A Level Biology, 3.3 - Organisms Exchange Substances with their Environment
1/126
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The internal environment of a cell or organism is different from its external environment. The exchange of substances between the internal and external environments takes place at exchange surfaces. To truly enter or leave an organism, most substances must cross cell plasma membranes. In large multicellular organisms, the immediate environment of cells is some form of tissue fluid. Most cells are too far away from exchange surfaces, and from each other, for simple diffusion alone to maintain the composition of tissue fluid within a suitable metabolic range. In large organisms, exchange surfaces are associated with mass transport systems that carry substances between the exchange surfaces and the rest of the body and between parts of the body. Mass transport maintains the final diffusion gradients that bring substances to and from the cell membranes of individual cells. It also helps to maintain the relatively stable environment that is tissue fluid.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
digestion + absorption
3.3.3 - D___________ + A___________
large biological molecules / hydrolysed / smaller molecules
Digestion: ______________________ _____________ into _________________ that can be absorbed across cell membranes.
salivary glands & pancreas / mouth & small intestine / starch / maltose
How are carbohydrates digested? (part 1)
Where is amylase produced?
Where does hydrolysis happen?
____________ → ____________
ileum epithelial membrane / disaccharides / monosaccharides
How are carbohydrates digested? (part 2)
Where are membrane-bound disaccharidase enzymes?
____________ → ____________
pancreas / small intestine / triglyceride / monoglyceride + fatty acids
How are lipids digested?
Where is lipase produced?
Where does hydrolysis happen?
____________ → ____________
liver / big lipid droplet + bile salts / smaller lipid droplets / small lipid droplets / micelles / monoglycerides & fatty acids / bile salts
How are Lipids Digested?
Where are bile salts made?
Emulsification: _____________________ → _______________
Lipase digestion of lipid: ______________ → ____________ (____________ stuck with ____________)
micelles / epithelial cells / lipid-soluble / ER / triglycerides / golgi apparatus / chylomicrons / epithelial cells / exocytosis
How are lipids absorbed?
_____________ contact with ___________ which release monoglycerides and fatty acids which are ___________ therefore can diffuse directly across the cell membrane.
In the ____________, the fatty acids link to become ______________.
In the _____________, the fat globules associate with cholesterol and proteins to form _____________.
These move into __________ by ____________.
cotransport
How are monosaccharides and amino acids absorbed?
stomach & pancreas / stomach & small intestine / polypeptide fragments / polypeptide end & amino acid
How are Proteins Digested?
Where are peptidases produced?
Where does hydrolysis happen?
Endopeptidases: polypeptide → ____________
Exopeptidases: polypeptide → ____________
Gas exchange
3.3.2 - G______ E____________
palisade mesophyll cell / xylem & phloem / spongy mesophyll cells / waxy cuticle / lower epidermis cell / stoma / guard cell / air space / upper epidermis cell / waxy cuticle
Label the structures present in a dicotyledenous plant leaf (1→10).
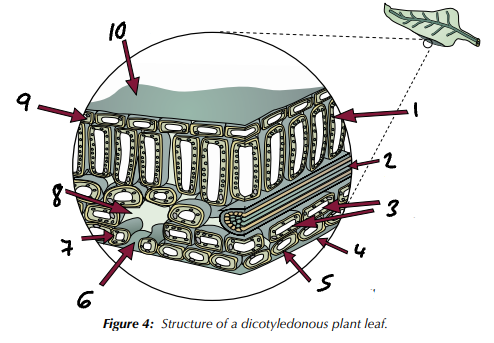
mesophyll cells / guard cells controlling stomata in epidermis
What is the main gas exchange surface in leaves? How do gases move in and out?
sunk / epidermis / curled leaves / stomata / cuticles
Gas Exchange in Xerophytic Plants - Adaptations
Stomata ____________ in pits to trap water vapour, reducing the concentration gradient of water between the leaf and the air. This reduces evaporation of water from the leaf.
A layer of ‘hairs’ on the ______________ to trap water vapour round the stomata.
________________ with the stomata inside, protecting them from wind (windy conditions increase the rate of diffusion and evaporation).
A reduced number of _______________, so there are fewer places for water to escape.
Thicker waxy, waterproof ________________ on leaves and stems to reduce evaporation.
turgid / stomatal pore / flaccid
Gas Exchange in Xerophytic Plants - Control of Water Loss
Plants’ stomata are usually kept open during the day to allow gaseous exchange.
Water enters the guard cells, making them __________, which opens the _____________________.
If the plant starts to get dehydrated, the guard cells lose water and become ___________, which closes the pore.
curled leaf traps water vapour & lowers exposed surface area / sunken stomata / upper epidermis with thick waxy cuticle / lower epidermis / epidermal hairs trap water
Label the adaptations of a xerophytic plant (1→5).
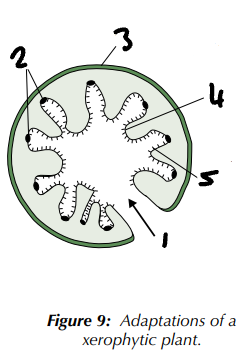
microscopic air-filled pipes / tracheoles / chitin / spiracles / exoskeleton / waterproof cuticle
Gas Exchange in Insects - Structure
Trachea - ____________________________.
Divide into ___________, continue to divide until they penetrate into individual body cells.
Stiffened with bands of ________ to prevent collapse.
Gas directly exchanged between cells and atmosphere.
Air enters trachea through pores on surface of exoskeleton called ______________ (openings along thorax and abdomen). CO2 & O2 diffuse in/out spiracles down conc gradient.
_______________ - rigid outer skeleton that covers the insects’ body surface, covered with _____________________ (layers of chitin form waterproof barrier on surface).
diffusion distance / highly branched / fluid / tracheal fluid / muscles / spiracles
Gas Exchange in Insects - Adaptations
Tracheoles have thin walls - shortens _______________ of gases to cells.
Tracheoles are _____________ - increased SA for gas exchange.
__________ in ends of trachea where joins tissue - gas exchange made faster from air to liquid through tracheoles; _______________ can be withdrawn into body fluid to increase SA of tracheole exposed to air.
___________ can pump body and force air in/out - maintains conc gradient for gasses.
__________ can be closed - prevents water loss.
trachea / abdominal pumping / pressure gradient / energy demands
Gas Exchange in Insects - Ventilation
Contracting muscles between each body segment means the insect can compress ____________ and so pump gases in/out of body.
______________________ - raises pressure in body and forces air out of spiracles down _________________.
Can be utilised to increase the removal of carbon dioxide when ________________ increase (respiration levels are highest).
gill filaments / bony gill arch / lamellae / countercurrent
Gas Exchange in Fish - Structure
Each gill made of lots of __________________ (thin plates), attached to ____________.
Gill filaments covered in ___________ (many tiny folds with lots of blood capillaries and thin layer of cells) which further increases SA.
Gas exchange happens at lamellae (through _________________ flow).
countercurrent / lamellae / capillaries / operculum
Gas Exchange in Fish - Adaptations
____________________ system ensures steep conc gradient maintained over whole length of gill - oxygen can diffuse from water into blood.
Thin walls of ______________ - shortens diffusion distance.
Large number of filaments and lamellae - increases SA.
Large number of _________________ around lamellae - circulation constantly removes oxygenated blood, maintains steep conc gradient.
Ventillation by _________________ - ensures fresh water flow over gills to replace lost oxygen, maintains steep conc gradient.
countercurrent / opposite / full length of lamellae / oxygenated / saturated
Gas Exchange in Fish - Ventilation: ________________
Water & blood flow over and through lamellae in __________ directions to each other.
Blood always flows next to water that has higher oxygen conc, so diffusion happens along ____________________.
Blood absorbs more and more ___________ as it moves along.
Even when blood is highly ______________, there is still a conc gradient so more oxygen can flow into blood.
Maintains favourable conc gradient.
Opposite to this is concurrent flow.
trachea / bronchi / bronchioles / alveoli / alveolar epithelium / capillary endothelium / blood
What is the order of movement of oxygen from the air to haemoglobin through the gas exchange system?
diaphragm contracts / external intercostal muscles contract / increased / below atmospheric pressure
Mechanisms of Breathing - Inspiration
________________ _____________ to move down and become flatter – this displaces the digestive organs downwards.
________________________ ____________ to raise the ribs.
Volume of the chest cavity is ____________.
Pressure in the chest cavity drops _______________________.
Air is moved into the lungs.
diaphragm relaxes / external intercostal muscles relax / decreased / above atmospheric pressure
Mechanisms of Breathing - Expiration
________________ _____________ and is pushed up by the displaced organs beneath.
________________ _____________ , and the ribs fall.
Volume of the chest cavity is ______________.
Pressure in the lungs increases ______________________.
Air is moved out of the lungs.
bronchoconstriction / protective / bronchodilation
Function of Smooth Muscle in Human Airways
_______________________ - contraction to reduce airflow.
Can occur in response to various stimuli such as allergens, irritants, cold air, or parasympathetic nervous system activation.
________________ mechanism to limit entry of harmful substances into the lungs.
_______________________ - dilation to increase aiflow.
Can occur in response to sympathetic nervous system activation, certain medications (such as bronchodilators), and increased levels of carbon dioxide in the blood.
Enhances airflow and gas exchange.
trachea / cartilage rings / ciliated epithelium & goblet cells
__________________
A flexible airway that is supported by ___________________ which prevent it collapsing as the air pressure inside falls when breathing in.
Its walls are made up of muscle, lined with ____________________________.
bronchi / cartilage / mucus / cilia
_______________
Two divisions of the trachea each leading to one lung. Amount of _____________ reduces as they get smaller.
Also produce ____________ to trap dirt particles and ______ that move this towards the throat.
bronchioles / contracts / epithelial
_________________
A series of branching subdivisions of the bronchi.
Walls are made up of muscle (which ______________ to control the flow of air in and out of the alveoli) lined with _________________ cells.
diaphragm / thorax / abdomen
_________________
A sheet of muscle that separates the _________ from the _____________.
alveoli / epithelium / collagen & elastic fibres
___________________
Minute air-sacs with a diameter of between 100µm and 300µm at the end of the bronchioles.
Lined with ________________.
Between the alveoli, there are some ______________________.
intercostal muscles / expiration / inspiration
____________________
Lie between the ribs.
Two sets - internal whose contraction leads to _____________ and external whose contraction leads to _______________.
air vol in each breath / 0.4-0.5 dm^3
What is the tidal volume? What is the normal value for adults?
number of breaths per minute / 15 breaths
What is the ventilation rate? What is the normal value for a healthy person at rest?
max air vol that can be exhaled in certain time
Whate is the forced expiratory value (FEV)?
max air vol possible to exhale forcefully out lungs after deep inhalation
What is forced vital capacity?
make it difficult to fully inhale by affecting elastic tissue
What do restrictive lung diseases do?
make it difficult to exhale as airways blocked
What do obstructive lung diseases do?
macrophages / alveoli / tidal volume
Lung Disease - Tuberculosis
Caused by inhalation of bacteria by droplet infection.
___________________ in the alveoli build a wall around the bacteria forming a tubercule.
The bacteria remains alive but dormant. Eventually the infected tissue dies, but damages the _____________.
Also causes fibrosis.
Reduction of __________________.
scar tissue / thicker & less elastic / tidal volume / FVC
Lung Disease - Pulmonary Fibrosis
Formation of _______________ after an infection (e.g. tuberculosis) or from inhaling substances like asbestos.
This is ___________________ than normal lung tissue so lungs are less able to expand and can’t hold as much air as normal.
Reduction of _______________ and __________.
smooth muscle / mucus / FEV1
Lung Disease - Asthma
Airways become inflamed because of an allergic reaction.
__________________ in bronchiole contracts and lots of _________ produced.
Reduction of _________.
emphysema / phagocytes / elastin / alveolar sa
Lung Disease - __________________
Foreign particles (eg from smoking or pollution) trapped in alveoli.
Causes inflammation, attracts ______________ which release an enzyme that can break down the ______________ in the walls of alveoli.
Reduction of ________________.
mass transport in plants
3.3.4.1 - M_____ T______ in P_______
biconcave / haemoglobin / nucleus
Erythrocyte (red blood cell) adaptations for transporting oxygens
_________________ structure gives high SA:V ratio
Contains a large amount of _________________ molecules (around 30 million)
The __________ is lost before they enter circulation so greater volume to carry haemoglobin.
conjugated / quaternary structure / oxyhaemoglobin
Haemoglobin
Four polypeptide subunits (2 alpha, 2 beta).
Each subunit contains haem (so a _____________ protein) which binds to oxygen in the lungs and releases oxygen in blood tissue. Haem group contains a Fe²⁺ ion so one haemoglobin can bind to 4 oxygen molecule.
When oxygen attaches to haemoglobin, the __________________ changes slightly to make it easier for oxygen to attach. This forms _____________________.
pO2 / O2Hb sat / sigmoid curve
On the oxygen dissociation curve…
What is on the X axis?
What is on the Y axis?
What is the shape of the curve called?
low affinity / 1 / positive cooperativity / 3 / 4
What does the oxygen dissociation curve tell us about haemoglobin?
Initially, as partial pressure of oxygen increases, there is a slow increase of saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen.
At low partial pressures of oxygen, haemoglobin has a _______________ for oxygen.
On avg each haemoglobin molecule is bound to ___ oxygen molecule.
Then, as partial pressure of oxygen increases, there is a general increase of saturation of haemoglobin.
__________________: once one oxygen molecule is bound, the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen increases and it becomes much easier to bind further oxygen molecules (due to change in quaternary structure of haem group).
On average each haemoglobin molecule is bound to ___ oxygen molecules.
Initially, as partial pressure of oxygen increases, there is a slow increase of saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen.
The chances of an oxygen molecule colliding with the ___th haem group is relatively low.
requires relatively small pO2 increase
What does positive cooperativity mean for increasing the oxyhaemoglobin saturation?
pO2 decreases / quaternary structure
How Can the Oxygen Dissociation Curve be Seen in the Human Body?
In the alveoli, the partial pressure of oxygen is high and the haemoglobin in red blood cells is around 97% saturated.
As red blood cells make their way into the body tissues, ________________ as tissues are carrying out aerobic respiration.
At a certain point, one oxygen molecule now unloads from the haemoglobin molecule which changes its ___________________ and decreases oxygen affinity of remaining haem groups.
If red blood cells move into more active tissue, oxygen partial pressure will be even lower and two more oxygen molecules will rapidly unload.
For final oxygen to unload, partial pressure of oxygen has to be very low. Unlikely to happen under normal conditions but could take place in very active tissues eg muscle tissue in intense exercise.
quaternary structure changes / uncovers another haem group to bind to
Why does binding of one O2 molecule make it easier for the second to bind?
pO2
What is the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen dependent on?
shifts dissociation curve to right / Bohr effect / CO2 decreases hb O2 affibity / H+ from carbonic acid combines w hb so quaternary structure changes
What happens to saturation of haemoglobin with oxygen when there is a high partial pressure of carbon dioxide?
Why? Elaborate.
Why does this effect happen?
pCO2 low / pO2
What are the effects of high partial pressure of carbon dioxide on the oxygen dissociation curve?
Haemoglobin has higher oxygen affinity where ____________, eg in the lungs.
Haemoglobin has lower _________ where partial pressure of CO2 is high, eg in active tissue undergoing aerobic respiration such as muscle tissue. As haemoglobin now has lower oxygen affinity, it is much more likely to unload bound oxygen in these tissues.
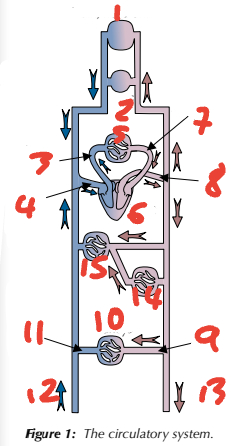
heart / lungs
Where does the pulmonary artery carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
lungs / heart
Where does the pulmonary vein carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
heart / body
Where does the aorta carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
body / heart
Where does the vena cava carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
body / kidneys
Where does the renal artery carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
kidneys / inferior vena cava
Where does the renal vein carry blood from? Where does it carry blood to?
gut
What is another name for the digestive tract or a part of it?
1 brain, head, neck / 2 arms / 3 pulmonary artery / 4 vena cava / 5 lungs
Label the circulatory system (1→5, place number before blood vessel)
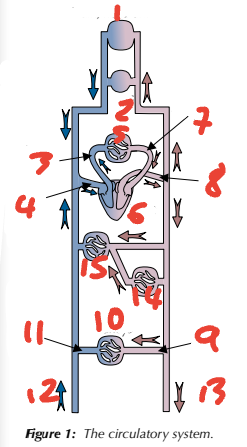
6 heart / 7 pulmonary vein / 8 aorta / 9 renal artery / 10 kidneys
Label the circulatory system (6→10, place number before blood vessel)
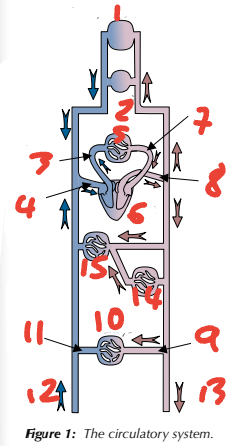
11 renal vein / 12 from lower limbs / 13 to lower limbs / 14 gut / 15 liver
Label the circulatory system (11→15, place number before blood vessel)
endothelium / folded / stretch & maintain high pressure / veins & capillaries
What is the inner lining of arteries called?
What is special about it?
What does this help it do?
Where else is this found?
tissue capillary network / arterioles & venules
What are capillary beds? What do they connect together in these?
tissue fluid
_______________
In the capillaries, fluid passes out of blood and bathes tissue cells.
Leaves blood at parts of capillary which are near the artery. Transfers molecules such as oxygen and glucose to tissue cells - waste molecules such as CO2 pass into tissue fluid which returns to bloodstream at parts of capillary near the vein.
arterial end / endothelial cells / gap / basement membrane / venous end
Label the capillary (1→5, place number before component)
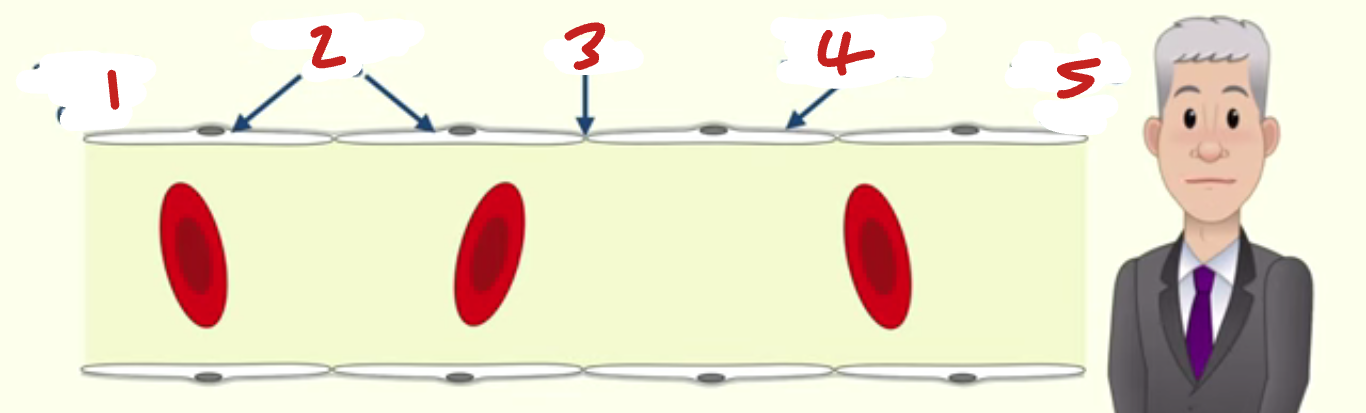
arteriole end / venule end
In the Capillary…
Where is the tissue fluid forced out of blood?
Where does the tissue fluid return to the blood?
hydrostatic pressure / hydrophilic
The Circulatory System - Tissue Fluid
At the arteriole end of the capillary, the blood has just passed through an artery and an arteriole so there is high ________________ which forces fluid out of blood into tissue.
Plasma proteins are ________________ so lower the water potential of blood plasma so tendency of water to move back into blood by osmosis.
hydrostatic / oncotic
The Circulatory System - Tissue Fluid
At the arteriole end of the capillary, which pressure is higher, compared to that of tissue fluid?
At the venule end of the capillary, which pressure is higher, compared to that of tissue fluid?
blind-ended vessels / lymph capillaries / lymphatic system / skeletal muscles / valves / collar bone
The Circulatory System - Tissue Fluid
Most of the tissue fluid reabsorbed back into the blood (90%) but 10% drains into a series of ___________________ called _________________ which connect into larger lymph vessels, forming the ___________________.
Lymph fluid moves along when lymph vessels are squeezed by nearby ________________ and _____________ keep them moving.
Eventually, lymph fluid returns to bloodstream via blood vessels under the ________________.
link atria to ventricles / stop blood backflow into atria when ventricles contract
What do the atrioventricular valves do in the heart?
blood vol pumped in each heartbeat / CO / HR
What is stroke volume? How is it worked out?
blood vol pumped by the heart per minute / stroke volume x heart rate
What is cardiac output? How is it worked out?
link ventricles to pulmonary artery & aorta / stop blood flowing back into heart after ventricles contract
What do the sumi-lunar valves do in the heart?
attach AV valves to ventricles to stop them being forced up into atria when ventricles contract
What do the cords do in the heart?
more powerful contraction so blood can be pumped around body rather than just to lungs
Why does the left ventricle of the heart have thicker, more muscular walls than the right ventricle?
so blood can be pushed out of heart rather than just to ventricles
Why do ventricles have thicker walls than atria?
vena cava
Right Atrium
Receives deoxygenated blood from ______________ from body.
The right atrium is the first chamber that deoxygenated blood flows through.
atrioventricular valves / pulmonary artery / semi-lunar valves
Right Ventricle
Receives: deoxygenated blood from right atrium.
______________________ prevent blood from flowing back into the atria from the ventricles.
Then the walls of the right ventricle contracts, blood is pumped out of the ____________________ to the lungs.
The _________________ prevent blood from flowing back into the right ventricle from the pulmonary artery.
pulmonary vein
Left Atrium
Receives: Oxygenated blood from the _____________________ from the lungs.
AV valves
Left Ventricle
Receives: oxygenated blood from left atrium.
The _____________ prevent blood from flowing back into the atria from the ventricles.
semi-lunar valves
Aorta
Receives: oxygenated blood from left ventricle.
Oxygenated blood leaves the heart through the aorta.
The _____________________ prevent blood from flowing back into the left ventricle from the aorta.
higher pressure behind / higher pressure in front
What forces valves open? What forces valves shut?
atrial systole / ventricular systole / diastole
What are the 3 stages of the cardiac cycle?
pressure / ventricles
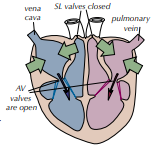
Cardiac Cycle - Stage 1: Atria Contract, Ventricles Relax
Blood from the lungs flows into the left atrium and blood from the body flows into the right atrium simultaneously.
The atria contract, increasing the ____________ in the atria.
The blood in the atria is forced into the ________________.
The ventricles are relaxed and fill with blood.
stage 1: atrial systole / ventricles relax, atria contract
Which stage of the cardiac cycle is shown by the photo? What happens?
pressure / AV valves
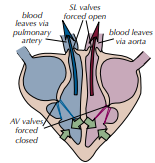
Cardiac Cycle - Stage 2: Ventricles Contract, Atria Relax
Contraction of the ventricles causes the ___________ to increase.
The pressure shuts the _____________ so that blood does not flow back into the atria.
The blood in the ventricles is forced out of the ventricle
stage 2: ventricular systole / ventricles contract, atria relax
Which stage of the cardiac cycle is shown by the photo? What happens?
pulmonary artery / aorta / SL valves / AV valves
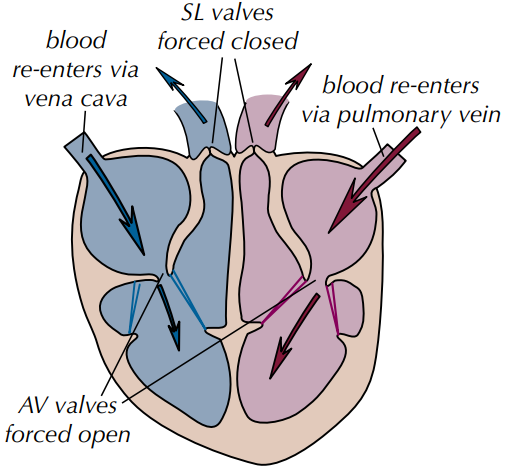
Cardiac Cycle - Stage 3: Ventricles Relax, Atria Relax
The blood in the _______________ and the ________ is at high pressure - pressure shuts the __________________ so that blood does not flow back into the ventricles.
Both the ventricles and the atria relax and the _________________ reopen.
Blood flows into the ventricles and the atria from the pulmonary vein and vena cava.
stage 3: diastole / ventricles relax, atria relax
Which stage of the cardiac cycle is shown by the photo? What happens?
atheromas / plaques / increasing bp / haemorrhage
Cardiovascular Disease - Aneurysms
Starts with the formation of _______________.
_______________ damage and weaken arteries.
Narrow arteries, _____________.
When blood travels through a weakened artery at high pressure, it may push the inner layers of the artery through the outer elastic layer to form a balloon-like swelling of the artery.
This aneurysm may burst, causing a __________________.
atheroma / plaque / endothelium / platelets & fibrin / blood clot / debris
Cardiovascular Disease - Thombrosis
Starts with the formation of _______________.
__________ can rupture the _______________ (inner lining) of an artery. This damages the artery wall and leaves a rough surface.
_______________________ accumulate at the site of damage and form a ______________ (a thrombus).
Can cause a complete blockage of the artery, or it can become dislodged and block a blood vessel elsewhere in the body.
___________ from the rupture can cause another blood clot to form further down the artery.
overweight / high bp / atheroma formation / blood clots
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease - High Blood Pressure
Not exercising, _________________, etc → _______________ → _______________ → _______________ → myocardial infarction.
high blood cholesterol / high bp / atheroma formation / blood clots
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease - High Blood Cholesterol & Poor Diet
1. Diet high in sat fat / 2. diet high in salt→ 1. _________________ / 2. _________________ → _________________→ myocardial infarction.
CO / less O2 in blood & tissues / fewer antioxidants / coronary artery wall damage / atheroma formation
Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease - Smoking
→ _________________→ _________________ → myocardial infarction.
→ _________________→ _________________ → _________________ → myocardial infarction.
light intensity / temperature / humidity / wind
What are the factors that affect transpiration rate?
humidity
Which of the factors affecting transpiration rate has a negative correlation?
stomata / CO2
Factors Affecting Transpiration Rate - Light Intensity
Positive correlation.
________________ open when light to allow diffusion of ______ into plant for photosynthesis.
kinetic energy / evaporate / water potential gradient
Factors Affecting Transpiration Rate - Temperature
Positive correlation.
Warmer water molecules have more _________________ so they ______________ from the cells inside the leaf faster. This increases the ________________________ between the inside and outside of the leaf, making water diffuse out of the leaf faster.
water potential gradient
Factors Affecting Transpiration Rate - Humidity
Negative correlation.
If the air around the plant is dry, the _____________________ between the leaf and the air is increased.