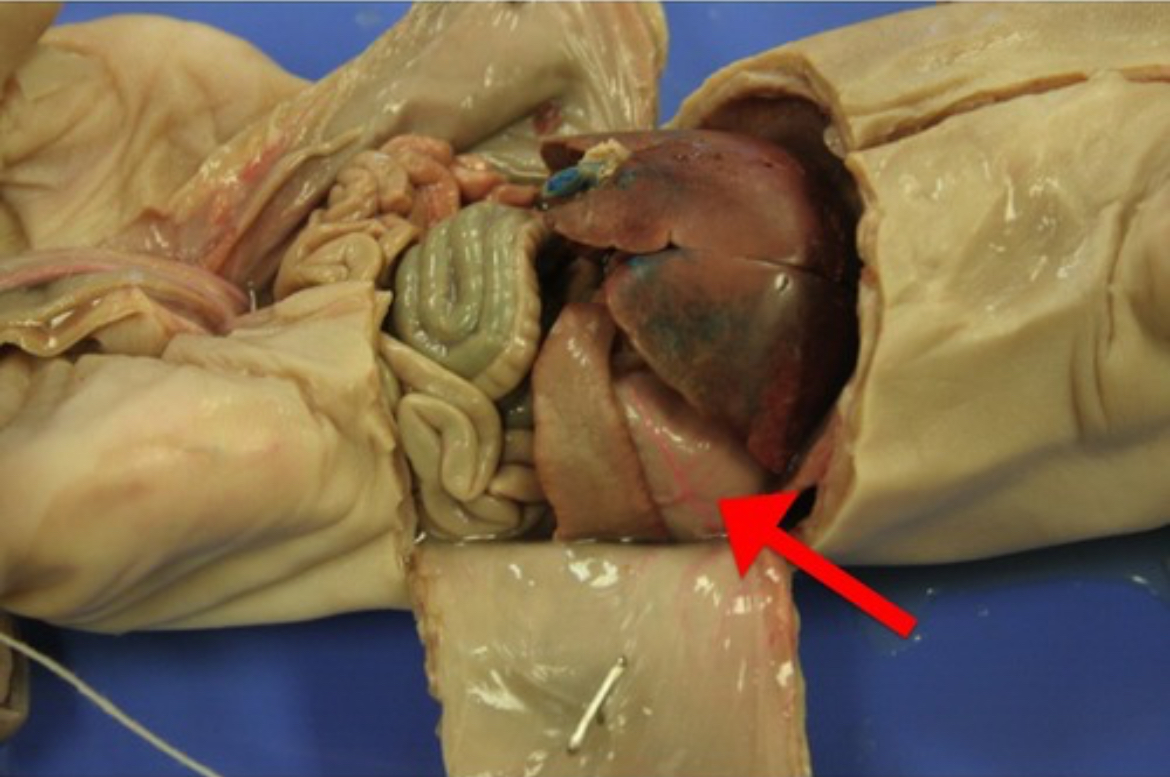
Heart
Hollow muscular organ that pumps blood through the circulatory system.
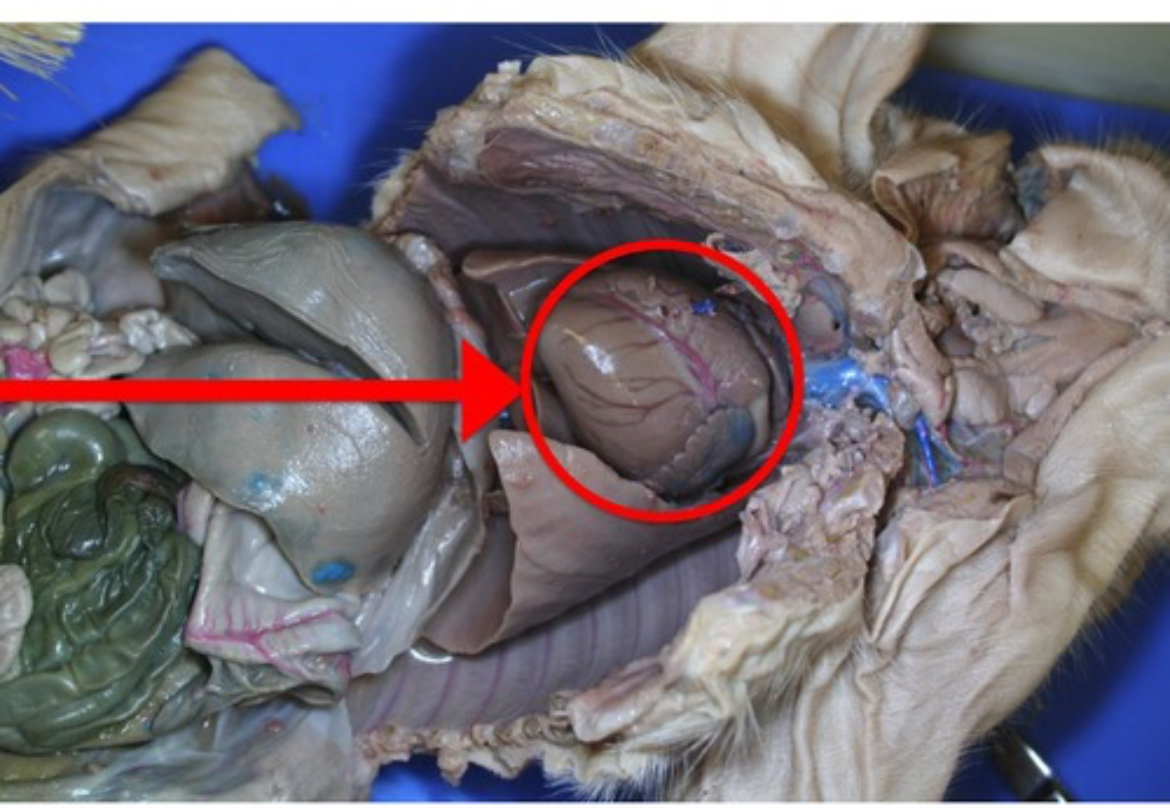
Lungs
Paired respiratory organs containing alveoli where gas exchange with blood occurs.
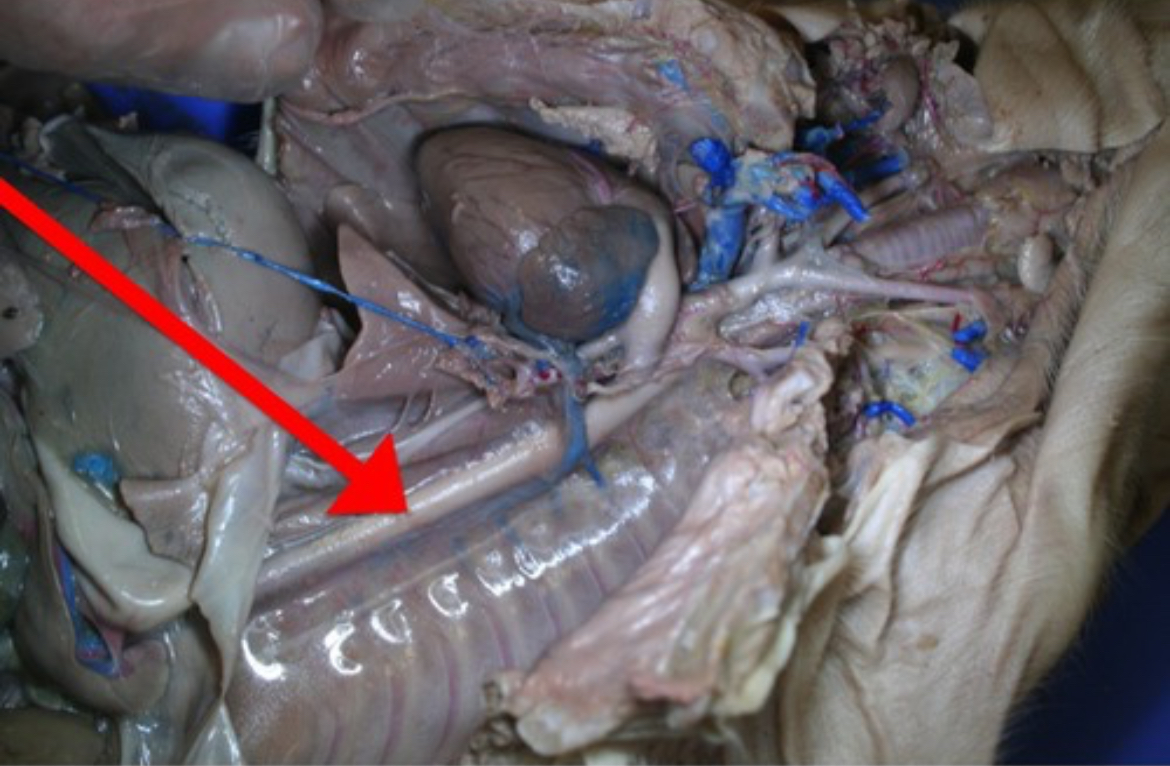
Aorta
Largest artery; carries oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body.
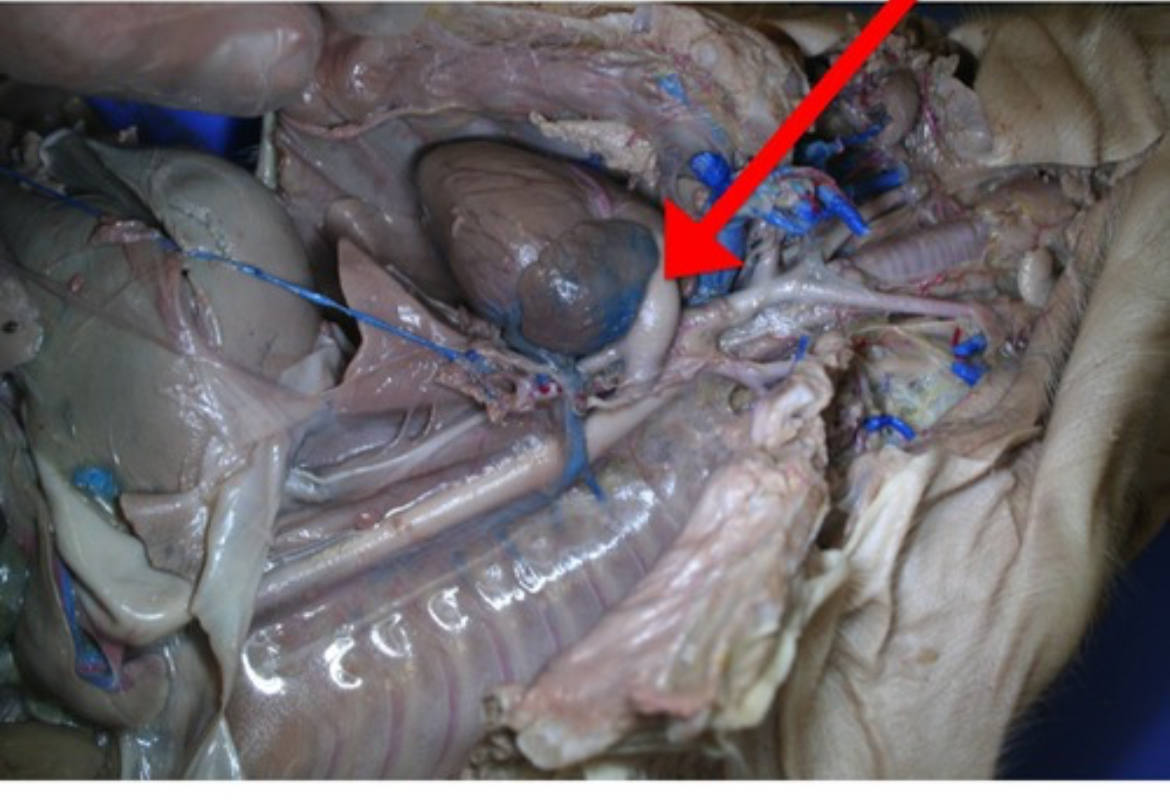
Pulmonary Artery
Major artery that transports deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
Coronary Artery
Branches of the aorta that supply oxygenated blood to heart tissue itself.
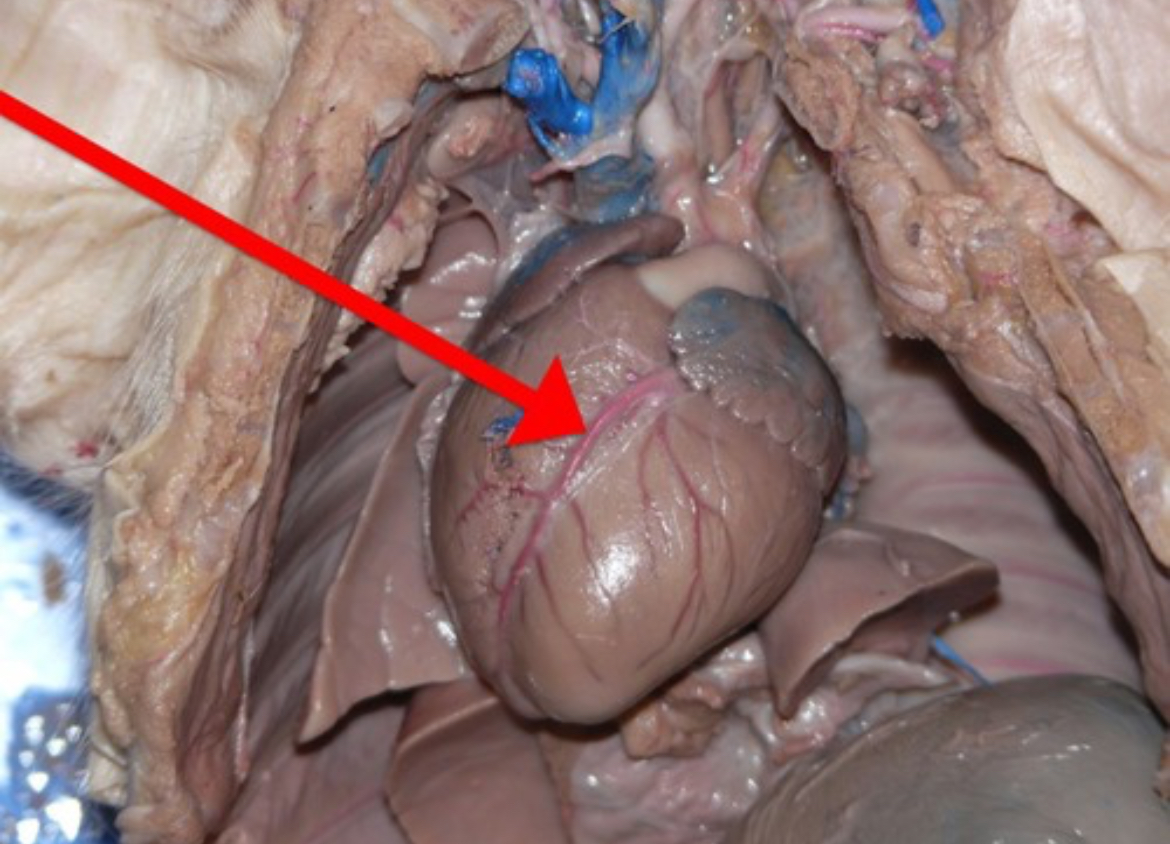
Left Atrium
Heart chamber that receives oxygenated blood from pulmonary veins and passes it to the left ventricle.
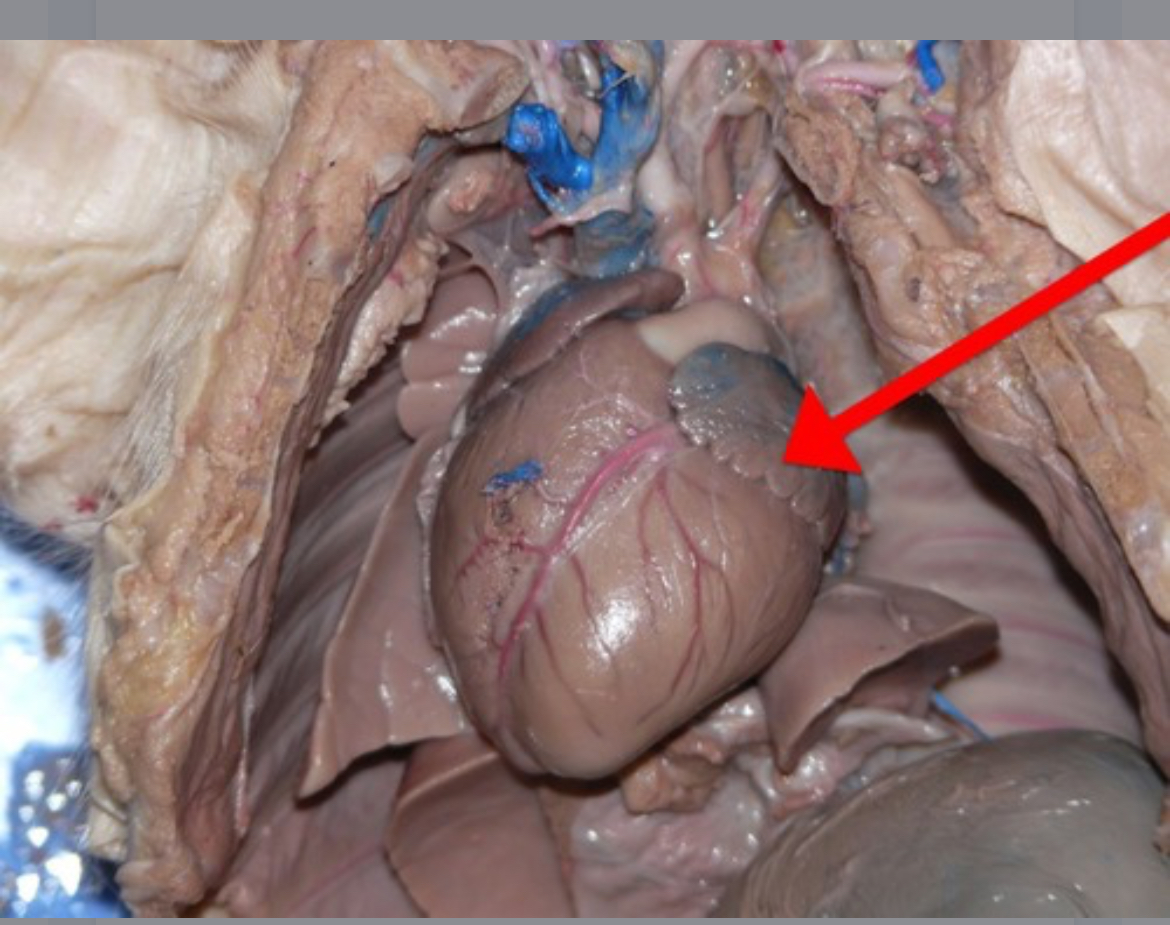
Left Ventricle
Pumps oxygenated blood from the left atrium into the aorta for systemic distribution.
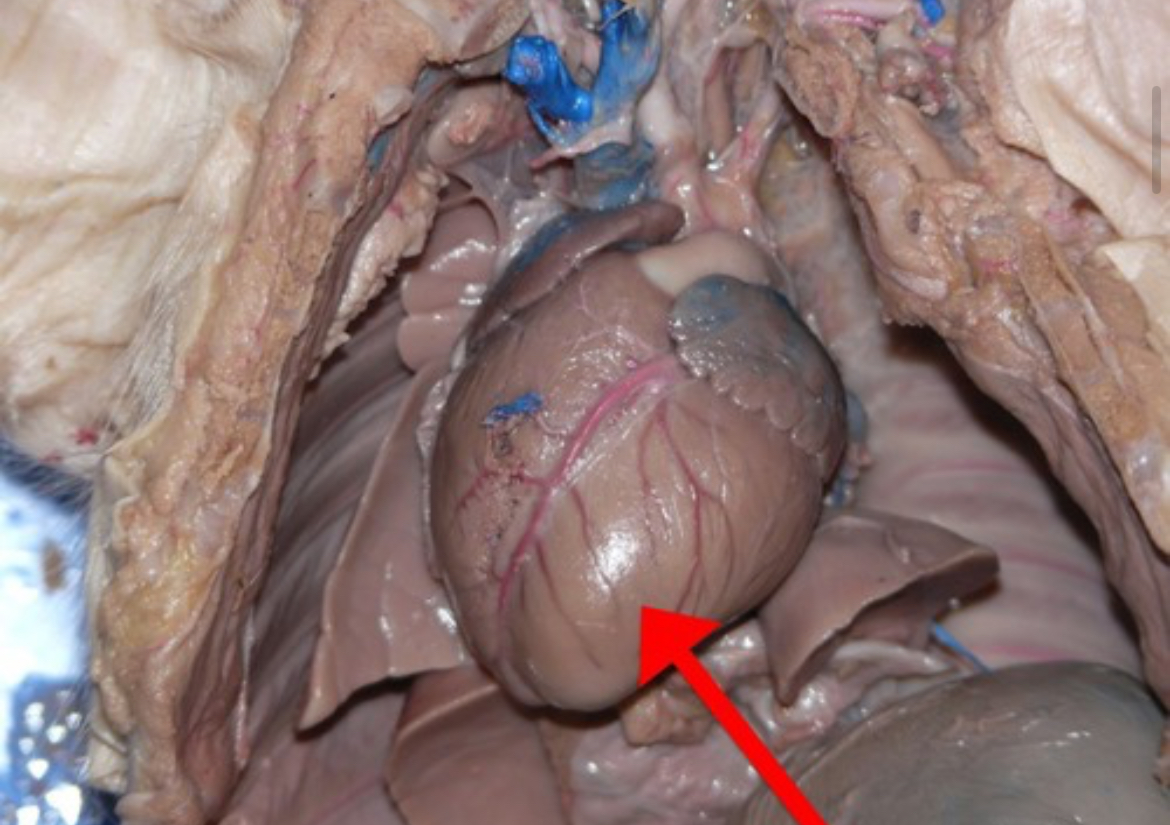
Right Ventricle
Pumps deoxygenated blood from the right atrium into the pulmonary artery.
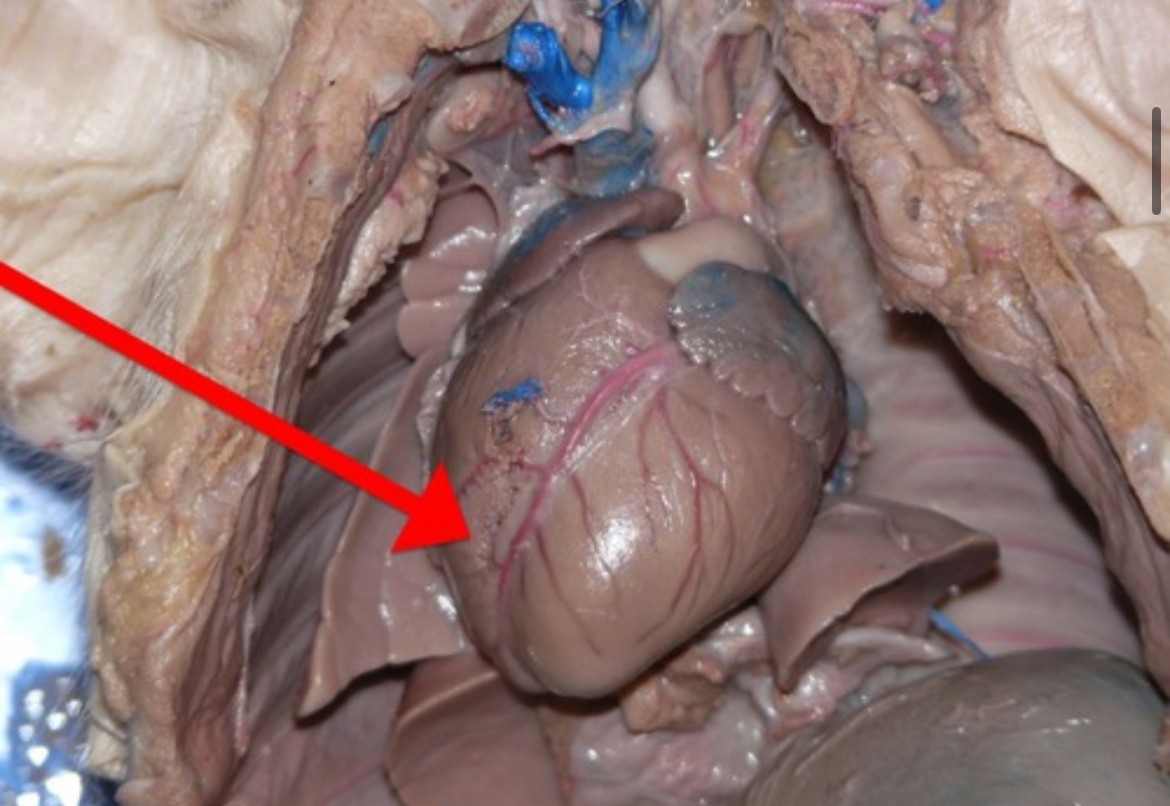
Right Atrium
Receives blood returning to heart
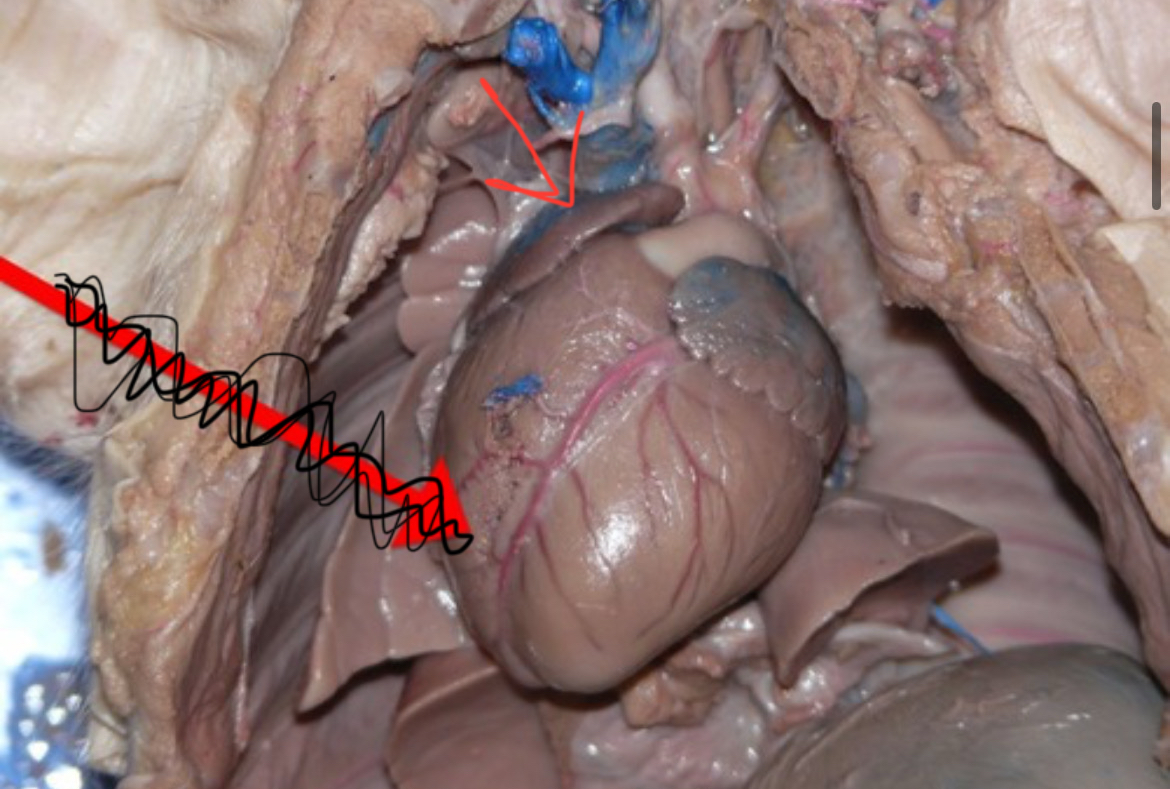
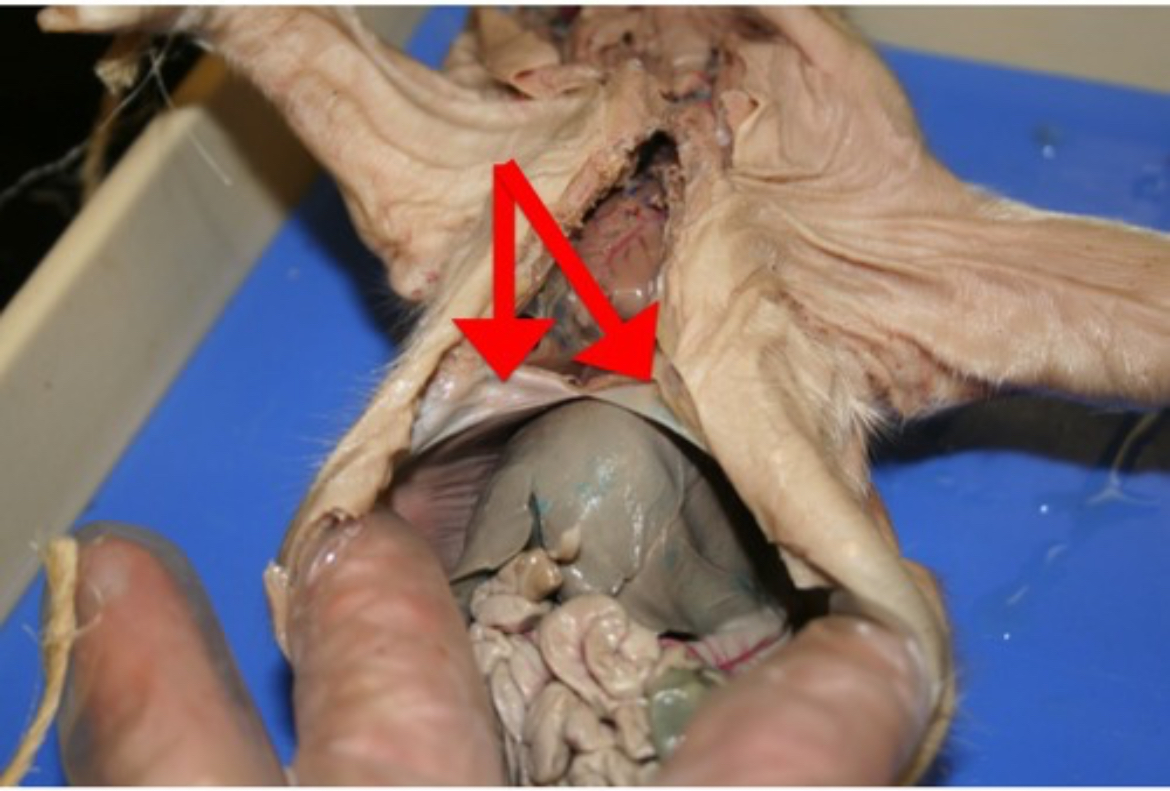
Soft Palate
Muscular posterior roof of the mouth; separates oral and nasal cavities during swallowing.
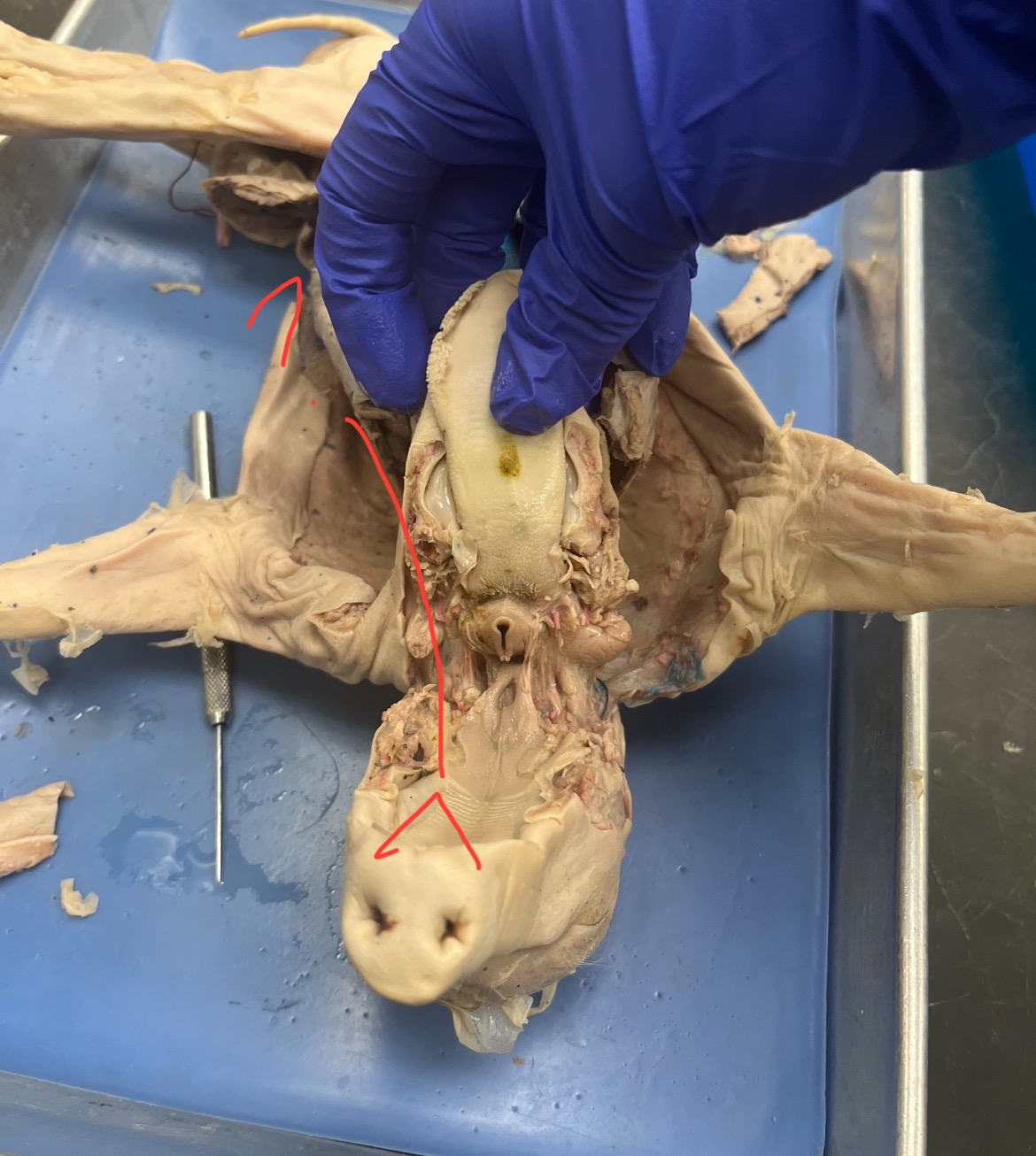
Nares
External openings of the nose that admit air to the nasal passages.
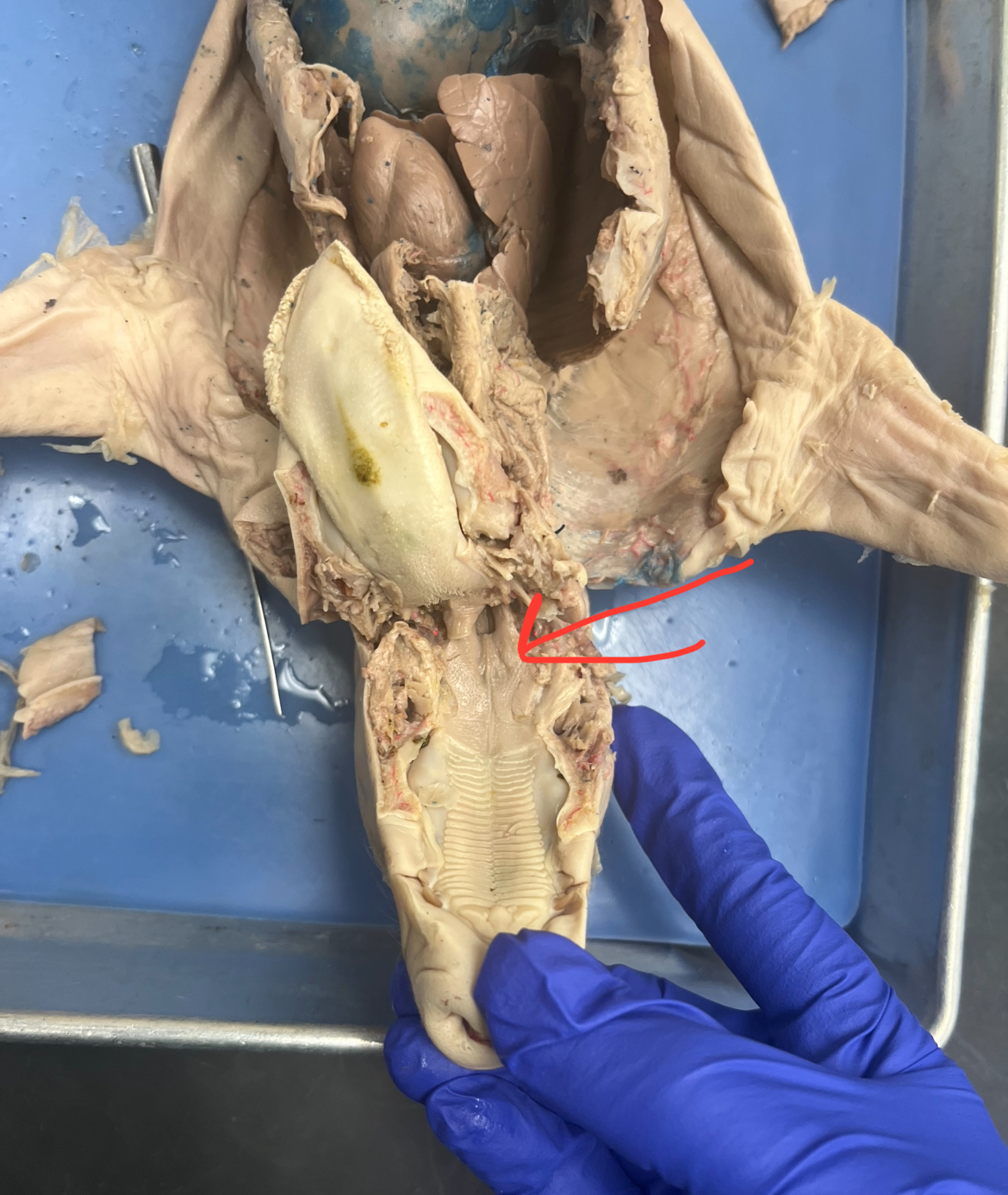
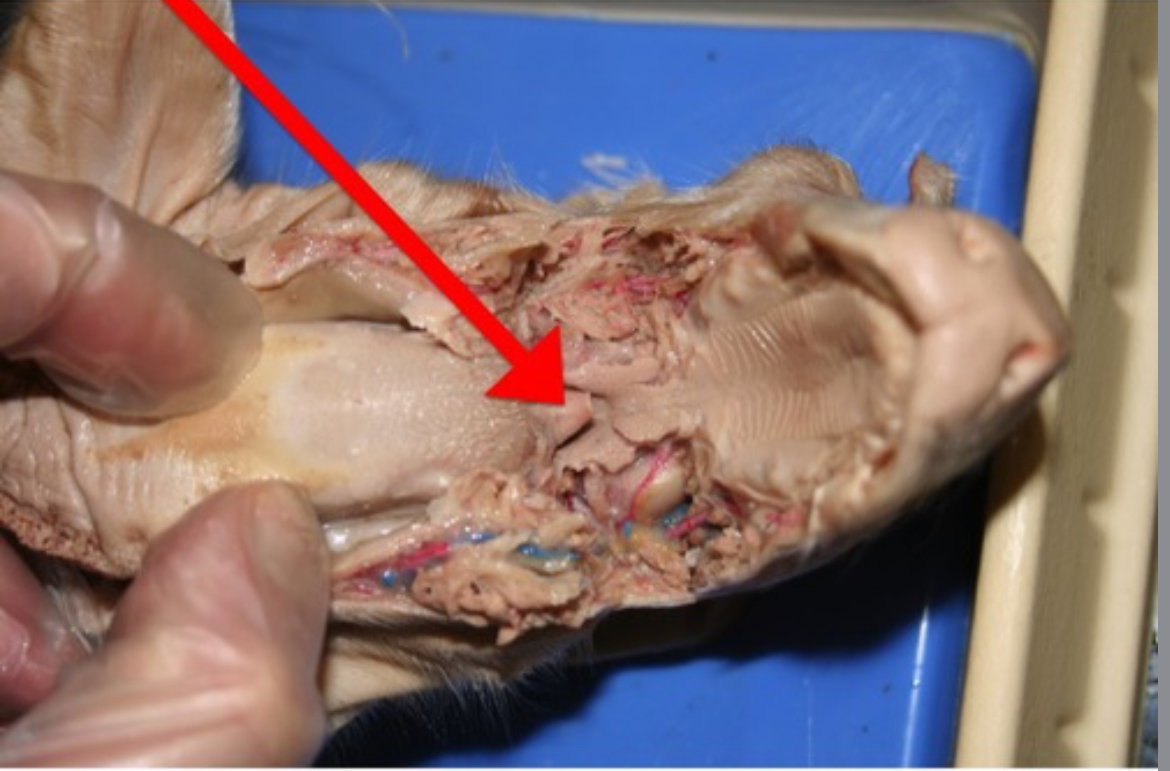
Epiglottis
Flap of tissue that covers the trachea during swallowing, preventing food from entering airways.
Hard Palate
Bony anterior roof of the mouth; aids mechanical digestion and separates oral/nasal cavities.
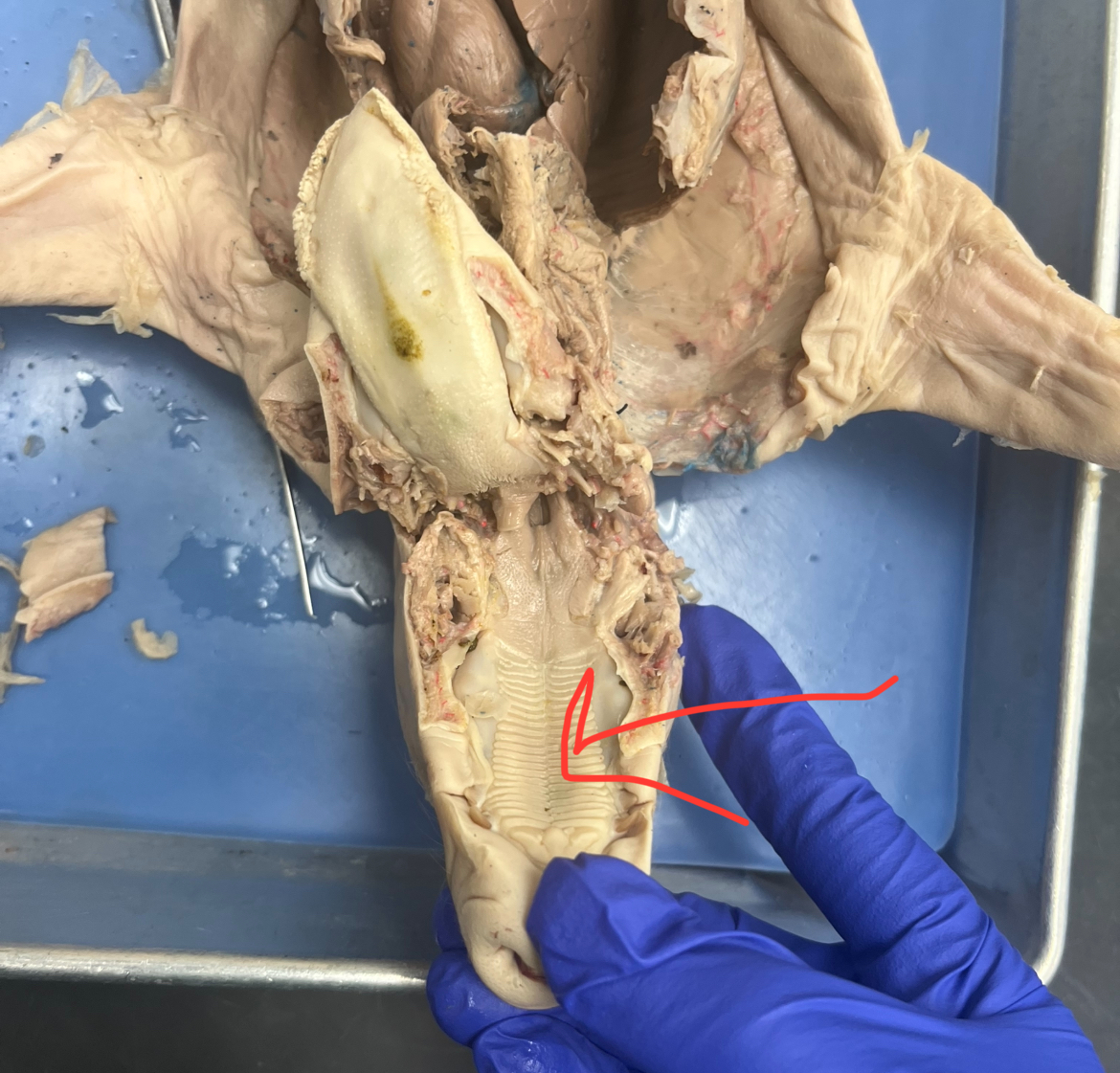
Trachea
Windpipe reinforced with cartilage rings; conducts air between larynx and bronchi.
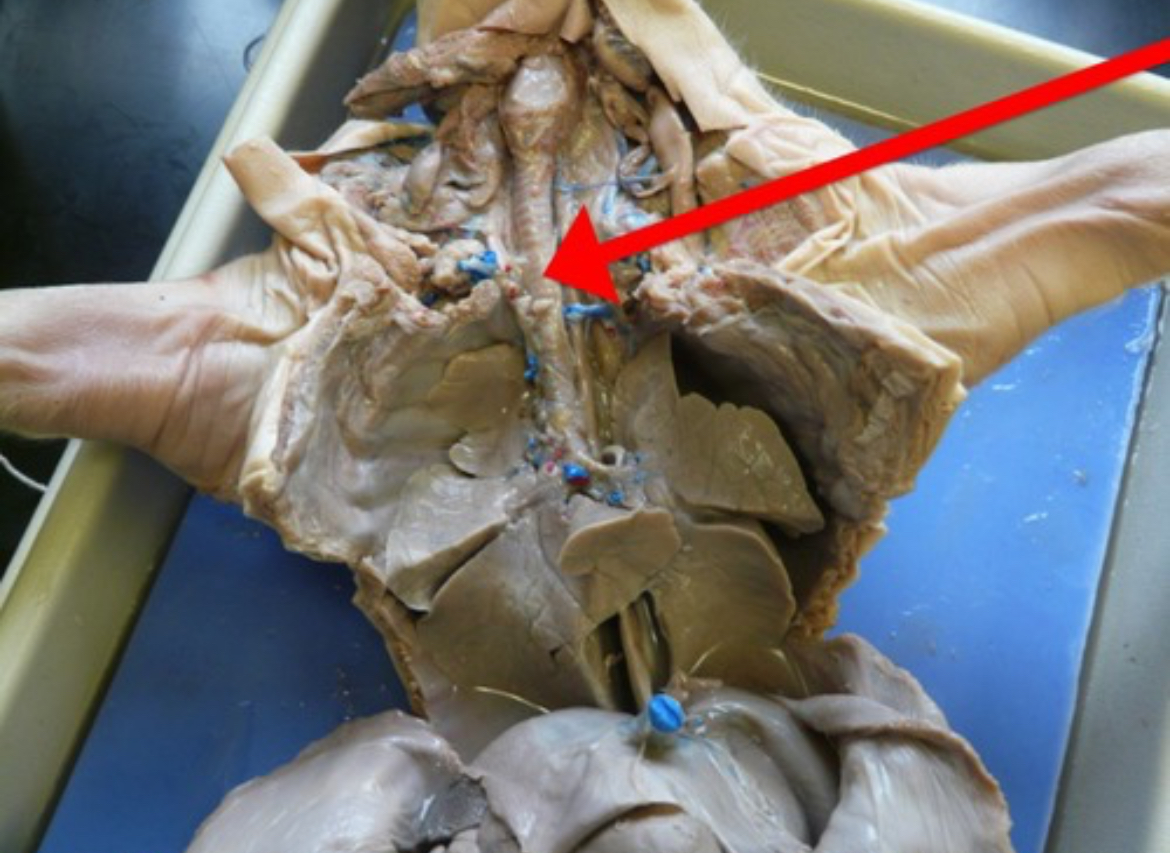
Larynx
Voice box containing vocal cords; located between pharynx and trachea.
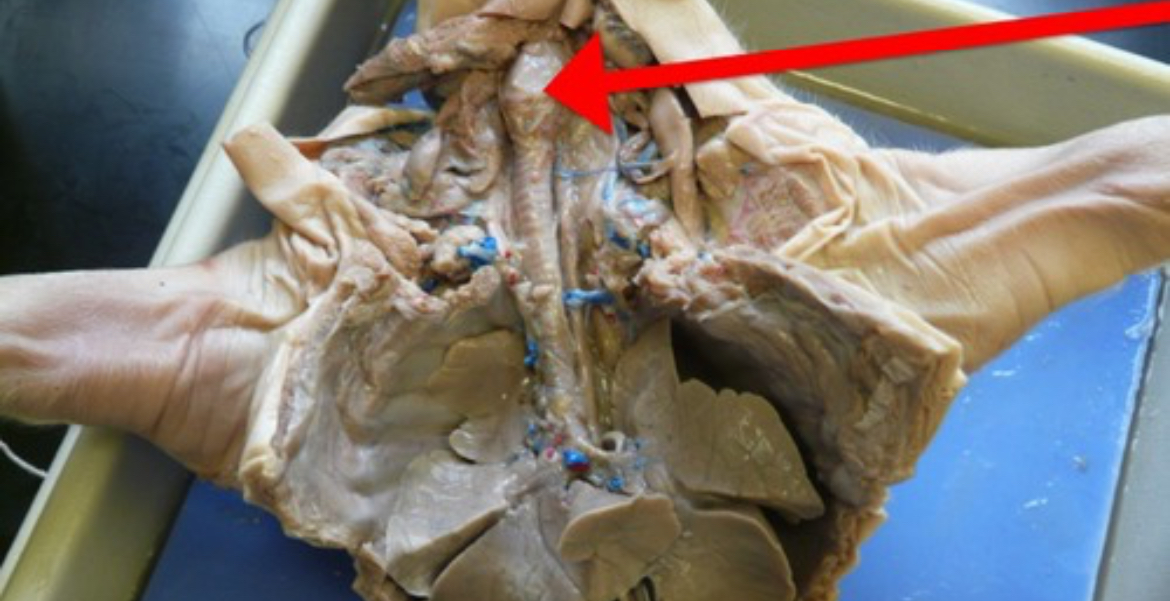
Primary Bronchi
First branches of the trachea that deliver air to each lung.
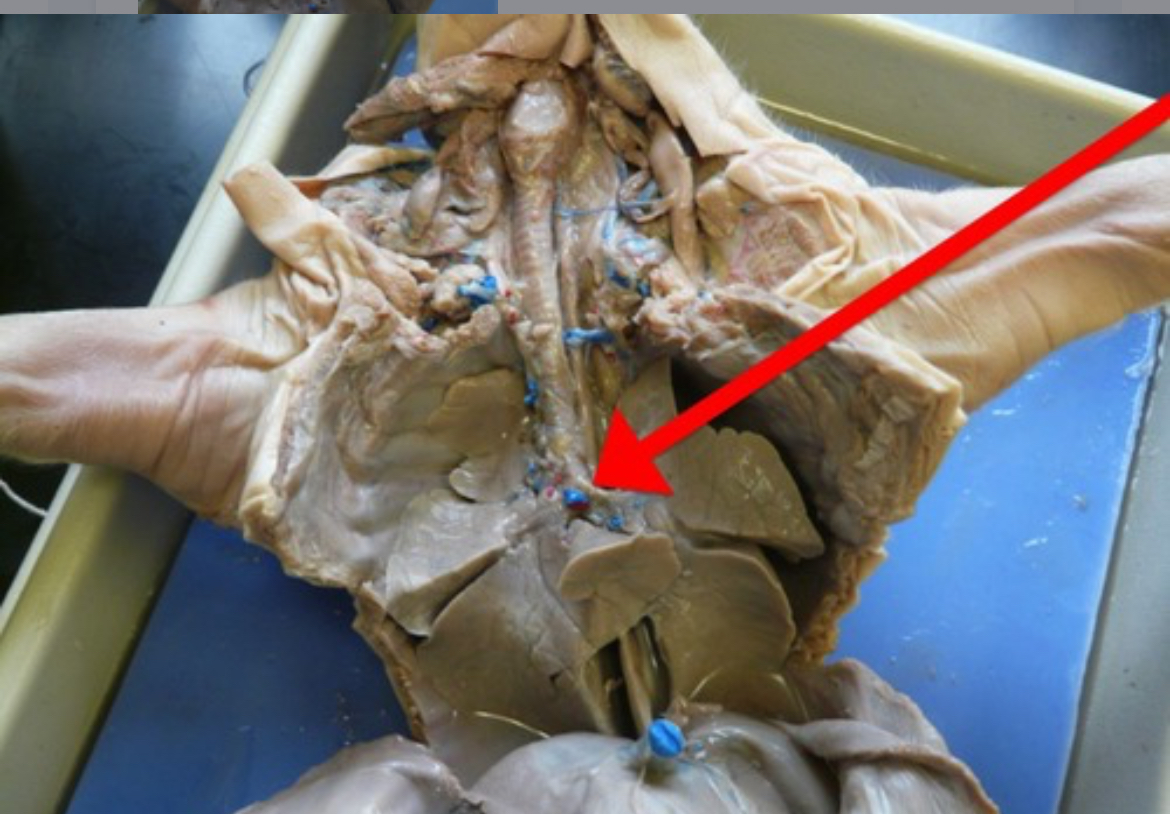
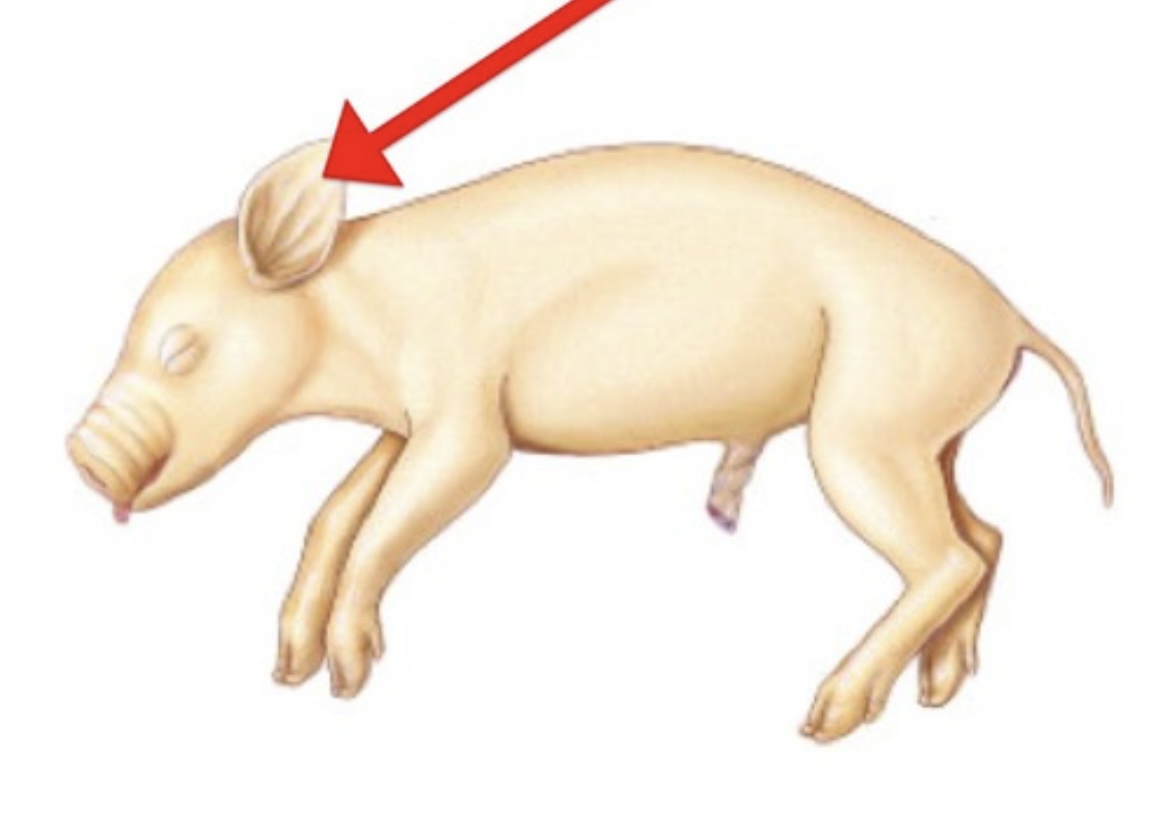
Pinna
External ear flap that directs sound waves into the ear canal.
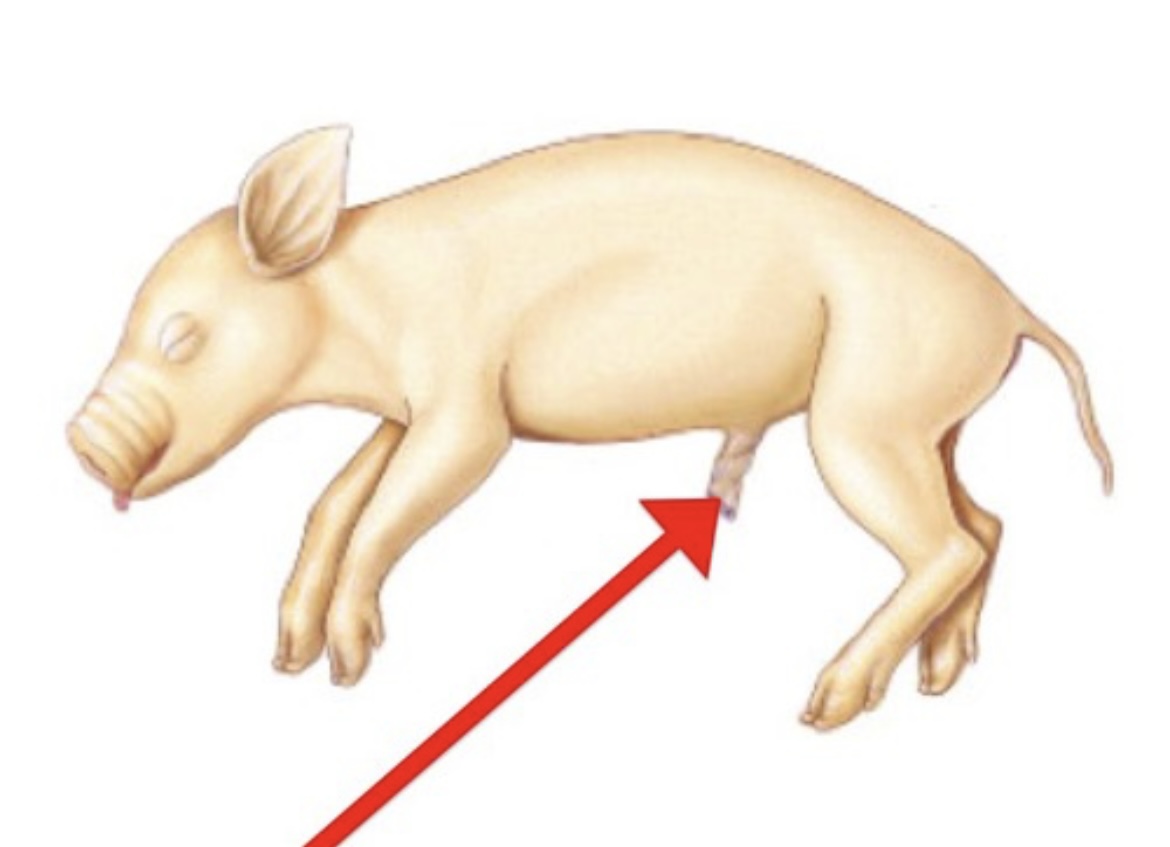
Umbilical Cord
Vascular connection between fetus and placenta transporting nutrients, gases, and wastes.
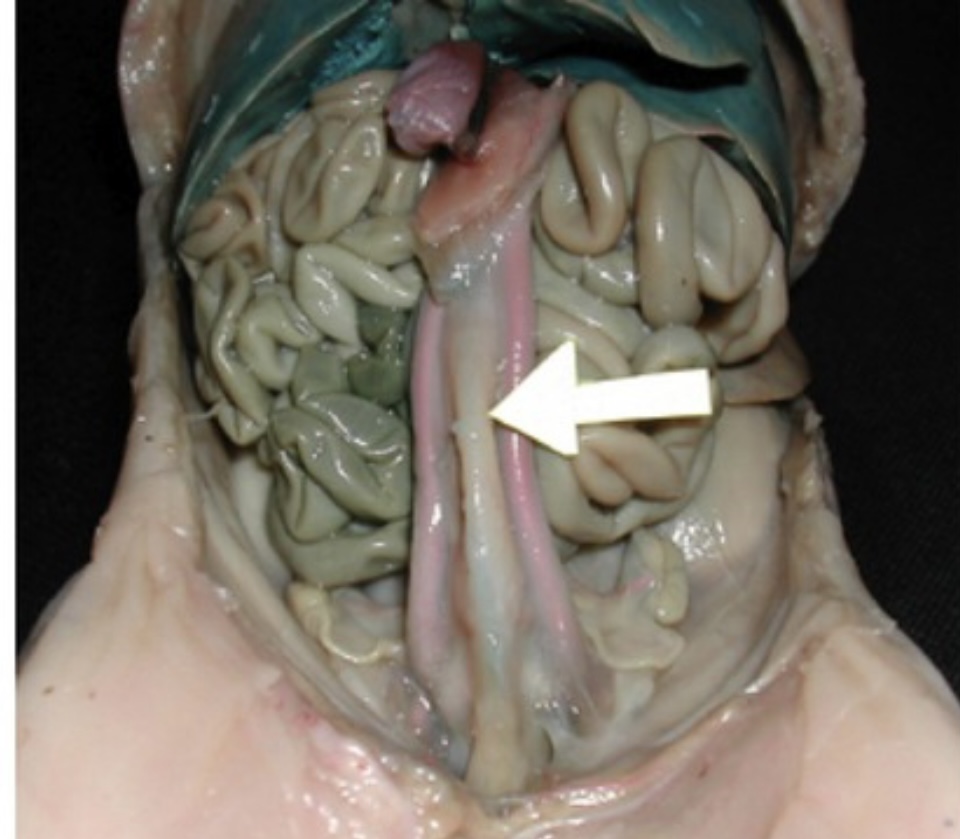
Urinary Bladder
Muscular sac that stores urine before excretion.
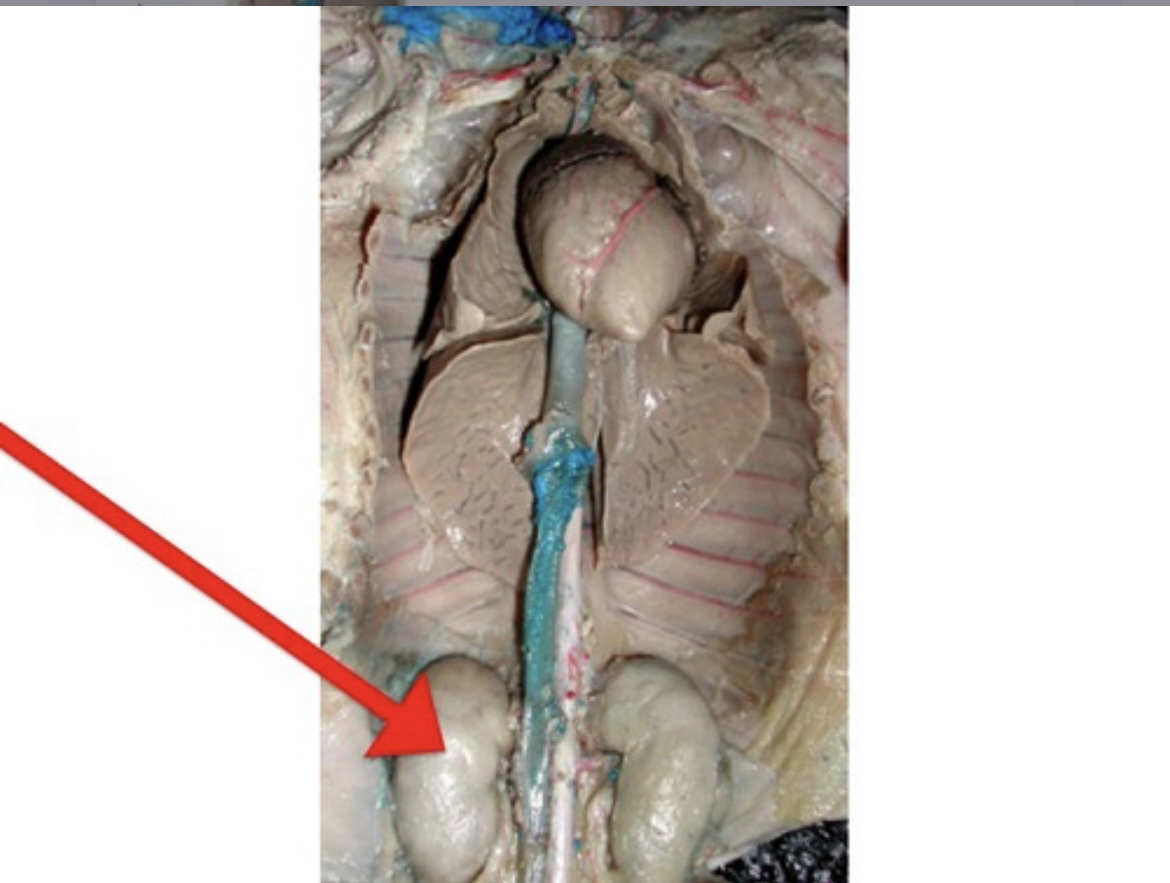
Kidney
Organ that filters blood, forming urine and regulating water and salt balance.
Transverse Plane
Horizontal body plane dividing the body into superior (cranial) and inferior (caudal) portions.
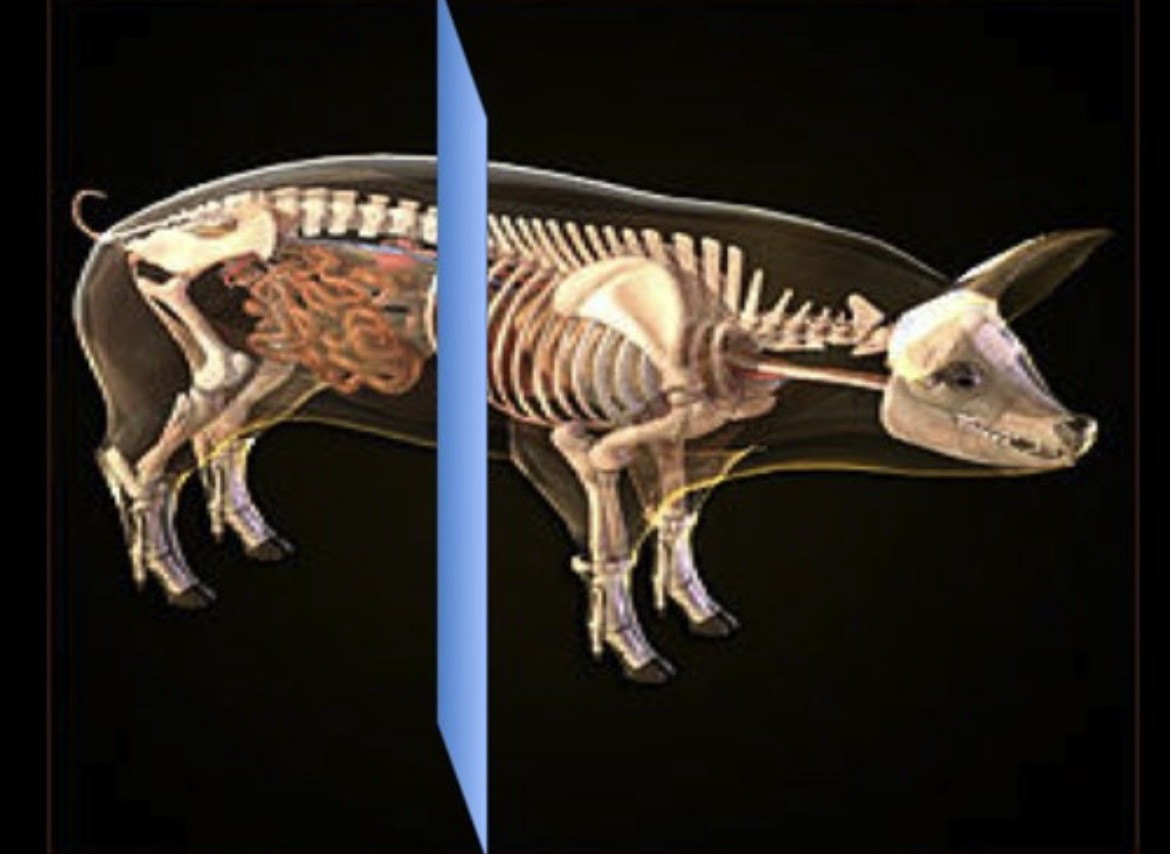
Sagittal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into left and right sections.

Frontal Plane
Vertical plane dividing the body into dorsal (back) and ventral (belly) sections.
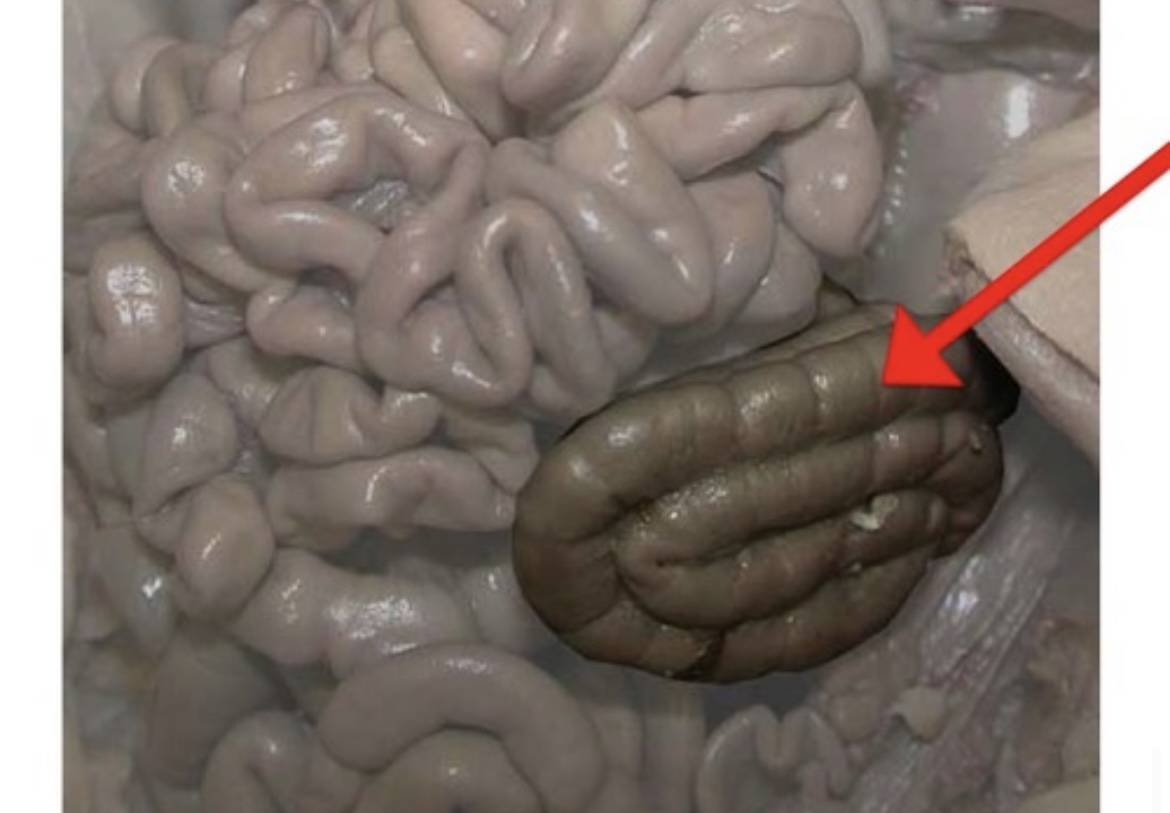
Large Intestine
Absorbs water, forms feces, and eliminates undigested material.
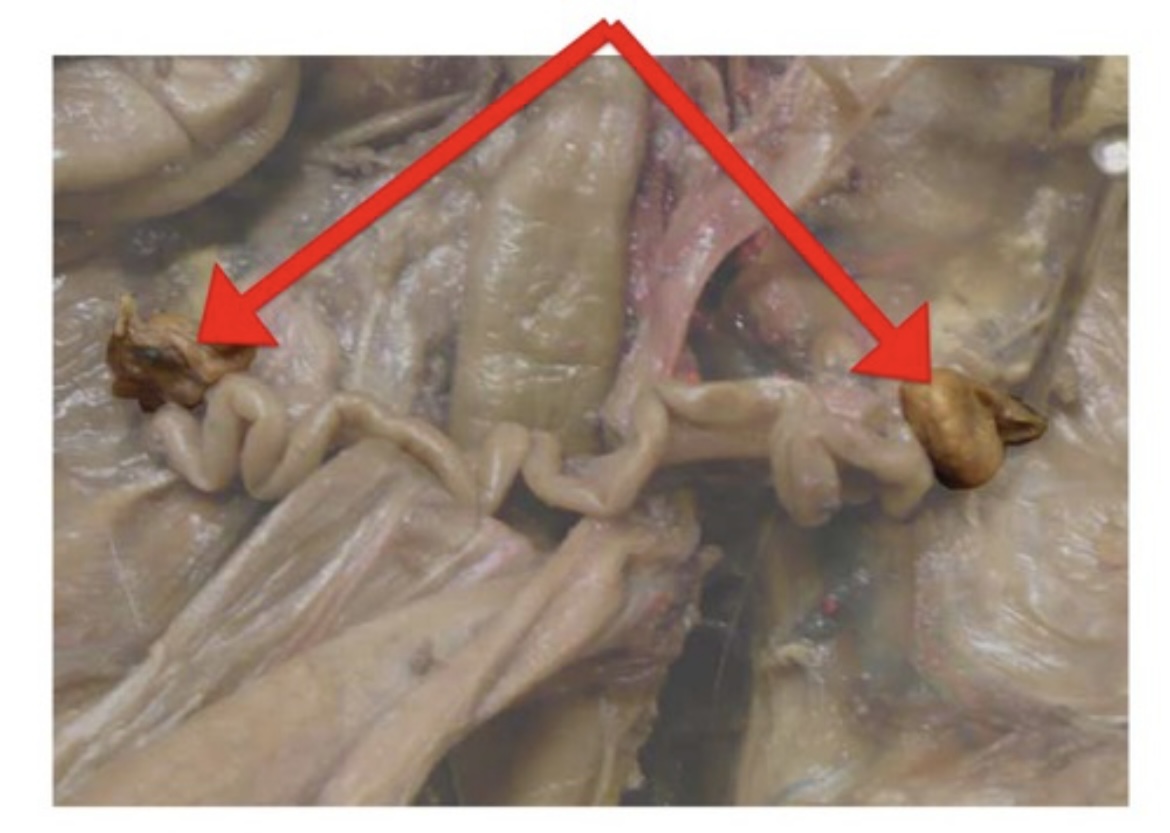
Ovaries
Female gonads that produce eggs and sex hormones.
Uterine Horns
Extensions where the uterine tubes meet the uterus; fetal development occurs here in pigs.
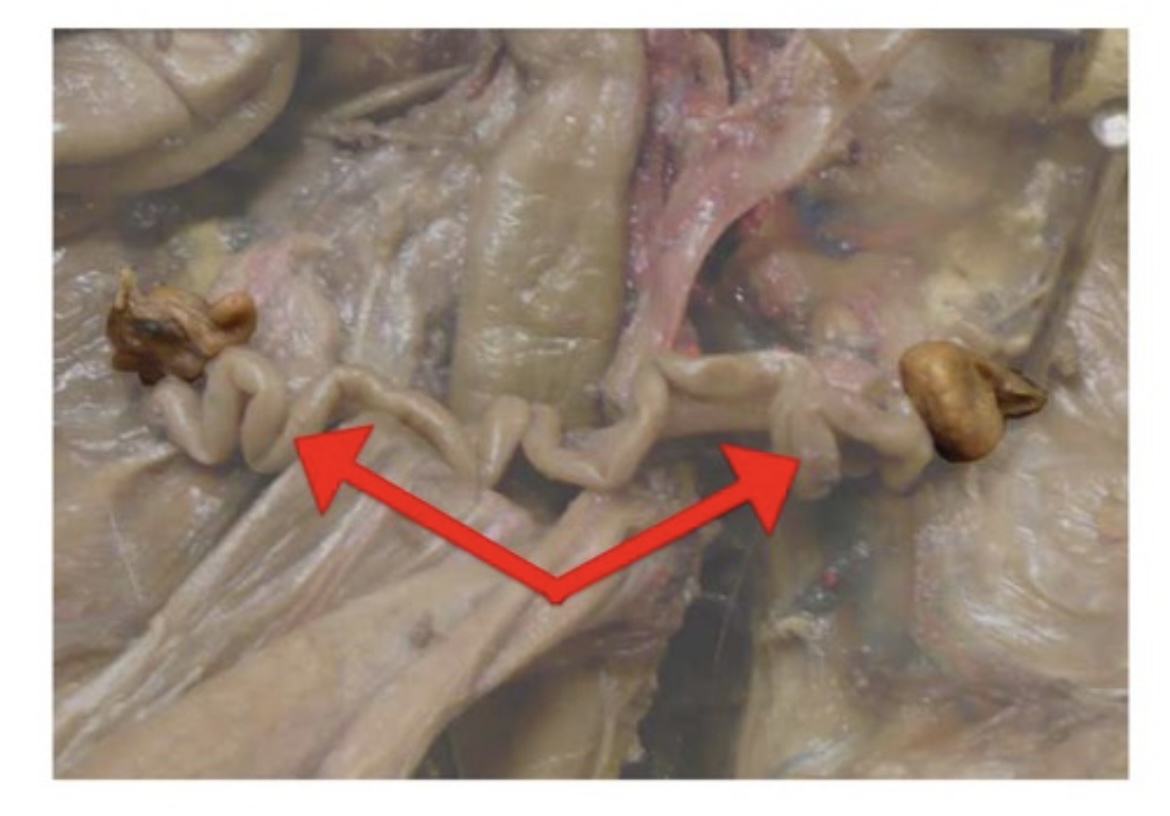
Rectum
Terminal part of the large intestine where feces are stored before elimination.
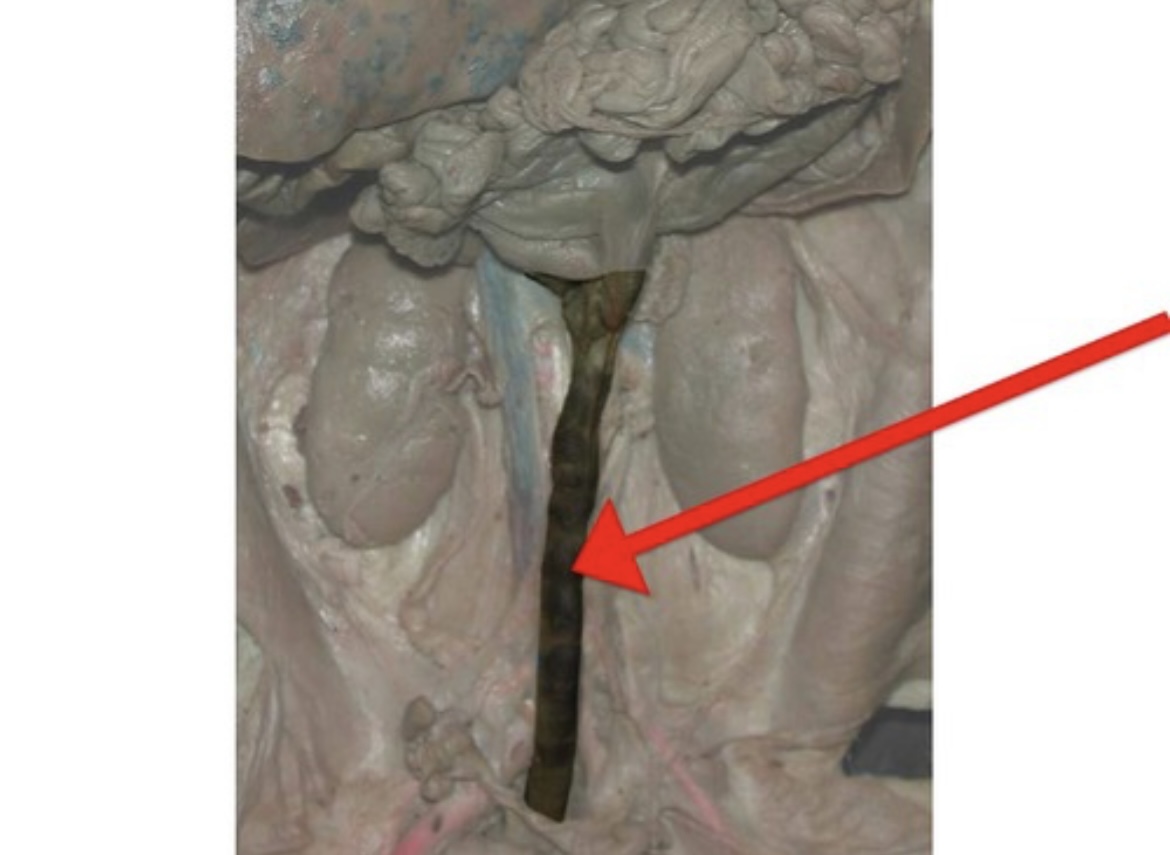

Umbilical Artery
Fetal vessel carrying deoxygenated blood and wastes from fetus to placenta.
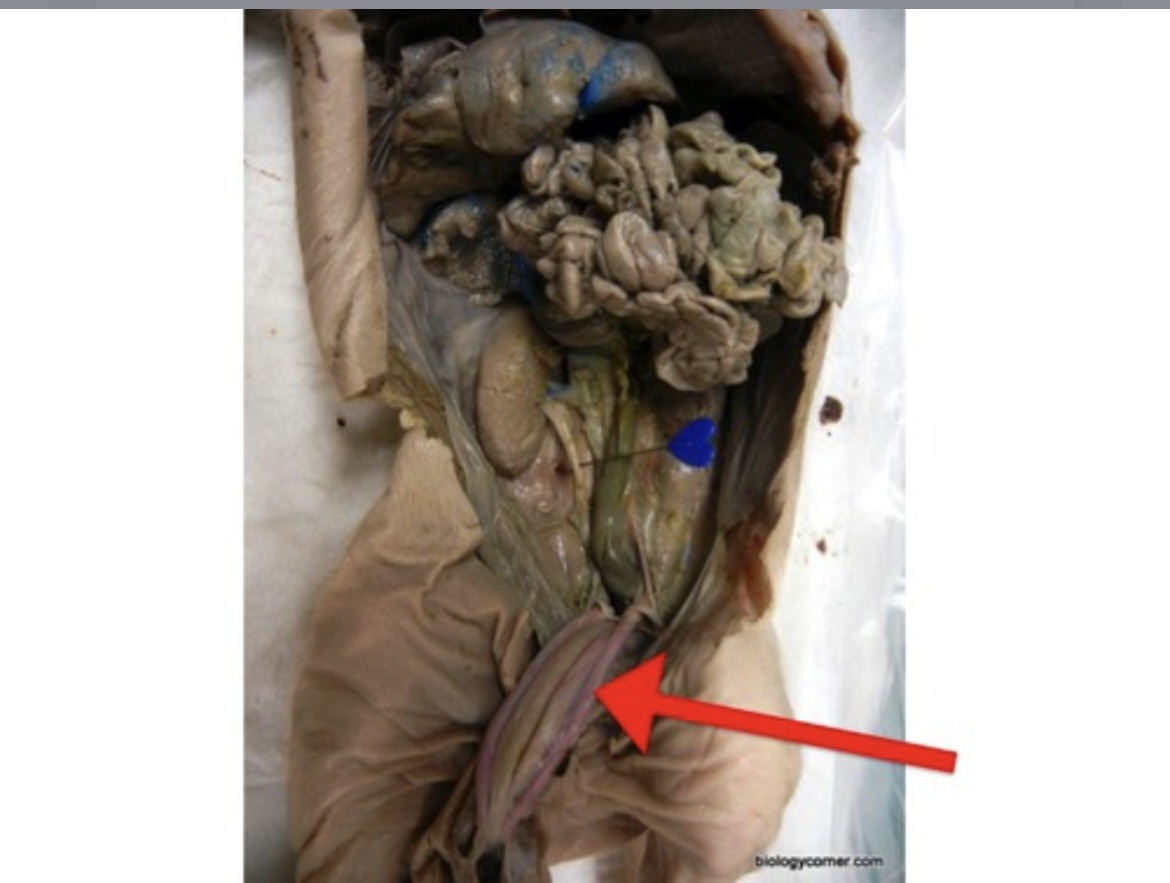

Ureter
Tube that carries urine from each kidney to the urinary bladder.
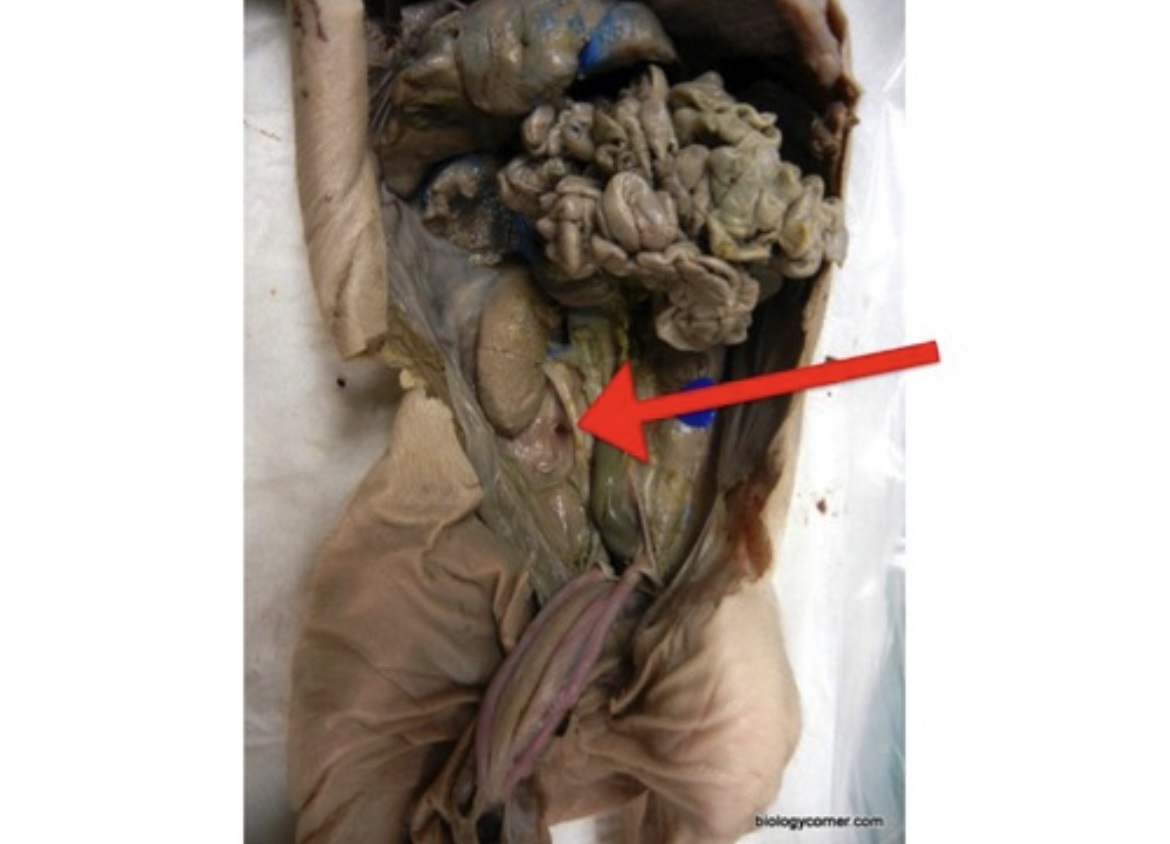

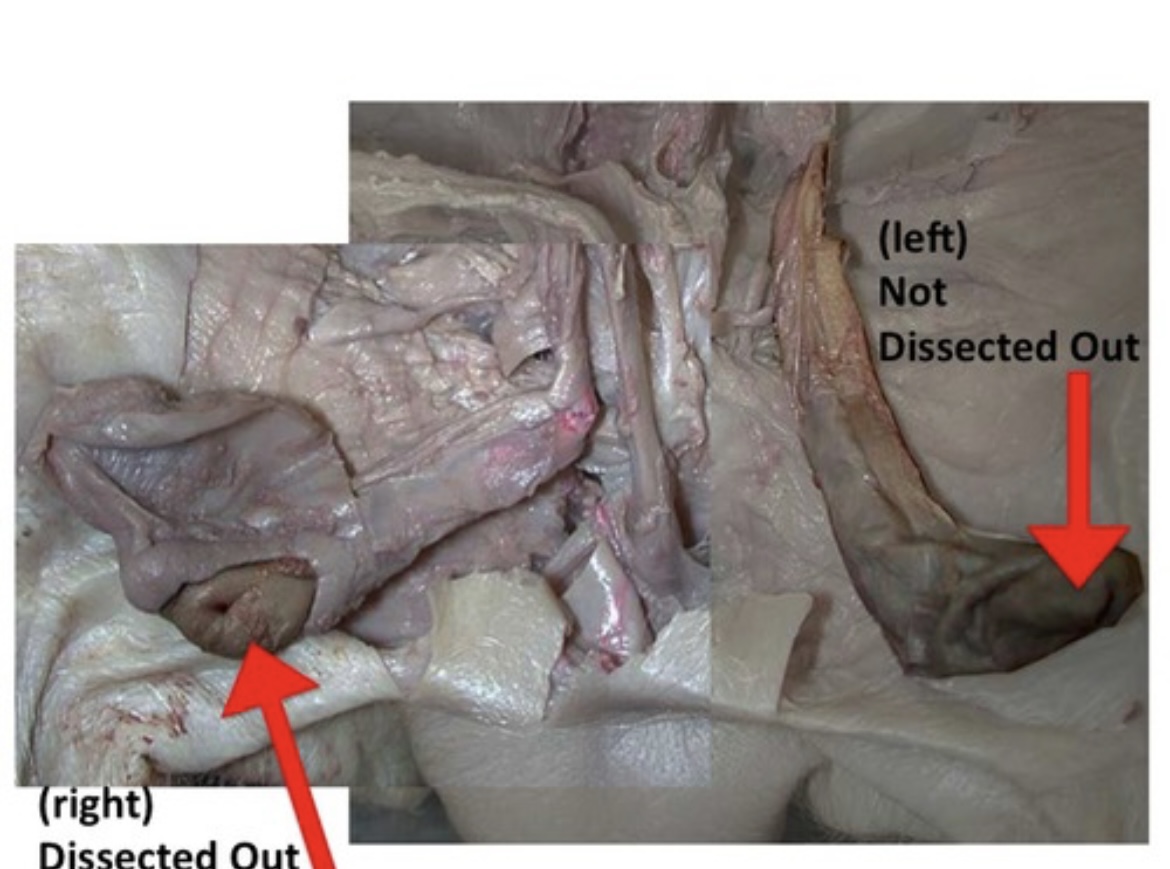
Testes
Male gonads that produce sperm and testosterone.
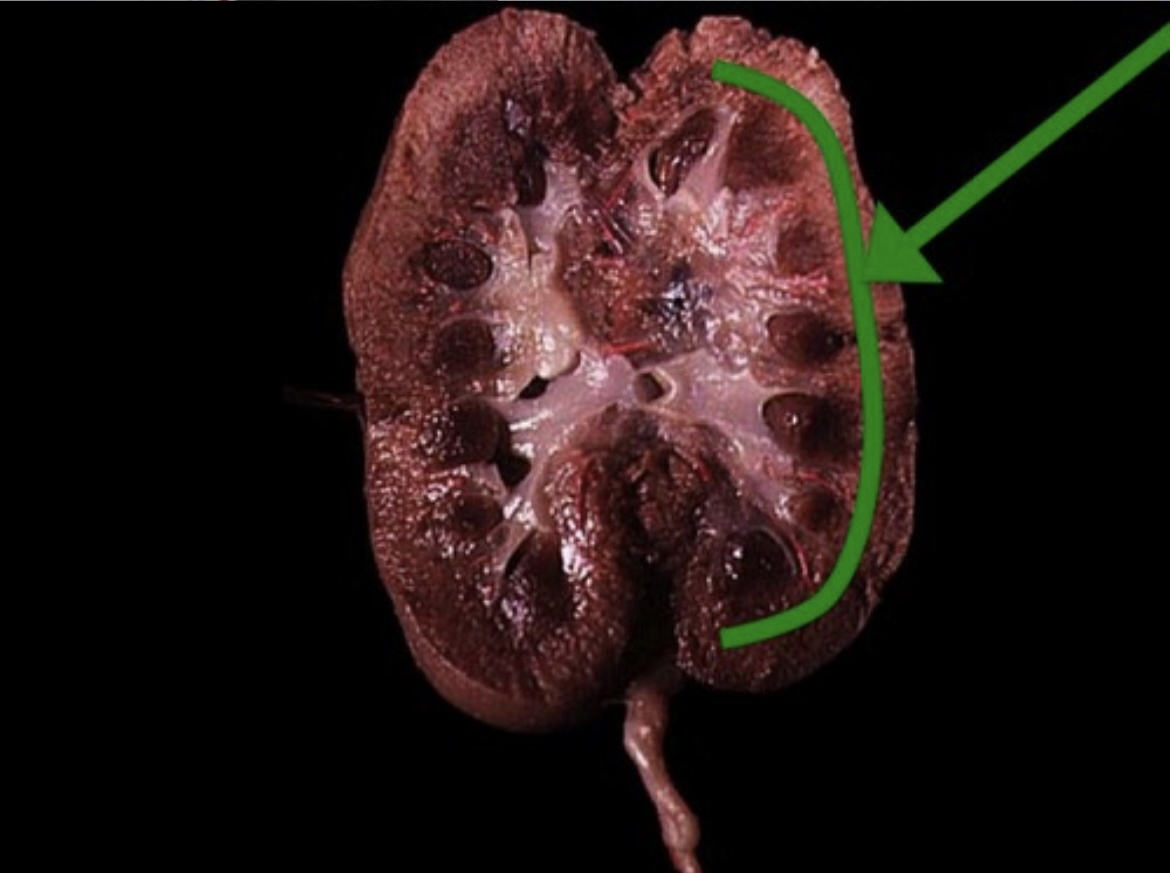
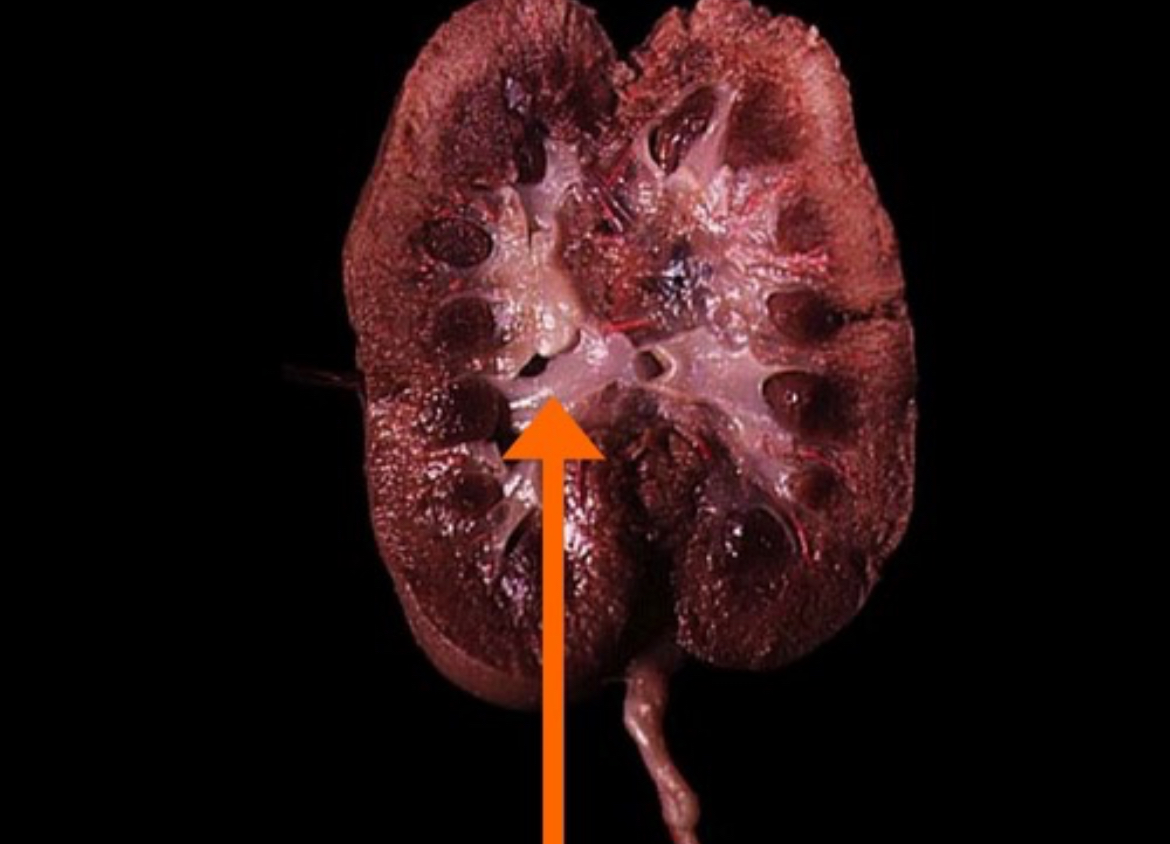
Renal Cortex
Outer region of the kidney containing nephrons’ glomeruli.
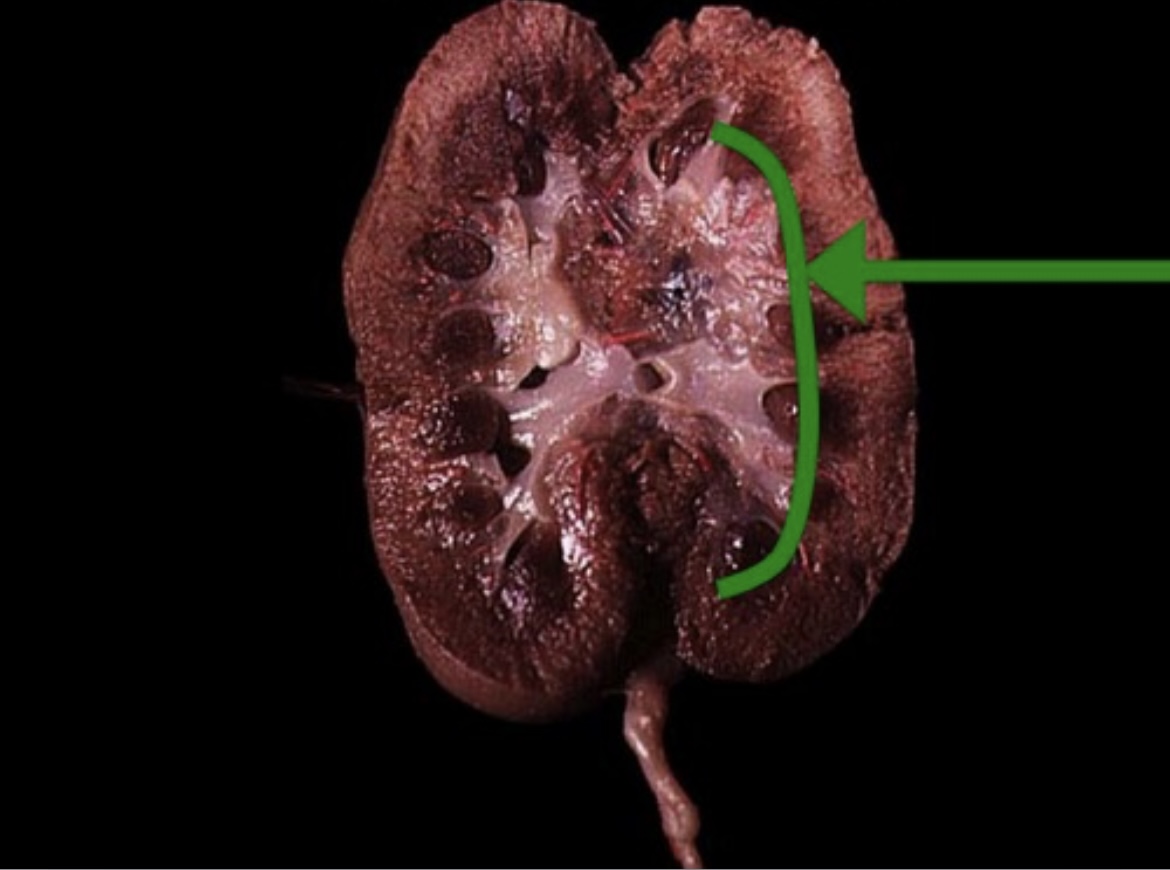
Renal Medulla
Inner kidney region composed of renal pyramids and nephron loops.
Renal Pyramid
Conical segment of the medulla that funnels urine into minor calyces.
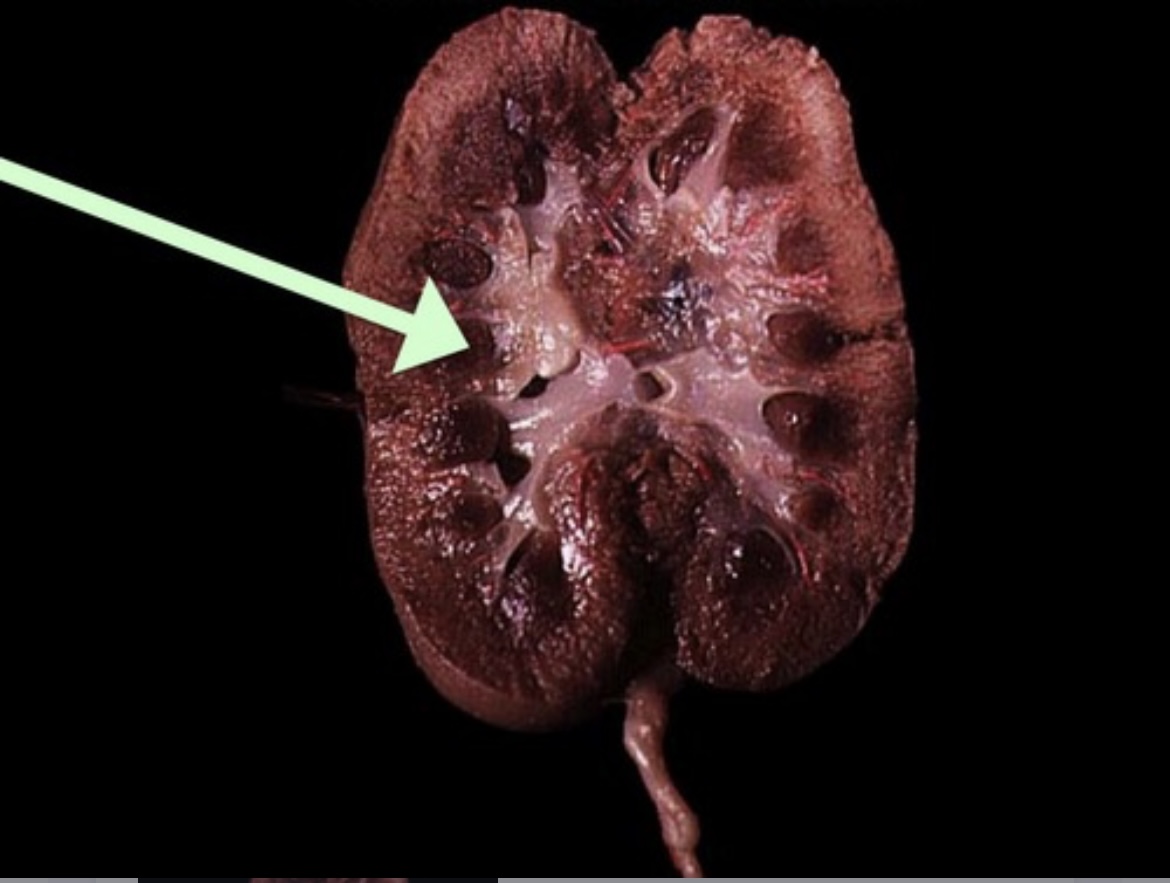
Renal Column
Inward extension of cortical tissue separating adjacent renal pyramids.
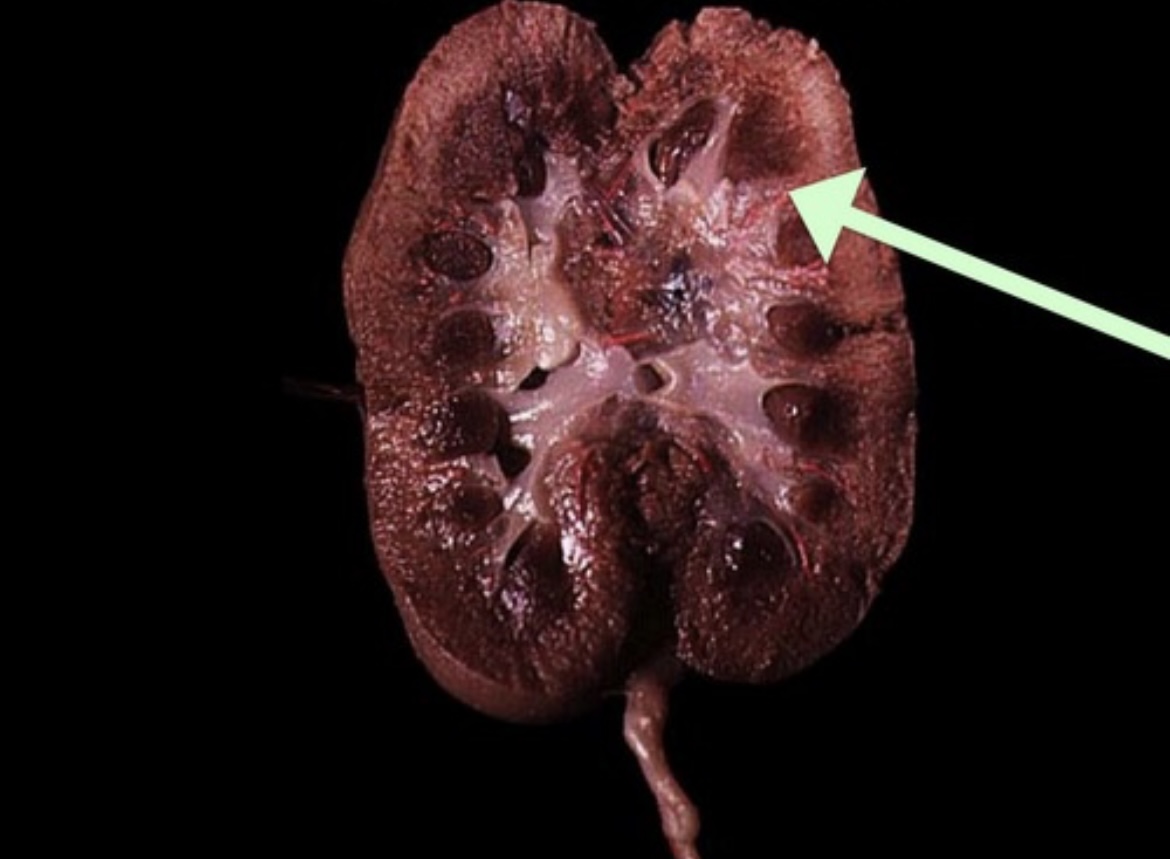
Renal Pelvis
Central funnel-shaped cavity where major calyces merge; narrows to form the ureter.
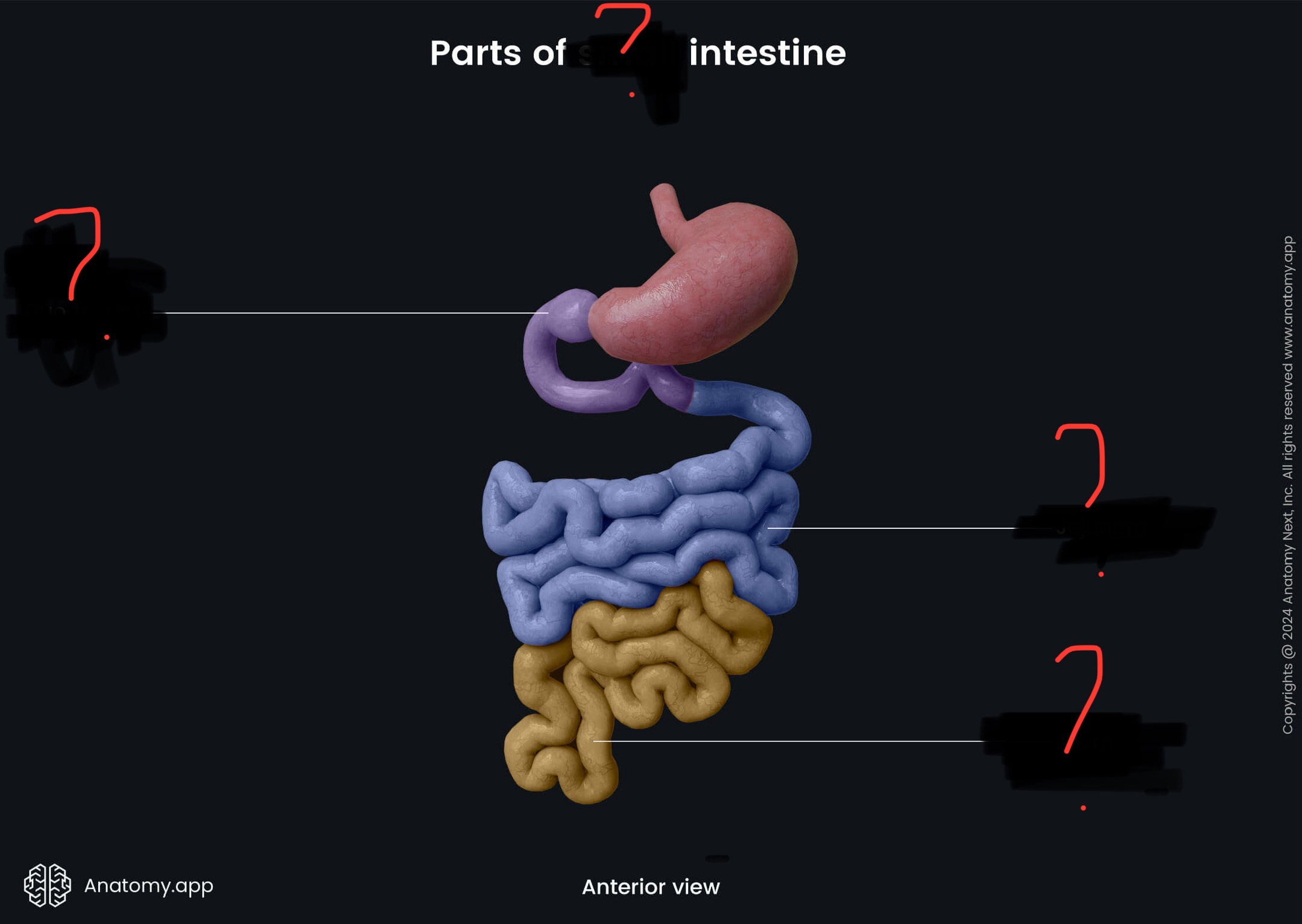
duodenum: enzymatic breakdown of food
jejuno-illeum: absorbs digestion products
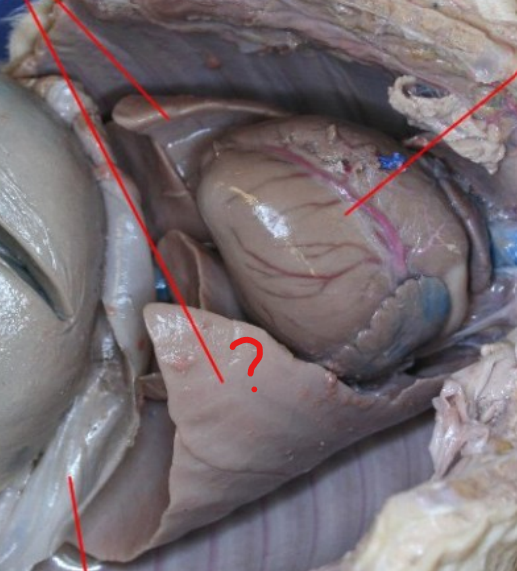
name each ? and their function
thymus
mature and produce T-lymphocytes (T-cells)
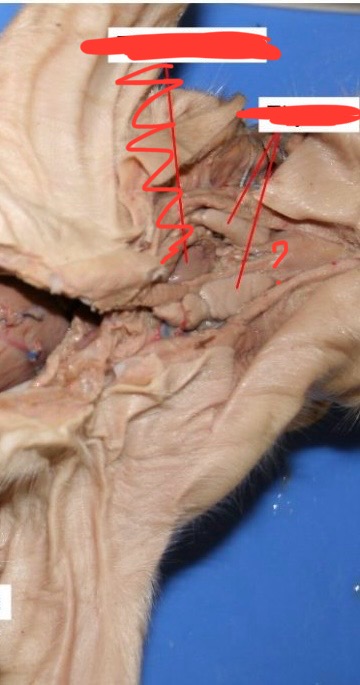
colon
reabsorbs water from waste
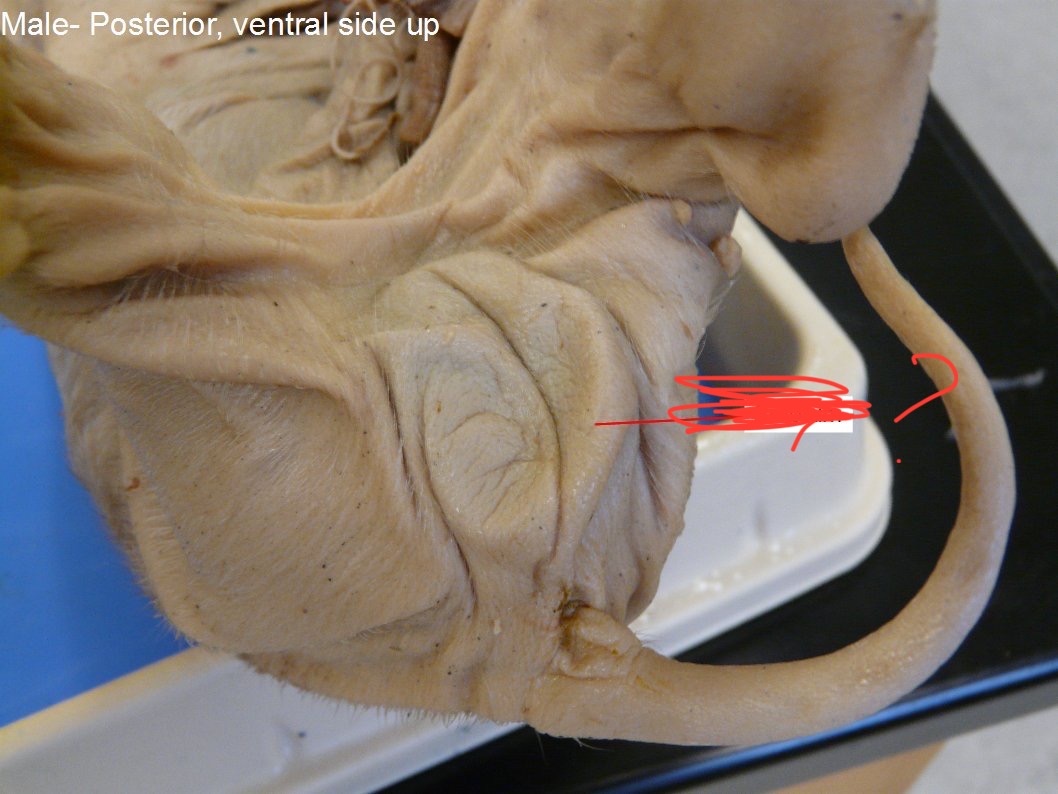
scrotum
holds testes; maintains proper temps.
epididymis
sperm storage & maturation
uterine tube
site of fertilzation
body of uterus
implantation site of embryo