Lecture 2: Upper Limb
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
The upper limb is specialized for mobility and fine motor manipulations. What are the 4 segments of the upper limb?
Shoulder (girdle) = scapula and clavicle with associated muscles
Arm - longest segment, formed by humerus
Forearm - connects elbow to wrist, form around radius and ulna
Hand = carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges; Consist of sensory nerve endings for touch, pain, and temp
Describe the clavicle with its function as well.
Clavicle has an acromial end (flat, forms joint with scapula)
Sternal end - forms sternoclavicular joint with manubrium
Functions:
Support scapula and upper extremity from axial skeleton
Protects large nerve trucks (brachial plexus) and vessels passing from neck to upper extremity
Where is the clavicle frequently broken?
the middle and lateral 1/3 area where the bone “changes direction”; subclavian groove
Describe the following parts of the shoulder osteology
Acromion
Coracoid process
Spine of Scapula
Suprascapular notch
Acromion - highest point of the shoulder and forms the acromioclavicular joint with the clavicle.
Coracoid process (Kaw!) - attachment site for coracoclavicular ligament that suspends the upper limb from the clavicle
Spine of scapula separates posterior side into supraspinous and infraspinous fossas
Suprascapular notch - a grove on the scapula that allows passage of the suprascapular nerve and vessels.
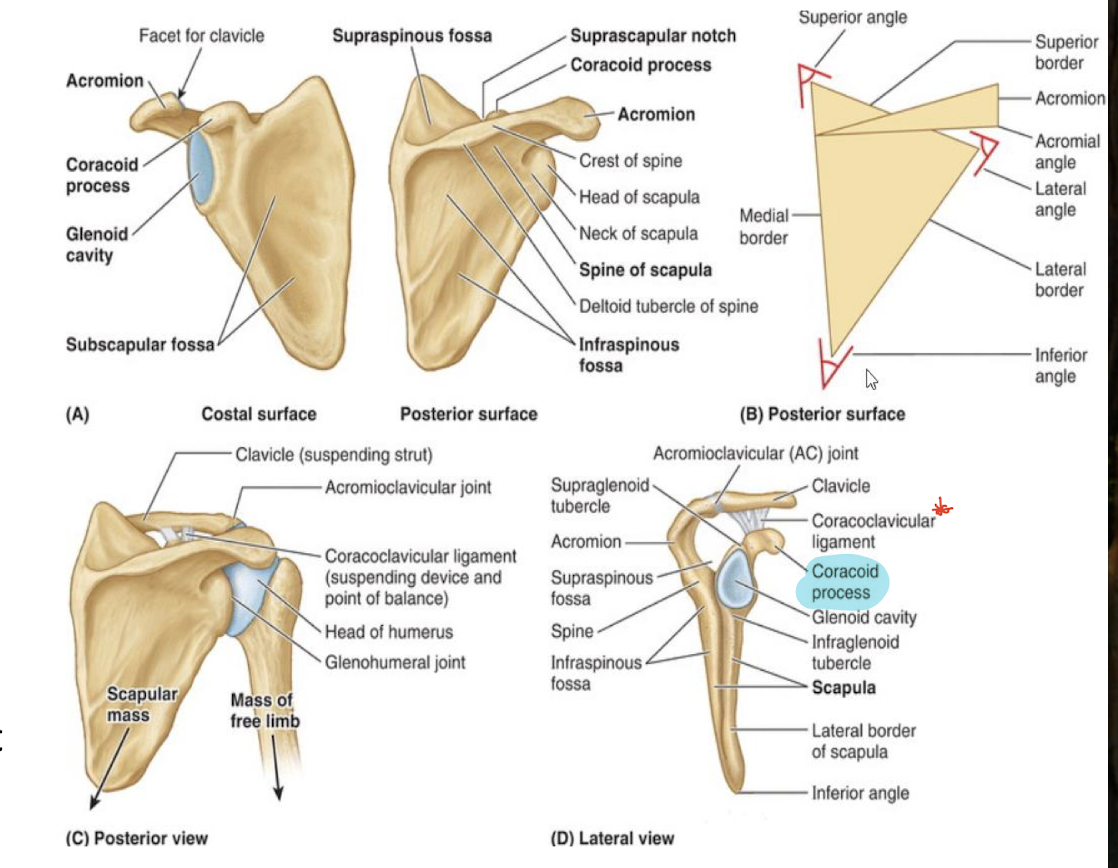
T/F: borders and angles serve as sites of muscle attachment
true
Which joint is considered a physiological joint in the shoulder between the thorax and scapula?
Scapulothoracic joint - serves as articulation between the shoulder blade (scapula) and the rib cage (thorax)
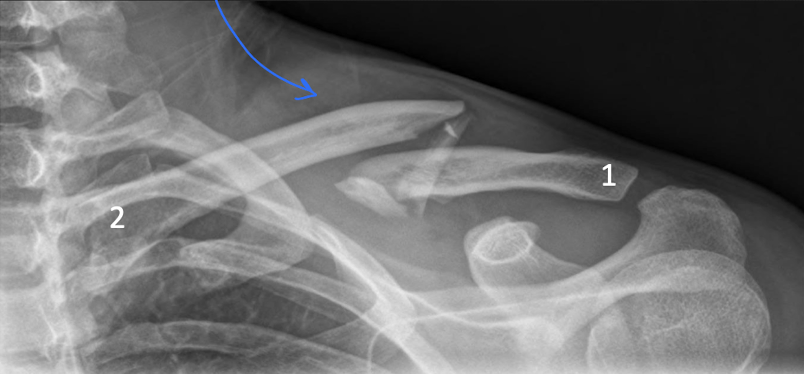
Review radiology of the shoulder
…
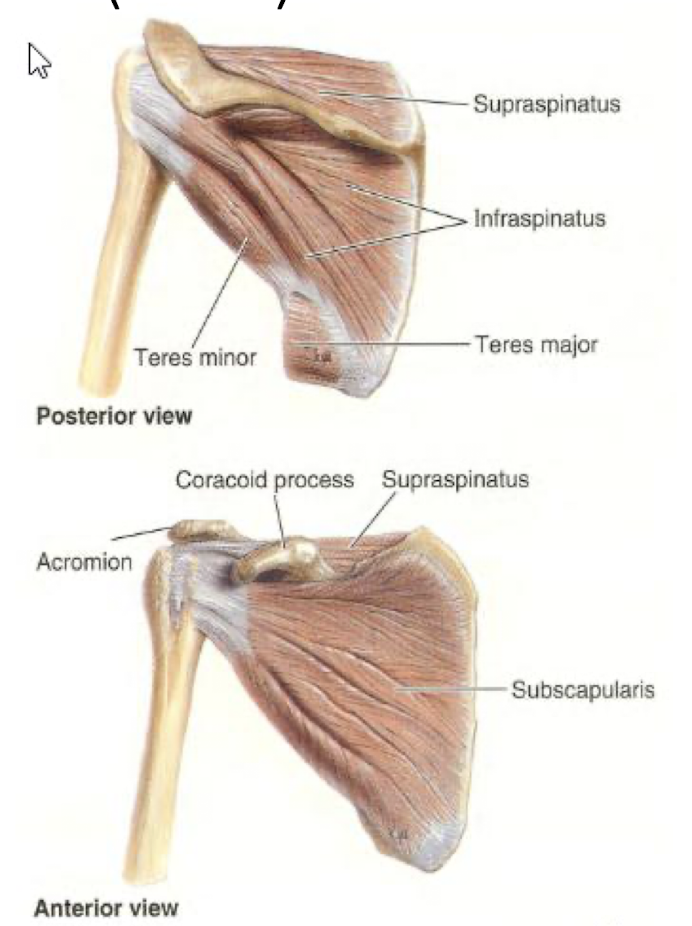
What are the 3 groups of shoulder muscles and the muscles that reside in each?
Posterior Axioappendicular
Trapezius
Latissiumus dorsi
Levator Scapulae
Rhomboid major and mind
Anterior Axioappendicular
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor
Subclavius
Serratus Anterior
Scapulohumeral mm (6 muscles that attach the scapula and humuers)
Deltoid
Teres Major
Teres Minor
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Subscapularis
Which of the three muscle groups functions to attach the scapula to the humerus?
a. Posterior axioappendicular
b. Anterior axioappendicular mm
c. scapulohumeral mm
c. scapulohumeral mm
Describe the muscles of the Anterior axioappendicular shoulder muscle group.
Action, Innervation, and possible blood supply
Pectoralis Major
Action: adduct and medially rotate arm
innervated by medial and lateral pectoral nerves
Pectoralis Minor
Action: Stabilizes scapula
Innervated by medial pectoral nerve (nerve goes through the muscle_
side: attaches coracoid process to ribs 3-5
Subclavius
Action: protects the nerves under the clavicle and anchors and depresses clavicle
Innervated by nerve to subclavius
side: attaches the clavicle to the 1st rib (sits on inferior side of clavicle)
Serratus Anterior
Action: protract and rotate scapula
Innervated by long thoracic nerve
Blood supply: long thoracic artery
Describe the muscles of the Scapulohumeral muscle group of the shoulder.
Action, Innervation, and possible blood supply
Deltoid
Actions: Abducts arm (medial side), flex and medially rotates arm (anterior side), and extend and lateral rotation (posterior side)
Innervated by axillary nerve
Blood supply: posterior circumflex humeral artery
Teres Major
Action: Adducts, and medially rotates the arm
Innervated by subscapular nerve
Blood supply: circumflex scapular artery
Teres Minor
Action: Laterally rotates arm
Innervated by axillary nerve
Supraspinatus
Action: Abducts arm from full adduction
Innervated by suprascapular nerve
Blood supply: suprascapular artery
Infraspinatus
Action: Laterally rotates arm
Innervated by suprascapular nerve
Blood supply: suprascapular artery
Subscapularis
Action: adducts and Medially rotates arm
Innervated by upper and lower subscapular nerves
What are the Scapulohumeral muscles of the rotator cuff superior to inferior?
Supraspinatus (related to rotator cuff disolations)
Infraspinatus
Teres Minor
Subscapularis
SITS
In the arm, describe the anatomical neck, surgical neck, and radial groove and their importrance.
Anatomical neck - the groove surrounding the head of the humerus and indicates limit of joint.
Surgical neck - The narrow part of the humerus and site of fractures
importance: related to axillary nerve damage as neck fractures
Radial groove - a groove on the posterior humeral shaft
importance: holds radial nerves adn deep branch of brachial artery
Damage to which nerve in the upper limb will cause hand drop?
A. Ulnar
B. Radial
C. Axillary
D. Basilic
B. Radial
Differentiate between the medial epicondyles and lateral epicondyles
Medial epicondyle - Attachment site for flexor muscles; ulnar nerves passes through here
Lateral epicondyle - attachment site for extensors of forearm
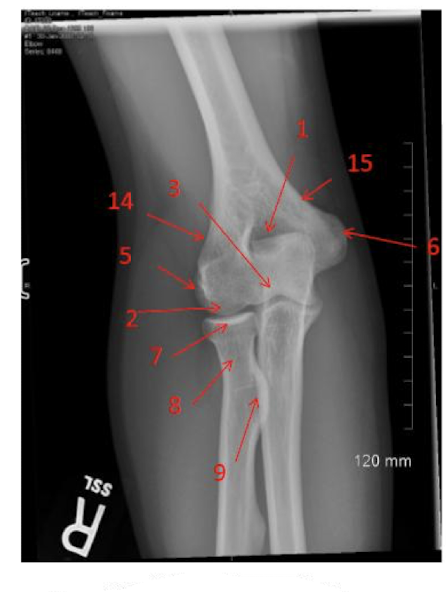
Label the Upper Extremity in the photo provided.

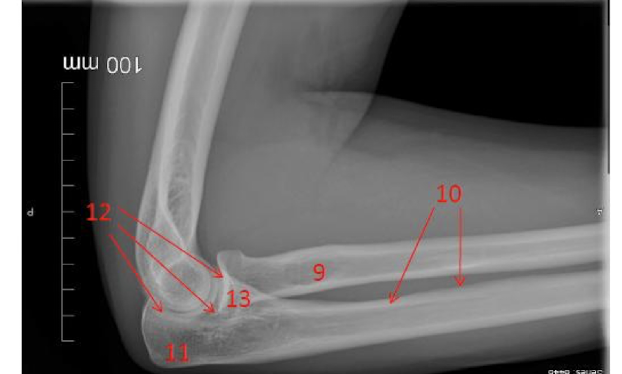
Label the Upper Extremity in the photo provided.

What is the Intermuscular septa?
Separates the arm into compartments
Anterior (flexors)
Biceps brachii
Brachialis
Coracobrachialis - attaches corocoid to arm
Posterior (extensors)
Triceps brachii
Anconeus
Describe the muscles of the anterior compartment of the arm with their action and innervation
Biceps Brachii
action: supination and flexion - put the cork in and pull out
innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
Brachialis
action: flexion of the elbow
innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
Coracobrachialis
action: flexion and adduction of the shoulder
innervation: musculocutaneous nerve
T/F: the biceps brachii attaches to the humerus
false
In the biceps brachii there are two heads. Which one is lateral and medial?
Describe the muscles of the posterior compartment of the arm with their action and innervation
Triceps brachii
3 heads (long, medial, and lateral)
action: extend forearm and resist dislocation
Innv: radial n
Artery: deep branch of brachial artery
Anconeus
action: assist extension of forearm and protects the bony structures under
Innv: radial n
What is the role of the ulnar bone?
Stablize forearm
What is the olecranon?
In ulnar bone
attaches and levers triceps
What is the styloid process of the ulnar bone?
at the distal end of the ulnar bone that provides attachment for the ulnar collateral ligament and stabilizes the wrist.
What is the interosseous membrane?
between the radial and ulnar bones - connects them together
prevents separation while bones are moving (ex: supination)
Which bone of the forearm is shorter? Radial or Ulnar?
Radial
Anterior Muscles of the forearm are arranged into 3 layers: Superficial, Intermediate, and Deep. Name the muscles in each section
Superficial
Pronator Teres
Flexor Carpi Radialis
Palmaris Longus
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Intermediate
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Deep
Flexor pollicis (thumb) longus
Flexor digitorum profundus
Pronator quadratus
Describe the superficial anterior muscles of the forearm including action and innervation
Pronator Teres
Action: pronates arm
Inn: Median nerve
Flexor carpi radialis
Action: Flexes and abducts the wrist
Inn: Median nerve
Palmaris longus
Action: Wrist flexor (sometimes absent)
Inn: Median nerve
Flexor carpi ulnaris
Action: Flexes and adducts wrist
Inn: Ulnar nerve
Describe the intermediate anterior muscle of the forearm including action and innervation
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Action: Flexes middle phalanges of fingers. Flexes wrist as well
Inn: Median nerve
Describe the deep anterior muscles of the forearm including action and innervation.
Flexor pollicis longus
Action: Flexes the thumb
Inn: Median nerve
Flexor digitorum profundus
flexes the distal phalanges of the fingers
muscle runs to end of fingers
Inn: Median nerve (digits 2 and 3) and Ulnar nerve (digits 4 and 5)
able to “come in peace”
Blood supply: anterior interosseous artery
Pronator quadratus
Action: Pronates the forearm
Inn: Median nerve
Blood supply: anterior interosseous artery
What do the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis and profundus have in common that is unique?
run in common flexor sheath through the palm = the tendons run in digital synovial sheaths to individual digits
allows flexion of digits and to anchor them by reducing friction and support
Where does the flexor digitorum superficialis split an insert in relation to the digital synovial sheath?
What about the flexor digitorum profundus?
splits and inserts on middle phalanx
inserts on distal phalanx
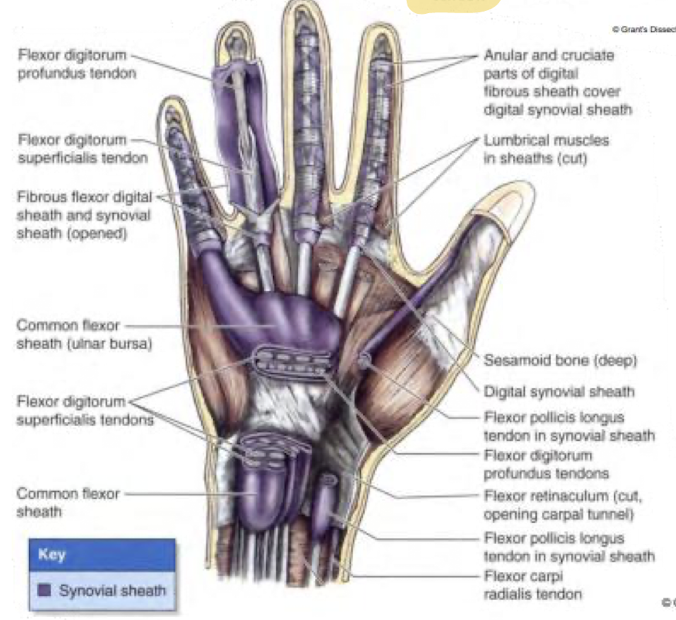
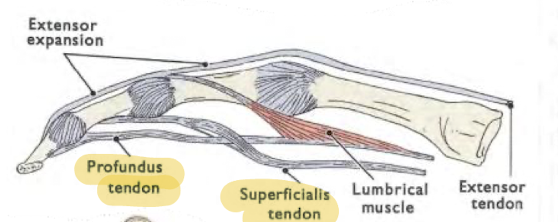
Which two tendons in the hands allow for grip strength together?
Superficialis tendon and profundus tendon
Name the posterior muscles of the forearm and the layers they reside in.
ALL INNERVATED BY THE RADIAL NERVE
Superficial layer - *proximal attachment at lateral epicondyle (around elbow)
Extensor carpi longus
Brachioradialis
Extensor carpi radialis brevis *
Extensor carpi ulnaris*
Extensor digitorum*
Extensor digiti minimi*
Deep layer
Supinator
Extensor pollicis longus
Extensor pollicis brevis
Abductor pollicis longus
Extensor indicis
What are the functions of the posterior superficial layer of the forearm?
ALL INNERVATED BY THE RADIAL NERVE
Extensor carpi longus - Extend and abduct wrist
Brachioradialis - Elbow flexor
Extensor carpi radialis brevis - Extend and abduct wrist
Extensor carpi ulnaris - Extends and adducts wrist
Extensor digitorum - Main extensor of fingers
Extensor digiti minimi - Extensor of digit 5
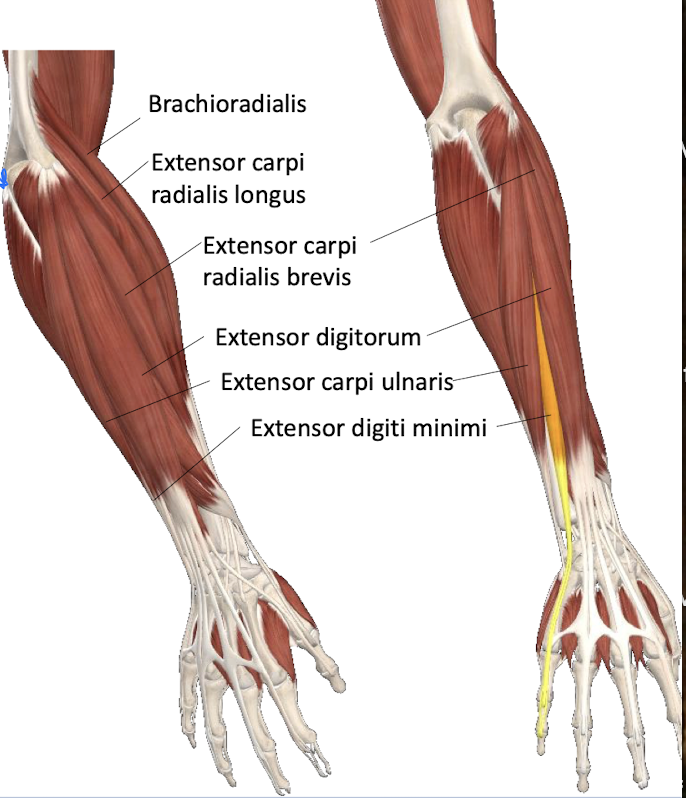
What are the functions of the posterior deep layer of the forearm?
ALL INNERVATED BY THE RADIAL NERVE
Supinator - Supinates
Extensor pollicis longus - Extends (laterally) the distal phalanx of thumb and other joints it crosses
Extensor pollicis brevis - Extends (medially) the proximal phalanx of thumb and other joints it crosses
Abductor pollicis longus - Abductor of thumb
thumb moves away from the body
Extensor indicis - Extends 2nd difit
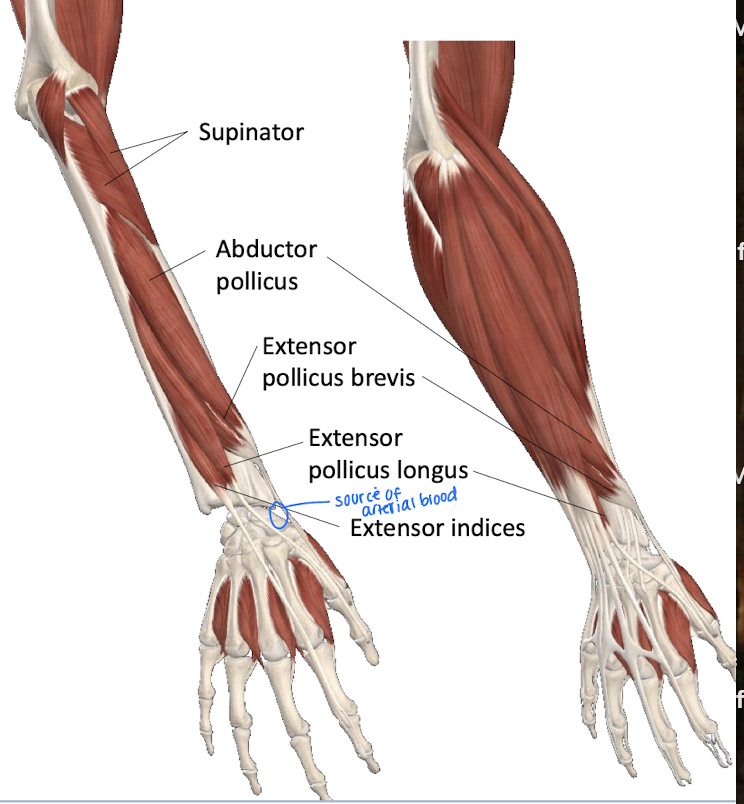
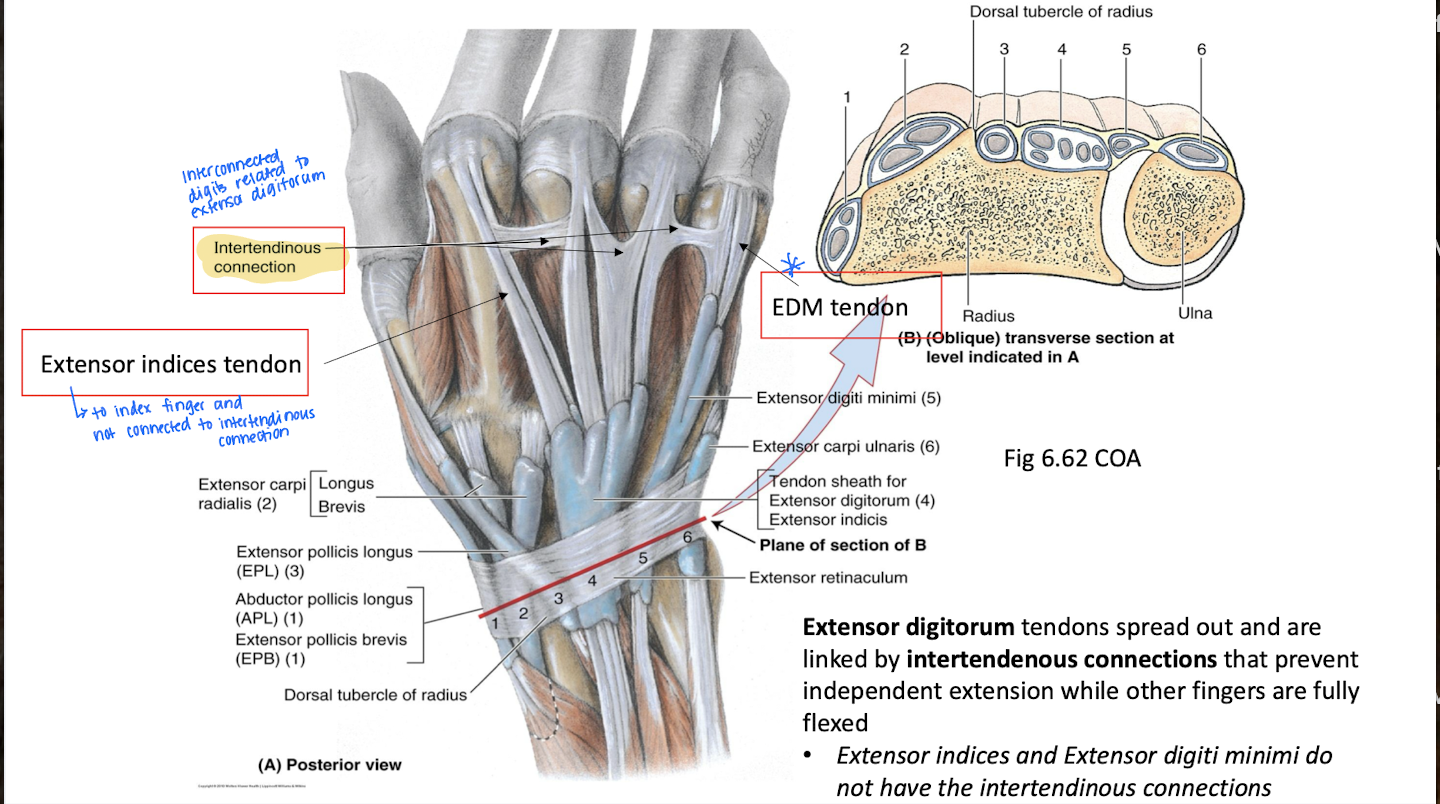
Which digits do the extensor indices tendon cover?
Index finger and not connected to intertendinous connection
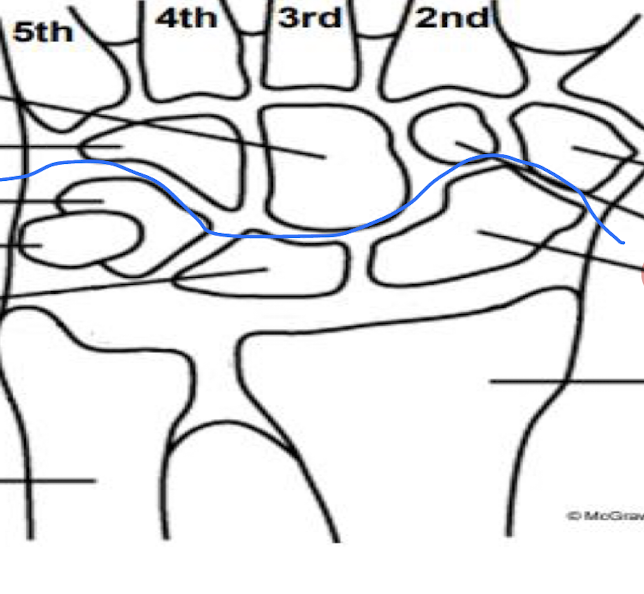
Which bone in the forearm is the most action of the wrist correlated with?
Radius
Define the function and placement of the Scaphoid, lunate, and Triquetrium bones of the wrist.
All 3 bones allow for abduction of the wrist
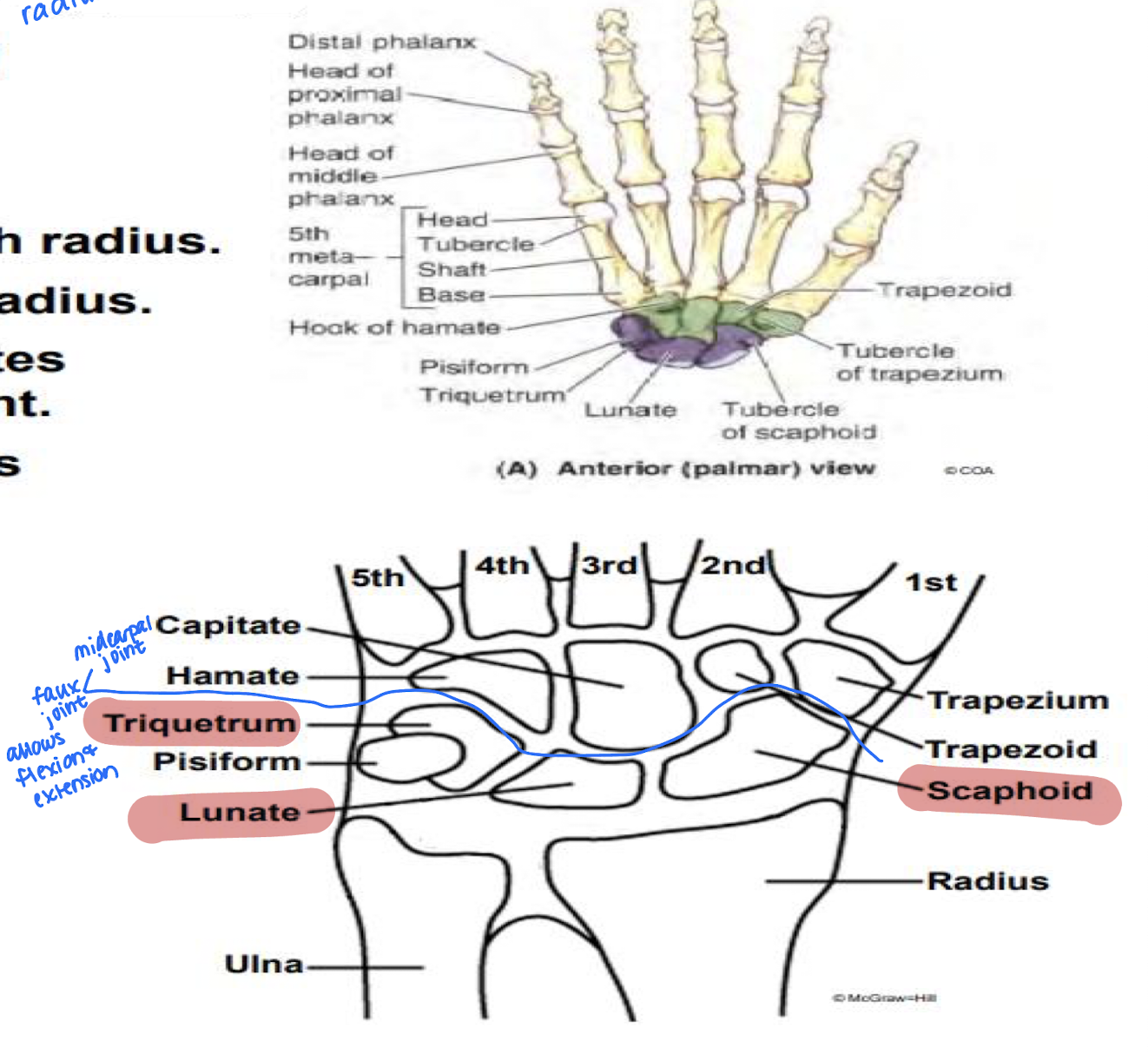
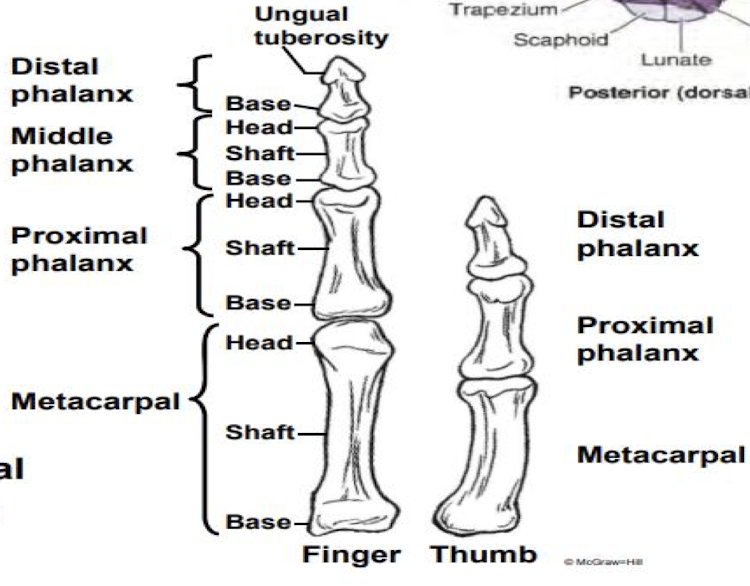
Describe the osteology of the hand.
Metacarpals
Proximal phalax
Middle phalanx
distal phalanx
From the base of the finger:
Metacarpal - In digits 1-5 beginning with thumb and articulates with carpals and phalanges
Proximal phalanx - largest; articulate with metacarpals
Middle phalanx
Distal phalanx - expanded and flattened distally for nails
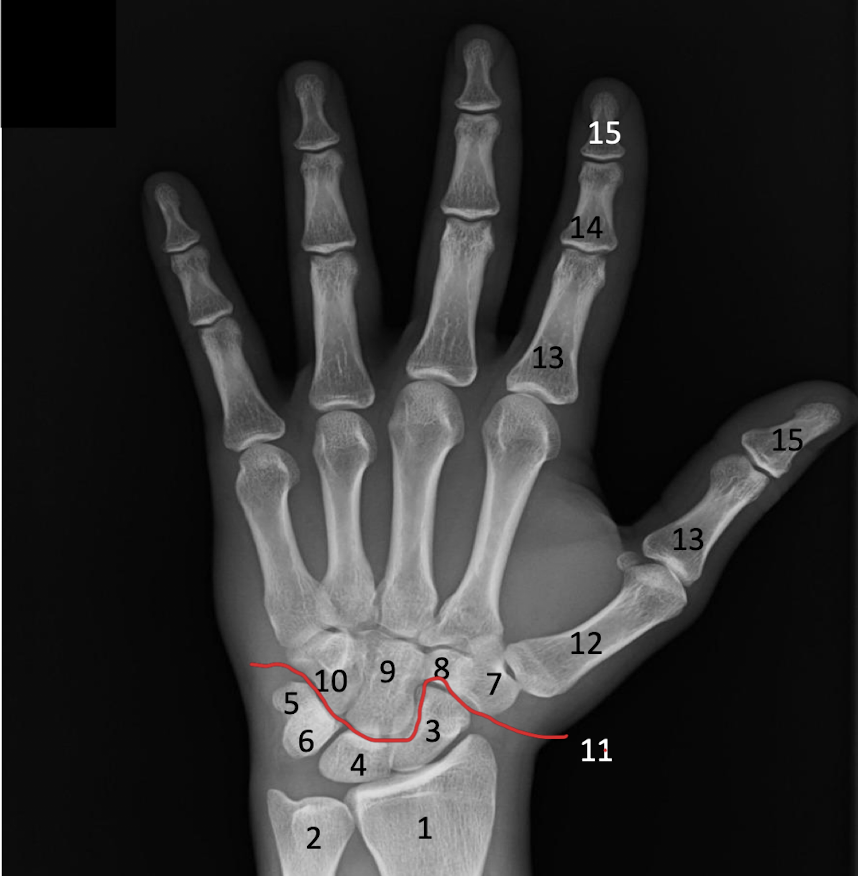
Identify the Scaphoid, lunate, triquetrium and Midcarpal joint in the x-ray.

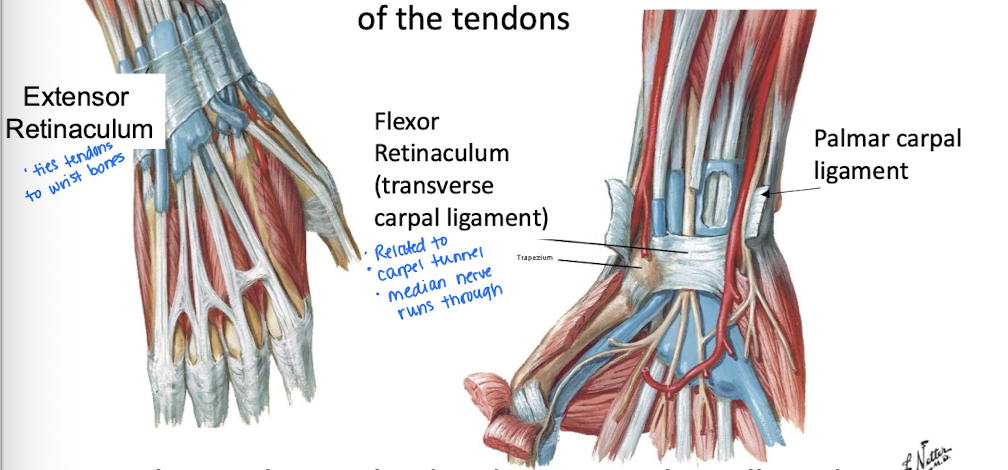
The deep fascia of the arm and forearm continue down toward the wrist and thicken in what four areas?
Bicipital Aponeurosis
Retinacula (Extensor and Flexor) -function is to act like straps to prevent “bowstringing” - when tendons pop up away from the bones as you move
Palmar Aponeurosis
Digital Sheaths
What are the Flexor Retinaculum and the Extensor Retinaculum?
Flexor R - aka transverse carpal ligament; forms the roof of the carpal tunnel
Medial nerve and flexor tendons pass underneath it
Extensor R - on back of the wrist and secures tendons so they don’t pop up when extending the hand
ties tendons to wrist bones
*Extend from the deep fascia
What is the Palmar aponeurosis?
What is the Palmaris brevis?
The palmar aponeurosis is a thick, fibrous layer of tissue in the palm of the hand that provides support and helps anchor the skin. It serves as a protective covering for the underlying flexor tendons and structures of the hand.
Serves to protect the underlying ulnar nerve and artery
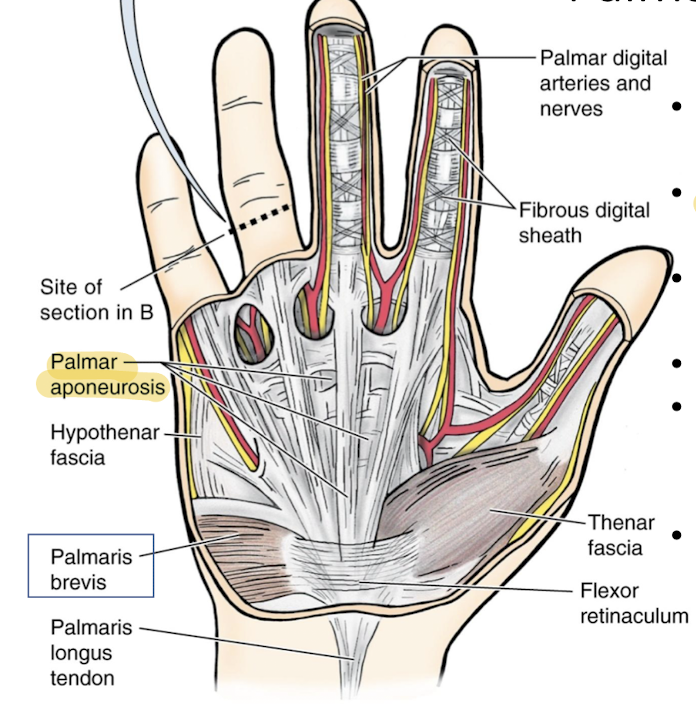
What are the functions of the digital (flexor) sheaths?
prevent bowstringing of tendons
The Intrinsic Hand Muscles consist of several groups: Thenar, Hypothenar, Adductor Pollicis, Lumbricals, and Interossei.
Describe the Thenar group
On the thumb side
all innervated by the Median nerve (except the flexor pollicis brevis)
Muscles
Abductor pollicis brevis
Flexor pollicis brevis
Opponens pollicis
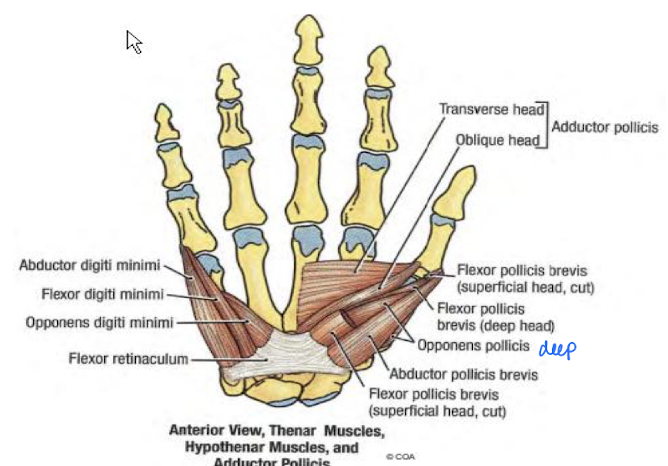
The Intrinsic Hand Muscles consist of several groups: Thenar, Hypothenar, Adductor Pollicis, Lumbricals, and Interossei.
Describe the hypothenar group
act on 5th digit
innervated by ulnar nerve
Muscles
Abductor digiti minimi
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
Opponens digiti minimi
The Intrinsic Hand Muscles consist of several groups: Thenar, Hypothenar, Adductor Pollicis, Lumbricals, and Interossei.
Describe the Adductor pollicis “group”
so deep it sits against the bone
adducts the thumb
innervatedby the ulnar nerve
The Intrinsic Hand Muscles consist of several groups: Thenar, Hypothenar, Adductor Pollicis, Lumbricals, and Interossei.
Describe the Lumbricals group
Four small worm-like muscles on digits 2-5
action: flex metacarpophalangeal joints
Innervation: 1 and 2 are by median; 3 and 4 are by ulnar
allow full extension of fingers
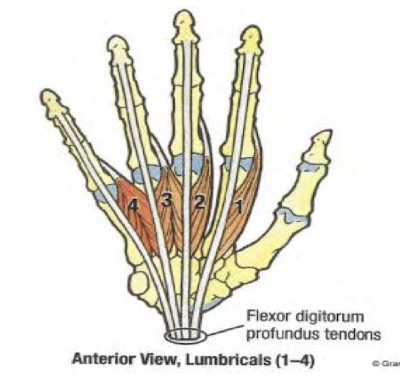
The Intrinsic Hand Muscles consist of several groups: Thenar, Hypothenar, Adductor Pollicis, Lumbricals, and Interossei.
Describe the Interossei group
7 total with 3 palmar (for adduction of fingers) and 4 dorsal (for abduction of fingers)
all innervated by ulnar nerve
Which area of the arm is considered the “distribution center” because it is a space in which all major nerves, lymph nodes and vessels pass through and communicate with the arm, shoulder and chest?
Axilla
Elements of the axilla are embedded in _____ and surrounded with fascia for protection.
A. Superficial Muscle
B. Deep Muscle
C. Lymph nodes
D. Adipose tissue
D. Adipose tissue
Describe the contents of the axilla
Arteries - axillary artery and branches
Veins - axillary veins and tributaries
Brachial plexus
Axillary sheath - CT sheath that invetsts and protects neurovascular structures in the axilla
Axillary lymph nodes
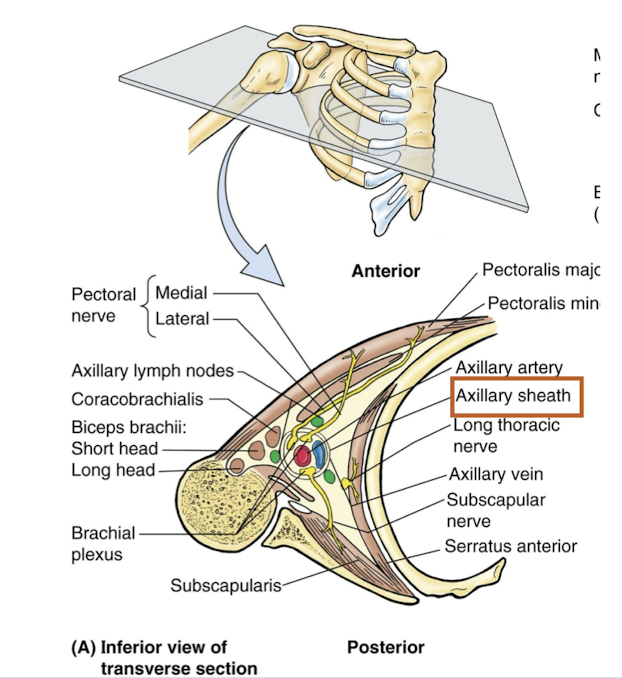
Describe the Brachial Plexus (overview)
Major nerve supply all segments of the upper extremity
Begins in neck from ventral rami of C5-T1 and runs through axila
Divided into 5 parts: Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Terminal Branches (Nerves)
Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beers (branches)
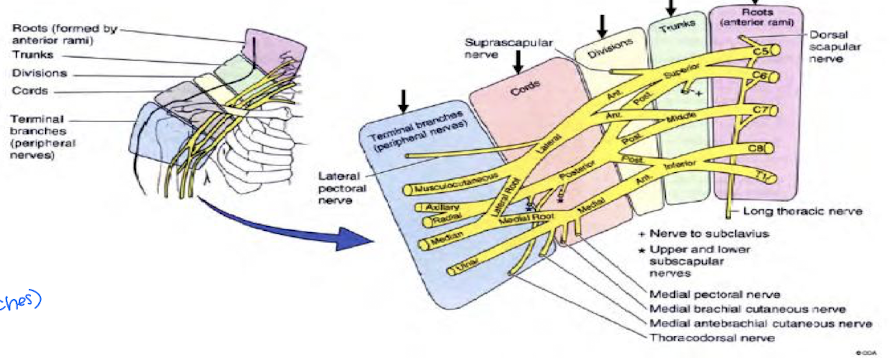
What kind of injuries can occur when injured at the ventral rami of C5-T1 (beginning of brachial plexus)?
Injuries at the ventral rami of C5-T1 can lead to upper trunk injuries, resulting in conditions such as Erb's Palsy, characterized by weakness in the shoulder and arm due to the affected nerve supply. These injuries often occur from trauma such as birth injuries or accidents.
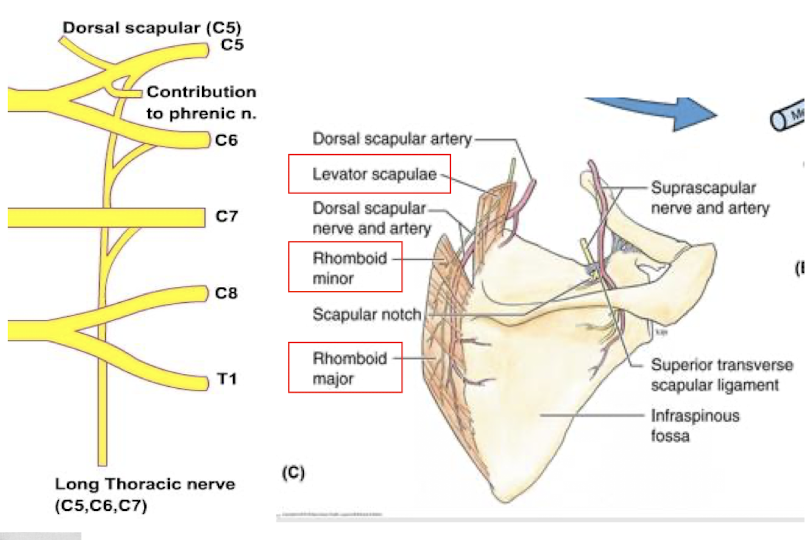
The Roots of the brachial plexus each give off important nerves. What are the two and what do they innervate?
Dorsal Scapular Nerve (C5)
Rhomboids, Levator Scapular
Long Thoracic Nerve (C5-C7)
Serratus Anterior
Frequent Damage here is called “winged scapula”
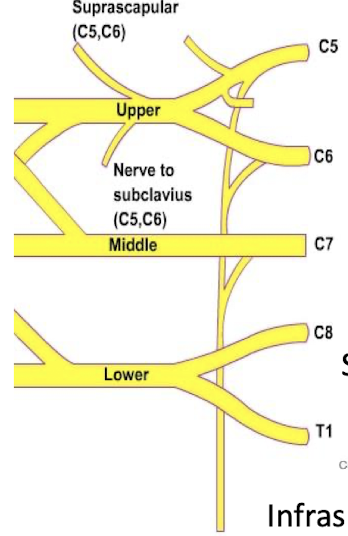
In the Brachial Plexus, roots will combine to form trunks. Describe the 3 trunks.
Upper Trunk (C5-C6)
Suprascapular nerve innervates supraspinatus and infraspinatus
Subclavius nerve - innervates Subclavian
Middle Trunk (C7)
Lower Trunk (C8-T1)
In the brachial plexus, what can be expected after the trunks?
Hint: Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beers
Divisions (anterior and posterior)
each trunk splits into anterior and posterior divisions
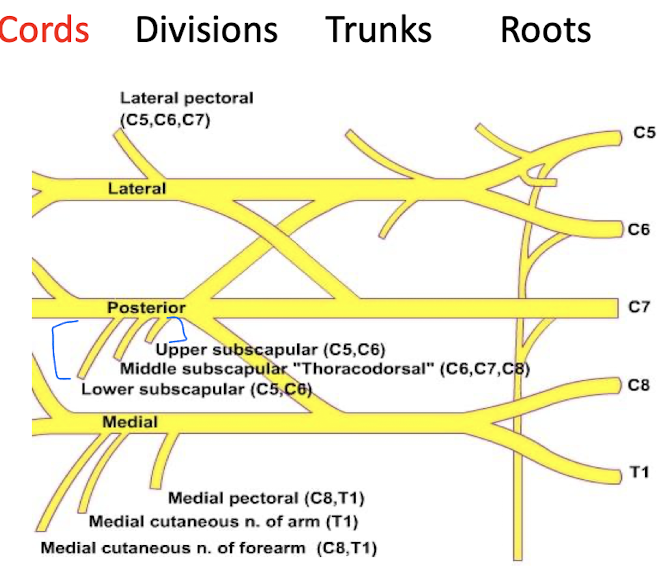
In the Brachial plexus, from the divisions, cords will form. Describe the 3 cords
Lateral Cord (C5-C7)
Lateral Pectoral nerve
innervates Pectoralis major
Posterior Cord (C5-T1)
Upper Subscapular nerve
innervates upper Subscapularis
Thoracodorsal Nerve
innervates Latissimus Dorsi
Lower Subscapular nerve
innervates subscapularis and teres major
Medial cord (C8-T1)
Medial pectoral nerve
innervates both pectoralis major and minor
From the cords of the brachial plexus, terminal branches will form. Describe them
Musculocutaneous nerve (C5-C7)
Biceps brachii, Brachialis, and Coracobrachialis
Axillary Nerve (C5-C6)
Deltoid, Teres Minor
Median Nerve (C5-T1)
All anterior forearm muscles EXCEPT flexor carpi ulnaris and medial half of flexor digitorum profundus
Thenar muscles and 1st two lumbricals
Ulnar Nerve (C8-T1)
Flexor carpi ulnaris
medial half of flexor digitorum profundus
All intrinsic muscles of the hand except Thenar and 1st and 2nd lumbricals
Radial Nerve (C5-T1)
all muscles of the posterior arm and forearm
MARMU (Most Alcoholics Really Must Urinate) mneumonic
Musculocutaneous, Axillary, Radial, Median, Ulnar
The terminal branches of the brachial plexus are the major _____ nerves that continue into the upper limb.
A. Sensory
B. Motor
C. Mixed
B. Motor
A mastectomy is used to remove a cancerous tumor. The procedure involves excision of the breast tissue to the pec major muscle, associated fascia, and into the medial axillary wall. After the procedure, the woman as a noticeable winged scapula. Which nerve was most likely damanged?
A. Spinal accessory n.
B. Long thoracic n.
C. Dorsal scapular n.
D. Nerve to the subclavius
E. Lateral pectoral
B. Long thoracic n.
Winged scapula is associated with the serratus anterior muscle which is innervated by the long thoracic n.
What are the nerves of the scapular region?
Suprascapular
runs under the superior transverse scapular ligament
supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
Upper Subscapular
Lower Subscapular
Thoracodorsal/Middle Subscapular
nerve to latissimus dorsi
Axillary Nerve
enters the quadrangular space along with the posterior circumflex humeral artery
Which of the scapular nerve(s) originate from the posterior cord and descend across the subscapularis to the target muscle?
Upper, Lower, and middle (thoracodorsal) subscapular nerves
What are the branches of the axillary nerve?
articular branch to the shoulder joint
anterior terminal branch, winds around the surgical neck of the humerus and supplies deltoid
the posterior terminal branch gives a branch to the teres minor and then branches to the deltoid becoming the upper lateral cutaneous nerve
A fracture to the proximal humerus may injure which nerve? It would produce loss of sensation over the skin of the shoulder and difficulty abducting the arm.
Axillary nerve
supplies deltoid which assists in abduction of the arm
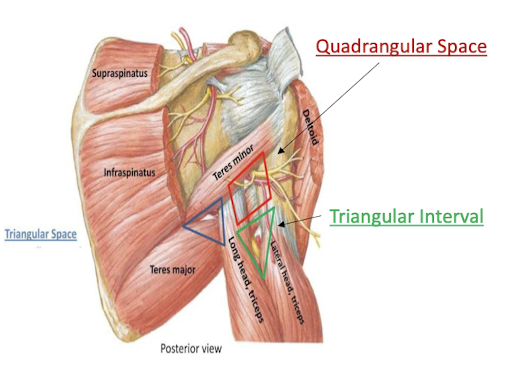
Define the Quadrangular space
A border made of the teres minor, teres major, triceps long head, and the surgical neck of the humerus
contains the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral vessels
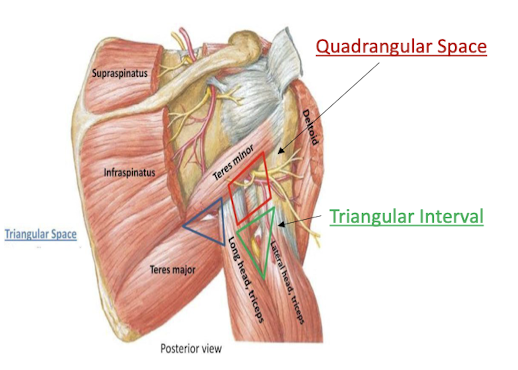
Define the Triangular space
Made by the teres minor, teres major, and triceps long head
contains the circumflex scapular artery
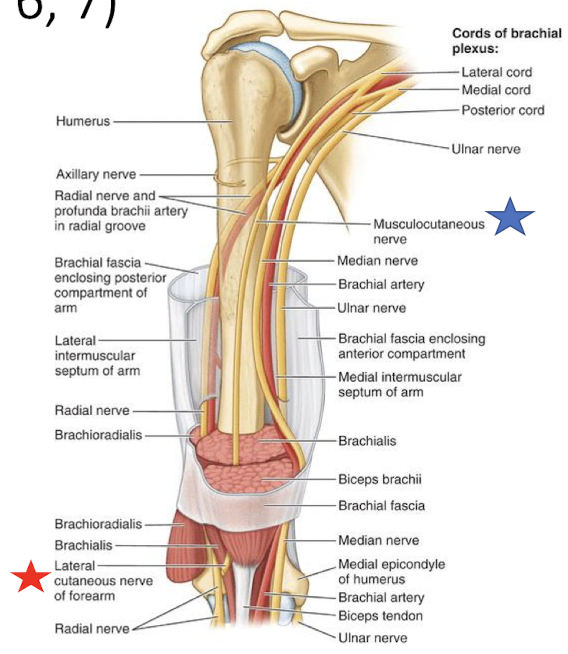
What are the 4 main nerves of the arm and where do they arise from?
*Which two pass through the arm but do not innervate the arm?
musculocutaneous - from lateral cord of brachial plexus
radial - from posterior cord
ulnar* - from medial cord
median* - from lateral and medial cord
The musculocutaneous nerve pierces through which muscle of the arm?
A. Coracobrachialis
B. Brachialis
C. Biceps Brachii
D. Triceps brachii long head
A. Coracobrachialis
The musculocutaneous nerve of the arm will emerge lateral to the biceps brachii and pierce the deep fascia becoming the ______ nerve
lateral cutaneous nerve
Describe the radial nerve of the arm
Arises from the posterior cord
supplies all muscles of the posterior arm and forearm
Branches to all heads of the triceps and anconeus
Which nerve of the arm will descend from the deep brachial artery and pass through the radial groove?
A. Musculocutaneous
B. Radial
C. Median
D. Ulnar
B. Radial nerve
_____ nerve of the arm will cross over the brachial artery, and lie medial to the cubital fossa
Median nerve
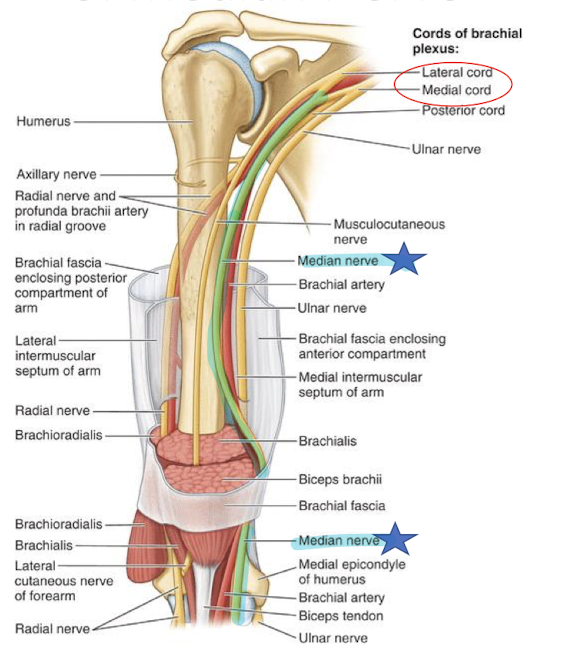
Describe the ulnar nerve of the arm
arises from the medial cord of the brachial plexus
pierces intermuscular septum ½ way down the arm
It has no branch in the arm
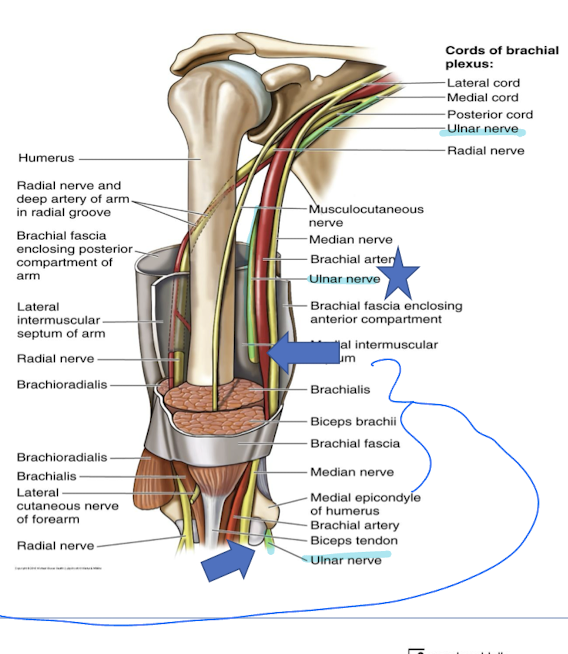
Describe the median nerve relation in the forearm
Crosses the ulnar artery and lies between the two.
Median nerve runs between the flexor digitorum superficialis and FD profundus and enters the carpal tunnel
Innervates all superficial forearm muscles directly and all deep indirectly with the anterior interosseus n
What is the anterior interosseus n responsible for innervating?
The deep muscles of the forearm including the flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus, and pronator quadratus.
The ____ nerve of the forearm will lie between the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon and the flexor digitorum superficialis tendon in the wrist and enter the Ulnar canal (Guyon’s tunnel)
Ulnar nerve
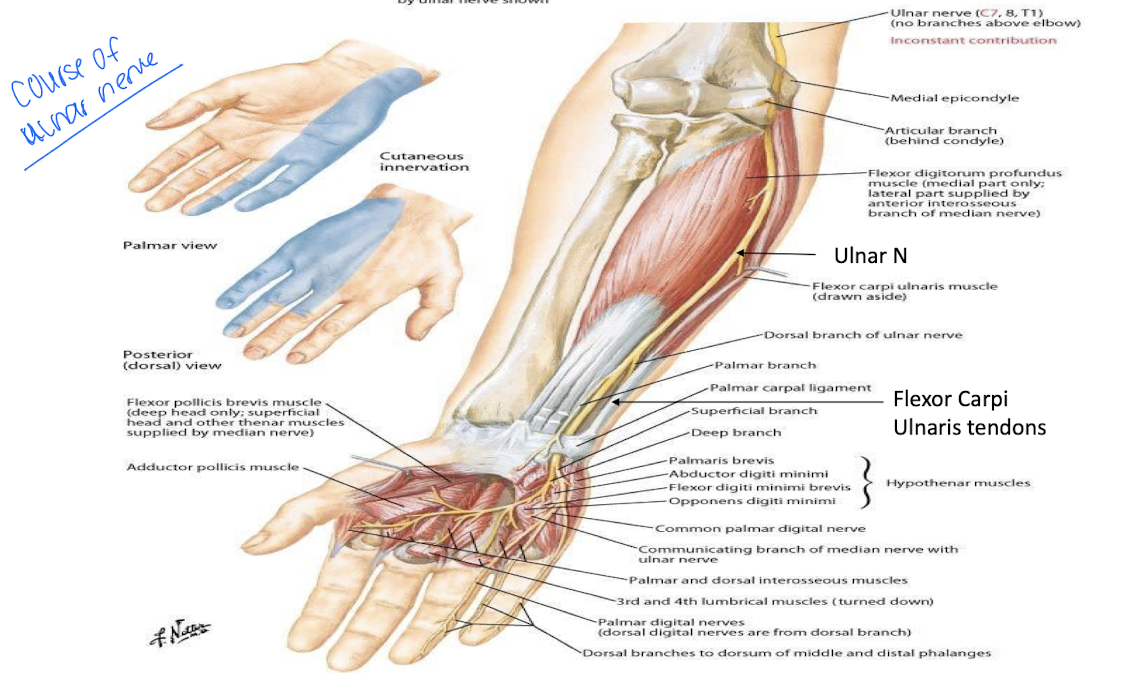
Describe the radial nerve of the forearm
Enters the forearm deep to the brachioradialis dividing into a superficial and deep branch
Deep branch passes b/t supinator and becomes the posterior interosseus nerve
Which nerve of the hand enters through the carpal tunnel and divides into recurrent branch of the median nerve and digitial branches?
Median nerve
Describe the ulnar nerve in the hand
enters hand through the ulnar canal
innervates the interossei, lumbrical 3 and 4, hypothenar muscles, and deep flexor pollicus brevis
T/F: the radial nerve of the hand has no motor innervation but has sensory innervation
true
Provide the arterial pathway of the upper limb to the hands and the names of the vessels included.
Upper limb arterial supply is subclavian artery
Subclavian artery becomes axillary artery (@ first rib)
Axillary becomes Brachial artery (at teres major)
Brachial artery will branch (at cubital fossa) to become radial and ulnar arteries
radial creates the deep palmar arch
Ulnar creates the superficial palmar arch of the hand
palmar arches become digital arteries
How is the axillary artery divided?
What is the range of Part 1 of the axillary artery?
What branch arises from Part 1 of the axillary artery?
Into 3 parts based on relation of the pectoralis minor
From the lateral border of the 1st rib to the superior border of the pectoralis minor.
Superior thoracic artery.
Axillary Artery of the shoulder
Where is Part 2 of the axillary artery located?
What branches arise from Part 2 of the axillary artery?
What is the range of Part 3 of the axillary artery?
What branches arise from Part 3 of the axillary artery?
Posterior to the pectoralis minor muscle.
Thoraco-acromial artery and lateral thoracic artery
From the lower border of pectoralis minor to the lower border of teres major.
Subscapular a., Anterior circumflex humeral artery, and Posterior circumflex humeral artery
Arterial Supply of the Arm
What is the main blood supply of the arm?
Which area can be palpated? Why is it important?
Where does the artery terminate?
Does it branch?
Brachial artery
Medial Bicipital groove (BP here)
Cubital Fossa
Yes, into radial and ulnar arteries
What is the branches off the brachial artery?
Deep branch of brachial a. - largest and first branch of brachial artery
travels with radial nerve through radial groove
What is the main branch off of the Ulnar Artery?
Common interosseus
the short branches split into the anterior interosseus and posterior interosseus
Which artery of the forearm will cross the anatomical snuffbox and is a site for arterial blood draw?
Radial artery
The hands are highly vascularized due to which two arteries?
Radial and ulnar arteries and their branches
Describe the Ulnar artery of the hand and it’s branch
Ulnar artery
enters the hand between the pisiform and hamate
contributes to superficial and deep arches
Branches to form the superficial palmar arch
main terminal branch of the ulnar artery
gives rise to digitial arteries
Describe the Radial artery of the hand and it’s branches
Radial Artery
Main contributor to deep palmar arch
Forms Deep Palmer Arch and Digital Branches
DPA is formed primarily with the radial artery and some ulnar artery
the digital branches supply the digits and arise from the DPA
What is the role of the superficial veins of the hand?
Where do the veins drain into after leaving the hand and into the forearm?
What is the median cubital vein?
Drain the superficial tissues and DO NOT accompany the arteries
The medial basilic vein and lateral cephalic vein.
Formed by the connection of the basilic and cephalic veins and runs across the cubital fossa - site for venipuncture
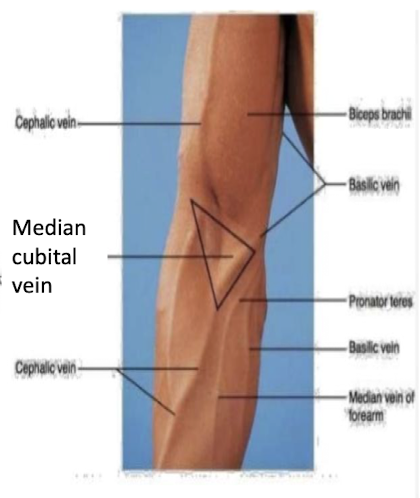
What occurs at the deltopectoral groove?
The cephalic vein ascends between b/t the deltoid and pec major.
Lymmphatic vessels from the right ¼ of the body drain into the ______ and the remaining ¾ of the body drains into the _____ (left side) or right.
A. Thoracic duct; Lymphatic duct
B. Thoracic duct; Deltopectoral nodes
C. Deltopectoral nodes, Lymphatic duct
D. Lymphatic duct; Thoracic duct
D. Lymphatic duct; Thoracic duct