Pericardial Disease
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Visceral pericardium
Parietal pericardium
What are the two layers of the pericardium?
Fibrous pericardium
Outermost layer of the pericardium.
Contiguous with the adventitia of the great vessels.
Serous pericardium
Inner portion of the pericardium.
Two-layered sac that breaks up into the visceral and parietal pericardium.
Visceral
Parietal
What are the two layers of the serous pericardium?
Parietal pericardium
The outer layer of the serous pericardium.
Visceral pericardium
The inner layer of the serous pericardium.
Also known as the epicardium.
Pericardial cavity
Area which normally contains a small amount of serous fluid to prevent friction.
Lies between the visceral and parietal pericardium.
Fixes cardial position anatomically
Prevents excess movement
Reduces friction between the heart and surrounding organs
Acts as a barrier to infection or malignancy from surrounding organs
What is the function of the pericardium (4)?
1-2 mm
What is the normal pericardial thickness?
<50 mL
What is the normal amount of pericardial fluid?
Pericarditis
Inflammation of the pericardium.
Infectious
Autoimmune
Reactive
Metabolic
Traumatic or iatrogenic
Neoplastic
MI
What are the causes of pericarditis (7)?
Pericardial chest pain
Pericardial friction rub
EKG features
New or increasing pericardial effusion
For the diagnosis of pericarditis, at least two of the four criteria must be met.
Widespread ST elevation
Diffuse PR depression
Diffuse T wave inversion
Normalization
What are the EKG features of pericarditis (4)?
Pericardial friction rub
“Scratchy” sound on auscultation.
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Tachycardia or palpitations
Fever
General weakness or malaise
Leg swelling
Cough
What are the symptoms of pericarditis (7)?
Sudden or gradual onset
Sharp
Aggravated by laying supine
What are the characteristics of chest pain associated with pericarditis (3)?
NSAIDs
Colchicine
Corticosteroids
Aspirin
What are the treatment options for pericarditis (4)?
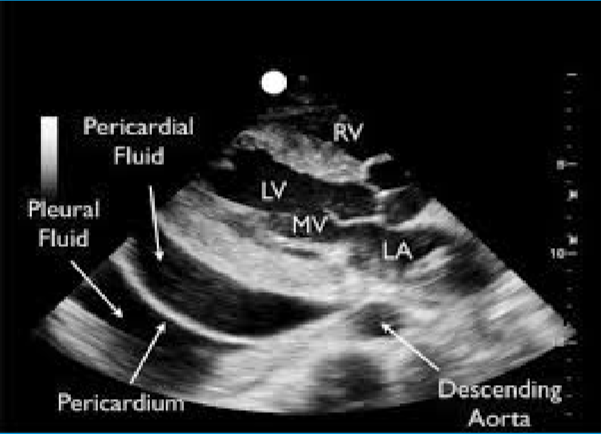
Pericardial effusion
Abnormal accumulation of pericardial fluid.
May be diffuse or loculated.
Fluid accumulation leads to an increased intrapericardial pressure, which can negatively affect heart function.
Infectious
Autoimmune
Neoplastic
Endocrine or metabolic
Trauma or iatrogenic
Radiation therapy
Volume overload states (CHF, cirrhosis)
MI
Idiopathic
What are the causes of pericardial effusion (9)?
Iatrogenic
Relating to illness caused by medical examination or treatment.
Dyspnea
Orthopnea
Chest pain
Cough
Painful breathing
Fainting or dizziness
Low-grade fever
Rapid heart rate
Fatigue or weakness
What are the symptoms of pericardial effusion (9)?
Asymptomatic pericardial effusion
A patient can have significant pericardial effusion and experience no signs or symptoms, particularly if the fluid has increased slowly.
More common if the effusion is caused by cancer or inflammatory disorders.
Echocardiography
The main diagnostic too used in the evaluation of pericardial effusion.
Swinging heart
Large effusions can produce a ___ .
50-100 mL
Volume of a small pericardial effusion.
100-500 mL
Volume of a moderate pericardial effusion.
>500 mL
Volume of a large pericardial effusion.
Trivial pericardial effusion
Echolucent space <10mm.
Seen only in systole.
Small pericardial effusion
Echolucent space <10mm.
Seen only in systole and disatole.
Moderate pericardial effusion
Echolucent space 10-20 mm.
Large pericardial effusion
Echolucent space >20 mm.
Cardiac tamponade
Constrictive pericarditis
Any time the indication for an echo is pericarditis or if a pericardial effusion is visualized, then extra images should be taken to evaluate for ___.
Ventricular interdependence
MV and TV inflow respiratory variation
Annulus versus
Expiratory hepatic venous diastolic flow reversal
What should be evaluate on echo when assessing for cardiac tamponade or constrictive pericarditis (4)?
Ventricular interdependence
Dysfunction of one ventricle secondary to a disorder of the other.
Annulus versus
Septal E’ velocity is greater than (>) the lateral E’ mitral annulus on TDI.