Complex -Oncology
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
154 Terms
carcinomas
cancer of organ/tissue lining
sarcomas
cancers of supporting tissues
leaukemias
cancer in blood
lymphomas
cancer of lymph nodes
most common types of cancer in US
melanoma, lung, prostate, breast ...
T =
tumor size
T stages
X, 1-4
N =
lymph nodes
N stages
X, 1-3
M =
metastasis
M stages
0-1
stage 0=
in situ
stage 1=
local
stage 2=
regional
stage 3=
regional into lymph
stage 4=
distant metastasis
high output failure lymphedma
transport capacity < lymphatic load (TOO MUCH FLUID)
low output failure lymphedema
transport capacity < lumphatic load (COMPROMISED SYSTEM)
combination lymphedema
transport capacity < lymphatic load (Compromised system, too much fluid)
secondary lymphedema
caused by insufficiency of the lymph system due to secondary factors
advanced clinical presentation of lymphedema
fibrosis, paillomas, hyperkeratosis, ulcerations, pitting edema
stage 0 lymphedema
Sub-clinical: lymph transport impaired, no obvious signs/symptoms, can last for years
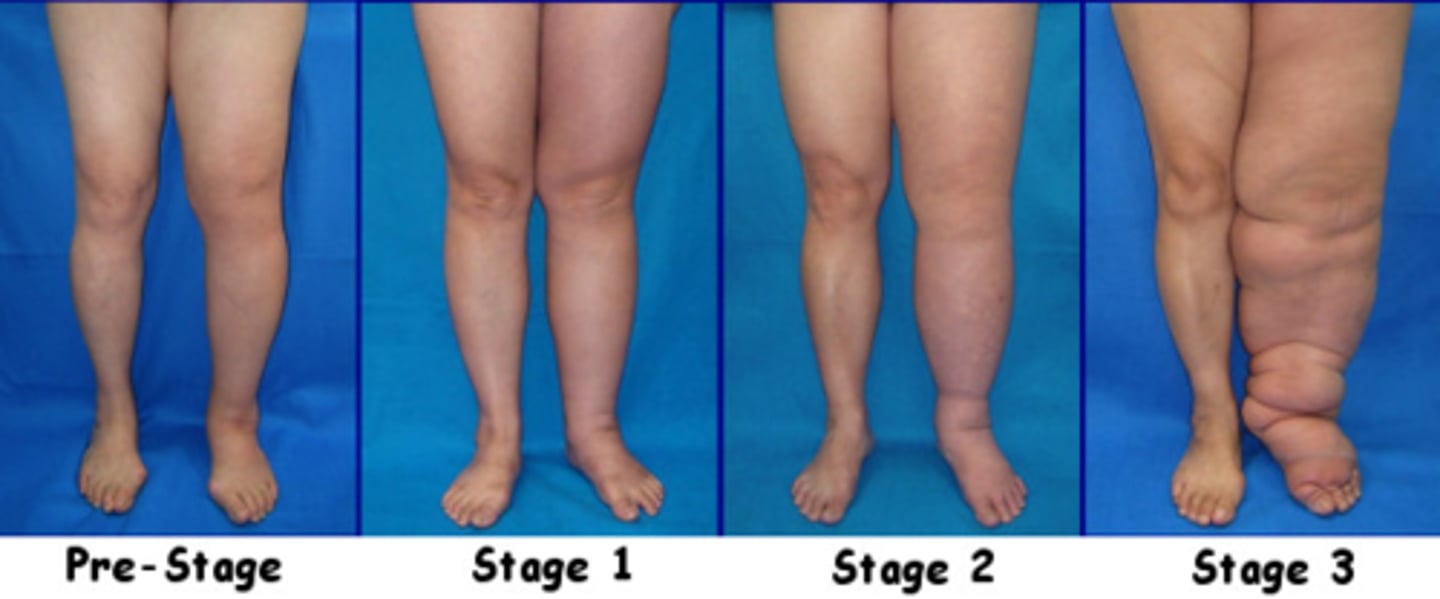
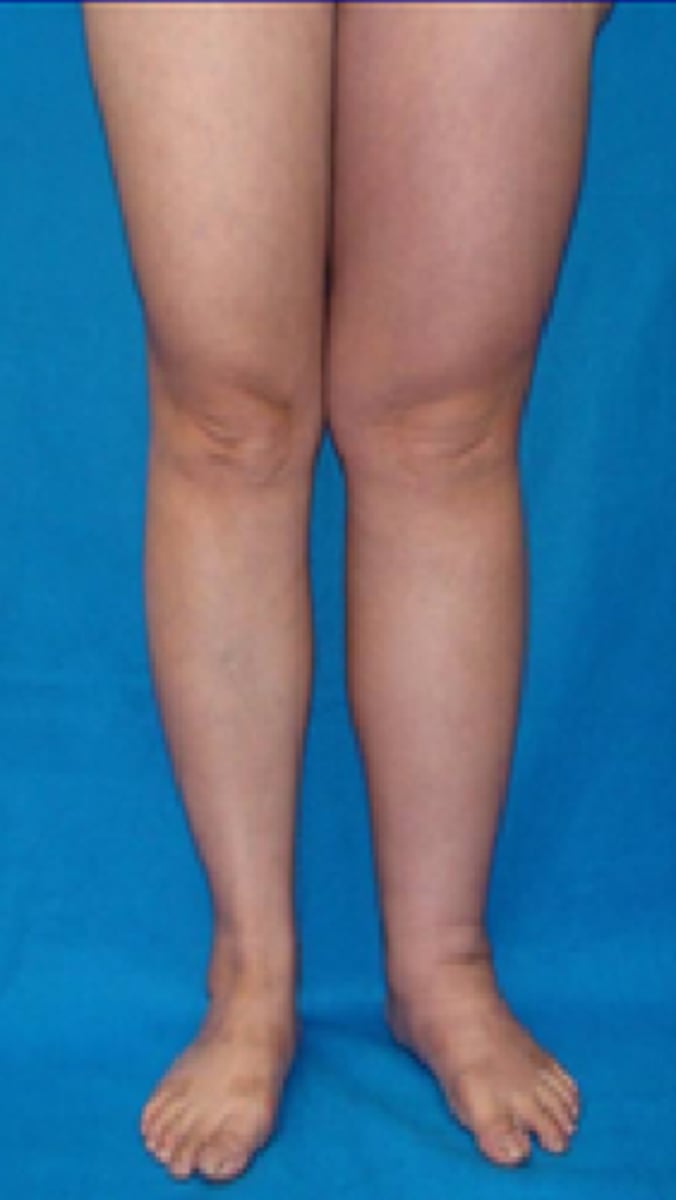
stage 1 lymphedema
Reversible, limb is soft and pitting, swelling may increase overnight
stage 2 lymphedema
spontaneously irreversible lymphedema; swelling with increase in fibrotic tissue; risk for infection
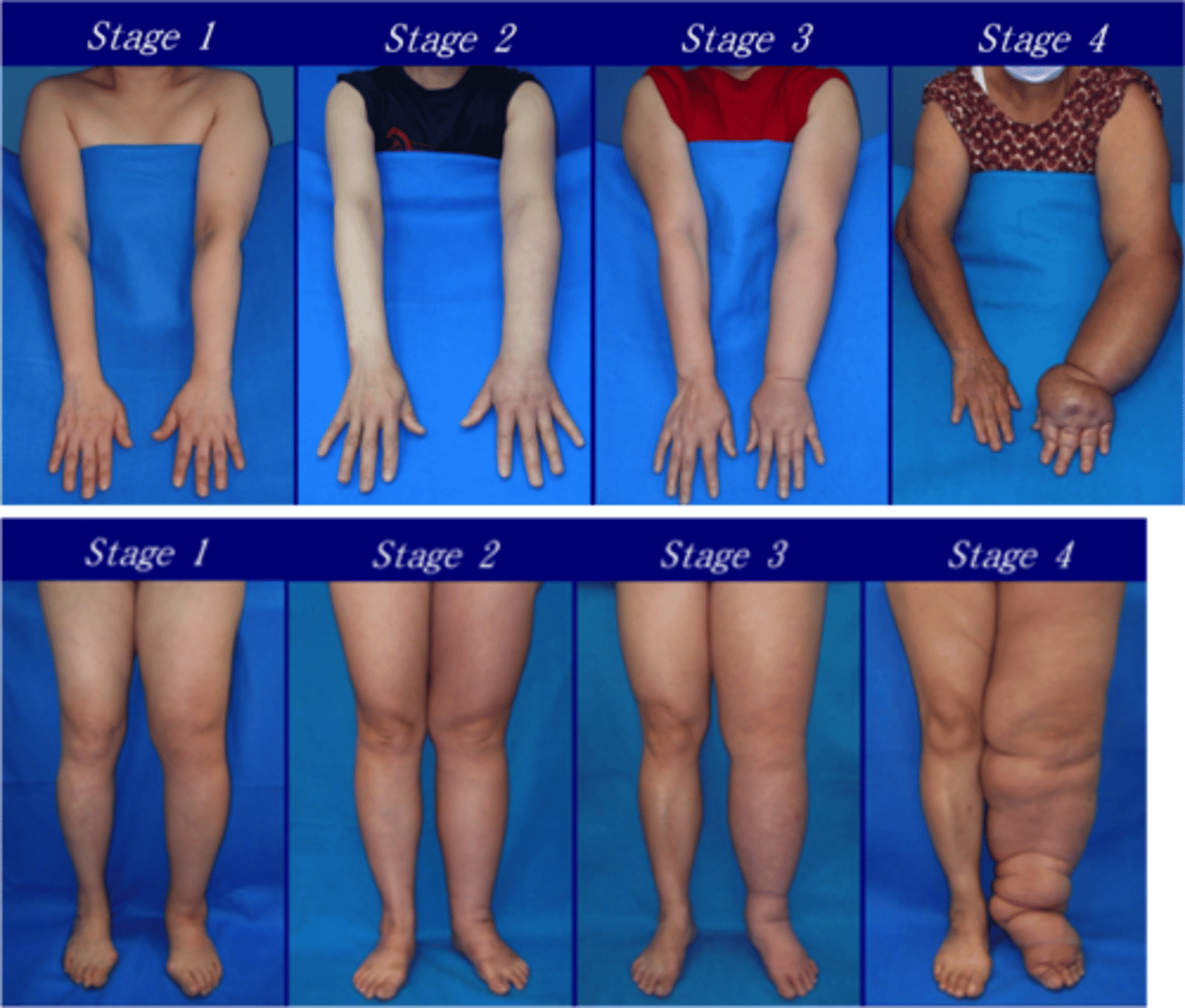
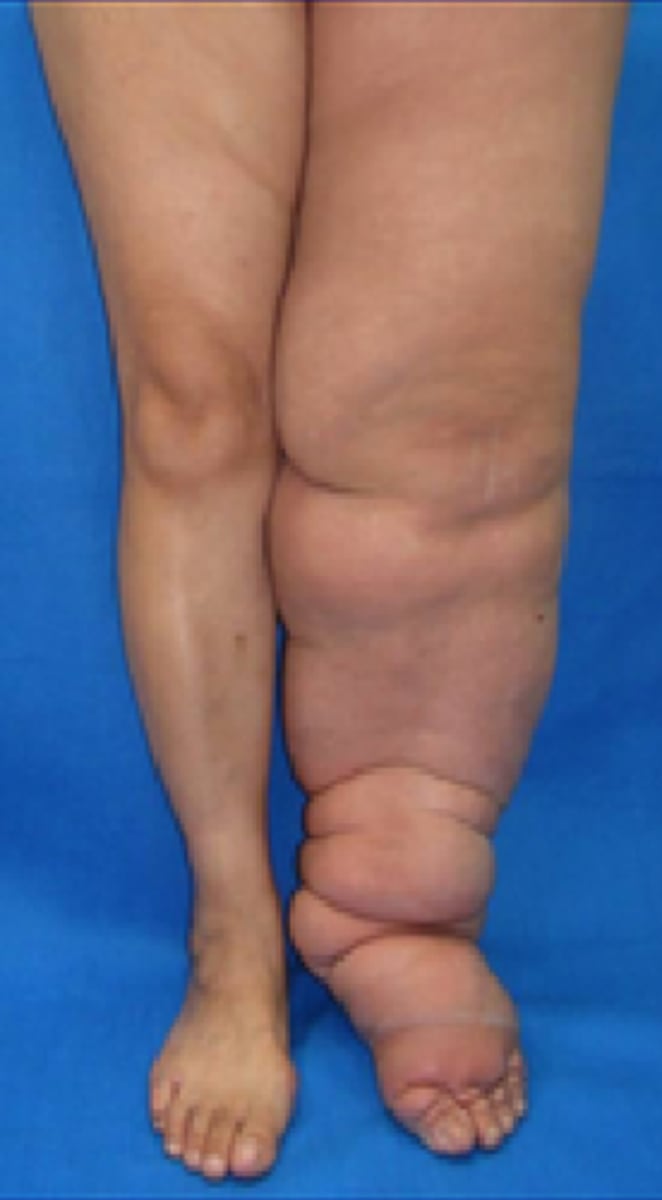
severe lymphedema
>5 cm difference between affected and unaffected limbs
what percent of pt with CA get cancer rehab?
2%
cachexia
a condition of physical wasting away due to the loss of weight and muscle mass that occurs in patients with diseases such as advanced cancer or AIDS
Dietz model
preventative, restorative, supportive, palliative
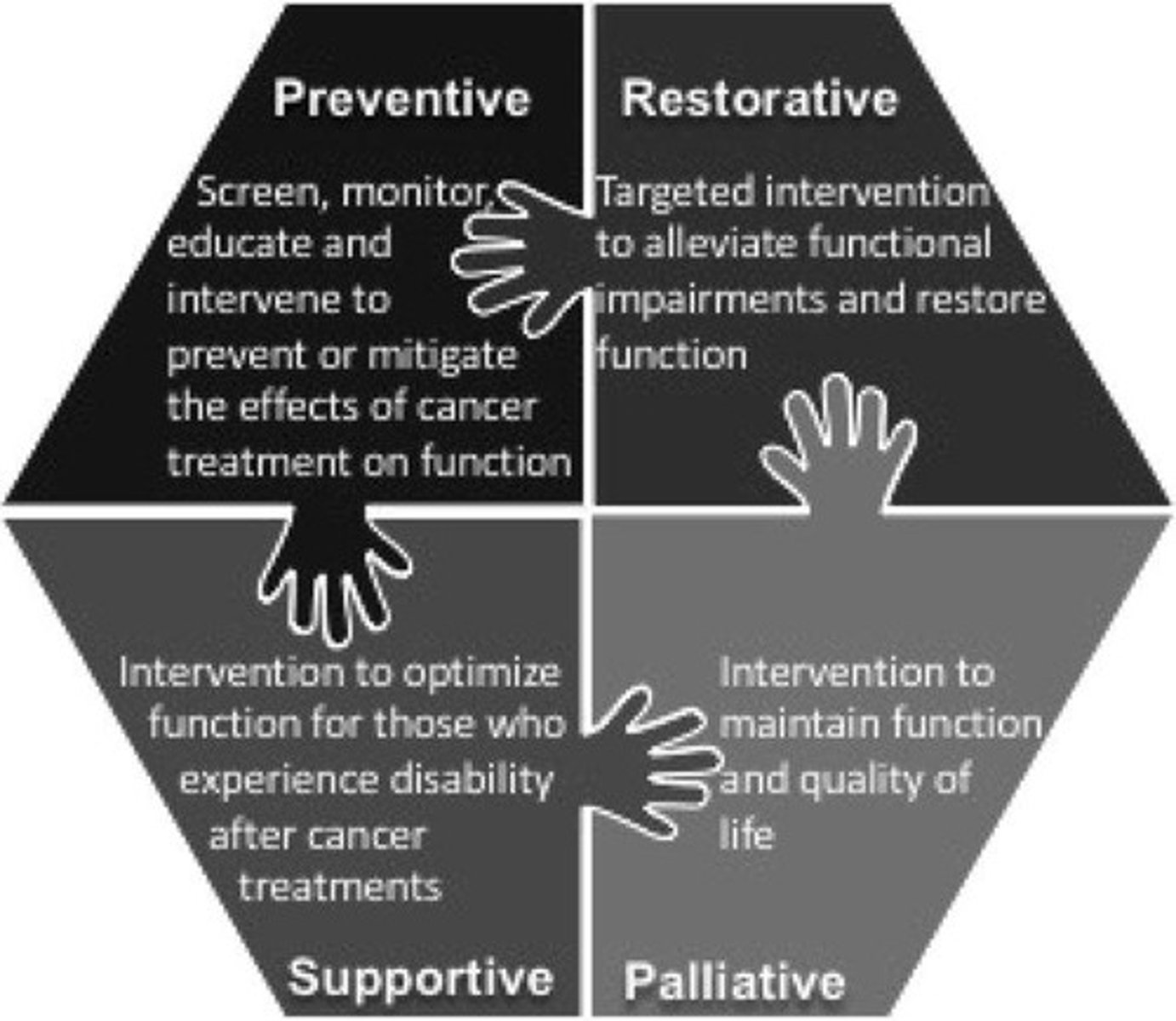
adjuvant
preventing recurrence, after main event
neoadjuvant
given prior to main event
induction
to induce remission
consolidation
to maintain remission
palliative
care to optimize quality of life
terminal
will result in death, uncurable
ER=
estrogen
PR=
progesterone
HER2
growth factor gene highly activated in cells of certain types of breast cancer
triple negative
ER/PR/HER2, most advance, can't use hormone drugs
global outcome measures (patient-reported)
PROMIS, WAI, CARG, FACT, brief-fatigue inventory, FACT-GOGNTX, mTNS
impairment specific outcome measures
DASH, NDI, ABC, SPADI
clinician based outcomes
vitals, ROM, strength, posture, circumferential, palpation
performance based outcomes
TUG, hand grip strength, 6MWT, 5TSTS, short performance physical battery
Hand grip strength predicts what?
physical decline, decreased QoL
TUG is a marker for
increased fall risk, fatigue, and pain
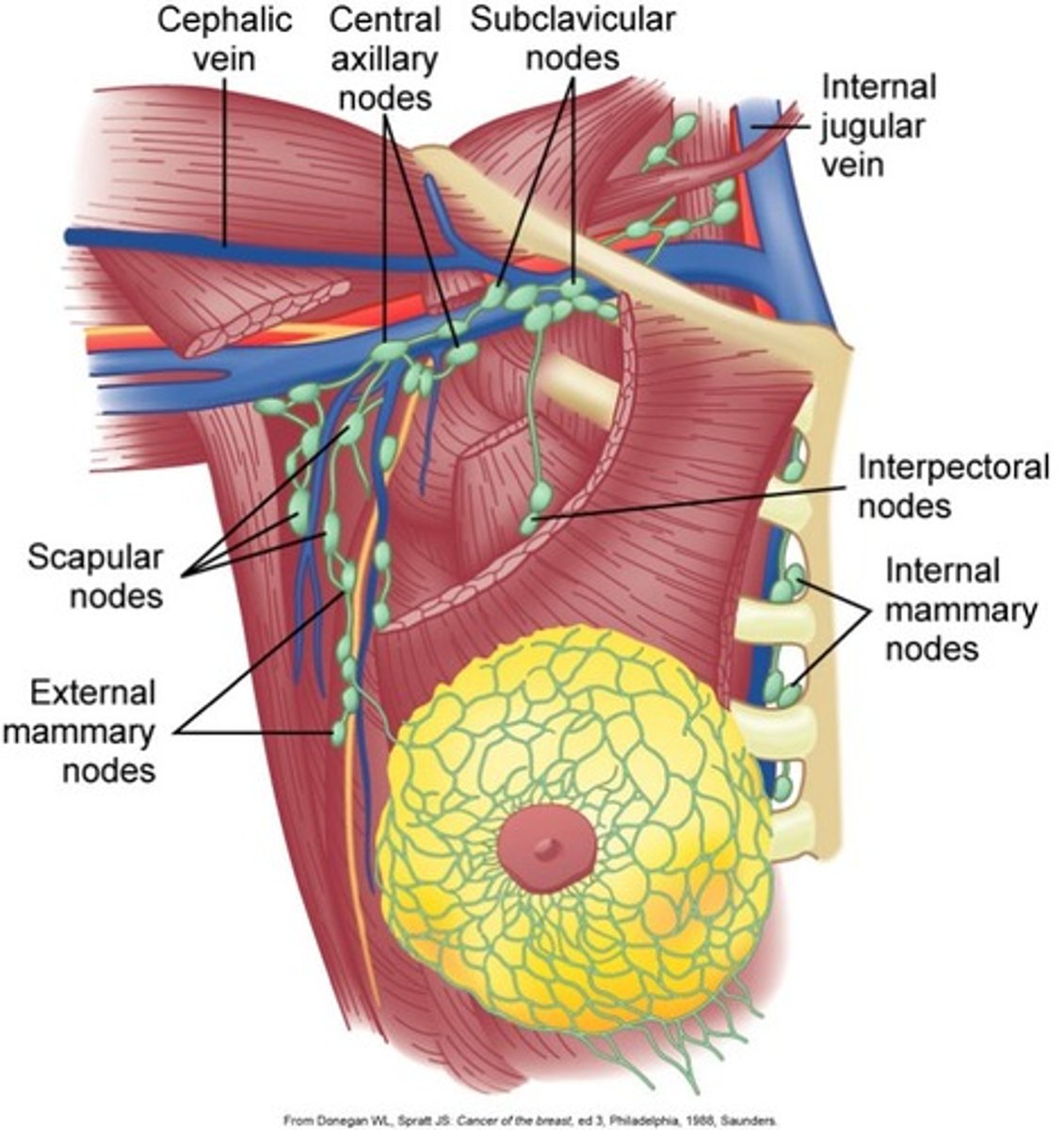
sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB)
removal of less than 5 nodes to check for spread
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection (ALND)
wedge resection of lymph nodes based on spread
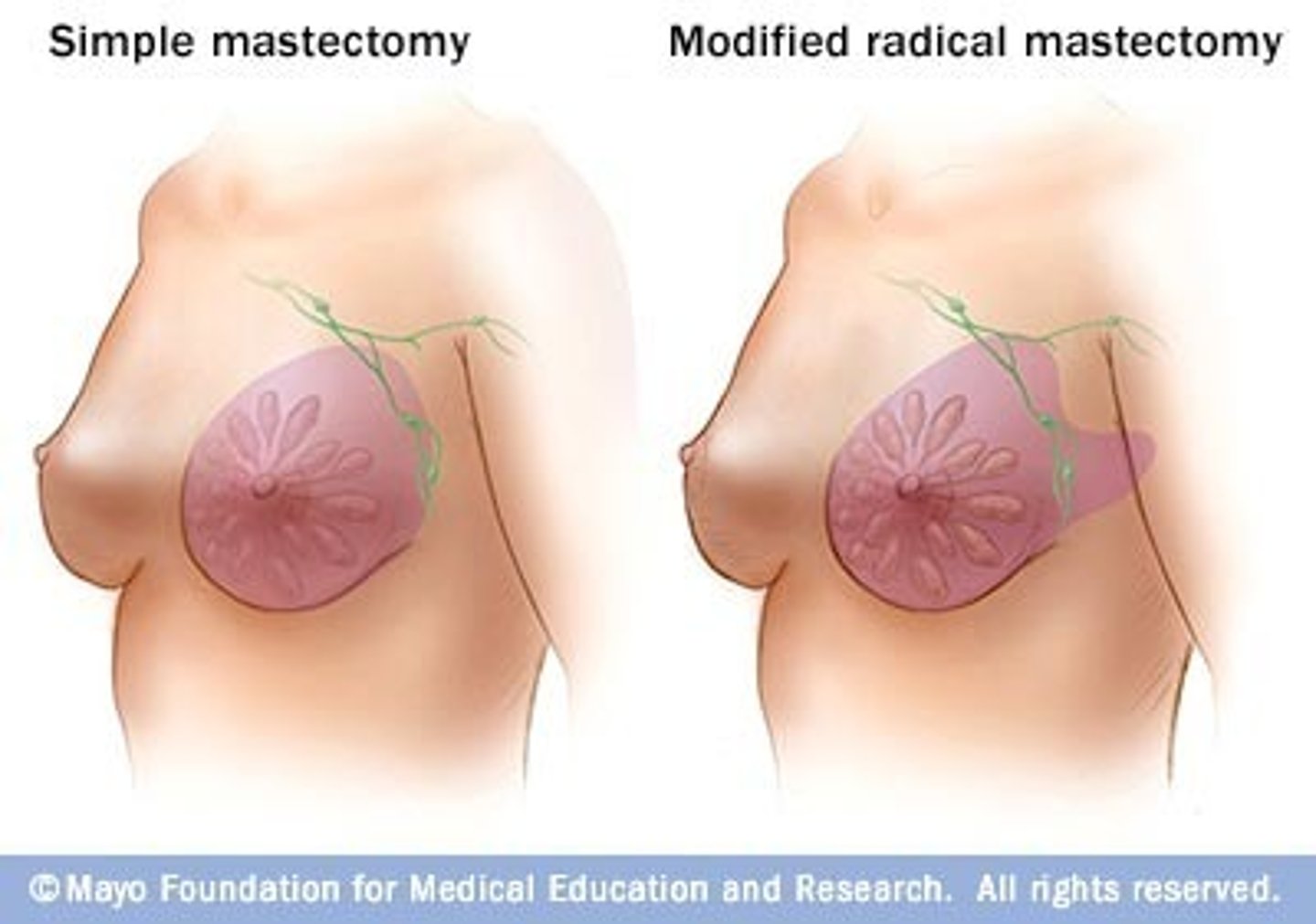
lumpectomy
minimal breast tissue + tumor
partial mastectomy
more breast tissue + tumor
total mastectomy
breast gland, nipple, skin, fascia
skin sparing mastectomy
breast gland and nipple removed
radical mastectomy
breast gland, nipple, skin, fascia, pec major, minor
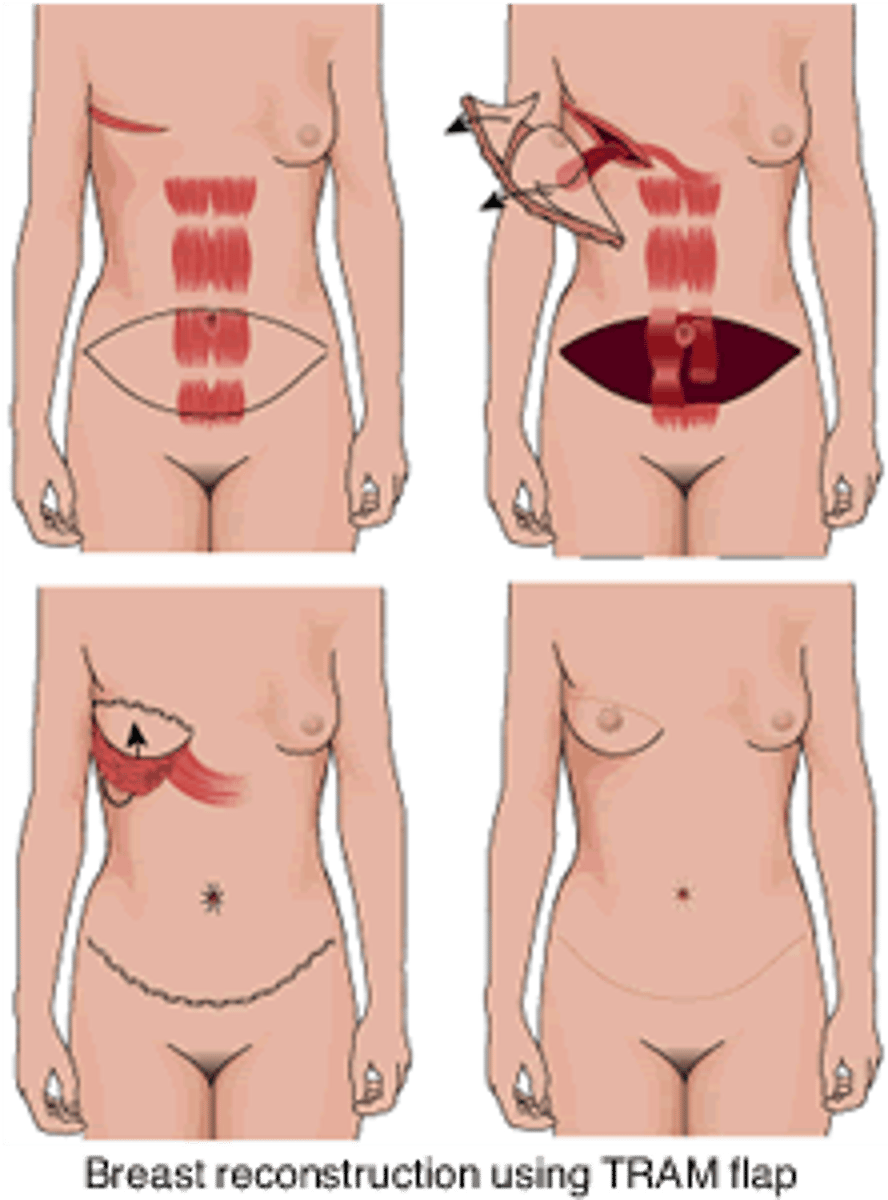
TRAM flap
post-surgical complications
infection, rippling, drain disruption, close/dirty margins, leak of implant capsular contraction, expander dysfunction
post-surgical side effects
lymphedema, scar adhesion, pain, swelling, neuromas, axillary web syndrome, decreased ROM, postural/breathing dysfunction
axillary web syndrome
after node removal, scarring of lymphatic system, pain, tightness
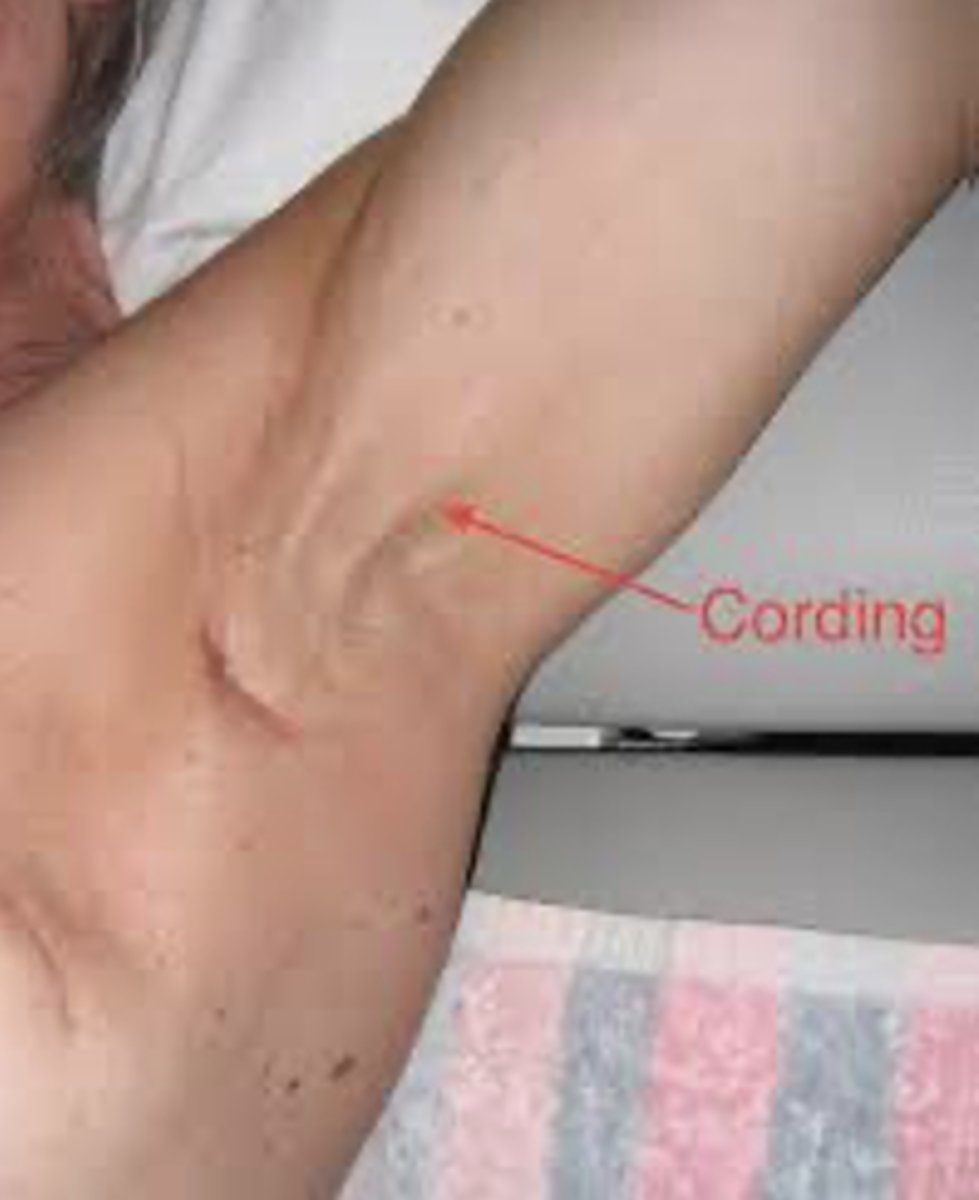
when does axillary web syndrome occur
within first 2-8 weeks, or months later
what type of surgery is more likely to have cording?
ALND > SLNB
where can lymphedema develop?
hand, arm, breast, chest, and/or trunk
when does lymphedema occur?
6 months to 3 years later
s/s of lymphedema
achiness/discomofrt, heaviness, N/T, loss of ROM, tightness, skin texture changes
risk factors of lymphedema
more nodes removed, multiple surgeries, radiation to axilla, taxane chemo, overweight, infection, rural setting
exercises
wall angels, nerve glides, supine cane flexion, wave bye bye, cane extension, pulley, cane ER, active cord release
manual therapy
skin rolling, lymphatic draining, IASTM, segmental, passive ROM, joint mobs, soft tissue massage, scar management
education topics
lymphedema triggers, cording care, expander precautions, compression garments, KT tape, precautions, infection control, importance of exercise
is chemo local or systemic?
systemic
is radiation local or systemic?
local
is targeted care local or systemic?
systemic
ACT
adriamycin, cytoxan, taxol
TC
taxotere, cytoxan
what does chemo do?
use drugs to target and kill rapidly dividing cells
other cells that are killed with chemo:
hair, stomach, blood
the four big C's
1. cancer related fatigue
2. cancer related cog decline
3. cardiotoxicity
4. chemo induced peripheral neuropathy
chemo side effects
hair loss, N/V, GI issues, insomnia, ototoxicity, mouth/throat sores, blood disorders, sarcopenia, osteopenia, allergy, falls, pain, appetite loss, sex dysfunction
what is the number 1 complaint among cancer pt?
FATIGUE
treatable causes of fatigue:
pain, anemia, emotional distress, inactivity
what is the only intervention found to reduce CRF?
exercise
highest connection between cancer related cognitive decline (chemo brain) and what dx?
breast cancer and lymphoma
cardiotoxicty
weakening and damage to heart mm
cardiotoxicity: strong link to chemo drug class called ____________________
anrhacyclines (adriamycin)
adriamycin=
red devil
sx of cardiotox:
dyspnea, edema, cough
chest pressure, increase SOB/HR, radiating pain =
NOTIFY ONCOLOGIST
drug categories that cause chemo induced peripheral neuropathies
platinum, vinca alkaloids, taxanes, immune checkpoint inhibitors
ways to assess peripheral neuropathy:
increased pain scale, decreased myotomes, decreased DTRs, increased vibration, decreased light touch, decreased sharp/dull, poor balance assessment, 9 hole peg, poor capillary refill, stocking glove
why does vibration increase?
because it is deeper pressure
treatment for chemo induced peripheral neuropathy:
foot massage
radiation: use to
control tumor growth, kills dividing cells by damaging DNA
radiation can be used ____________________ or __________________
curatively or palliatively
effects of radiation can take up to _____ weeks
2
conventional radiation
broken into fractions delivered 5 days a week for 2-8 weeks
hypofractionated radiation
single fraction, large doses, fewer sessions
bracytherapy radiation
inside out, implanted radioactive seed
acute side effects of radiation
radiation burns, redness, peeling skin, decreased swelling, follicultis, pleuritic pain, muscular pain, N/V
subacute side effects of radiation
radiation pneumonitis, cough, fever, chest pain, hypo/hyperpigmentation
late side effects of radiation
fibrosis, fat necrosis, rib fracture, graft fracture, pulmonary malignancy, lymphedema, brachial plexopathy, cardiac issues, phlebitis/thrombosis
s/s of radiation fibrosis
tight tissue, axillary webbing, altered sensation, OP, mucositis, diarrhea, frequency, urgency, urinary stenosis, fertility issues
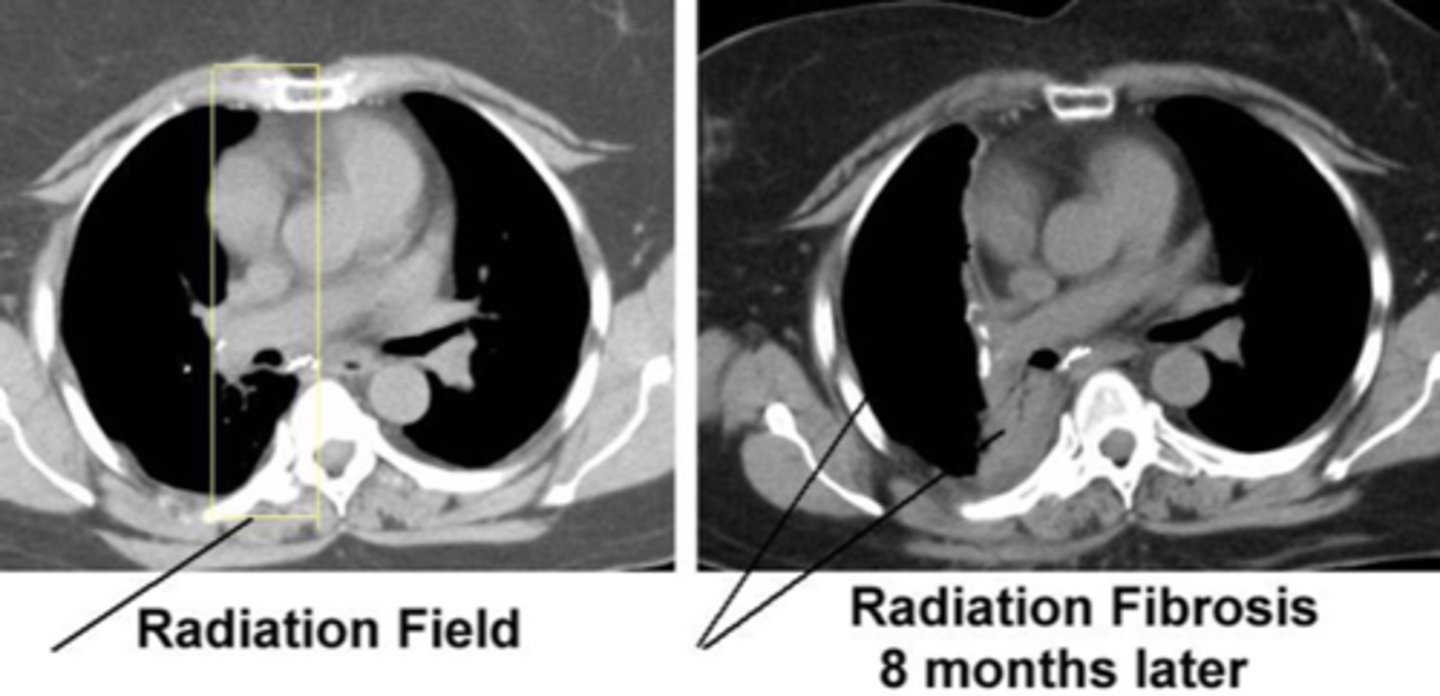
when does radiation fibrosis start?
3 months after finishing radiation
avoid what during/after radiation:
sun exposure, excessive antioxidant use, sedentary lifestyle
how to care for skin
use bland moisturizer, cortisone cream, good deodorant, watch for broken skin, use sunscreen
for ____ weeks post-radiation, DO NOT DO STM
6