human memory exam 1
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
chapter 1 and 3
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
hermann ebbinghaus
was first to study memory scientifically
developed the method to study memory
believed in the importance of unconscious, Lionshare is unconscious
“Savings”
verbal learning
a term applied to an approach to memory that relies principally on the learning lists of words and nonsense syllables
gestalt psychology
an approach to psychology that was strong in Germany in 1930s and that attempted to use perceptual princlp;es to undertsnad memory and reasoning
clive wearing
case study of an extreme case of amnesia due to Herpes breaking the blood-brain barrier
cannot move memory into the LTM
he didn’t forget how to play the piano and music
shows memory is not a single simple system
reductionism
the view that all scientific explanations should aim to be based on a lower level of analysis: Psychology in terms of physiology, physiology in terms of chemistry and chemistry in terms of physics
mere exposure effect
we like familiar things more than novel things
subconsciously will pick the familiar object
modal model
bottle neck effect
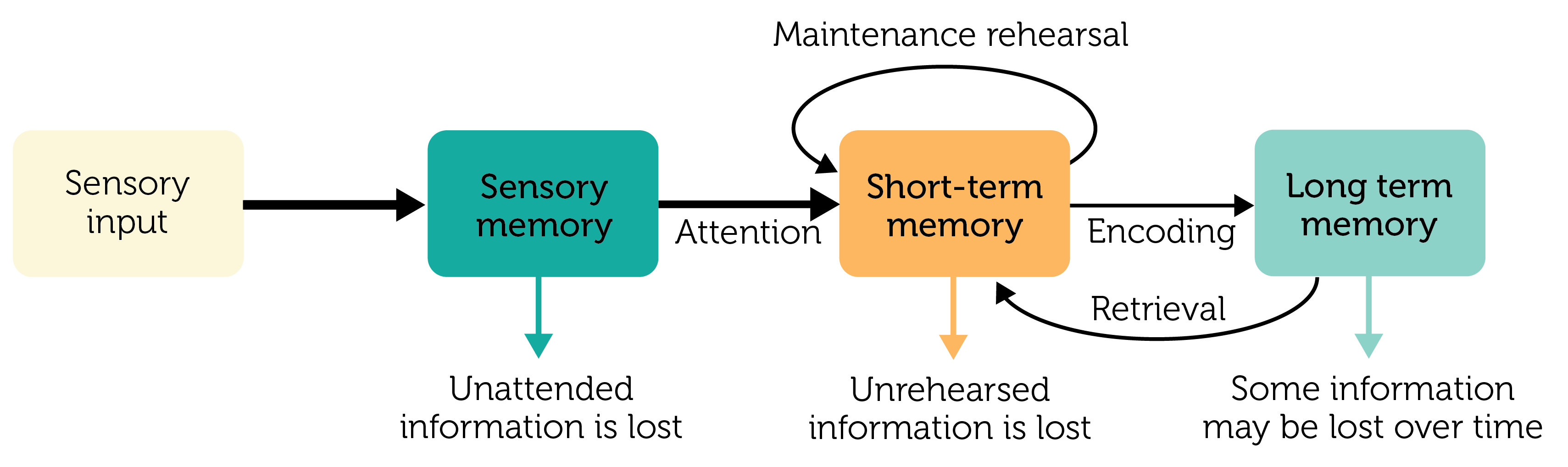
a different modal model
everything starts as episodic → things that are repeated become semantic
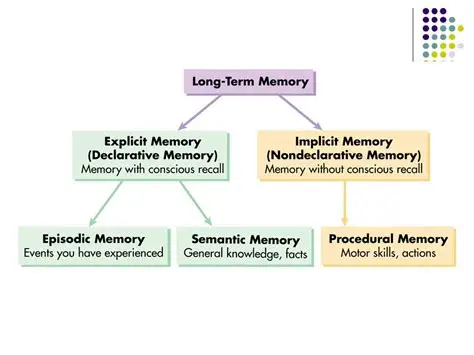
explicit/declarative memory
concious
memory that is open to intentional retrieval, whether based on recollecting personal events of facts
episodic memory
from explicit memory
assumed to underpin the capcity to remember specific events
semantic memory
from explicit memory
assumed to store assumalative knowledge of the world
implicit memory - nondeclarative
unconcious
retrieval of information from long term memory through performance rather than explicit concious recall or recognition
turns into conditioning, skills, priming, performance
Endel Tulving
episodic memory allows us to mental time travel
iconic memory
a term applied to the brief storage of visual information
echoic memory
a term applied to the brief storage of auditory information
masking
a process by which the perception and/or storage of a stimulus is influenced by events occuring immediately before presentation (forward masking) more commonly after (backwards masking")
visual memory
a quarter of a second
auditory memory
two-three-four seconds
short-term memory / working memory
7-10 seconds
long term memory
any memory longer than 10 seconds
order of ebbinghaus’ contributions
1 He developed a method of studying memory
2 He is credited as being the first to discover certain empirical findings, such as the learning curve and the forgetting curve.
3 He contributed significantly to an overarching theory of memory.
savings formula
time of intial learning - time for relearning
time for intitial learning times 100
burtt study
played meaningless materical (selection from greek dramas) and were read to a 15 month child everyday for 3 months
tested at 5, 11, 15 years
learning curve
one of Ebbinghaus’ contributions

forgetting curve

three phases of memory
encoding → retention time passing → retrieval
intentional encoding
a person actively tries to commit something to memory
incidental encoding
some other “cover task” is used by the experiences, most of what we remember in our lives was not encoded intentionally (what you ate for breakfast)
common encoding manipulations
repetition - memory increases with increased repetition (learning curve)
encoding time - being exposed to stimulus for longer
“elaboration” - attaching meaning, visualizing, etc memory increases with elaboration
retention
retention interval: millisecond to half century
experimenters can manipulate what happens b/w encoding and retrieval
free recall
tell me anything that you remember in any order
explicit test
serial recall - recall in order, usually only for short term memory tasks
clustering
in free recall, the tendency to group related or neighboring items together during free recall, reflecting the way the memory is organized in the mind
cued recall
you are given a “hint”, a cue to help you remember “a bit of furniture”
recognition
“did you see this before”
Montana (Y or N) Wyoming (Y or N)
or forced choice
oregon or idaho
facial recognition
hits and false alarms
associative recognition test
everything can look familiar
harder test than standard recognition
difference between familarity and recollection
familiarity- a vague, nonspecific feeling of past occurrence
recollection - retrieval/access to details about a past occurrence; more specific
source memory
where did you learn/see/hear/ or read it
gets worse with age
source monitoring framework - Johnson
people infer the source by evaluating qualitative features of memories
physical memories
perceptual details
contextual details
cognitive operations
destination memory
remembering to whom you told something to
repeating the same stories to friends
even harder than source memory, especially for older adults
implicit memory test
the task does not refer back to the encoding episode
asked to complete regular test
perceptual ID test
encoding phase- incidental - expose people to words under some other guise
on the test, participants simply have to try and read words that are presented very quickly and or obscured in some way (masking)
encoding phase is not referred to during the ID phase
called repetition priming, perceptual priming, positive priming
explicit memory test
a memory test that elicits conscious memories of previously experienced events.
examples
free recall
serial recall
cued recall, multiple choice tests
top down processing
using stored knowledge → memory
primacy effect
better memory for beginning of the list
due to extra attention/rehearsal of items at the beginning of a list transfers these items into LTM
developed gradually with age
recency effect
better memory of the end of the list
modality effect
larger recency effect for auditory information due to the lingering auditory trace
only affects the end of the list because it is the only part not affected by “auditory masking”
suffix effect
an auditory stimulus after the list wipes out the modality effect
saying end at the end of list instead of silence → no modality effect
why STM vs LTM
intuition (remembering information just experienced “feels” different than retrieving information from more remote
evidence of very rapid forgetting of information not rehearsed
Clive Wearing → intact STM and impaired LTM
Recency effects
ways to test STM
explicit memory tests
digit span
letter span
phonological similarity effect
block tapping test?
phonological similarity effect
a tendency for immediate serial recall of verbal material to be reduced, when the items are similar in sound
bat vs vat
Miller 1956 “ magic number”
digit span test - most people’s limit was 7±2 numbers recalled
information is chunked in a meaningful way
chunking / recoding
using long term memory to reduce the number of separate items you need to remember
grouping items and remembering the groups instead of the items
chase and ericsson study
trained a student to reach a digit span memory of 82
stupidizing
4 or lower- immediately can tell its number
5 or higher- have to count it quickly
Irrelevant sound effect
a tendency for verbal STM to be disrupted by concurrent fluctuating sounds, including both speech and music
corsi block tapping
visuo-spatial counterpart to digit span involving an array of blocks that the tester taps in a sequence and the patient attempts to copy
short term memory test
visuo-spatial STM
retention of visual and/or spatial information over brief periods of time