100 Psychology terms
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms

Serial Position Effect
Remembering the first and last items in a list.

Closure
Gestalt psychology principle where incomplete stimuli are perceived as a whole.

Proximity
Elements placed close together are perceived as a single unit.
Figure-Ground
Distinguishing the focal point (figure) from the background (ground).

Reciprocity Norm
Expectation to return a favor when helped by someone.

Group Polarization
Group members' beliefs becoming more extreme after discussion.

Confirmation Bias
Seeking information that supports existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.

Belief Perseverance
Holding onto beliefs despite evidence discrediting them.

Self-Serving Bias
Overstating role in positive outcomes and understating in negative ones.

Stereotype Threat
Anxiety about confirming negative stereotypes affecting performance.
Foot-in-the-Door Phenomenon
Agreeing to a small request makes accepting a larger one more likely.

Door-in-the-Face
Rejecting a large request makes accepting a smaller one more probable.

Hostile Aggression
Intent to cause physical harm.

Instrumental Aggression
Aggression used to achieve other goals.

Afferent (Sensory) Neurons
Transmit information to the brain.

Efferent (Motor) Neurons
Control movements, exiting the brain.
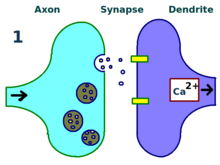
Long-Term Potentiation
Strengthening synaptic connections with frequent activation.

Arousal
State of alertness or being awake.

Sympathetic Nervous System
Increases heart rate in response to stress.

Reticular Formation
Controls arousal and focus in the brain stem.
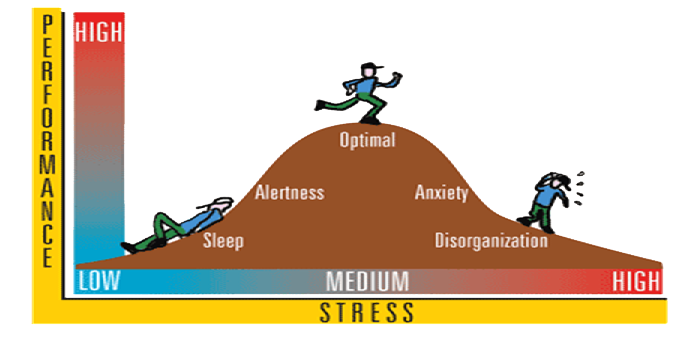
Arousal Theory
Motivation to adjust behavior to raise or lower arousal levels.
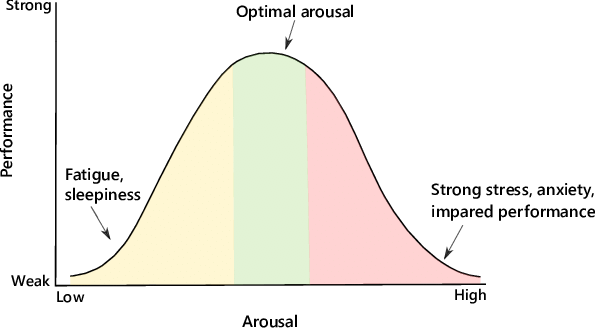
Yerkes-Dodson Law
Optimal performance at a moderate level of arousal.

Common Sense Theory
Stimulus leads to emotion and arousal.
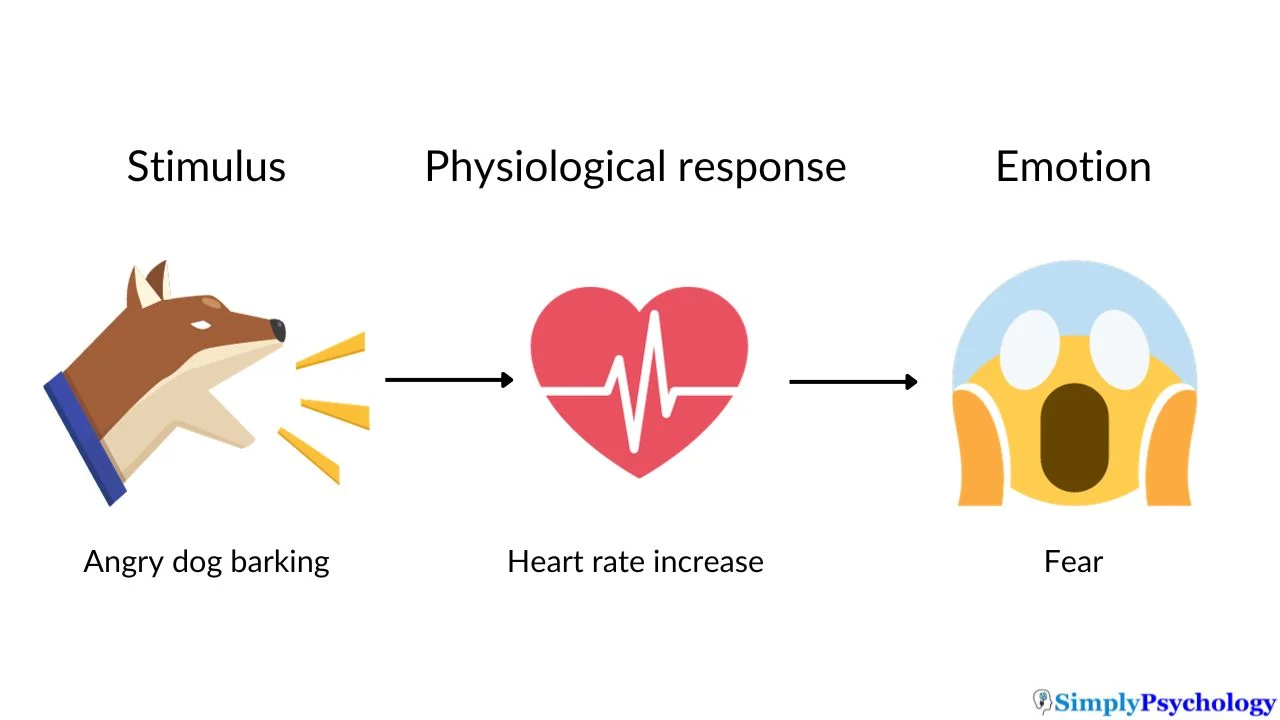
James-Lange Theory
Stimulus triggers physiological arousal leading to emotion.
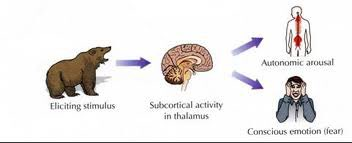
Cannon-Bard Theory
Stimulus elicits emotion and arousal simultaneously.
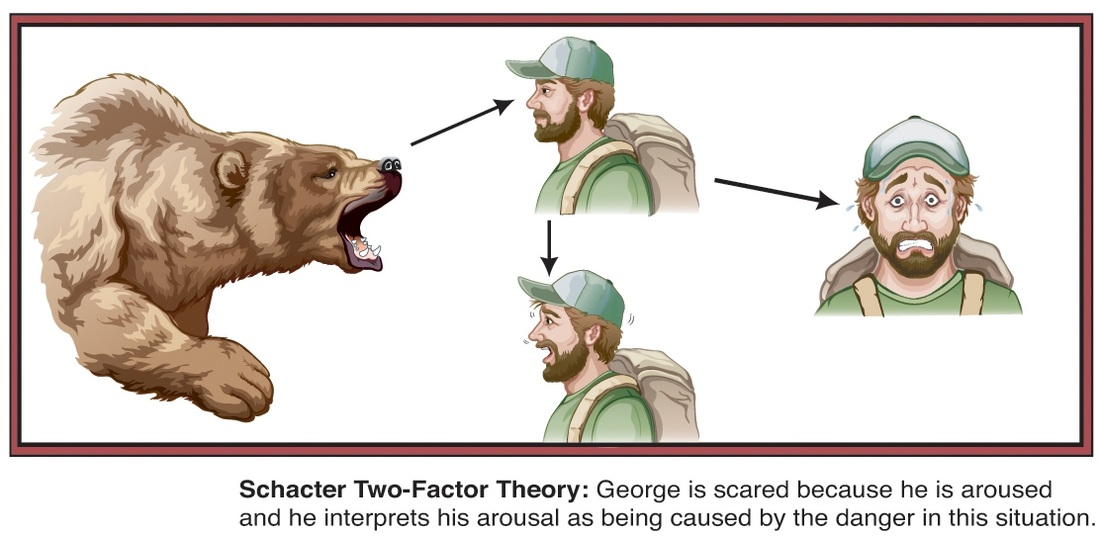
Schachter-Singer Two-Factor Theory
Arousal leads to cognitive appraisal and emotion.
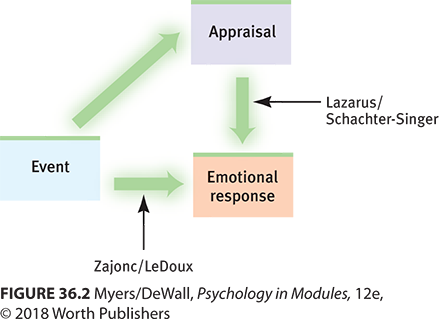
Zajonc & LeDoux
Cognition doesn't always precede emotional responses.
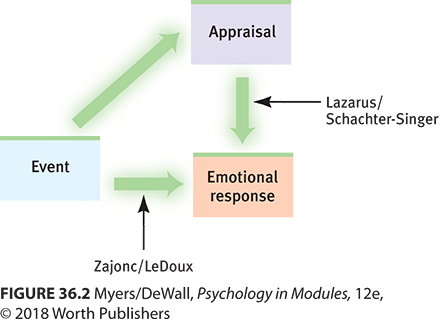
Lazarus Cognitive Appraisal Theory
Stimulus evaluation leads to simultaneous emotion and arousal.

Cerebellum
Controls motor function and balance.
Broca's Area
Responsible for speech production.
Wernicke's Area
Interprets spoken language.
Angular Gyrus
Converts visual stimuli into auditory information.
Inattentional Blindness
Failing to notice stimuli due to focused attention elsewhere.
Cocktail Party Effect
Ability to focus on one stimulus while ignoring others.
Cognitive Maps (Tolman)
Mental representation of environmental layout.
Approach-Approach Conflict
Choosing between two desirable outcomes.
Avoidance-Avoidance Conflict
Choosing between two undesirable outcomes.
Approach-Avoidance Conflict
Decision involving both attractive and unattractive features.

Multiple Approach-Avoidance Conflict
Choosing between options with mixed features.

Habituation
Diminished response to a repeated stimulus.
Algorithm
Step-by-step procedure ensuring problem-solving.
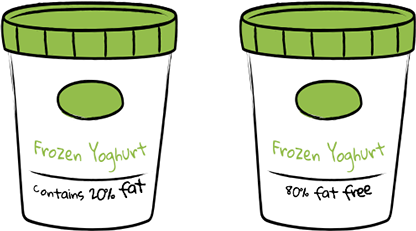
Framing
Presenting a situation to influence perception.

Source Amnesia/Misattribution
Incorrectly identifying the source of a memory.
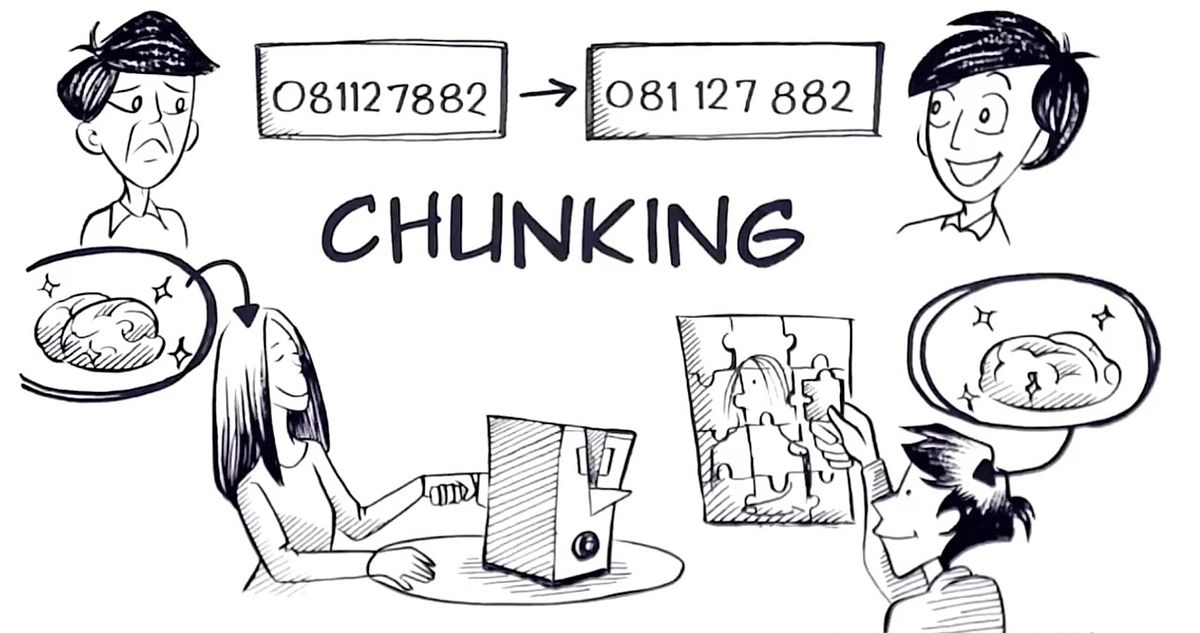
Chunking
Organizing information into meaningful units for memory.
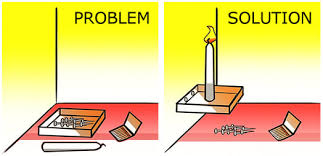
Functional Fixedness
Bias limiting object use to intended purpose.

Mental Set
Applying past solutions to current problems.

Reciprocal Determinism
Belief in mutual influence of thoughts, behavior, and environment.
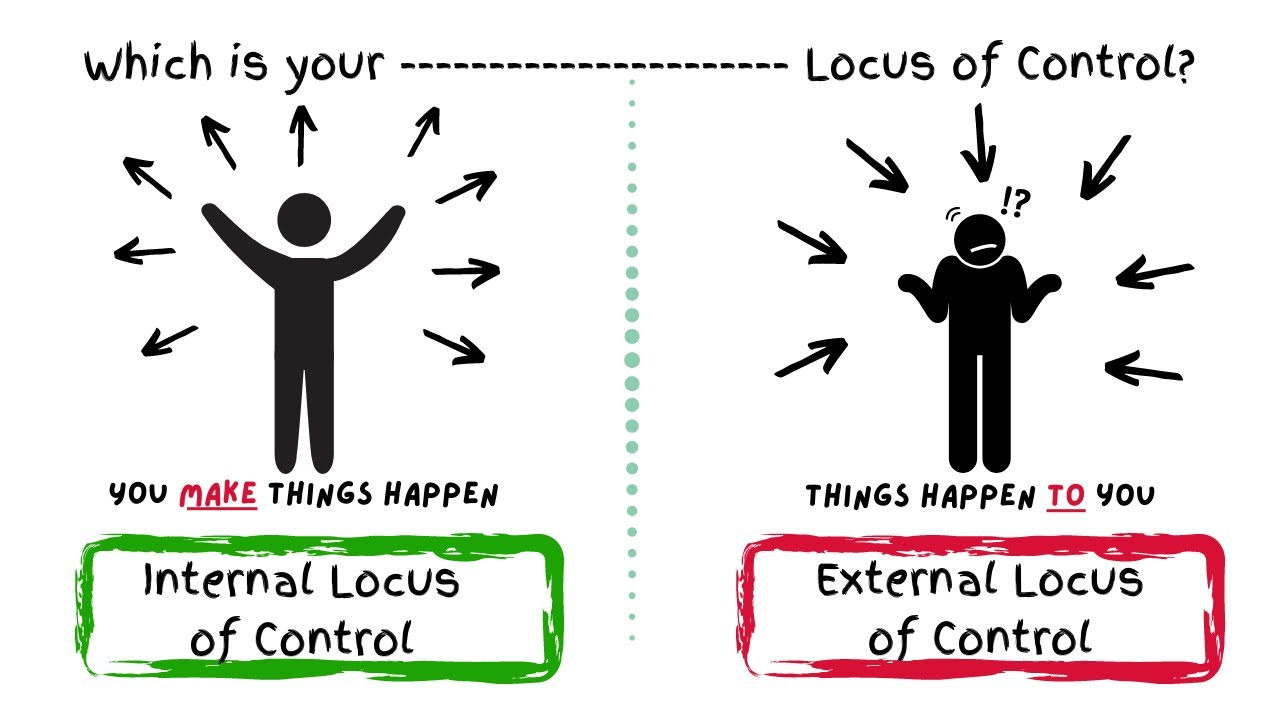
External Locus of Control
Perception of fate controlled by external forces.
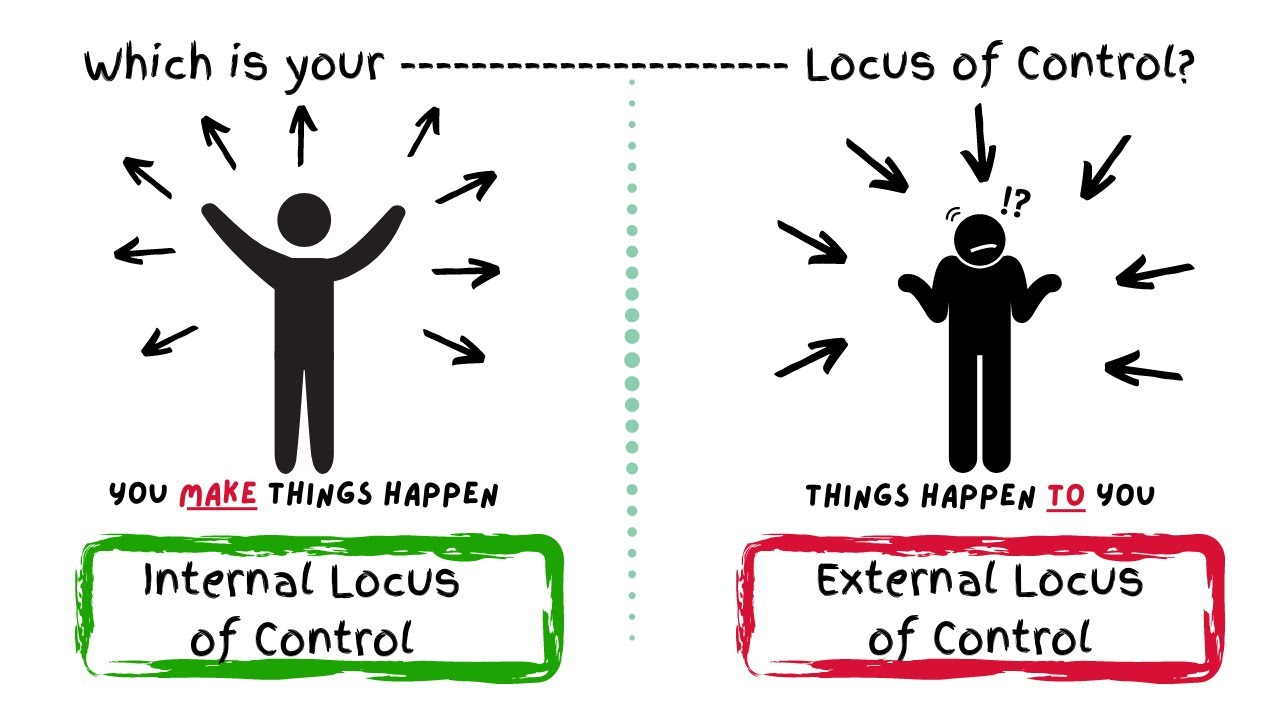
Internal Locus of Control
Belief in personal control over fate.
Learned Helplessness
Pessimistic outlook from inability to change outcomes.
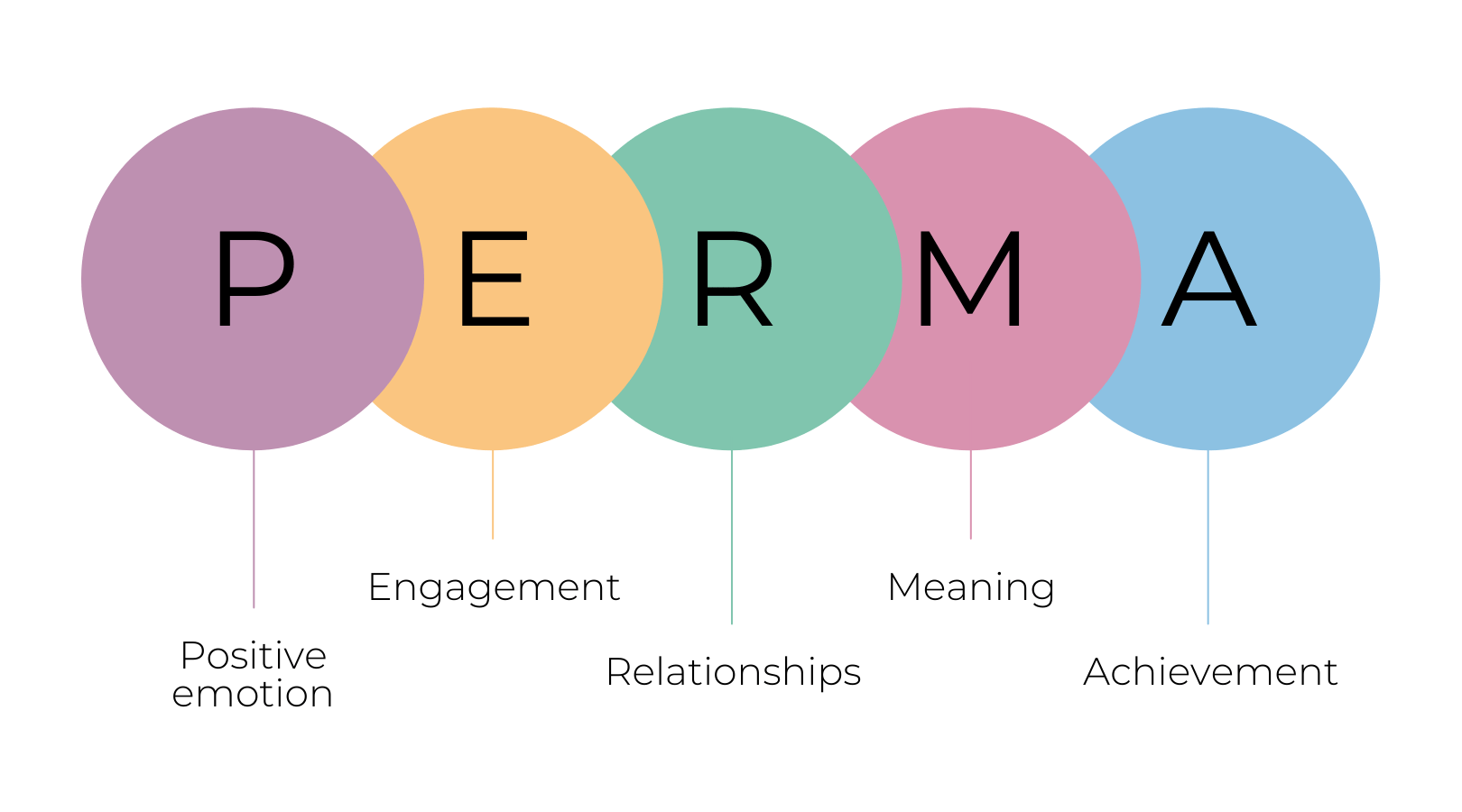
Positive Psychology
Challenging beliefs to encourage self-improvement.

Humanistic Psychology
Focus on self-fulfillment and happiness.
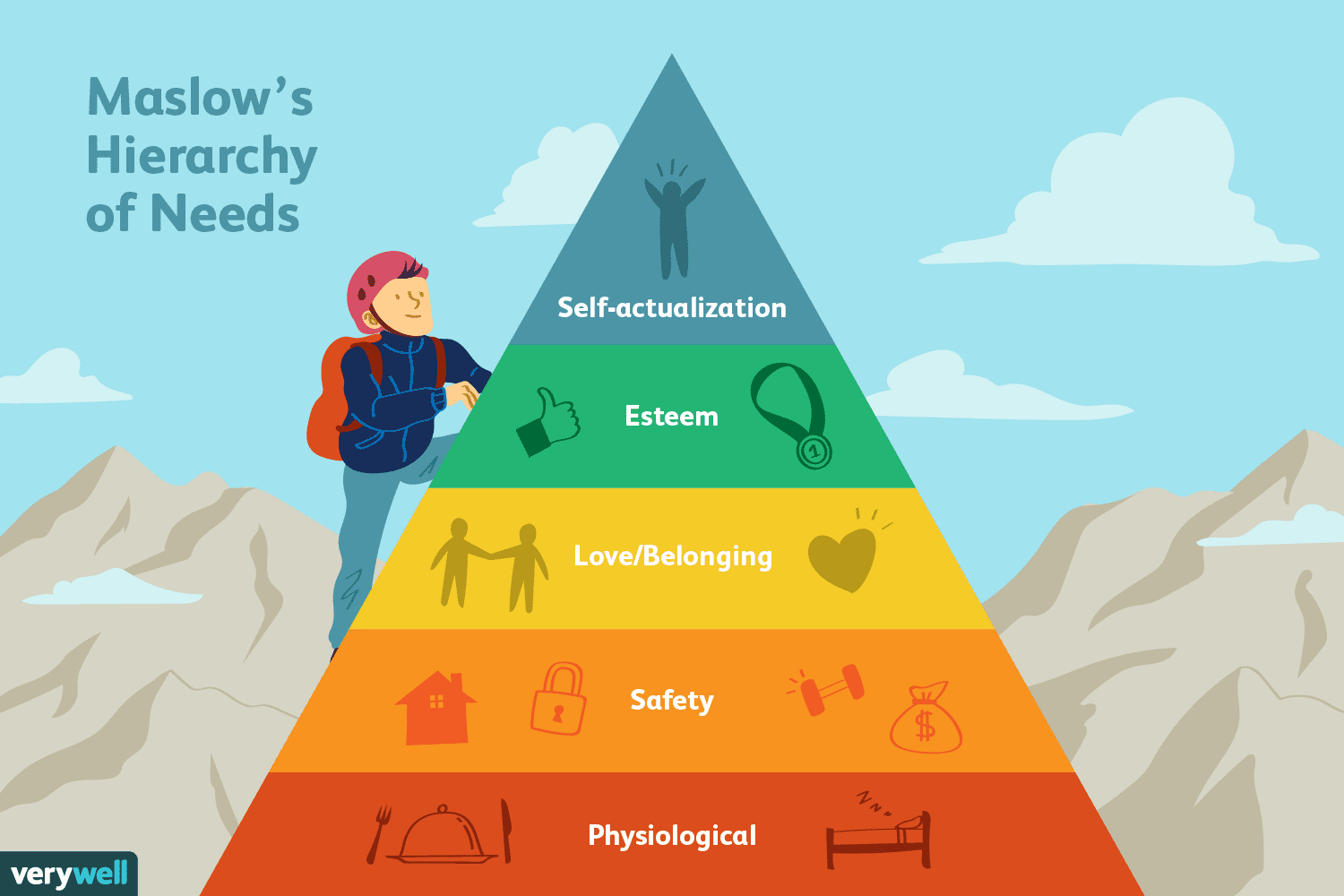
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Hierarchical progression of human needs. Striving for self actualization.
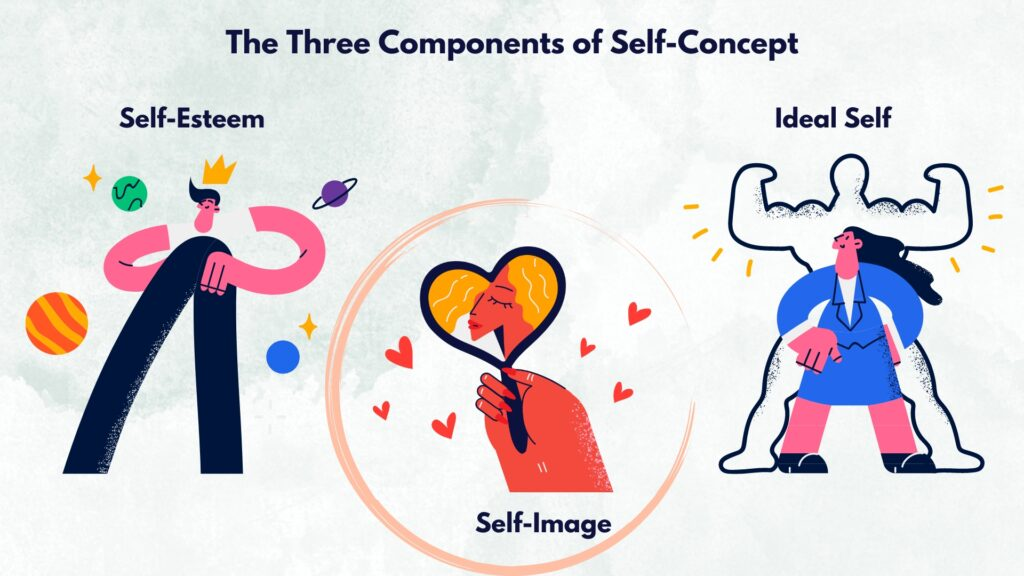
Self-Concept
Perception of oneself as ideal versus real self.

Unconditional Positive Regard
Acceptance of others regardless of behavior.

Self-Esteem
Feelings of self-worth based on congruence.

Narcissism
Inflated self-view leading to attention-seeking behavior.
Mean
Average value in a dataset.
Median
Middle value in a dataset.
Mode
Most frequently occurring value in a dataset.
Range
Difference between the highest and lowest values.
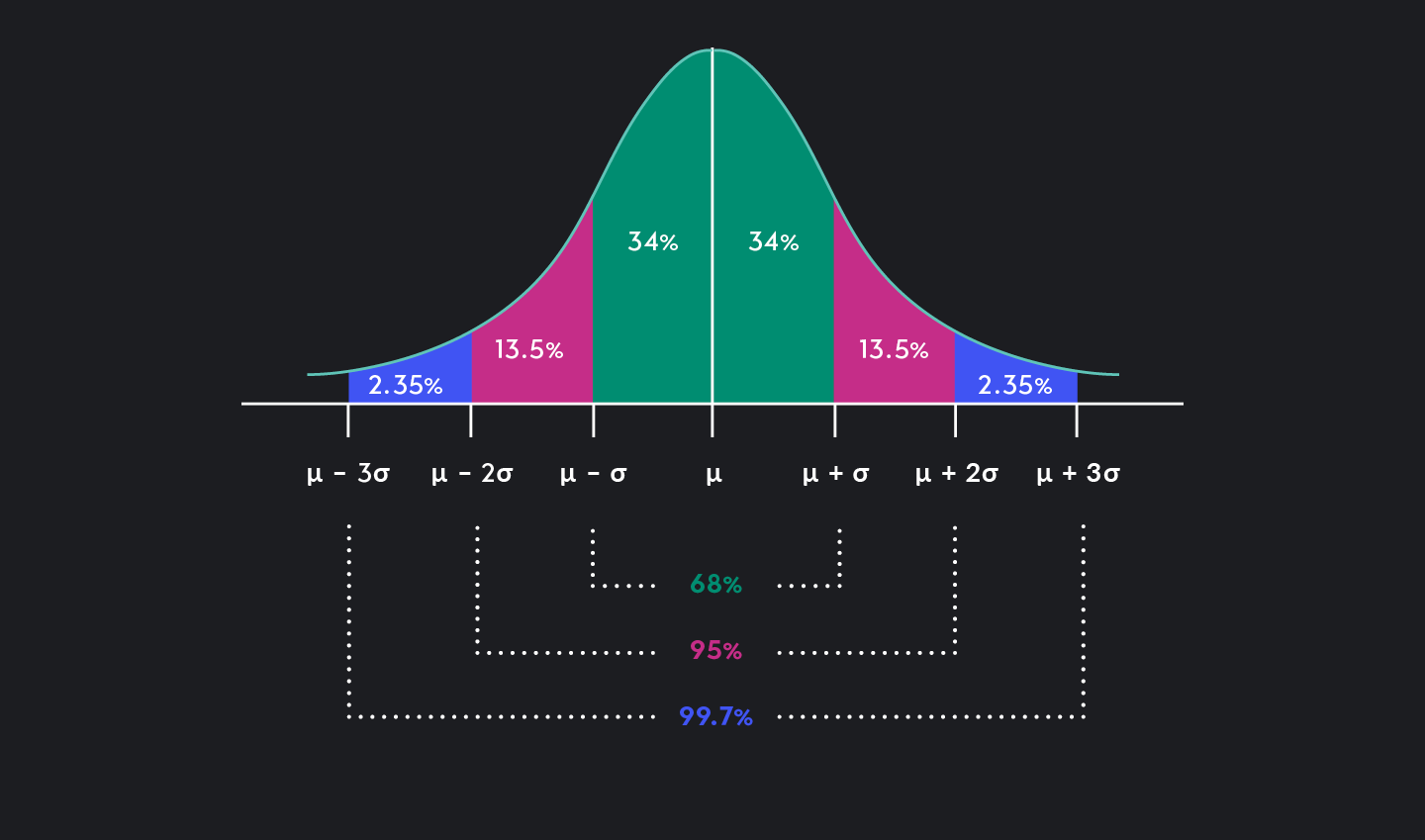
Standard Deviation:

Integrity vs despair
The stage in Erikson's theory where individuals in late adulthood reflect on their lives and ask if they are happy with who they have become.
Absolute Threshold
The minimum amount of stimulation needed to trigger a sensation, like touch, taste, smell, vision, or hearing, detectable 50% of the time.

Difference Threshold (Just Noticeable Difference)
The minimum, (lowest) amount of change that an individual can detect, is detectable 50% of the time.

Adrenal Glands
Endocrine system glands secreting hormones like norepinephrine and epinephrine (adrenaline) for the fight-or-flight response.

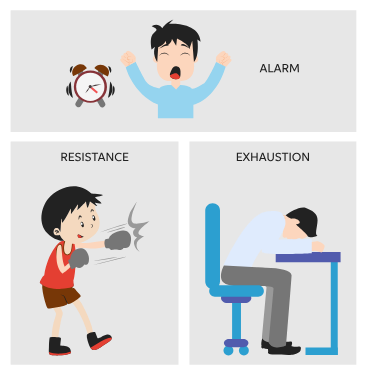
Hans Selye's General Adaptation Syndrome (G.A.S)
Three stages - Alarm, Resistance, and Exhaustion - in response to stress affecting the body's resources and health.

Prospective Memory
Remembering to perform a task at the intended time, like taking a daily pill.

Social Loafing
When individuals exert less effort in a group setting compared to working alone, as seen in group projects.


Cocktail Party Effect
Ability to focus on a single voice amidst multiple conversations in a noisy environment.
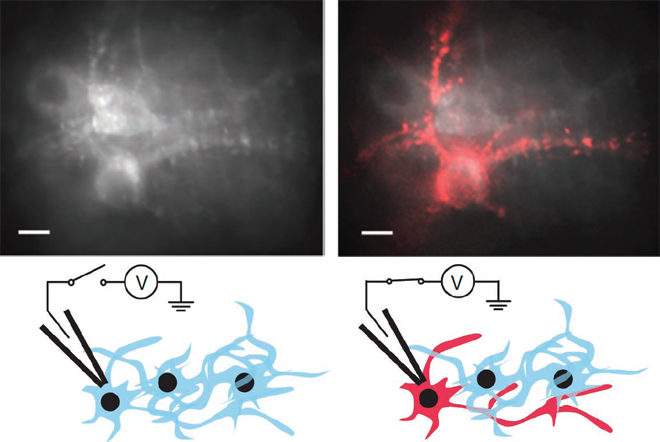
Neuron Firing Process
Involves dendrites receiving neurotransmitters, firing based on threshold, myelination for faster transmission, action potential when firing, and resting potential when not firing.
Neurotransmitters
Chemical messengers like acetylcholine, dopamine, serotonin, epinephrine/norepinephrine, GABA, endorphins, and glutamate influencing various functions in the brain and body.
