ANP W1-4 Combined
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
What are the 2 unspecialized precursors (characteristics) to all tissue?
They can divide repeatedly
They can become specialized
(ex. Stem cells → can differentiate into a multitude of cells/tissues)
What are the 2 types of Stem cells? Define each.
Embryonic Stem cells
Found in early embryos
Source of all cells
Pluripotent → can differentiate into any cell type
Adult Stem Cells
Found in babies, children, adults as they remain after birth
Can differentiate into different cell types of their tissue of origin (ex. adult stem cell in bone can differentiate into the different types of cells found in bone tissue)
Assist with growth and repair
List the classification of Epithelial tissue: Shape and Layers
Shape → squamous, cuboidal, columnar
Layers → simple, stratified, pseudostratified, transitional
Give an example of simple and complex squamous epithelium.
Simple → Capillary walls (single layer)
Complex → Outer layer of skin (many layers)
Give an example of simple and complex cuboidal epithelium.
Simple → Tubules and ducts in kidney (single layer)
Complex → not common, some glands can have this. (many layers)
Give an example of simple and complex columnar epithelium.
Simple → Lining of stomach
Complex → uncommon; larynx and some ducts
Give an example of simple and complex pseudostratified epithelium
Simple → lining of respiratory passage (single layer)
Complex → none
Give an example of simple and complex transitional epithelium
Simple → none
Complex → lining of the urinary bladder (elastic, multi layered)
Most epithelial tissues secrete…? (4+1)
mucous, sweat, digestive juices, hormones, and/or other substances
What are the 2 types of glands? Describe each.
Exocrine glands → has a duct and empties its secretions directly to the location where secretion is to be used (ex. sweat glands)
Endocrine glands → NO DUCT. Secretions are deposited directly into the surrounding tissue to be absorbed by the bloodstream and carried to the target tissue. (ex. hormones from pituitary gland)
What are the 2 types of connective tissue? Describe each.
Circulating CT
Cells are in a liquid matrix (ex. blood or lymph)
located in blood and lymphatic vessels
Generalized CT
Denser connective tissue (ex. tendon, ligaments)
Widely distributed and not highly specialized
Subtypes: Structural CT (ex. bone and cartilage)
What are the 4 types of Generalized connective tissue?
Loose
Dense
Cartilage
Bone
Describe Loose connective tissue
Loose connective tissue, also known as areolar tissue, is a type of connective tissue characterized by a loose arrangement of fibers and a relatively large amount of ground substance.
most widely distributed connective tissue in the body
serves as a packing material, holding organs and tissues in place
Subtypes of Loose CT → Areolar space/tissue, Adipose Tissue (fat storage)
Describe Dense connective tissue
Dense connective tissue is characterized by its firm matrix, a high density of collagen fibers and some elastic fibers which provide protection, support, flexibility and attachment.
two main subtypes: dense regular and dense irregular.
Irregular Dense CT is composed of ? and can be found in ?
Mostly composed of collagen fibers in RANDOM arrangement
Can be found covering various organs (fibrous membrane, organ capsule)
Regular Dense CT is composed of ? and can be found in ?
Mostly composed of collagen fibers in PARALLEL alignment
Can be pulled in one direction, stretch and return to its original shape (vocal cords, ligament, tendons)
Describe the 3 types of Cartilage
Hyaline → tough, translucent (covers ends of bones, in nose tip)
Fibrocartilage → firm, rigid (between vertebrae, some joints)
Elastic → high in elastic fibers, can stretch and return to original size (epiglottis, outer ear)
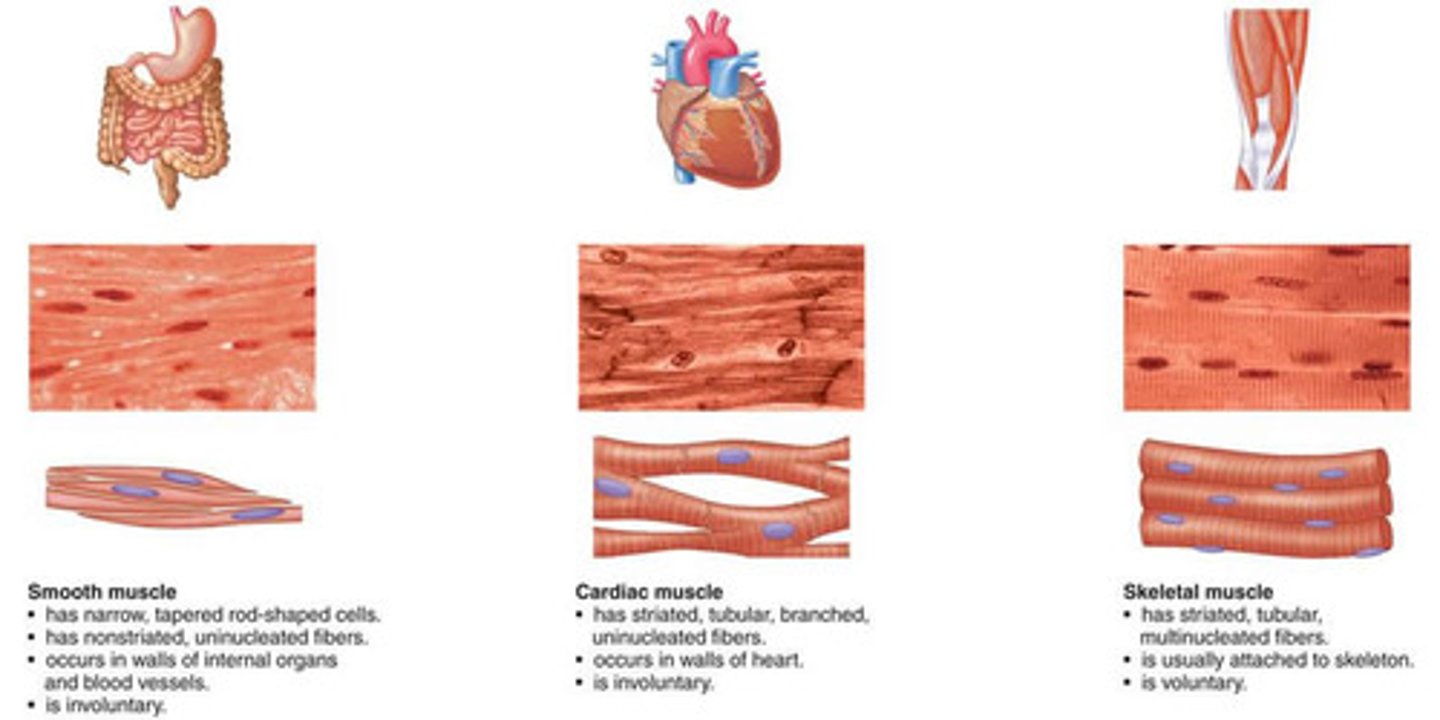
What are the 3 types of Muscle tissue? Describe each.
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary control
Striated, multinucleated cells
Cardiac Muscle aka myocardium
Involuntary control
Striated, uninucleated cells
INTERCALATED DISKS connecting each cell together
Smooth Muscle aka Visceral muscle
Involuntary control
Not striated, single central nucleus
What are the 2 types of cells that make up Nervous tissue?
Neuron and Neuroglia (glial cells)
Draw and label the parts of a Neuron (nerve cell). What are the functions of each structure?
Dendrites → carries nerve impulse to nerve cell body
Axon → carries impulses away from the nerve cell body
Myelin sheath → protective layer around axon that also acts as insulation
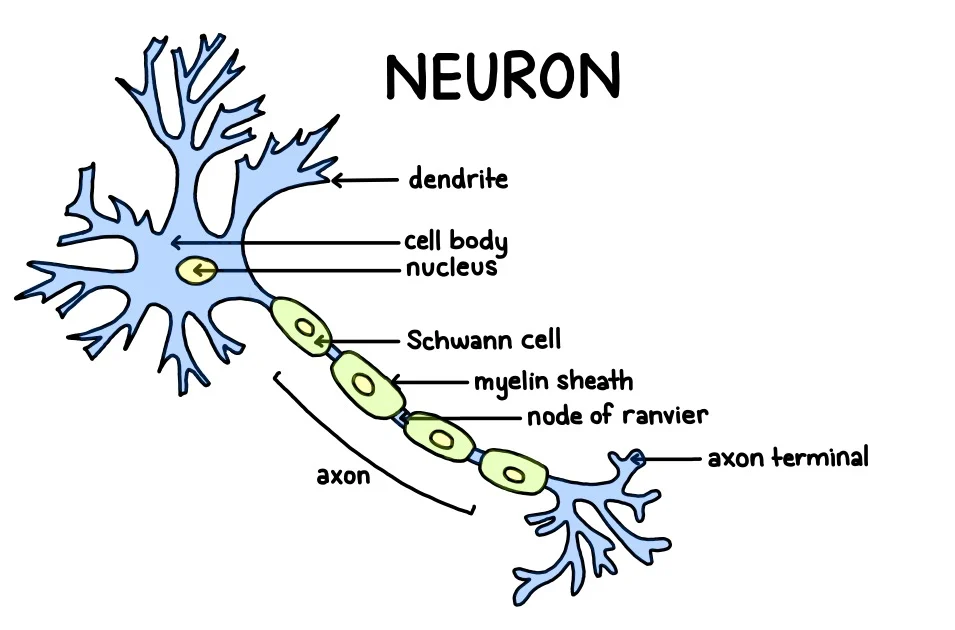
A nerve is…?
A bundle of nerve fibers held together with connective tissue.
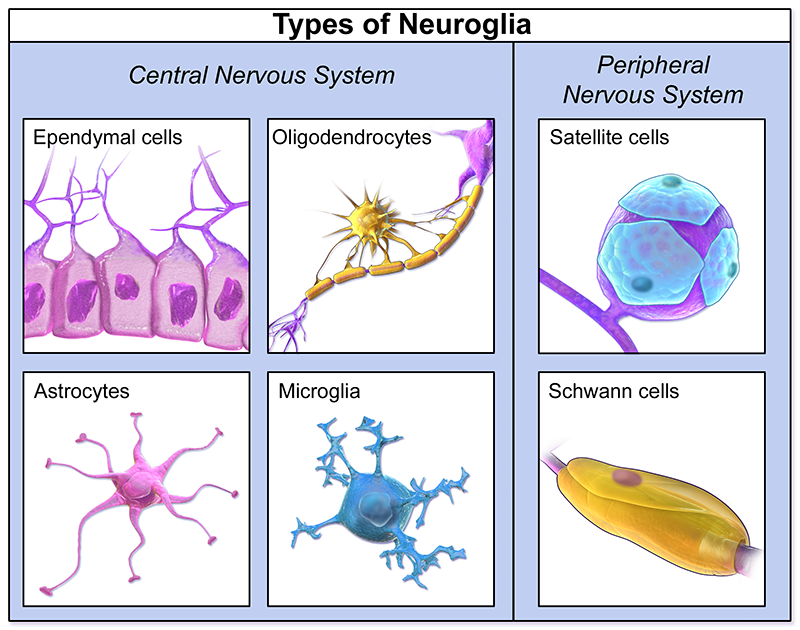
What are Neuroglia (glial cells?). What are its 3 main functions?
Specialized cells that support and protect nervous tissue. **does not transmit nerve impulses
fx:
Protect the brain from harmful substances
Get rid of foreign organisms and cellular debris
form myelin sheath around axons
What are 3 types of Epithelial Membrane? Describe each.
Serous membranes → is a bilayer, lines body cavities, covers internal organs
Mucous Membranes → lines tubes and ducts that open to the outside of body
Cutaneous Membrane → skin
Epithelial membranes are always composed of:
outer layer → epithelium
inner layer → CT
What is mesothelium?
Mesothelium is a simple squamous epithelium that forms the epithelial layer of serous membranes
smooth and glistening tissue
What are the 2 layers of Serous membranes (its a bilayer)?
Parietal Layer → layer attached to the wall of a cavity or sac
Visceral serous layer → membrane attached to organs
What is the area between layers of serous membrane called?
Potential space
it is not always present → present during infections
What are 3 types of Serous membranes?
Pleura → serous membrane lining the lungs and chest cavity
Parietal layer is touching the thoracic cavity;
Visceral layer is covering the lung
Serous Pericardium → lines the heart and pericardial sac
Parietal → lines pericardial sac
Visceral → covers the heart
Peritoneum → lines the abdomen
Parietal → lines abdominal cavity wall
Visceral → covers the abdominal organs
Mucous membranes can vary in structure and function. What are 3 examples of their fx?
Trap and remove foreign particles → helps ciliated cells in nasal cavity
Protect deeper tissue → membrane lining the stomach
Absorb food material → digestive tract
Connective Tissue Membranes are only composed of CT, and no epithelium.
What are 4 types of connective tissue membranes?
Synovial membranes (lining joint cavities)
Meninges (covers brain and spinal cord; several layers)
Fascia → superficial and deep (supports organs and holds them in place)
Membranes that surrounds organs → fibrous pericardium, periosteum, perichondrium
How do membranes play a part in the disease process?
Membranes can become inflamed or infected
Membranes can act as pathways for diseases to spread into the body
Frequently involved in autoimmune disorders (ex. rheumatoid arthritis)
Benign tumours are generally considered harmless unless they…
increase to a size, or is in a location where it compresses vital tissues/nerves/organs.
Benign tumours are often encapsulated and do not invade other tissues or spread.
Malignant tumours are classified by their tissues of origin. What would be the type of cancer that originates from the epithelium? connective tissue?
Carcinoma → most common cancer originating from epithelium (can be a epithelial layer of some organ)
Sarcoma → cancer originating from connective tissue; can be found anywhere in the body (bone, muscle, fat, nervous tissue)
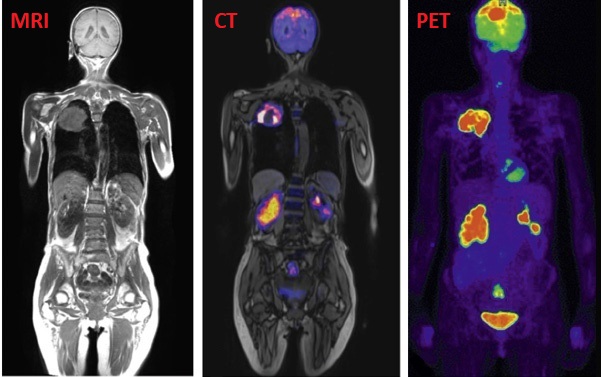
What are the types of diagnostic imaging that can be used to diagnose Cancer?
Radiography → xray, mammography
Ultrasound
Computed tomography (CT scan)
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Positron emission tomography (PET)
How does Aging affect our Tissues?
As we age, CT looses elasticity because the collagen becomes less flexible. This can cause:
Reduced capacity in vessels
Posture and joint issues b/c of tendon and ligaments becoming stiff
Bones become more brittle
Muscles begin to atrophy and decrease in size
What are the 3 main functions of the Cell membrane?
Enclose cell contents
Regulates what enters and leaves the cell
Participates in many cell activities such as growth, reproduction, cell to cell communication/interaction
What are the 3 components of the Plasma membrane?
Phospholipid Biplayer
Cholesterol (adds strength and flexibility)
Proteins
The plasma membrane can have microvilli. What is its functions? where can it be found?
Increases SA for greater absorption of materials.
Found in kidneys and small intestines
What are the 6 types of proteins that can be found embedded in the cell membrane? List their functions.
Channels - pore allowing passage
Transporter - shuttles substances across membrane (in our out)
Receptors - cell to cell signalling
Enzymes - catalyst in chemical reactions that occur on surface of membrane
Linkers - gives structure and add stability to the membrane by linking to other proteins within the cell or attach to adjacent cells
Cell identity markers - Unique proteins to a persons cell → important for immune system
What is the Nucleolus? What is its function?
An area inside the nucleus also known as the little nucleus.
fx: ribosome production and assembly
Fx of Smooth and Rough ER
Smooth = lipid synthesis
Rough = manufacture proteins with the ribosomes studded into it
Fx of Golgi Apparatus?
Packages proteins, sorts and prepares them for export from cell or to other parts of the cell.
Fx of Lysosomes.
Destroy old and damaged cells
Destroys pathogens in phagocytosis
Fx of Centrioles
Rod-shaped organelle near the nucleus involved in cell division.
helps form the spindle fibres needed during metaphase.
Fx of Peroxisomes? How are they different to Lysosomes.
contains enzymes to destroy harmful substances
active in disease prevention, active in metabolism
Lysosomes are primarily involved in cellular digestion and waste recycling, while peroxisomes focus on detoxification and breaking down fatty acids
The plasma membrane is selectively permeable. What factors determine whether the molecule can “freely” pass through?
Molecule size (small)
Solubility (lipid soluble only - hydrophobic molecules)
Electrical charge (non-polar)
What are the 3 types of In-active/Passive Transport?
Diffusion
Osmosis
Filtration
Define Diffusion
Type of Passive transport.
Movement of molecules from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration
driven by a concentration gradient
Define Osmosis
Type of passive transport
The movement of water (or solvent molecules/liquid/other substances) from an area of low solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane into an area of high solute concentration.
Define FIltration
Type of passive transport
Filtration moves WATER and dissolved substances DOWN a pressure gradient (often created by blood pressure) through a semi-permeable membrane.
Define Isotonic, Hypotonic and Hypertonic.
Isotonic - same solute concentration in and out of cell
Hypotonic - a solution that has a lower concentration of solute compared to the cell (low [solute] outside cell than inside cell] → water moves into the cell → cell may burst (lysis)
Hypertonic - higher solute concentration outside of the cell than inside the cell. → water moves out of the cell → cell crenates (shrinks)
Define Active Transport
Active transport is the movement of molecules against a concentration gradient (from low to high concentration) that requires energy (ATP).
Define Bulk Transport
Movement of large amounts of material through the plasma membrane using vesicles (aka vesicular transport).
Requires energy.
What are 5 types of Bulk Transport? Define each.
Endocytosis → bulk movement of materials INTO cell
Phagocytosis → Engulfing large particles by the cell membrane INTO the cell
Pinocytosis → Droplets of fluid engulfed by the cell membrane (cell drinking)
Receptor mediated Endocytosis → Intake of substances using specific binding sites on the plasma membrane
Exocytosis → bulk movement of materials OUT of the cell
What are nucleotides composed of?
Nitrogenous base, sugar (deoxy or oxy ribose) phosphate
DNA is double stranded. What type of bond holds the strands together?
weak Hydrogen Bonds
What are the 3 types of RNA. What are their fx?
Messenger RNA (mRNA) → transcribes DNA and becomes a template of that DNA strand, carries it to ribosome
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) → site of protein synthesis; translates the mRNA to make the protein
Transfer RNA (tRNA) → carries the required amino acid to build the protein at the ribosome.
Describe the 2 steps of Protein synthesis
Transcription
Occurs in the nucleus
DNA uncoils and is transcribed into mRNA by nucleotide base pairing
Translation
Occurs in the cytoplasm at the ribosome
mRNA leaves the nucleus and travels to the ribosome in cytoplasm
Ribosome and tRNA translate mRNA into protein amino acid sequence
tRNA carries specific amino acids t hat can be added to the protein chain at the ribosome
Which organelle coils, and folds the amino acid chain into a protein’s the proper shape?
Endoplasmic Reticulum
What are the 4 stages of Mitosis? What is interphase?
Prophase
Metaphase
Anaphase
Telophase and Cytokinesis
Interphase is when the cell is preparing to divide, DNA replicates. → “resting phase”
Describe what happens during Prophase.
DNA coils into chromosomes
Nucleolus and nuclear membrane disappear
Centrioles move to opposite poles and form spindle
Describe what happens during Metaphase.
Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell (metaphase plate)
Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
Describe what happens during Anaphase.
Centromeres split (region connecting the sister chromatids)
Spindle fibres pull chromosomes towards the opposite poles of the cell towards the centrioles
Describe what happens during Telophase.
Chromosomes continue to move towards poles
Nuclear membrane forms around chromosomes (on both ends of the cell)
Plasma membrane pinches off in the middle (cytokinesis) to form 2 new identical daughter cells (46 xsomes).
What are 5 reasons that lead to cell damage/death?
Free radical injury
Enzyme injury
Gene mutation
Slowing cell activity (decreased metabolism)
Apoptosis (programmed cell death)
What are some risk factors for cancer?
Genetics
Carcinogens/Chemicals
Radiation
Diet → Poor nutrition, Obesity
Physical Inactivity
Viruses (HPV)
96% of the human body is composed of which 4 elements?
O, C, H, N
What are the 9 elements that make up 4% of the human body?
Ca, P, K, Na, Fe, S (sulfur), Cl, Mg, I
The number of bonds an anatom needs to fill its outer most energy level to become stable is…
Valence
Formula for # electrons in shell
2n²
n= shell number
Define Ionic bonds
Weak electrostatic bonds between oppositely charged ions.
Electrons are donated/accepted
Usually between metal and non-metal
What are electrolytes?
Compounds that separate into ions when put into a solution
Define covalent bond. What are the 2 types.
Form when two atoms share electrons to complete the energy level and thus become stable.
Usually between non-metal and non-metal
2 Types:
Nonpolar - bond shared equally
Polar - bond shared unequally between atoms
What is the difference between mixtures and solutions?
Mixture: Substances maintain their individual identities
Solutions: Substance is dissolved into a liquid (solute into solvent).
What is the difference between suspensions and colloids?
Both are solutes that are NOT dissolved in solvent.
Suspension: Solute will settle down to the bottom when suspension is not constantly agitated (ex. RBC in blood plasma)
Colloid: Solute will NOT settle out of a colloid (ex. proteins in body body fluid, think emulsion)
What is an aqueous solution?
An aqueous solution is a solution where water acts as the solvent. In simpler terms, it's when a substance (the solute) dissolves in water.
Define Isotopes
Forms of an element that have the same atomic number but different atomic weight (due to different number of neutrons)
*may be stable or unstable (radioactive)
What are the 3 uses of radioactive isotopes?
Medical research, diagnosis, treatment
What are the 3 main types of organic compounds?
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins
What is the anatomical position?
standing erect, facing forward, upper limbs at the sides, palms facing forward and thumbs out
Directional term: superior and inferior
above/below
Directional term: Anterior, ventral, posterior, dorsal
Anterior - towards front of the body
Ventral - Anterior surface of a surface
Posterior - towards the back of the body
Dorsal - Posterior surface of a structure
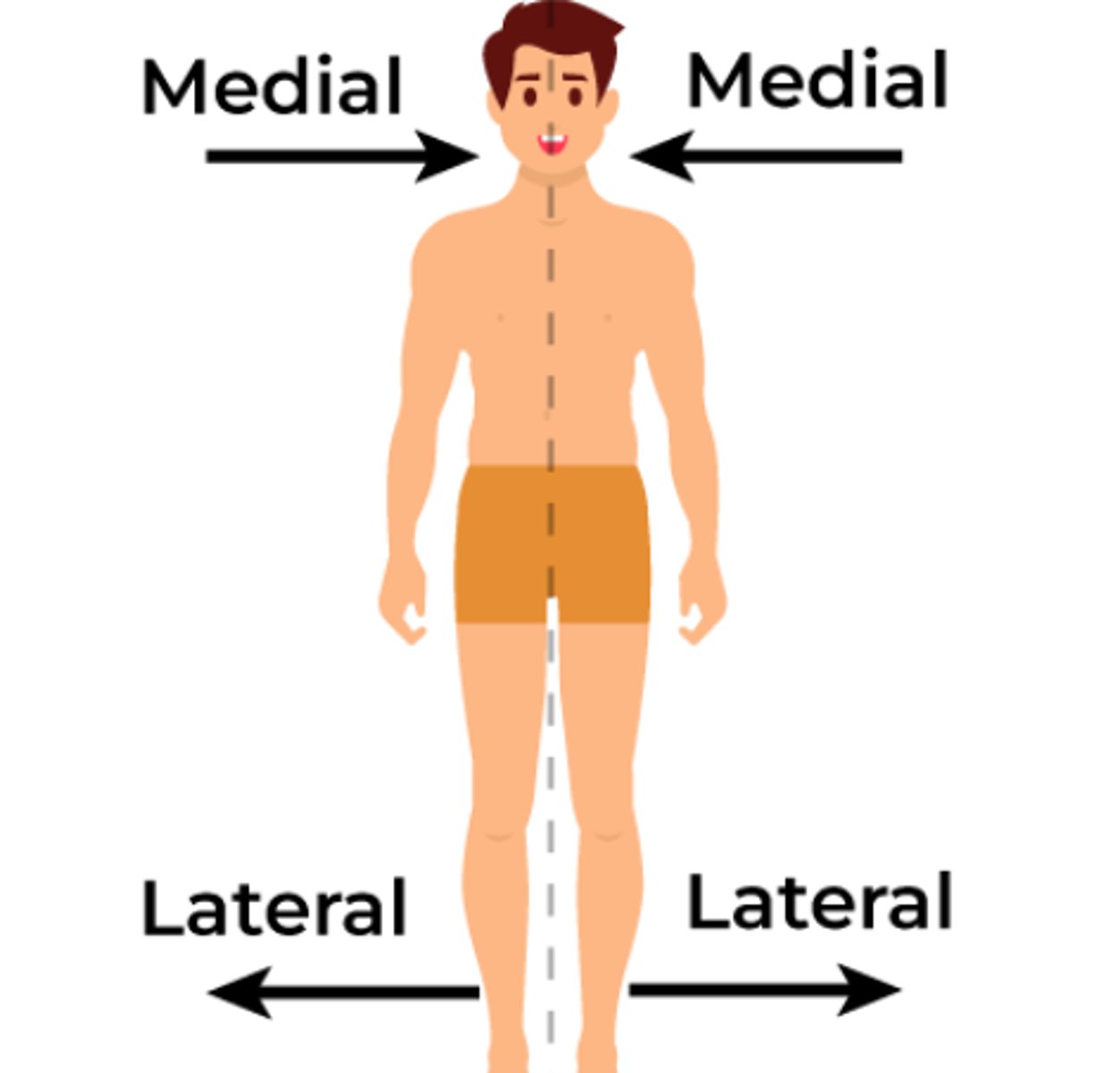
Directional term: Medial and Lateral
Medial: towards the midline
Lateral: away from the midline
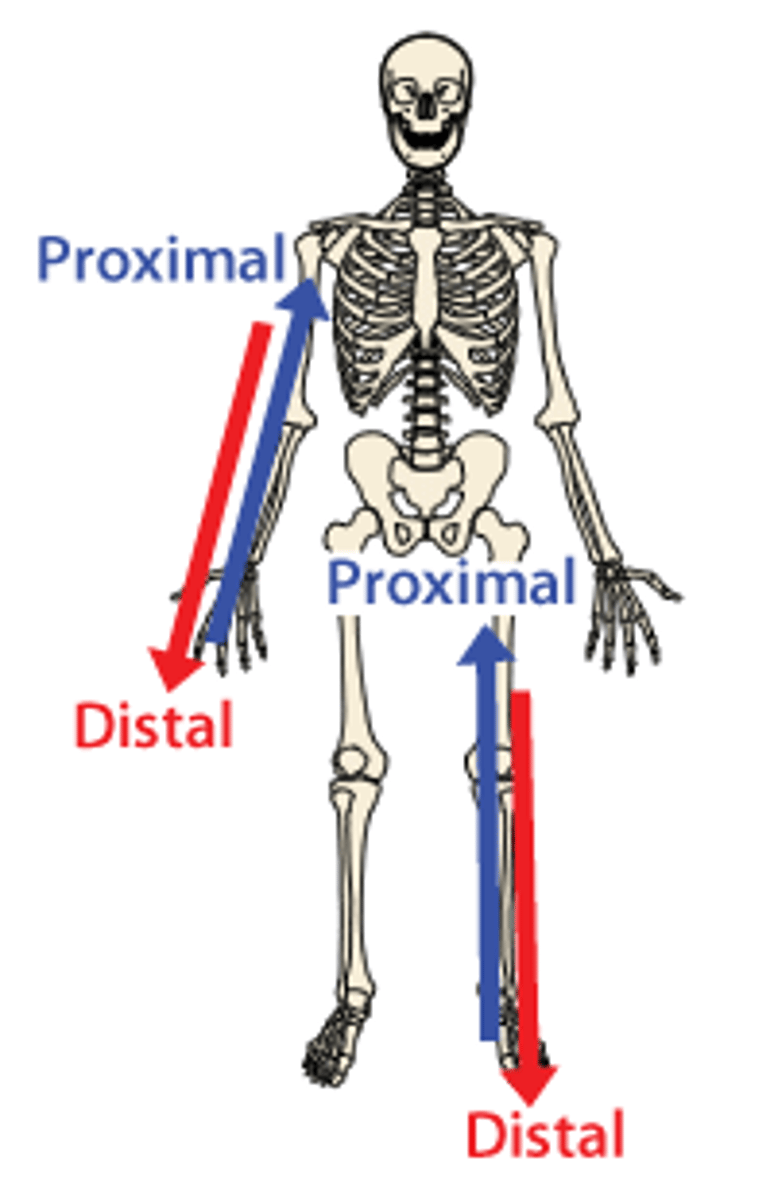
Directional term: Proximal and Distal
Proximal: closer to the midline/trunk OR closer to the point of origin of a structure
Distal: away from the midline/trunk OR away from the point of origin of a structure
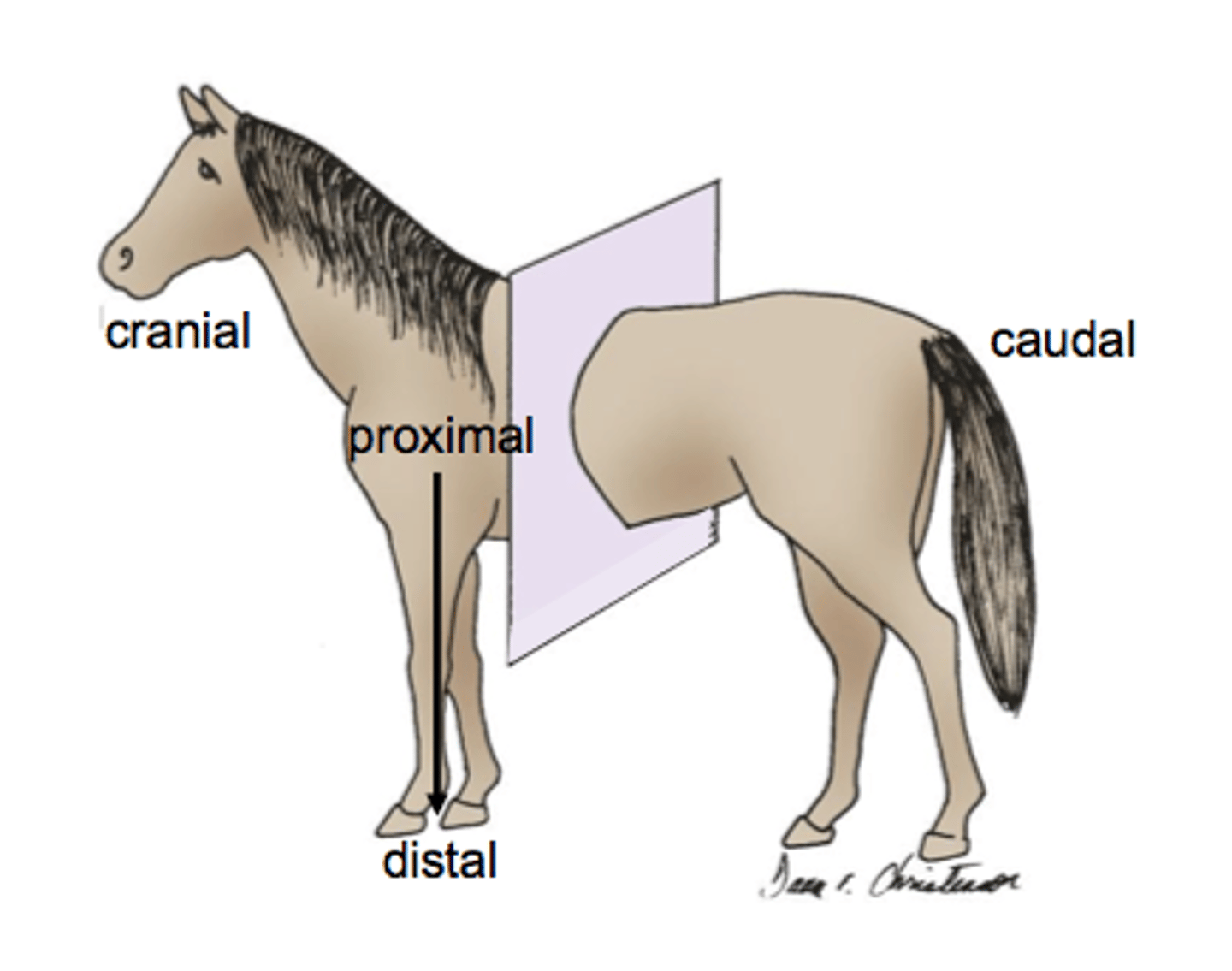
Directional term: Cranial and caudal
Cranial: closer to the skull
Caudal: closer to the bottom/tail end of the body
Planes of Division: Sagittal
Divides body in left and right parts
Plane is from front to back.
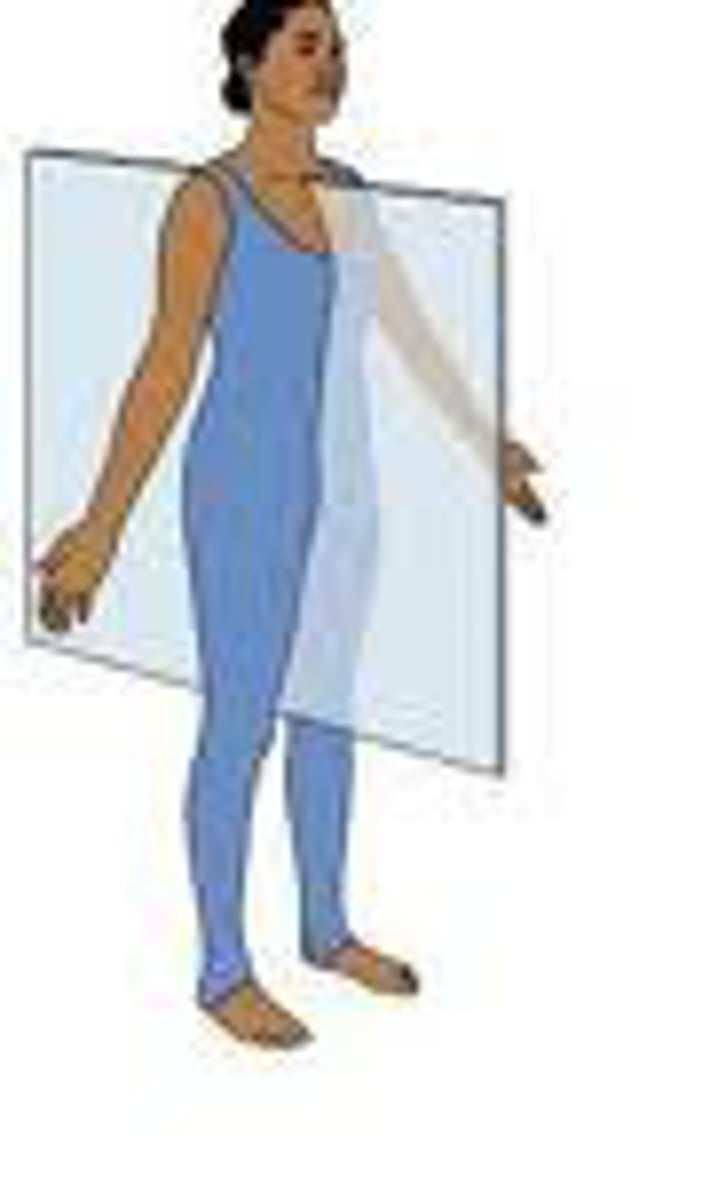
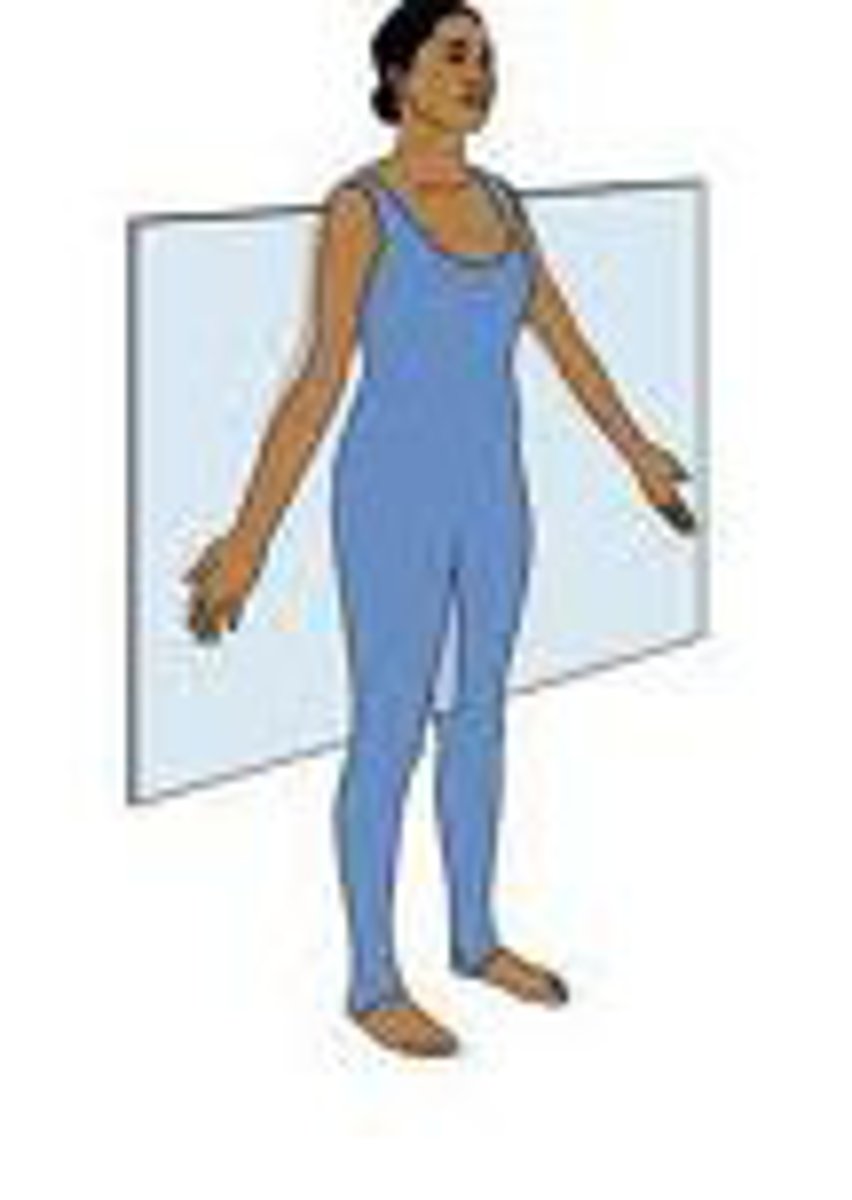
Planes of Division: Frontal (Coronal)
Divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
Plane is from left to right.

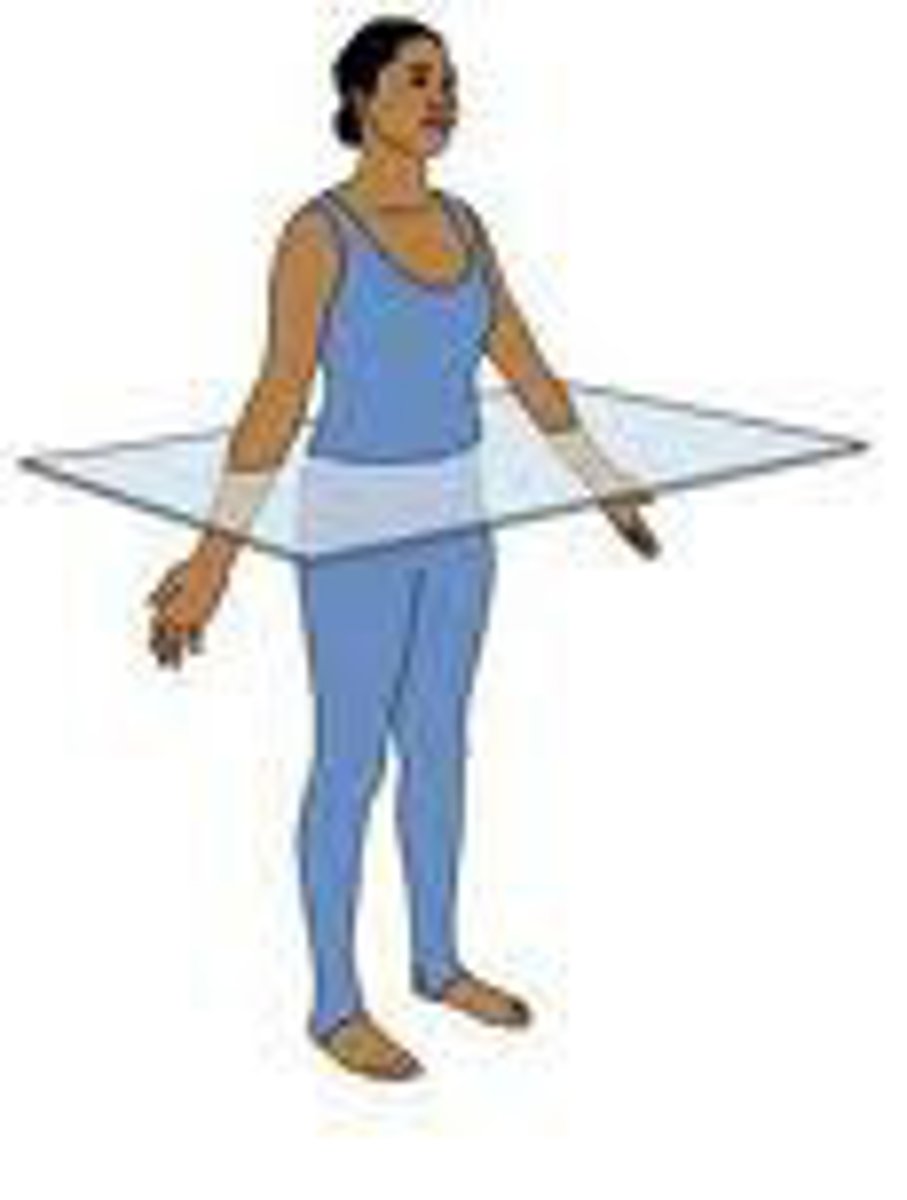
Planes of Division: Transverse (horizontal)
Divides the body into superior and inferior parts
Plane is horizontal, through the body
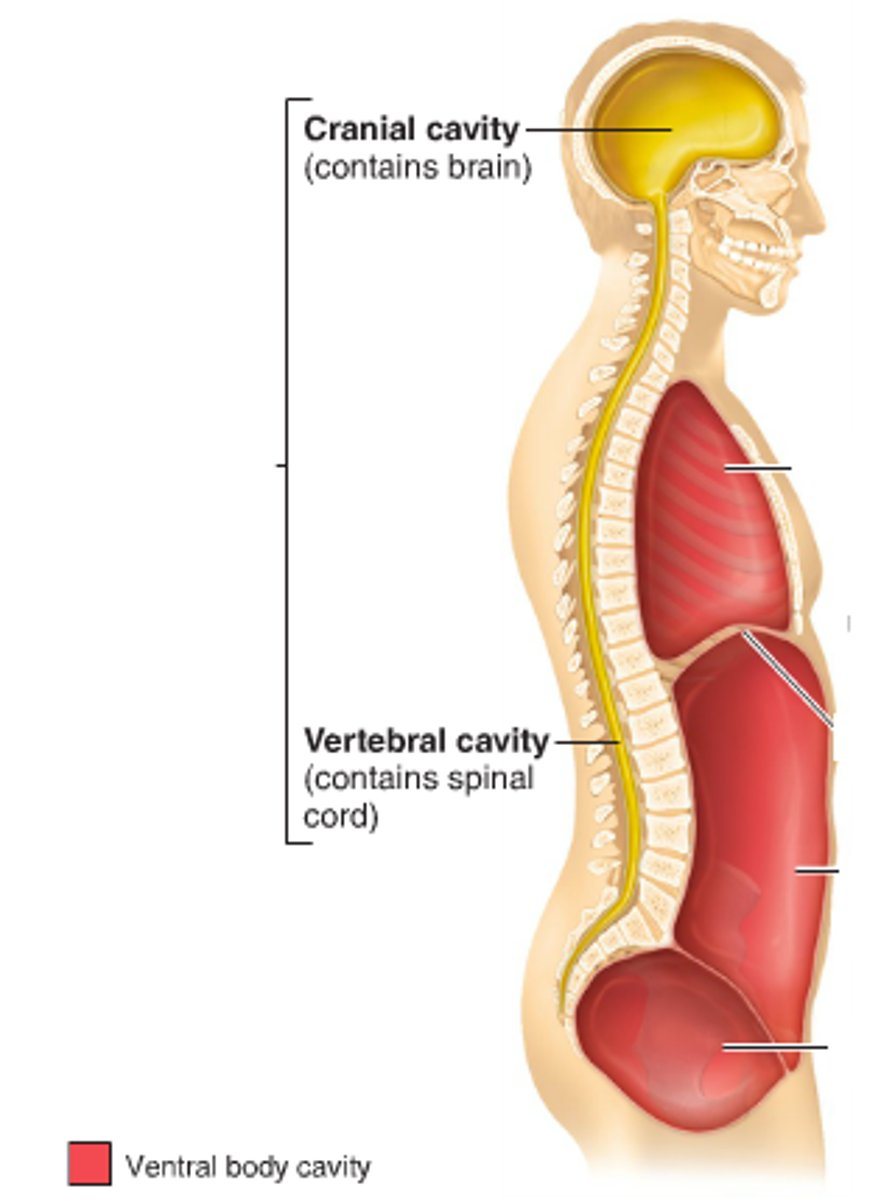
What are the 2 main subdivisions of the Dorsal cavity?
Cranial cavity and spinal cavity.
They are one continuous space
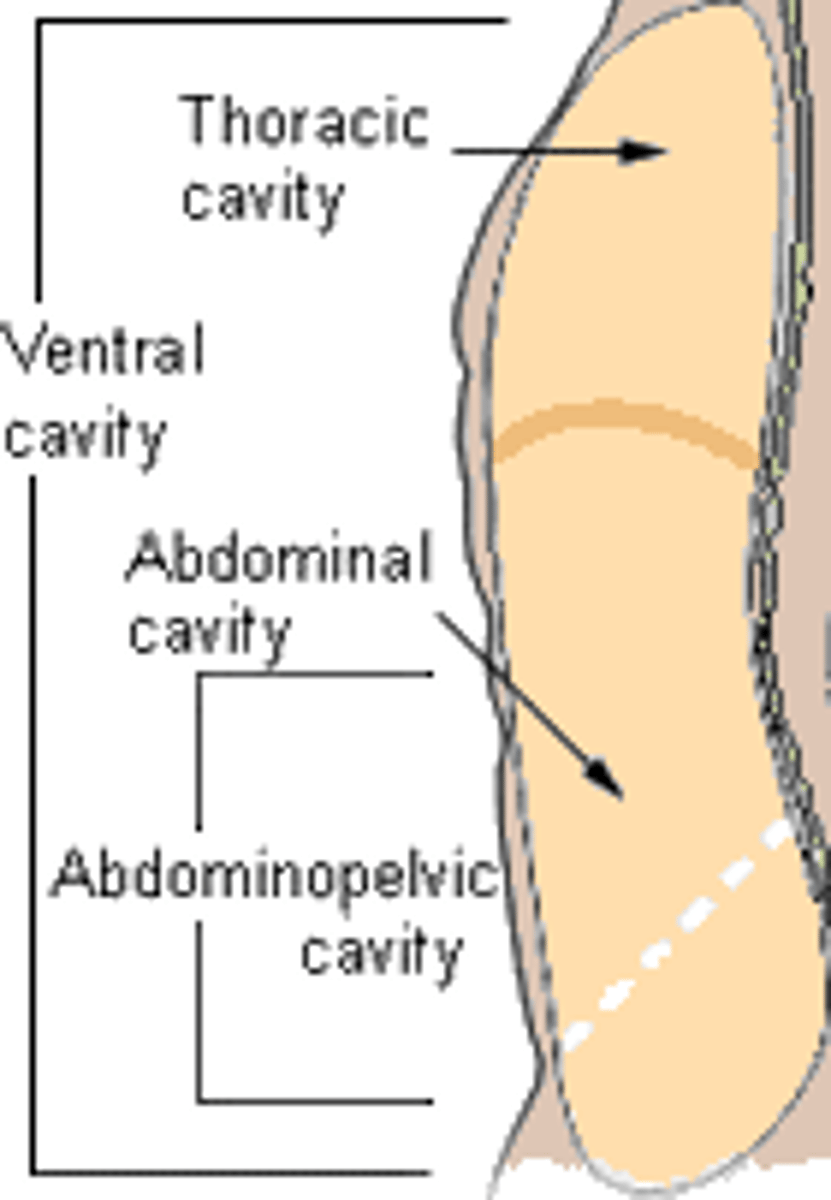
What are the two main subdivisions of the Ventral cavity? What is are they separated by?
Thoracic cavity and Abdominopelvic cavity
separated by the diaphragm
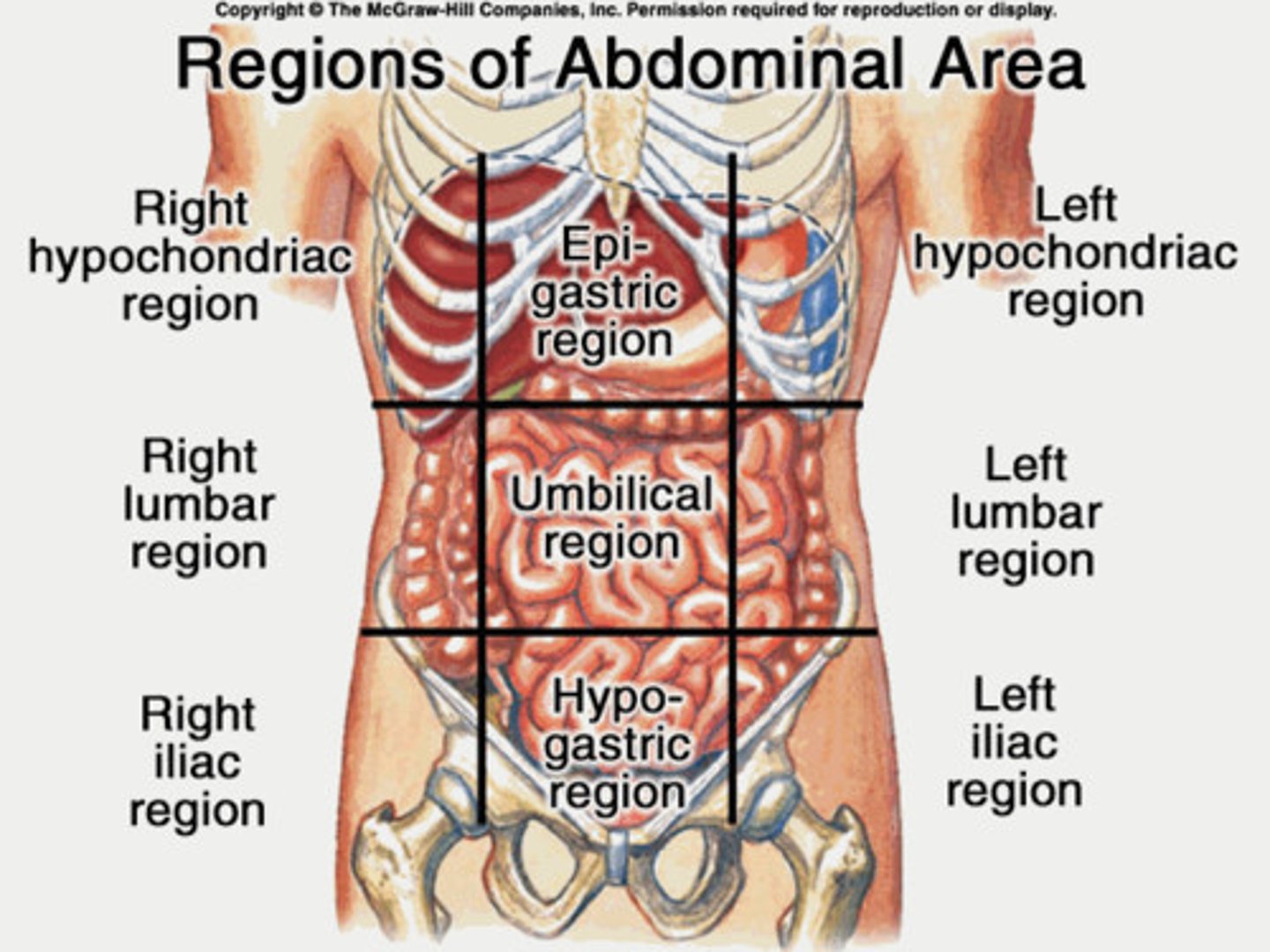
9 regions of the abdomen *see picture
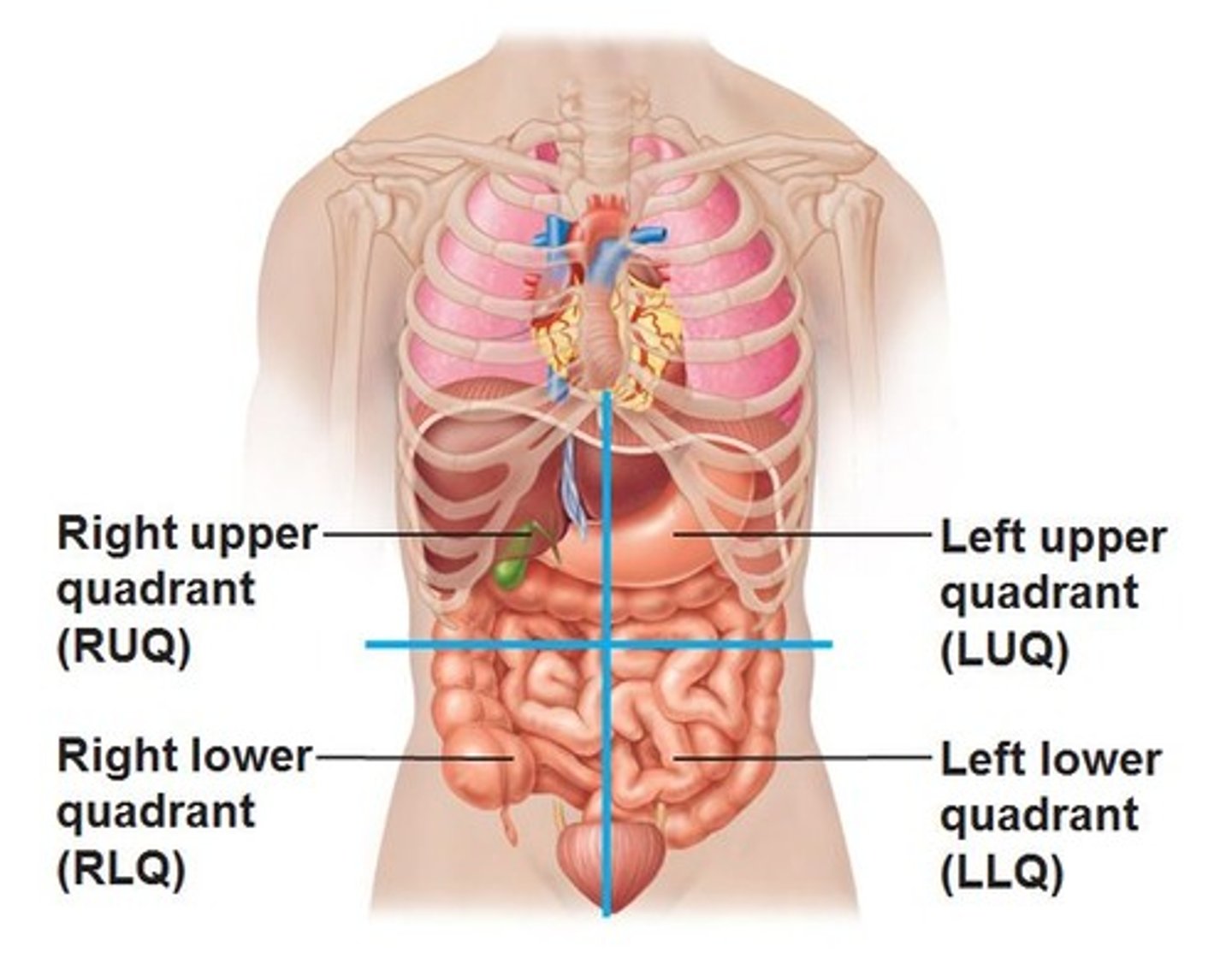
4 quadrants of the abdomen *see picture
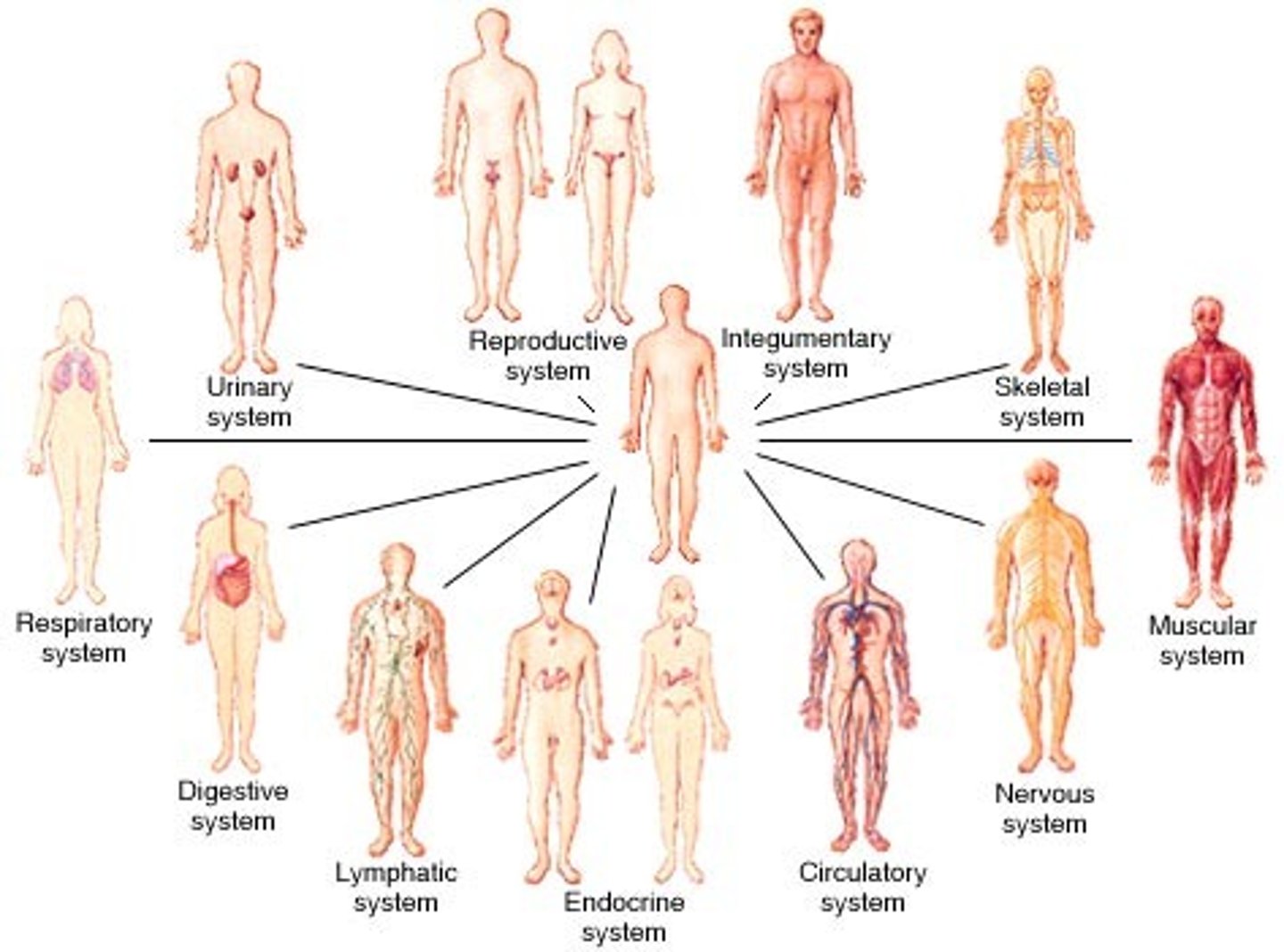
Name the 11 Systems of the body
integumentary, skeletal, muscular, nervous, endocrine, cardiovascular, lymphatic, respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive
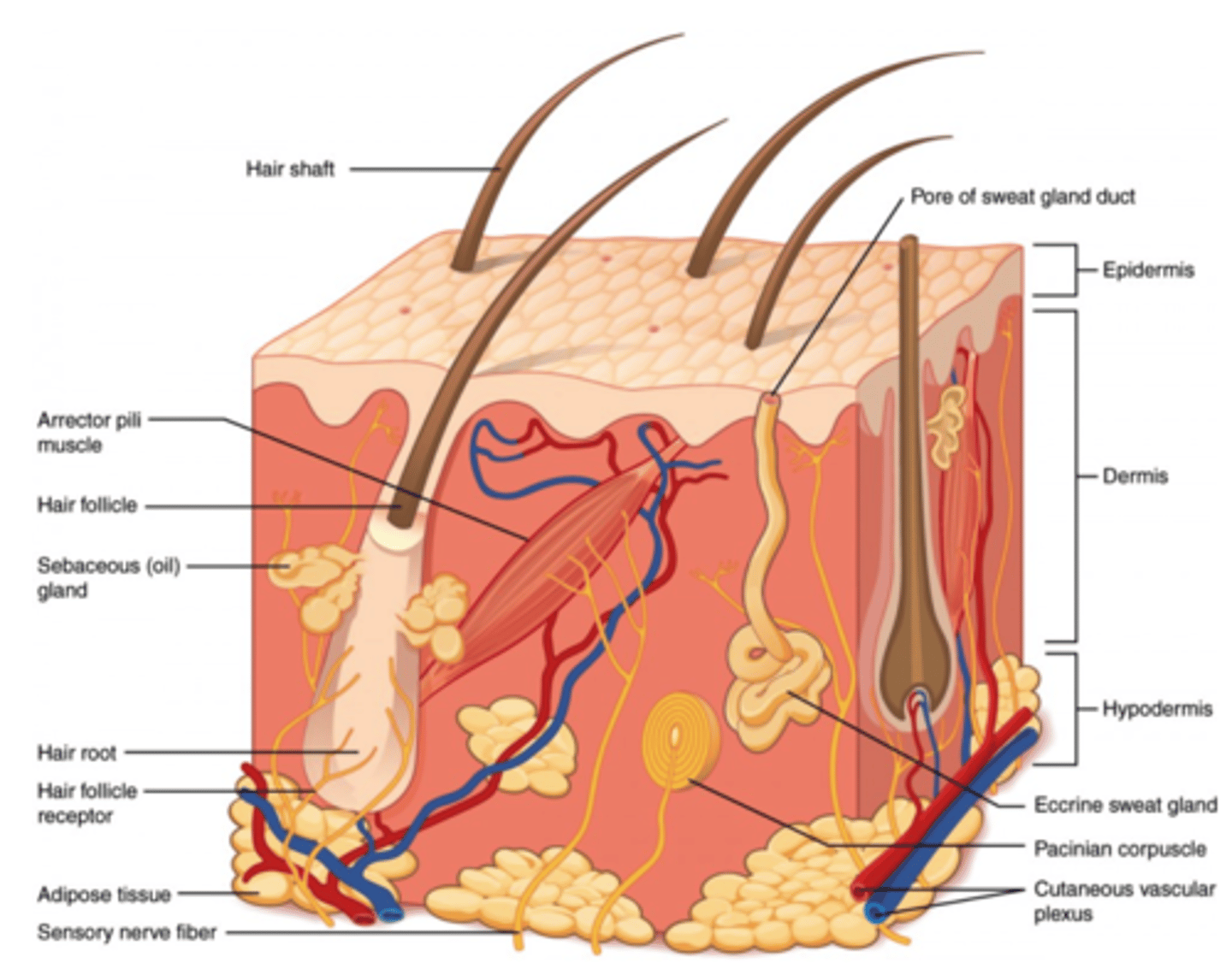
What is part of the integumentary system?
skin, hair, nails, sweat and oil glands
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, smooth (found in walls of vessels and hollow organs
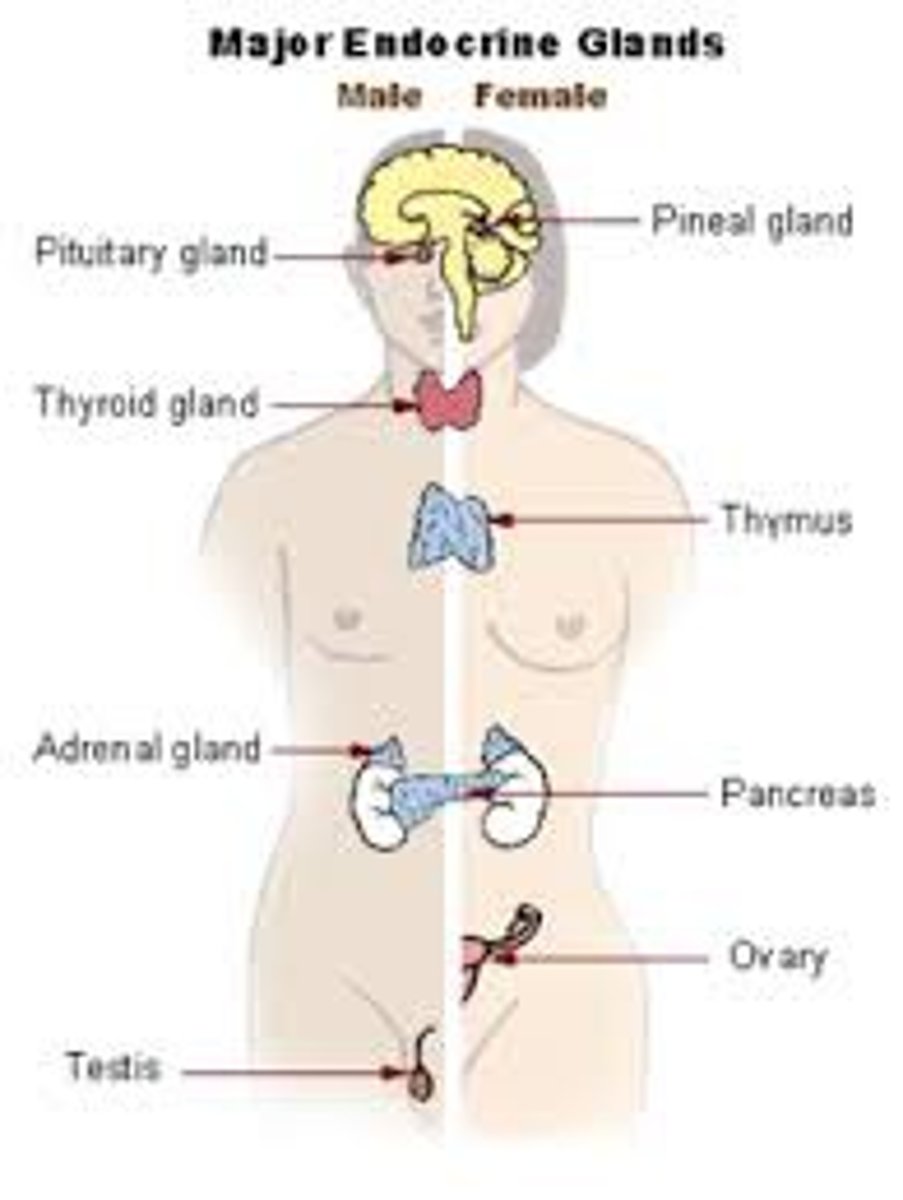
What are the major organs of the Endocrine system?
pituitary gland, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal glands, gonads (ovaries/testes)
Define homeostasis
maintenance of a stable internal environment
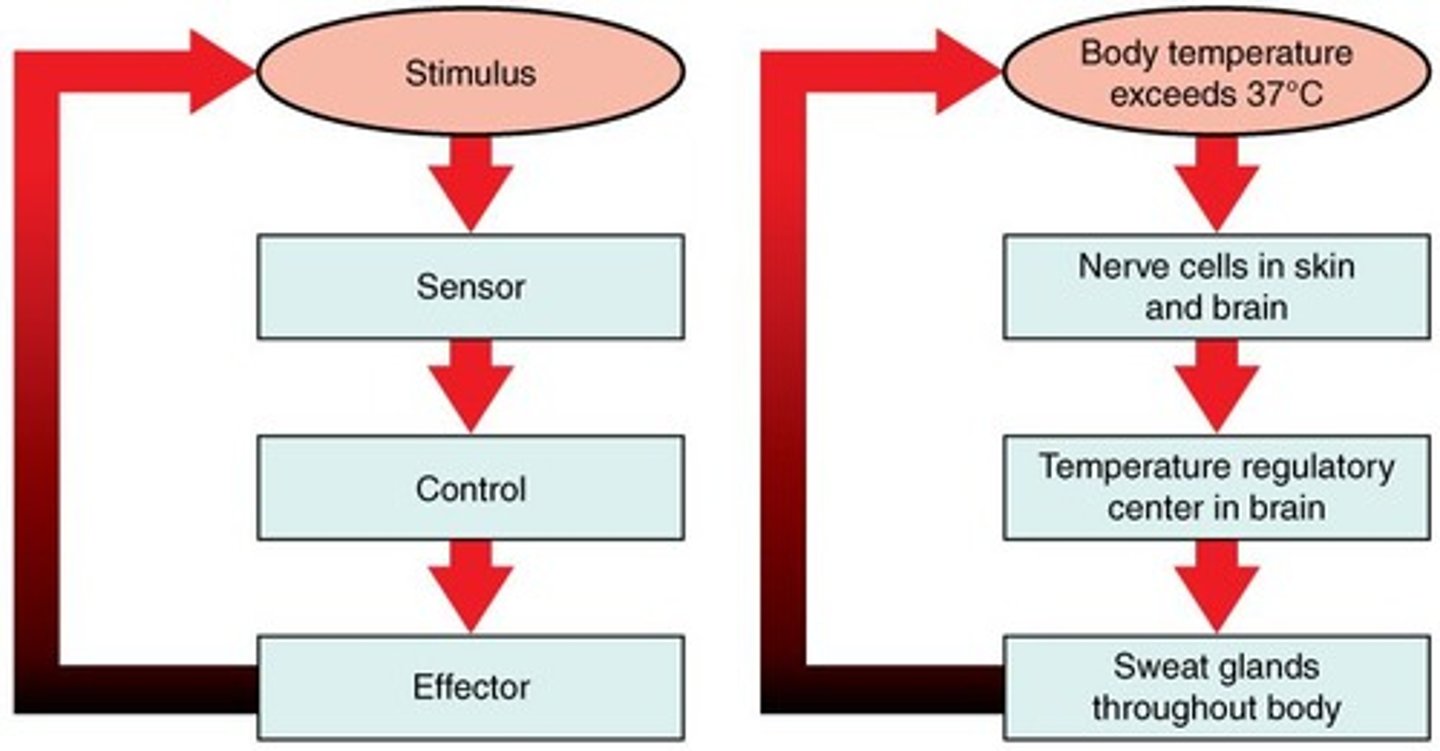
What is a negative feedback loop? What are the 3 components?
A negative feedback loop is a system where an increase in output leads to a decrease in the original input, essentially counteracting the change and promoting stability
3 Components: sensory, control centre, effector
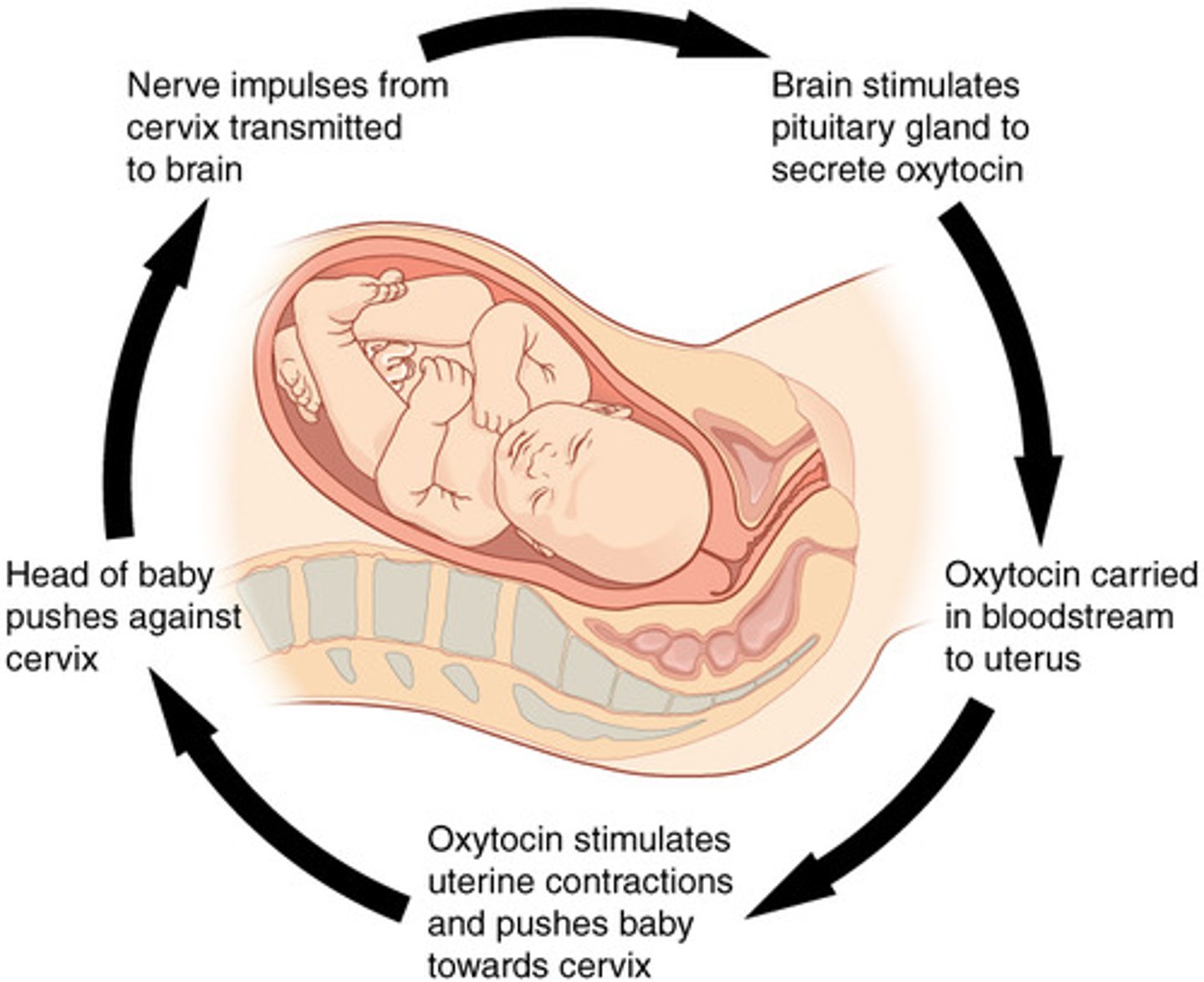
What is a positive feedback loop?
A positive feedback loop is a process where a change in a system leads to further changes in the same direction, amplifying the initial change
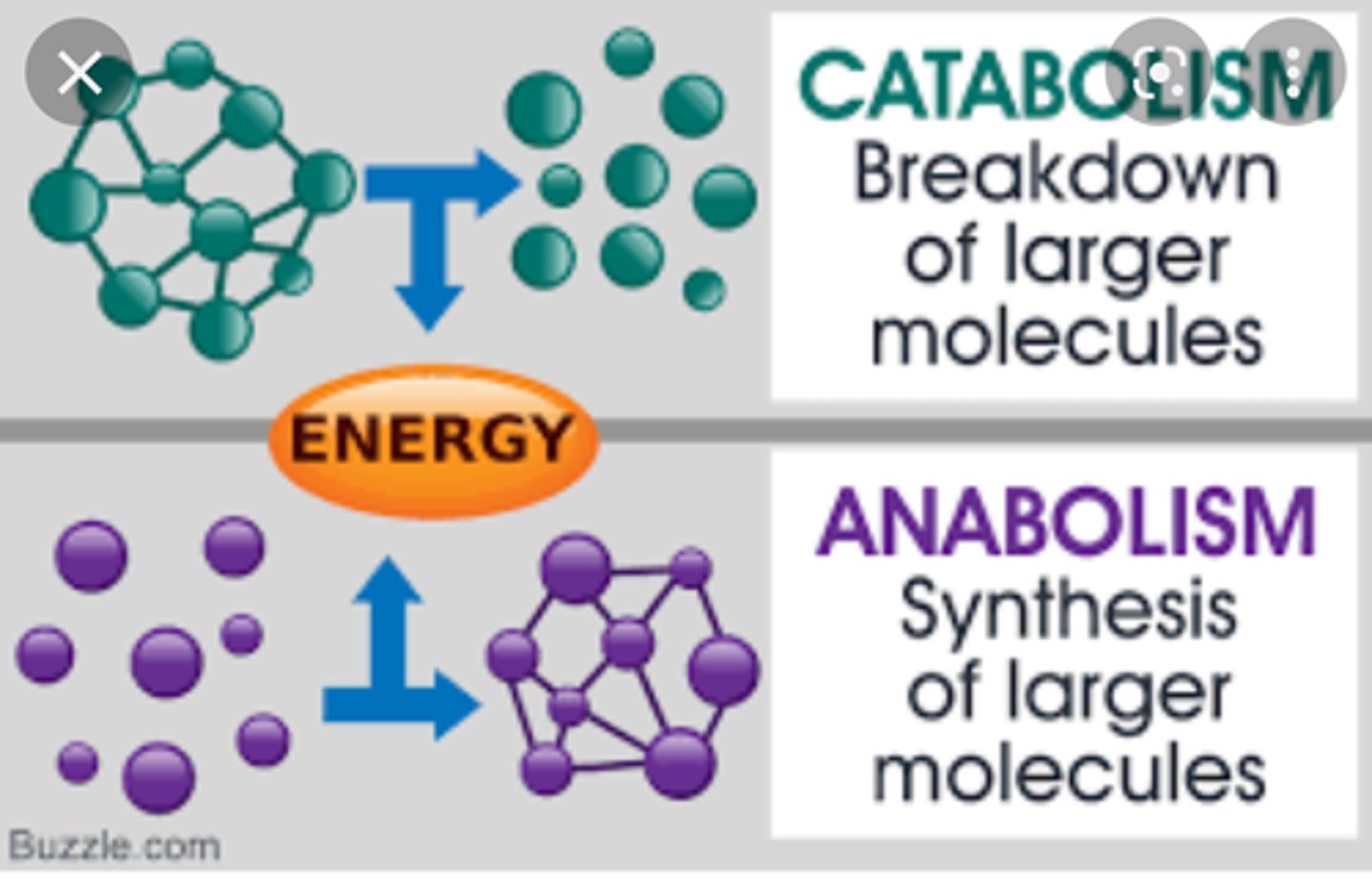
What are the 2 types of metabolism?
catabolism and anabolism