Microbio Lab Midterm Review
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Material Safety Data Sheet (MSDS)
contains details of the hazards associated with a chemical, and gives information on its safe use
act quickly and help pat down person on fire, then guide them to nearest fire safety station
what do you do in case of a fire?
Sterility
The absence of all living microorganisms, spores and viruses
Asepsis
The prevention or reduction of the probability of contamination by micro-organisms. A lack of growing microorganisms
sepsis
The presence and growth of pathogens within a living system, typically tissue such as blood
cidals
A process or material that kills living things.
Statics
A process or material that harms but does not kill living things
Fimbriae
attachment structures on the surface of some prokaryotes
Adhesin proteins
proteins used for attachment to different surfaces
Fomites
nonliving surfaces
Surfactants
the ability to change the shape of other select molecules
Antimicrobial
An agent or action that will kill or inhibit microorganisms
Antiseptic
An agent or action typically designed to be used on living tissue that rarely kills but does inhibit the growth of micro-organisms but has no effect on "spores"
Autoclave
A device which uses live steam (typically at 121 ºC or higher)or toxic gas to destroy both microbes and the spores created by manymicrobes. Theoretically results in a complete absence of living organisms
Bacteriocide
An agent, usually a chemical, that kills bacteria
Bacteriostat/ Bacteriostatic
An agent that inhibits the growth of bacteria, but does not necessarily kill bacteria
Commensal(s)
Typically non-pathogenic micro-organisms that live and reproduce on or in humans and animals normally not affecting the host directly
Contamination
The introduction of or inoculation with undesired microorganisms of sterile areas and or materials.
Disinfectant
An agent that will kill or remove microorganisms but will not necessarily destroy spores
Nosocomial
refers to contamination by pathogenic or nonpathogenic microorganisms in a clinical or hospital setting. Usually results from failure to observe Aseptic Technique in those settings
Pasteurization
A process that uses very high temperatures (water or steam) for very brief period of time to kill many microorganisms while inhibiting the remainder
Pathogenic/Pathogen
Refers to a microorganism capable of or prone to causing a disease state
Sanitation
A process that reduces microbial populations to low or acceptable numbers.
Sterile
The absence of all living microorganisms, spores and viruses.
Sterile Field
An area wherein microorganisms have been killed or removed with a reasonable degree of certainty, usually for a specified period of time
Aseptic Field
An area wherein microorganisms have been sufficiently inhibited such that they present a manageable or negligible risk
Sterilization
The process by which complete destruction or removal of all living microorganisms including spores and viruses is accomplished
Subculture
The process of transferring a specimen from one growth chamber to another for the purpose of continued cultivation or analysis.
to limit the probability of infection or contamination as much as possible
what are the goals of hand washing?
hand-washing, gloves, 70% ethanol or isopropyl alcohol, bunsen burner
the methods and instruments used in this lab to practice the aseptic technique: disinfectant
used to sterilize inoculating loops and needles
the methods and instruments used in this lab to practice the aseptic technique: Use of flame
used to transfer specimens in an antiseptic and safe way
the methods and instruments used in this lab to practice the aseptic technique: Inoculating Loop/needle
Ubiquity
the state of being everywhere at once (or seeming to be everywhere at once)
Microbial Competition
The interaction between microorganisms as they compete for limited resources.
Mutualism
Both the host organism and the microorganism benefits from the interaction
Commensalism
Microorganism will benefit and prosper from living in or on the host. The host is not always advantaged or disadvantaged by this
Parasitism
Only the microorganism benefits at the cost of the host organism, which is usually harmed to some degree by the interaction
lower, acidic
Staphylococcus species will _________ the pH of the skin to _________ levels
oral cavity
where would you expect to find Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacillus acidophilus growing in or on a healthy person?
hair follicles and sweat glands
Propionobacterium acnes are bacteria that live within the
skin; nostrils; nasal cavity
Staphylococcus spp such as S. aureus and S. epidermidis, Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Neisseria meningiditis grow over most of the area of the ___________ but especially in and around the ____________ and within the______________ in the case of Staph
lower respiratory tract
The WHAT is normally not colonized by microorganisms
pharynx
where do Streptococcus pneumonia and Haemophilus influenza reside?
stomach
this organ is not usually colonized by microorganisms but where does Helicobacter pylori reside?
intestinal tract
where does Enterobacteracieae reside?
Genitourinary tract
where does Lactobacillus acidophilus reside?
Eyepiece or Ocular Lenses
Final magnification of specimen image
Interpupillary Distance Scale/Adjustment
Adjust the ocular lenses to match the distance between the observer's pupils. Necessary to see image in 3D
Observation Tube Clamping Screw
Used to enable the Head of the microscope to rotate
Arm
Main body of the microscope that connects the head of the scope to the base. One of two carry points for the microscope
Revolving Nosepiece
Also known as Turret, mounting point for the objective lenses, allows observer to change magnification
Objective Lenses
Provides for the initial magnification of specimen image. Each is color coded and marked with magnification power
Mechanical Stage
platform upon which the specimen slide is moved in two dimensions to scan the slide and a third dimension to focus
Specimen Holder
also known as Slide Clip, holds microscope slide in position so that it can be moved precisely
Coarse Adjustment Knob
makes large and fast vertical movements of the stage to rapidly change focus. Is only used when viewing with the scanning or low power objective lens
Fine Adjustment Knob
makes small and slow vertical movements of the stage to slowly and precisely change focus
Specimen Manipulation Controls
moves the slide clip in two dimensions so that observer can view different areas of the slide without changes focus
Base
Main body of the microscope, contains light source and its controls; second of two carry points for the microscope
Arm Rests
textured areas used to steady hands when manipulating microscope controls
Power Switch
Control that turns power to the microscope light source on and off
Voltage Control Dial
controls the amount of power going to the light source, varying its intensity in large increments; numbered 1 to 10
Power Cord
supplies electricity to the microscope
Condenser Clamping Screw
Holds the condenser in place
Aperture Iris Diaphragm Lever
Adjust intensity of image in precise increments; left increases intensity, right decreases intensity
Filter Holder
used to mount colored filters for specialized viewing procedures
Condenser
a lens assembly that focuses all the light directly on the image; required to view images on a bacterial scale
Pre-Focusing Lever
Locks the Coarse Focus Knobs in position so that observer can't use them when viewing with other than the scanning objective; Down unlocks these knobs
Fuse Holder
location of fuse for light source
Power Cord Receptacle
socket into which the power cord plugs in
Condenser Height Adjustment Knob
raises and lowers the condenser for specialized viewing procedures, normally condenser is in the full up position
Filter Mount
additional mounting point for colored filters used in specialized viewing procedures
multiplying the objective lens power X the ocular lens power
how to calculate total magnification
cloudy
what does turbidity mean/look like in a broth
sediment/grain at bottom of broth
what does Sedimentation mean/look like in a broth
sediment/grain at top of broth
what does Pellicle mean/look like in a broth
grain/spots throughout broth
what does Flocculant growth mean/look like in a broth
puntiform, circular, rhizoid, spindle, irregular, filamentous, concentric
what does Colony shape or form mean/look like in agar
flat, raised, ingrowing, crateriform, convex, pulvinative, umbonate, hilly
what does elevation mean/look like in agar
Butyerous, Dull, Friable
what does texture mean/look like in agar
The margin of a colony is the actual edge ofthe colony, the point where bacteria stopgrowing.
what does margin mean/look like in agar
color of colony on agar
what does Pigmentation mean/look like in agar
NH2-CHR-COOH
general formula for amino acids
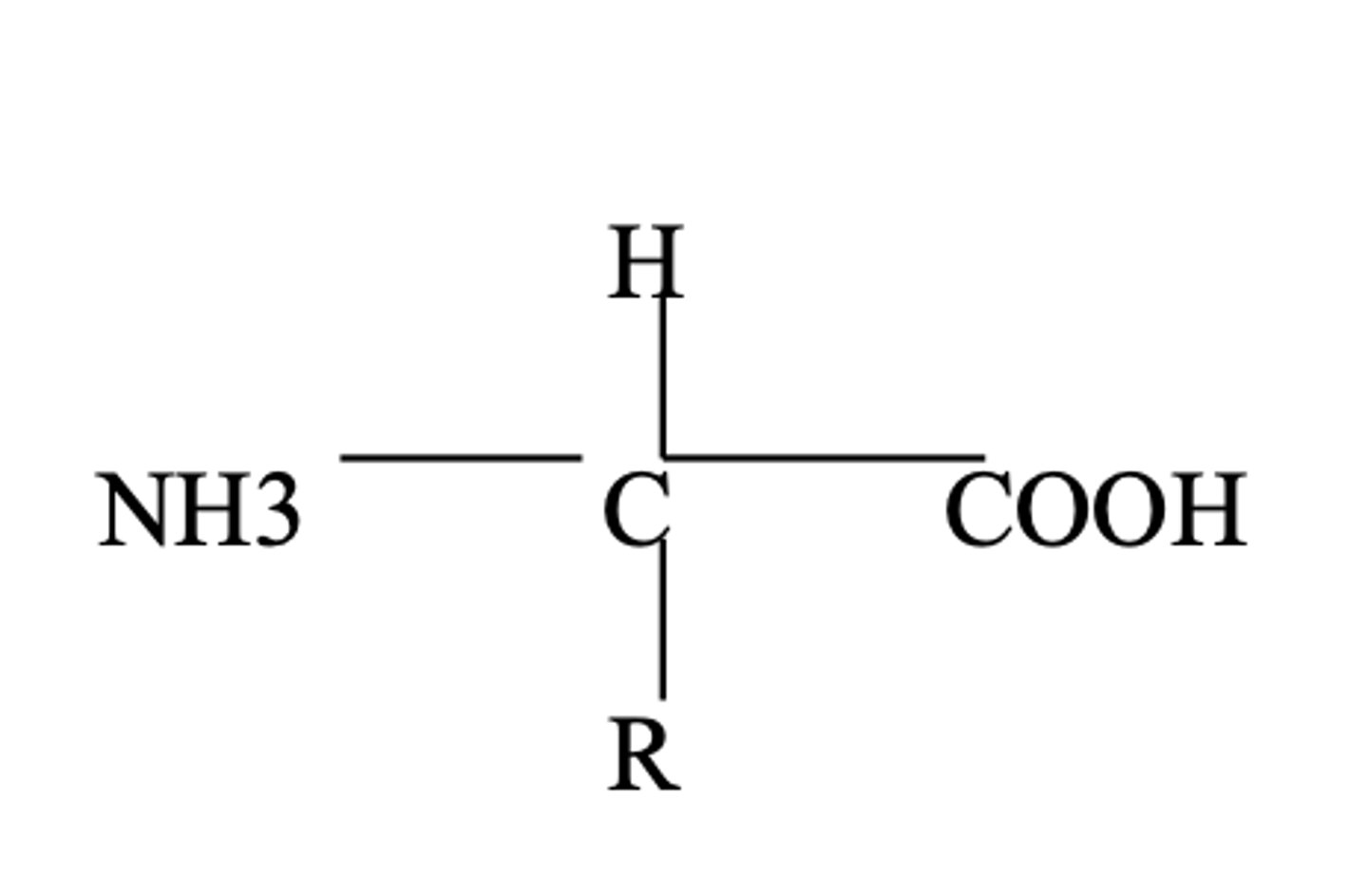
by forming peptide bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the next amino acid
how do amino acids link to form proteins
shape determines function
the role of SHAPE in the function of proteins
heat denatures proteins
how does temperature changes affect proteins
due to evolutionary adaptations in their amino acid sequences, which allow them to maintain their folded structure and function even under extreme temperatures
why do some proteins function at high temperature or low temperature
acidophiles
grow at extreme acid pH
Neutrophiles
grow best in a narrow range around neutral pH; pH 5.5-8.5
Alkalophiles
grow at pH above 8.5
hypotonic
a microorganism that lives in an environment where the solute concentration is lower outside the cell than inside the cell
Hypertonic
a microorganism that is placed in an environment with a higher concentration of solute outside the cell
Halophiles
"salt-loving" microbes that live in environments that have very high salt concentrations
lysis
the process of breaking down a cell's membrane.
Crenelation
the process by which a cell shrinks and develops a scalloped or notched surface due to water loss through osmosis
Isotonic
a solution that has the same solute concentration as the cell cytoplasm
Halotolerant
can survive at higher salt concentrations but grow best at low or zero concentations
many bacteria require significant amounts of atmospheric oxygen for basic metabolism. some species cannot tolerate the presence of oxygen, others tolerate the presence of oxygen and might use it, but do not always require it.
what role does oxygen plays in cells
some microbes lack the necessary enzymes to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS) produced when oxygen is present, leading to damage to their cellular components and ultimate death
How is oxygen harmful?
oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor for the electron transport chain which leads to the production of ATP
how is oxygen helpful?
superoxide dismutase and catalase
How do cells deal with the harmful effects of superoxides?