BIO94 QUIZ 1
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
How many named species are currently known?
Approximately 2 million+
Who introduced binomial nomenclature
Carl Linnaeus
What does binomial nomenclature consist of?
Genus ( last name for a group of related species) and species (specific name within that group) names
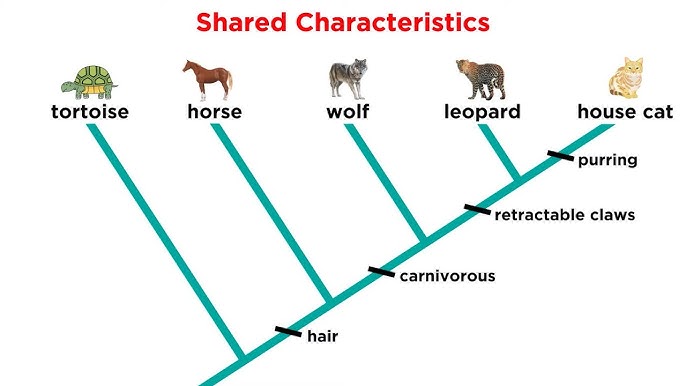
What is a cladogram? What is the primary basis for cladograms today?
A tree-like diagram showing evolutionary relationships between organisms
DNA, RNA, and protein analysis: mutate over time, scientists use to see how species r related
shows which species more closely related
How many domains of life are there?
Three (Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya)
What is the definition of a hypothesis?
A proposed explanation for a specific phenomenon or set of observations
Why is tuberculosis still common despite the discovery of antibiotics?
Some bacteria survived the antibiotic treatment. These surviving bacteria were slightly resistant to the antibiotics. The resistant bacteria reproduced, passing on their resistance genes. Over time, more and more TB bacteria became resistant to antibiotics.
evolution because The bacteria changed over time (evolved) to survive in an environment with antibiotics. This is natural selection in action - the bacteria most able to survive antibiotics passed on their genes.
What are two hypotheses for why giraffes have long necks?
Are the hypotheses for giraffe neck length mutually exclusive?
1. Competition for food (reaching higher leaves) 2. Competition for mates (male giraffes fighting)
No, both could be true simultaneously
What does "extant" mean?
Still living; not extinct.
What hierarchical levels are used to classify organisms?
Domain → Kingdom → Phylum → Class → Order → Family → Genus → Species
How were organisms primarily classified in the past?
Based on morphological traits: the form and structure of an organism
Body shape and size
Number of limbs
Type of teeth
Skin or fur patterns
Leaf shapes in plants
Limitations:
Sometimes led to incorrect groupings
Couldn't see internal or genetic similarities
What are the two components of a scientific theory?
Pattern component (general description of what is observed) and process component (hypotheses about what generates the pattern)
What are two major elements of the pattern component of evolutionary theory?
1. Organisms are produced by other organisms 2. Species are not static - they change over time
Define natural selection
The process by which individuals with certain heritable traits tend to produce more surviving offspring
Is natural selection a random process?
No, natural selection is non-random
What are the four steps in Darwin's reasoning that led to natural selection?
rsvp
1. All organisms have great capacity for reproduction
2. Most populations maintain stable sizes over time
3. Individuals within populations vary in their traits
4. Individuals with traits best suited to the environment tend to produce more surviving offspring
Why don't populations grow exponentially despite high reproductive capacity?
Limited resources and environmental constraints lead to death of many offspring before reproducing
Is the mortality of offspring random?
No, some individuals have genetic variations that make them better adapted to survive
What is meant by adaptive evolution?
Over generations in a stable environment, populations become more adapted through natural selection
What was a major line of evidence for species changing over time in the 19th century?
Fossils, showed animals and plants that no longer exist today, Different rock layers contained different types of fossils
what this told scientists: Life on Earth has changed over time, Some species have gone extinct, species might be related to extinct ones
Why is natural selection not random?
It acts on existing genetic variation, favoring traits that provide a reproductive advantage, unlike mutation, which introduces random genetic changes.
How does modern medicine affect evolution?
Modern medicine can slow down evolution by allowing individuals with traits that might otherwise be selected against to survive and reproduce.
What is mutation in evolution?
ultimate source of genetic novelty since it introduces new alleles into a population
randomly when DNA is copied like radiation or chemicals
Without mutations, there wouldn't be new traits for evolution to work with.
ex: mutation help make bird beak longer, if help bird get more food it might have more baby, over time more birds in that population might have longer beaks
What are three main types of evidence for species changing over time?
Fossils, remains of ancient life
Homologies, similarities in body structures, genes, or development between different species, ex arm bones in humans, cats, whales, and bats are very similar, suggesting a common ancestor
Biogeography, study of where species are found around the world, ex example, similar but different species on separate continents can show how they evolved after landmasses split apart.
What are the three types of homologies?
1. Structural 2. Developmental 3. Molecular/Genetic
What is a transitional feature?
characteristic in a fossil organism that shows traits intermediate between its ancestors and its descendants, gives evidence of change over time.
It's found in fossils
It shows in-between traits
It links ancestors to descendants
It demonstrates evolution in action
What is homoplasy?
Similarity between organisms not due to common descent, often resulting from convergent evolution: unrelated species develop similar traits independently
usually happens because they live in similar environments or face similar challenges
Why are vertebrate embryos useful for studying homologies?
Vertebrate embryos are useful because they all start out looking similar and use similar genes to develop. This makes it easier to see how different animals are related, even if they look very different as adults.
How are molecular homologies useful?
By comparing the (DNA) or "building blocks" (proteins) of different species, we can see how closely related they are. This helps us draw accurate family trees of life, showing how different species are connected through evolution.
What is convergent evolution?
Adaptation of different lineages to similar environments, resulting in similar traits
Example: bats and birds have wings for flying, but they evolved these independently bc flying was useful in their environments.
Why are multiple lines of evidence important in evolutionary studies?
They provide coherent support for evolutionary patterns across different scientific fields
What is the "Law of Succession"?
fossils found in an area look similar to the living species in the same area. meants: modern species evolved from ancient( descent with modification) , species evolve but keep some ancestor features
How has modern technology improved the study of evolutionary relationships?
It allows for rapid and cheap genetic sequencing, enabling detailed molecular comparisons
can build more accurate "family trees" of species, how species have changed over time
What is the definition of the process of evolution?
Change in allele frequency in a population over time
allele?
Form of a gene
genotype?
specific set of genes an organism carries for a trait
trait in evolutionary biology?
measurable aspect of an organism (morphology, physiology, behavior)
What does "heritable" mean in the context of evolution?
can be passed from parents to offspring due to genetic variation.
What is the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
In a large population, genotype frequencies do not change from generation to generation in the absence of evolutionary processes
In a large population, the mix of genes stays the same over time if nothing is changing the population.
What does p^2 + 2pq + q^2 = 1 represent in the Hardy-Weinberg equation?
Genotype frequencies
Which mechanism of evolution is the only one that leads to adaptation?
Natural selection
What is the ultimate source of genetic novelty in evolution?
Mutation
Which mechanism of evolution can result in the random loss or fixation of alleles?
Genetic drift: A random change in gene frequencies in a population
It happens by chance, not because of any advantage or disadvantage
What mechanism of evolution can offset the effects of genetic drift between populations?
Gene flow: transfer genetic variation between population, when indiv move from one popul to another
True or False: Whales evolved from hippopotamuses
False. Whales and hippopotamuses are extant species that share a common ancestor
What is the best way to calculate allele frequencies from genotype frequencies?
Count all alleles in homozygotes and half the alleles in heterozygotes for each allele type, then divide by the total number of alleles
What are the four types of natural selection (patterns of how traits change in a population)
Disruptive, Stabilizing, Directional, and Balancing
disruptive selection?
Selection favoring both extreme phenotypes over intermediate ones
ex: tree bark has patches of light/dark areas not any in between, birds prey on the moths, light color moths camouflage on light bark, dark color moths camouflage on dark bark, med color moths are visible on both light/dark bark
stabilizing selection?
Selection favoring intermediate
ex: babies that are avg size are healthiest, small/large babies face health issues
directional selection?
Selection favoring one extreme phenotype over others
ex: giraffe develop longer necks to reach higher leaves during food shortage
balancing selection?
no one phenotype is favored
ex: having one copy of sickle cell gene give protection against malaria but two copies cause sickle cell disease. ts maintain both version of the gene in populations where malaria is common
viability selection?
those w certain traits can survive until theyre able to reproduce
What is fertility/fecundity selection?
A form of natural selection where individuals with certain traits produce more offspring than others.
What is sexual selection?
Natural selection resulting from differences in mate getting success
How do mutation and natural selection work together in evolution?
Mutation creates new alleles, and natural selection acts on those alleles, resulting in changes in allele frequencies
What is gene flow?
change in allele frequency due to migration between established populations, resulting in increased genetic similarity between them
genetic drift?
change in allele frequency due to chance, especially in small populations
genetic bottleneck?
A sudden reduction in population size that can lead to random changes in allele frequencies
What is the founder effect?
type of genetic drift, a small portion of population breaks off main popullation, potentially leading to reduced genetic diversity
True or False: Genetic drift can result in random loss of alleles, particularly in small populations
True
True or False: Natural selection can result in non-random loss of alleles in populations of any size
True
Adaptation
A specific trait that has evolved because it increased the fitness of individuals with that trait in a particular environment
Fitness
The ability of an individual to produce viable offspring relative to others of the same population
Cladogenesis
The splitting of two lineages
Two main types of reproductive isolation
1. Prezygotic isolation: barrier that prevent mating/fertilization between diff species
2. Postzygotic isolation: barries that happen after egg is fertilized, making hybrid offspring weak fertility
Three types of prezygotic isolation where mating does not occur
1. Temporal isolation (breed at diff times) 2. Habitat isolation (breed diff habitats) 3. Behavioral isolation (diff practice)
Two types of prezygotic isolation where mating occurs but no zygotes are produced
1. Mechanical isolation (incompatible reproductive structures) 2. Gametic barrier (sperm and egg incompatibility)
Two types of postzygotic isolation
1. Hybrid inviability (hybrids die before reaching reproductive age)
2. Hybrid sterility (hybrids survive but can't produce functional gametes)
Morphological species concept
do organisms from two populations look different?
Pros of morphological species concept
Mating success and gene flow not necessary for concept - Can be used for extinct
Cons of morphological species concept
Very subjective - Cannot identify polymorphic (multiple diff forms in same species) or cryptic species (look identical, but diff species)
Phylogenetic species concept
do members of two populations have unique genetic histories?
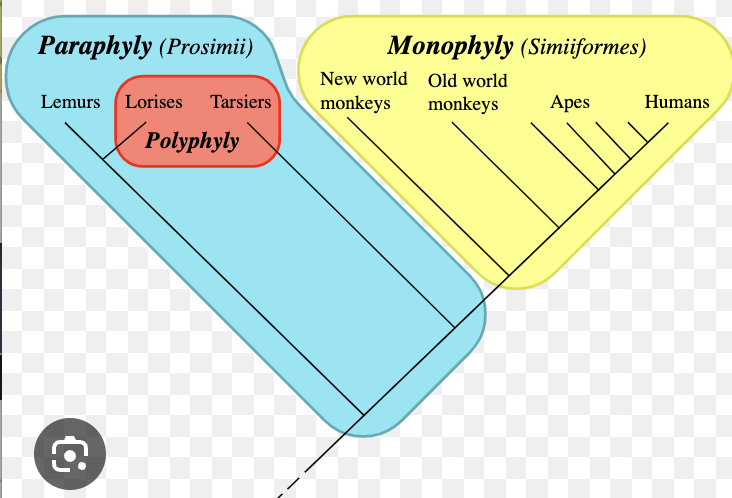
defines species as being the smallest monophyletic group on the tree of life
Synapomorphy
trait shared by two or more taxa from their most recent common ancestor
Parsimony
prefers the simplest tree with the fewest evolutionary steps
Speciation
formation of new species when populations become reproductively isolated
monophyletic
Includes an ancestor and all its descendants.
Polyphyletic
collection of organisms or taxa that are grouped together but do not share a common ancestor.