OSCE Dental Hygiene
1/340
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
341 Terms
Bass Method
Most widely used method. Bristles are angled at a 45 degree angel towards the gingiva.
Stillman's Method
Bristles are positioned on the gums rather than into the pockets and directed at a 45 degree angle.
Charter's Method
Bristles are directed occlusally, away from the gingiva. Useful for cleaning orthodontic brackets, prosthesis, and areas treated with surgeries.
Fone's Method
Bristles are moved in large circular motion on the buccal and lingual surfaces. Useful for children, those physically impaired, or adults who lack manual dexterity.
Fluoride Varnish
-Dries immediately upon contact with saliva.
-Does not require a professional prophylaxis before hand.
-Can eat and drink immediately after.
-Avoid brushing, rigorous rinsing, or hard foods for 3 to 4 hours.
-Easier and more effective method
Fluoride is recommended for patients who:
-Have xerostomia
-High caries risk
-Undergoing cancer therapy
-Orthodontics
Fluoride Gel or Foam (office application)
-Applied onto tray and placed in patient's mouth usually for 4 minutes (Read manufactures label).
-Do not eat, drink, or smoke for 30 minutes.
-Most popular types are 1.23% APF and 2% Neutral sodium fluoride.
Stannous Fluoride
-0.4% available for non-prescription use.
-1% neutral sodium fluoride gels available for prescription use.
-Can cause extrinsic staining (especially in patient's with inadequate plaque control).
Acidulated Phosphate Fluoride (APF)
-Do NOT use of composites, porcelain, or sealant materials as it causing pitting and roughening.
-Also avoid on root surfaces.
Neutral Sodium Fluoride
Agent of choice on root caries, implants, cosmetic restorations, and reduced salivary flow.
Second trimester
safest trimester for dental treatment.
Pregnancy gingivitis
-Caused by an elevation of hormones estrogen and progesterone. Hormones increase can cause exaggerated gingival response to microorganisms.
Pyrogenic granuloma (Pregnancy tumor)
localized area of gingival enlargement, typically involving interdental papilla, usually diminishes after delivery of baby.
What category of LA can use administer to a pregnant patient?
Category B (lidocaine and prilocaine)
Can you use Nitrous oxide sedation and general sedation on a pregnant patient?
relative contraindication (gas interferes with the absorption of B-12 and other nutrients).
Early Childhood Caries (ECC) index
-presence of 1 or more areas of decay on a child younger than 6 years of age
Severe-Early Childhood Caries (S-ECC) index
-Presence of decay in a child younger than 3 years old.
When should a child's first dental appointment occur?
-Within 6 months of the eruption of the first tooth or before 1-year of age.
When should you first start brushing a child's teeth?
-When the first tooth appears.
Erosion causes
-Anorexia Nervosa
-Bulimia Nervosa
Anorexia Nervosa
extreme weight loss caused by self-starvation, excessive exercise, use of laxatives, self-induced vomiting.
Bulimia Nervosa
compulsive disorder that involves periods of starvation, binging, and purging.
Signs and Symptoms of erosion
-dental caries from vomiting
-Perimolysis: erosion from vomiting mostly on the maxillary lingual surfaces. Raised appearance of restoration margins.
Abrasion
-V-shaped notch in the gingival portion of the facial aspect of the tooth.
-Results from forces of friction between the teeth or external objects.
-Can happen from improper brushing technique or the use of a toothpick or pipe.
Attrition
-Results from forces between the teeth.
-Wear on the incised and occlusal surfaces from grinding.
Abfraction
-Biomechanical destruction related to fatigue, flexure, and deformation of tooth structure.
-Can appear as a wedge-shaped lesion at the cervical third of the tooth.
What is the most effective public health measure to prevent tooth decay?
Community Water Fluoridation
New recommended level of fluoride is?
0.7 ppm
Old level of fluoride is?
0.7-1.2 ppm
HIV can cause:
-Linear gingival erythema
-Kaposi Sarcoma
-Delayed healing
-Larger than usual ulcers
-Candidiasis
-Etc.
Diabetes can cause:
-Delayed healing
-Periodontal disease
-Candidiasis
-Etc.
ASA 1
Normal, Healthy
ASA 2
Pt. with mild systemic diseases.
-Allergies
-Controlled hypertension
-Asthma
-Mild obesity
-Pregnancy
-Cigarette smoking without COPD
-Diabetes without systemic effects
ASA 3
Pt. with severe systemic disease and some functional limitation.
-Controlled disease of more than one body system
-Controlled CHF
-Poorly controlled hypertension
-Morbid obesity
-Respiratory Problems (COPD)
-Stable angina
ASA 4
Pt with severe systemic disease that is a constant threat to life.
-Possible risk of death
-Unstable angina
-Symptomatic COPD and CHF
ASA 5
Moribund patient not expected to survive for more than 24 hours without surgery.
ASA 6
Brain dead pt.
Radiolucency
Dark areas on the film. Produced by less dense structures that allows the passage of x-rays. (i.e. cysts)
Radiopaque
Light areas on the film. Produced by denser structures. (i.e. Lamina Dura)
Overlap
inappropriate horizontal angulation
Foreshortening
too much vertical angulation
Elongation
not enough vertical angulation
Mark across film
bent film
Circular white boarder on film
Cone cut

Herringbone or waffle pattern on film
backwards film
Darker film with outlines of many teeth
double exposure
Film too dark
too much development time; temperature too high
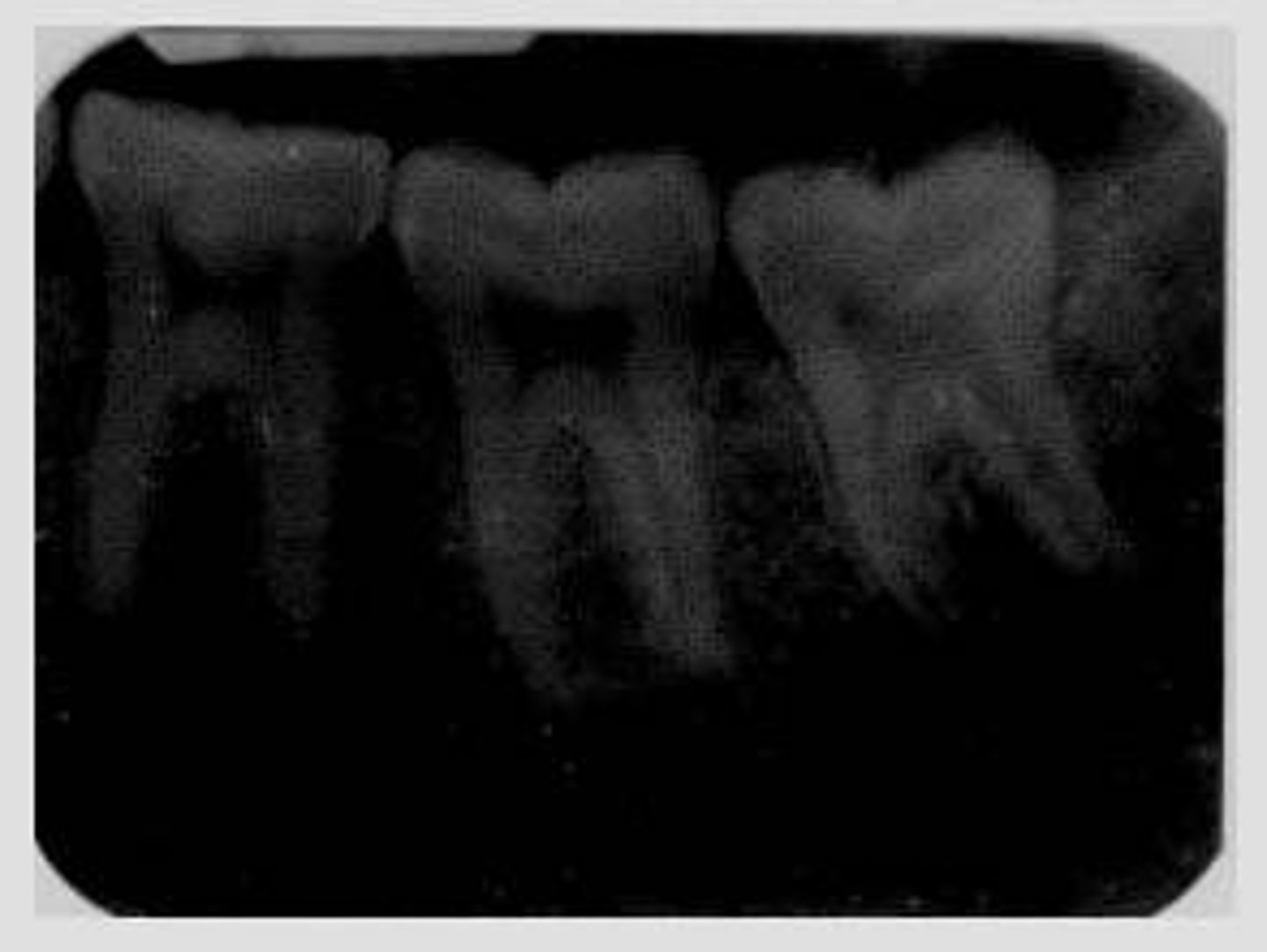
Film too light
not enough development time; temperature too low

Cracked emulsion
sudden temperature change between developer and fixer.
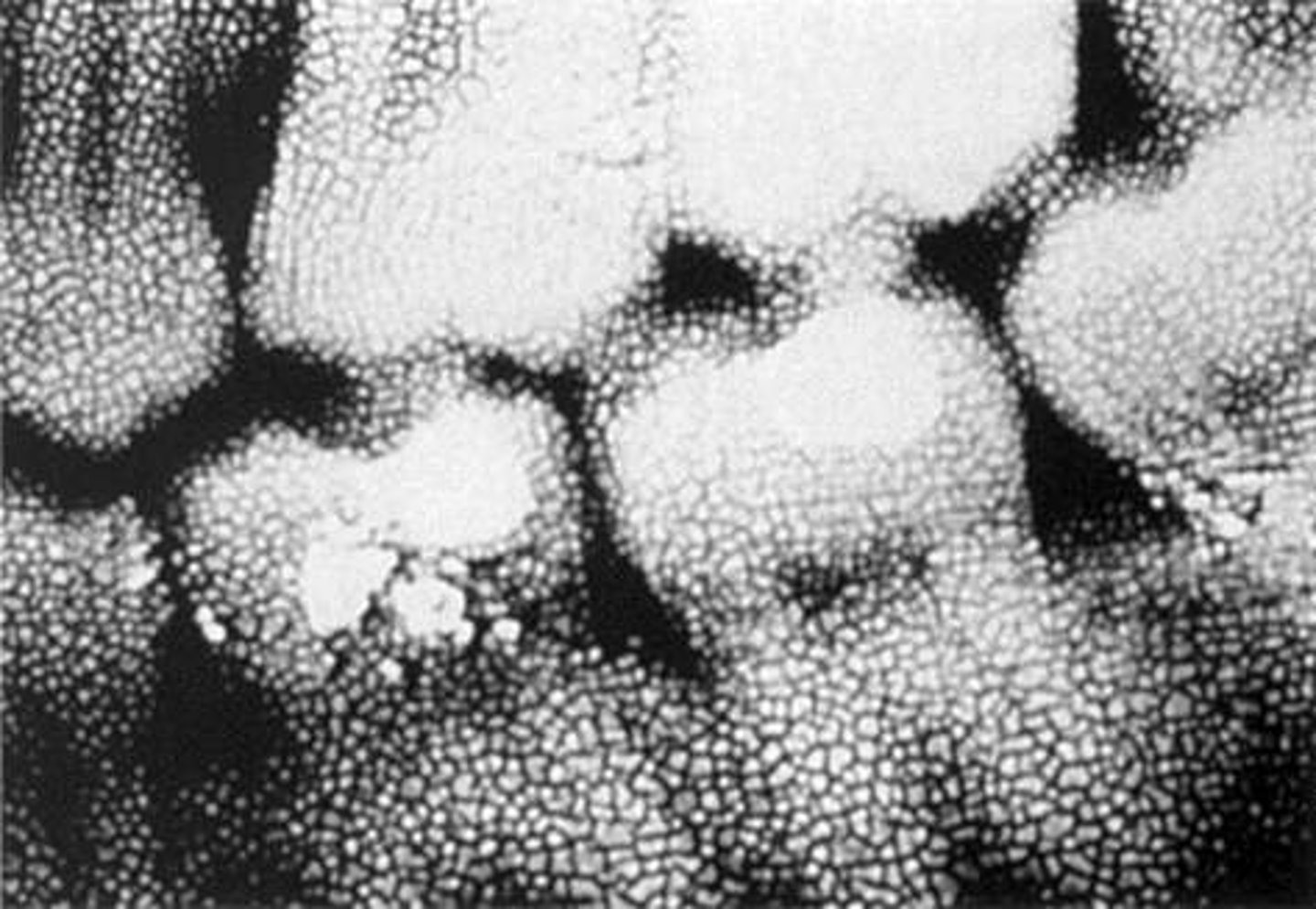
Darker areas
developing solution touches film before processing procedure.
Lighter areas
fixer solution touches film before processing procedure.
Yellow/brown stains on film
exhausted solutions or insufficient washing.
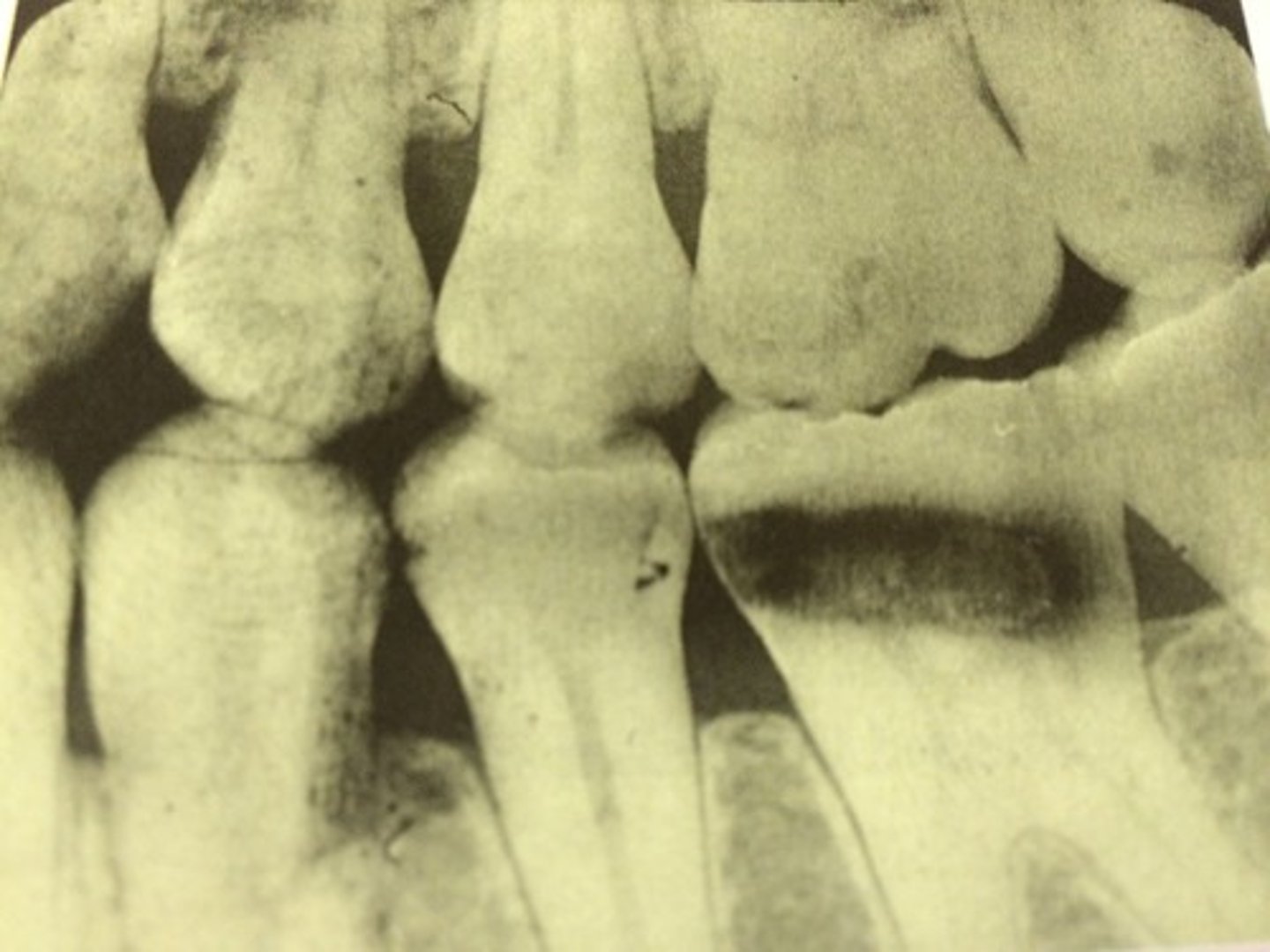
Straight white border on film
developer cutoff caused by incomplete immersion of film into developer.
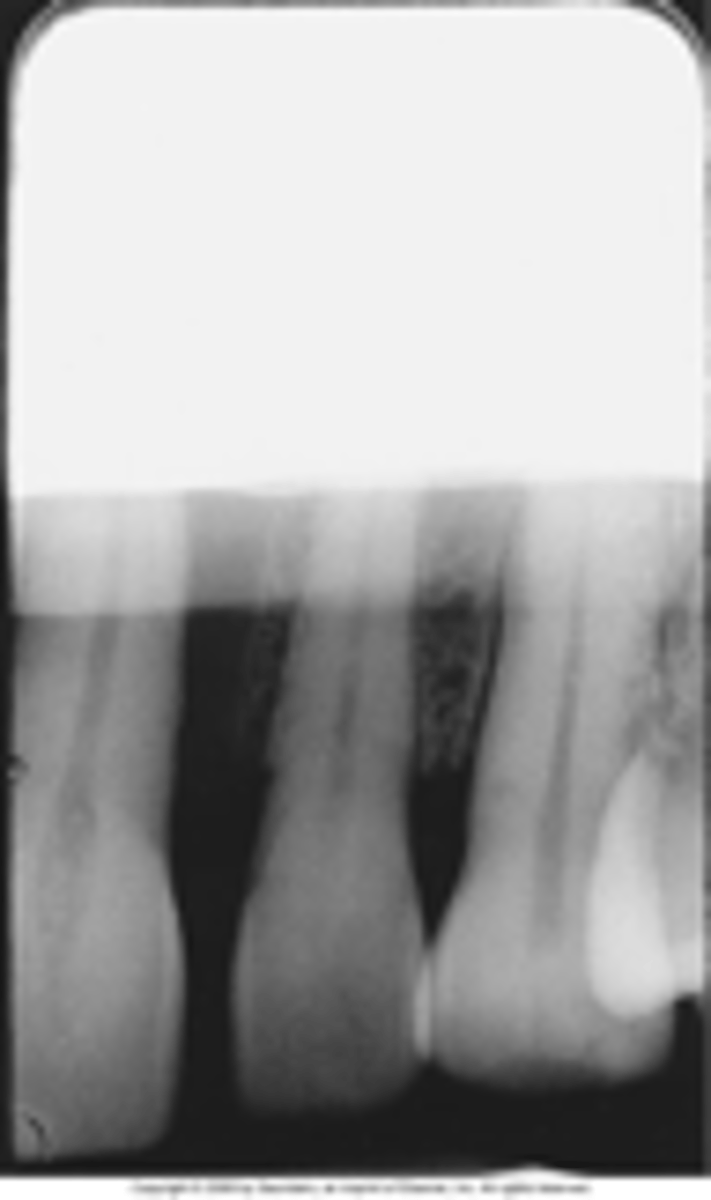
Straight black border
fixer cutoff caused by incomplete immersion of film into fixer.
Outline border of another film
Films stuck together in solutions.
White spots on film
air bubbles trapped during processing.
Thin, black, branchlike lines on film
Static lines caused by low humidity and opening film packet too quickly.
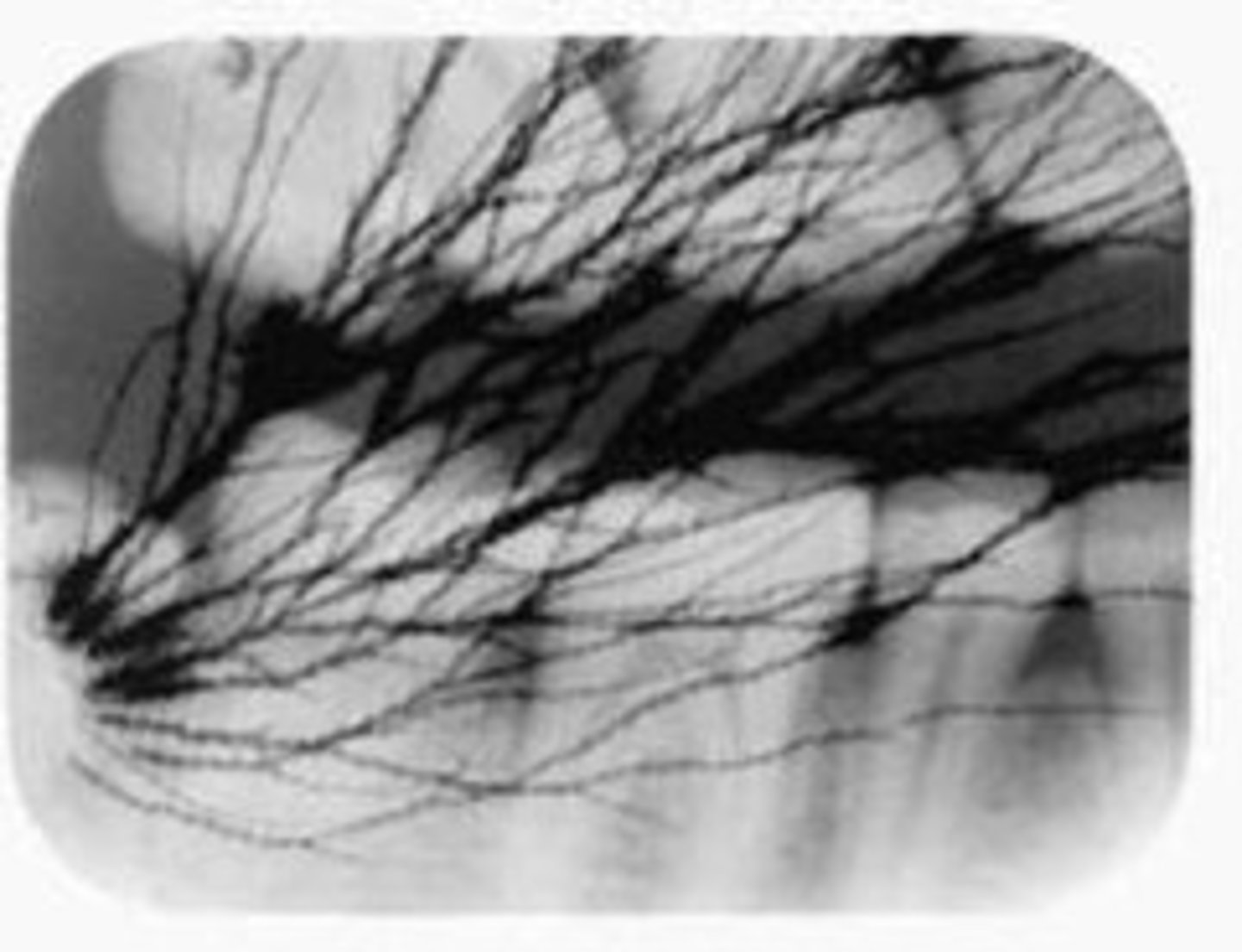

Fogged films
improper safelight, light leaking into dark room, outdated film.
"V" or "Sharks fin" on pano
caused by lead collar.
Exaggerated smile on pano
chin tipped down too far
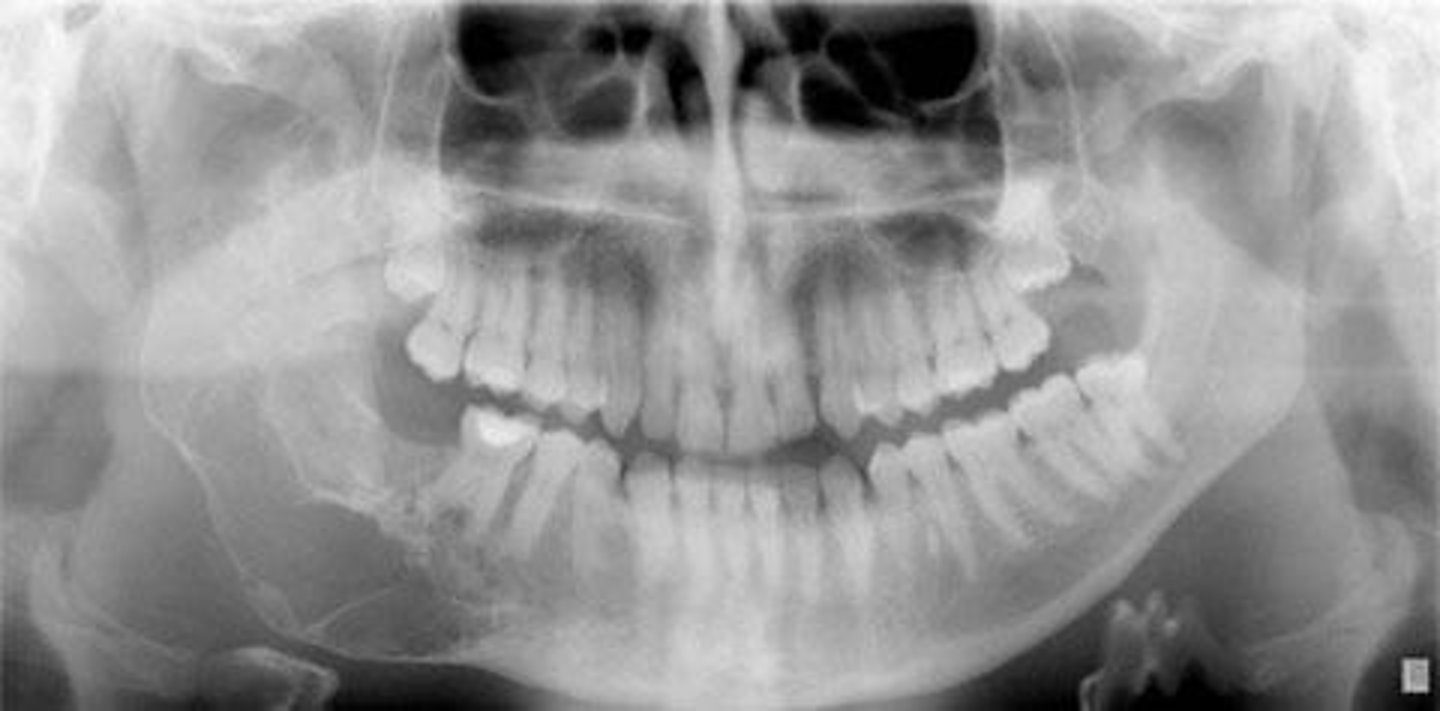
Flat smile on pano
chin tipped too far up
Mandibular incisors roots blurred on pano
chin tipped too far down
Maxillary incisors roots blurred on pano
chin tipped too far up
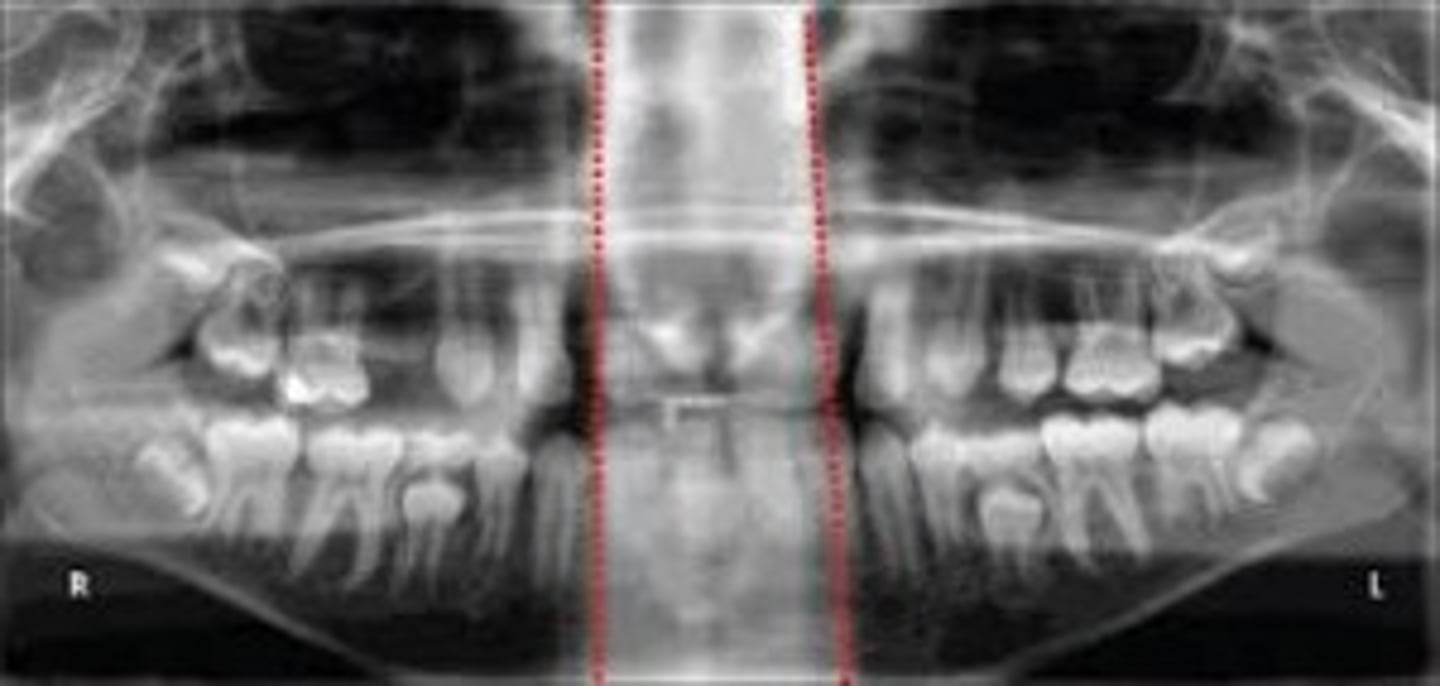
One side shows larger teeth/condyle
patient head is twisted (the larger side is the distant side)
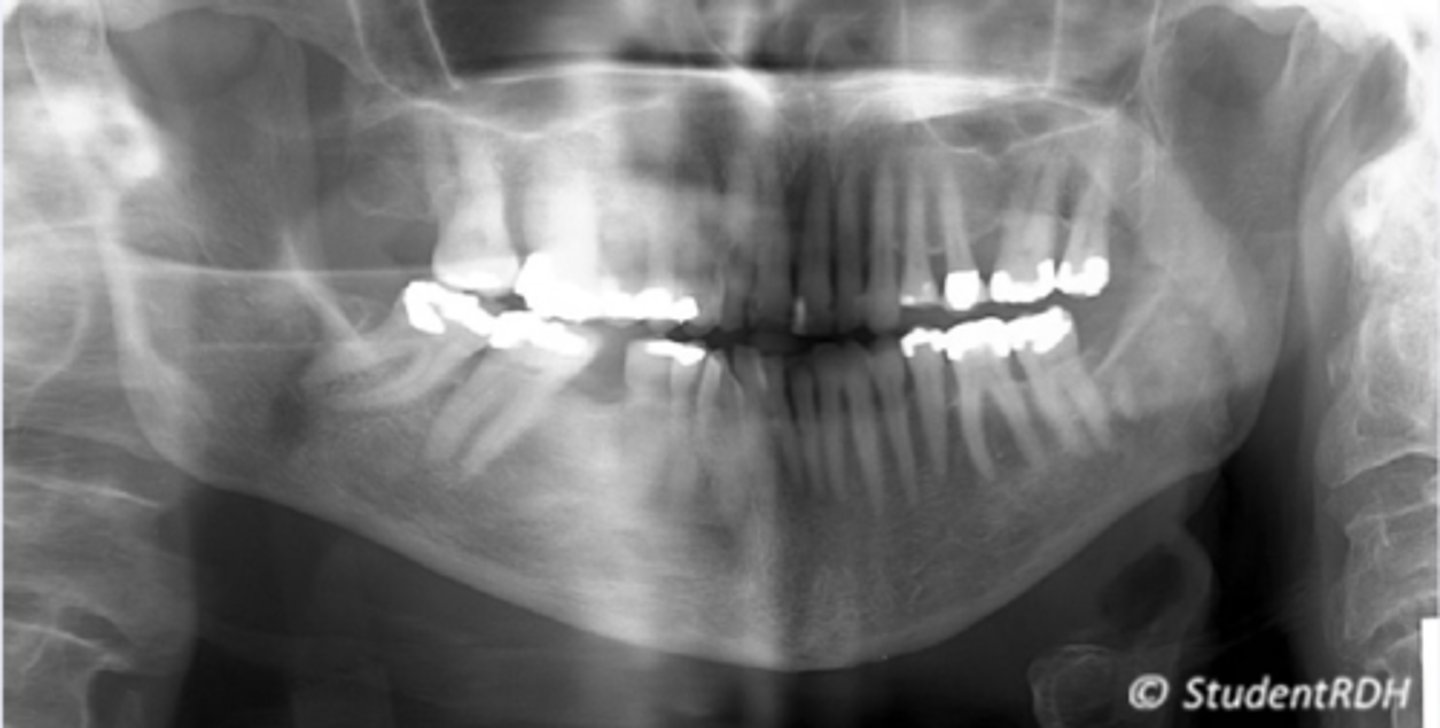
White straight opacity
slumping causing ghost image of spine
Shadow over maxillary teeth
tongue not touching rough of the mouth
Airway shadow in an arch shape
tongue not touching rough of the mouth
Anterior teeth thicker and wider
chin placed behind the focal trough. Enlarged incisors (head too far back).
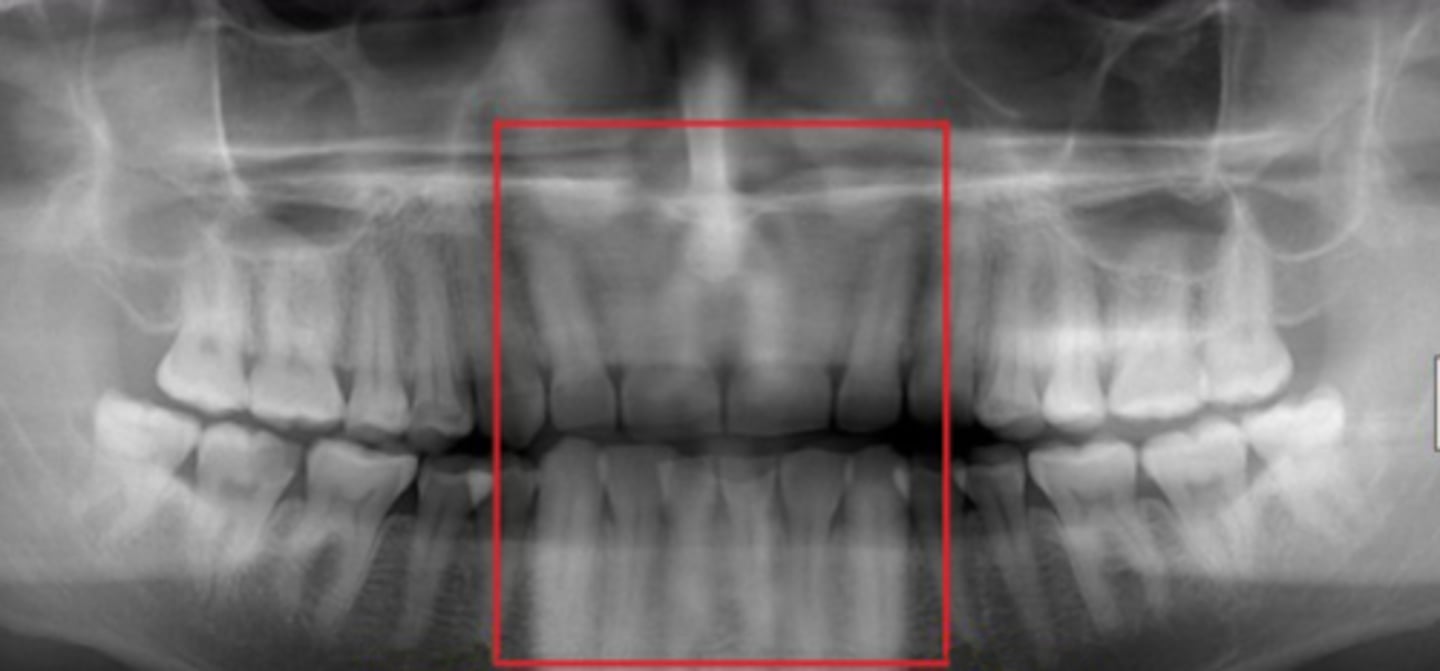
Skinny anterior teeth
chin placed too far forward. Small incisors (head too far forward).
Dark shadow on anteriors
Patient not closing lips around biting blocks.
Ghost image
Jewelry not removed
Incisive foramen on film
-Passageway for nasopalatine nerves.
-Small radiolucent oval between roots of maxillary central incisors.
median palatine suture
vertical radiolucent thin line in the middle of the palate.
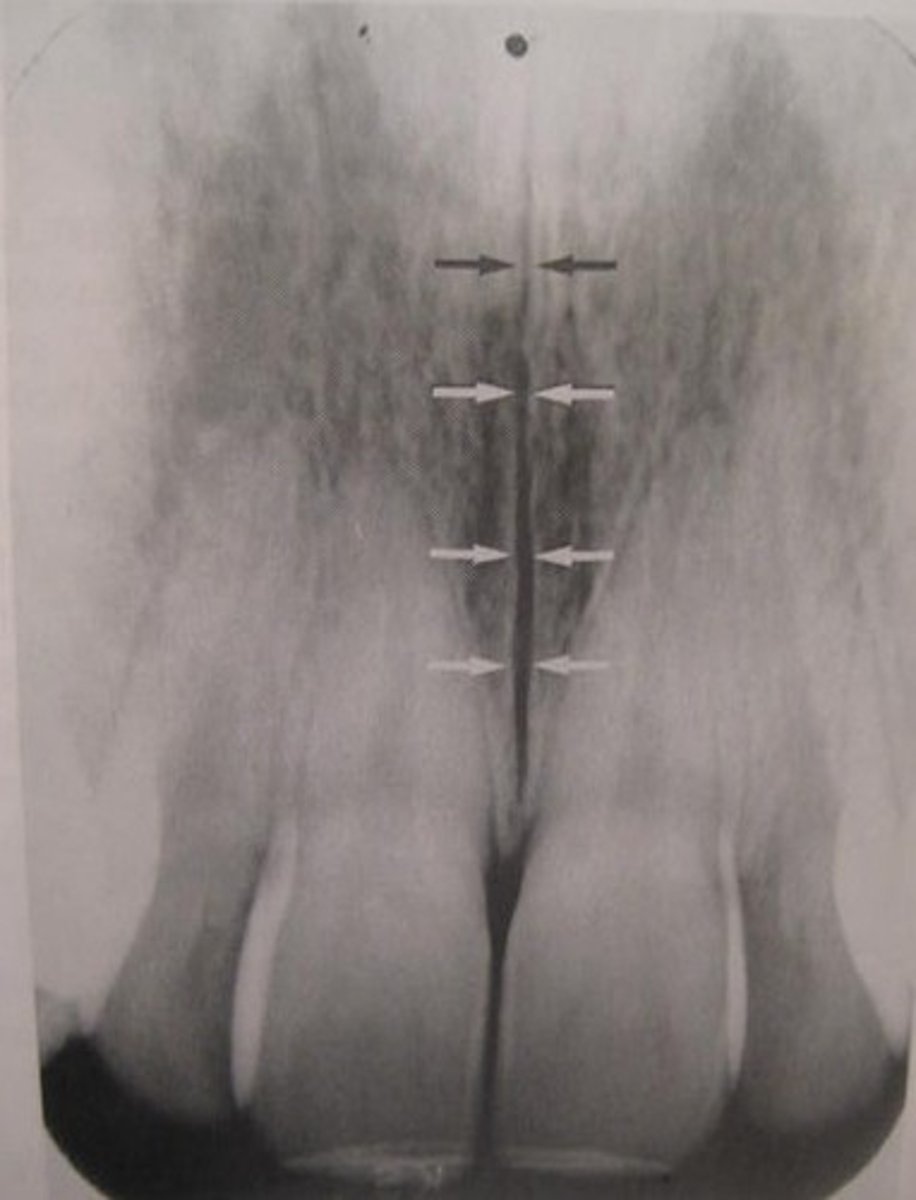
Nasal septum
-Thin wall that divides the nasal cavity into two.
-Radiopaque vertical strip.
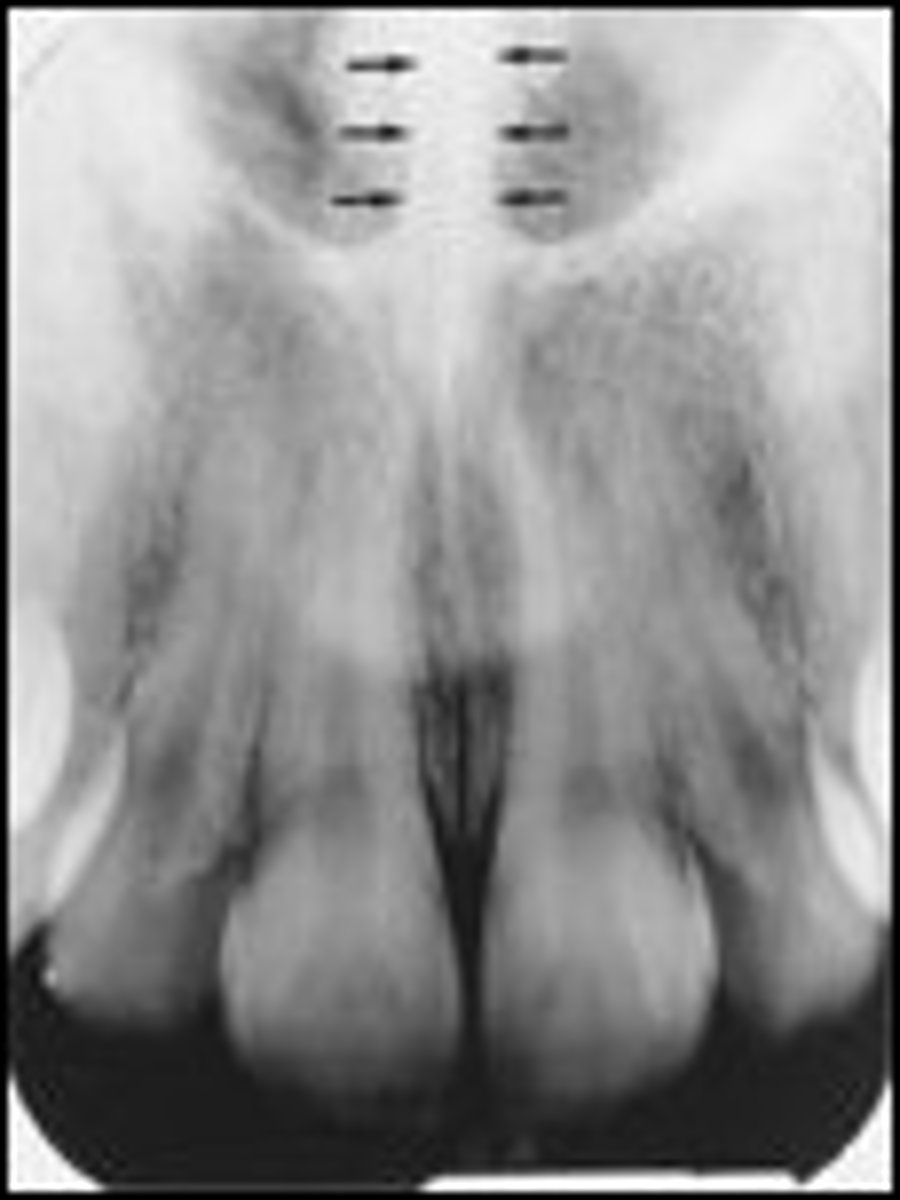
Nasal Spine
-Projection of bone anteriorly.
-Radiopaque triangle shape at medical palatal suture where nasal septum and fosse meet.
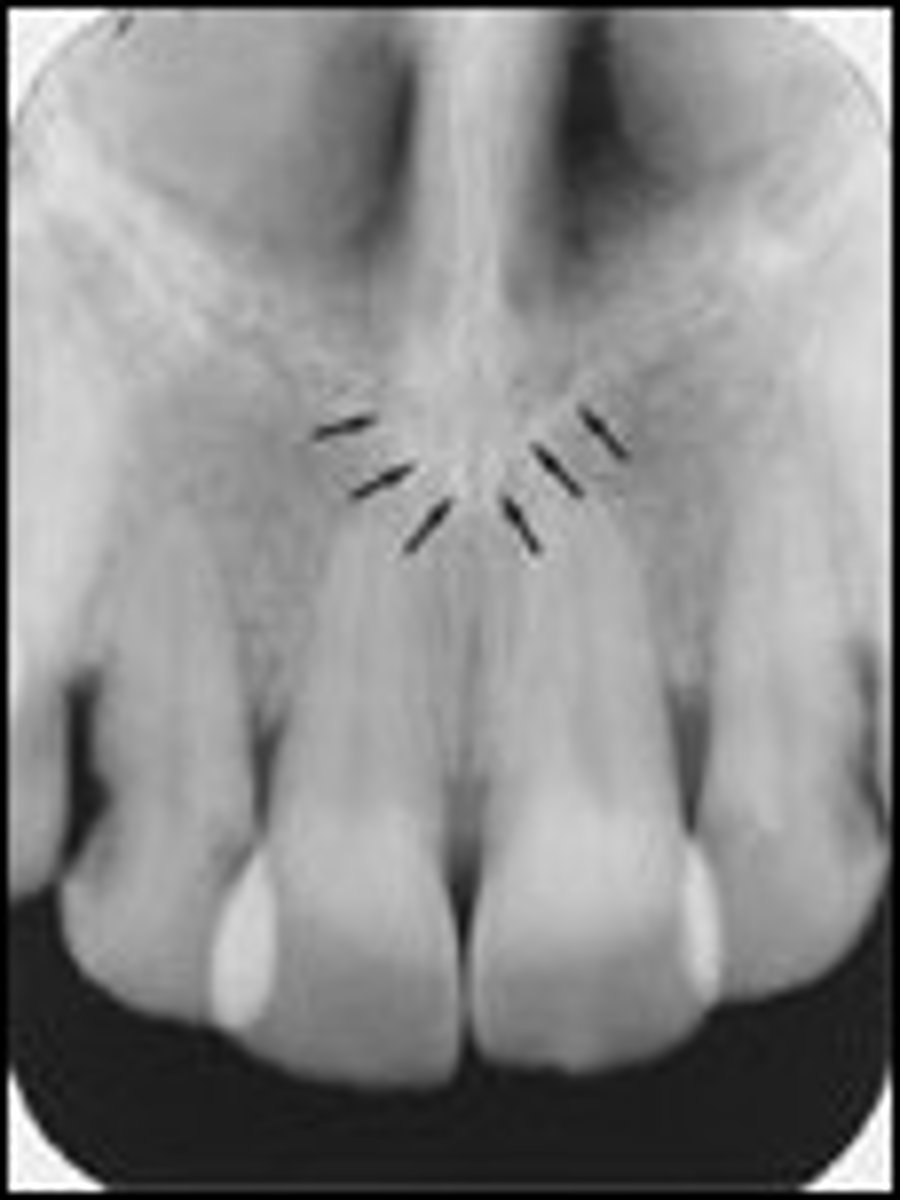
Nasal cavity (Nasal fossae)
-Large air-filled space above and behind the nose in the middle of the face.
-Radiolucent oval shapes superior to central incisors.
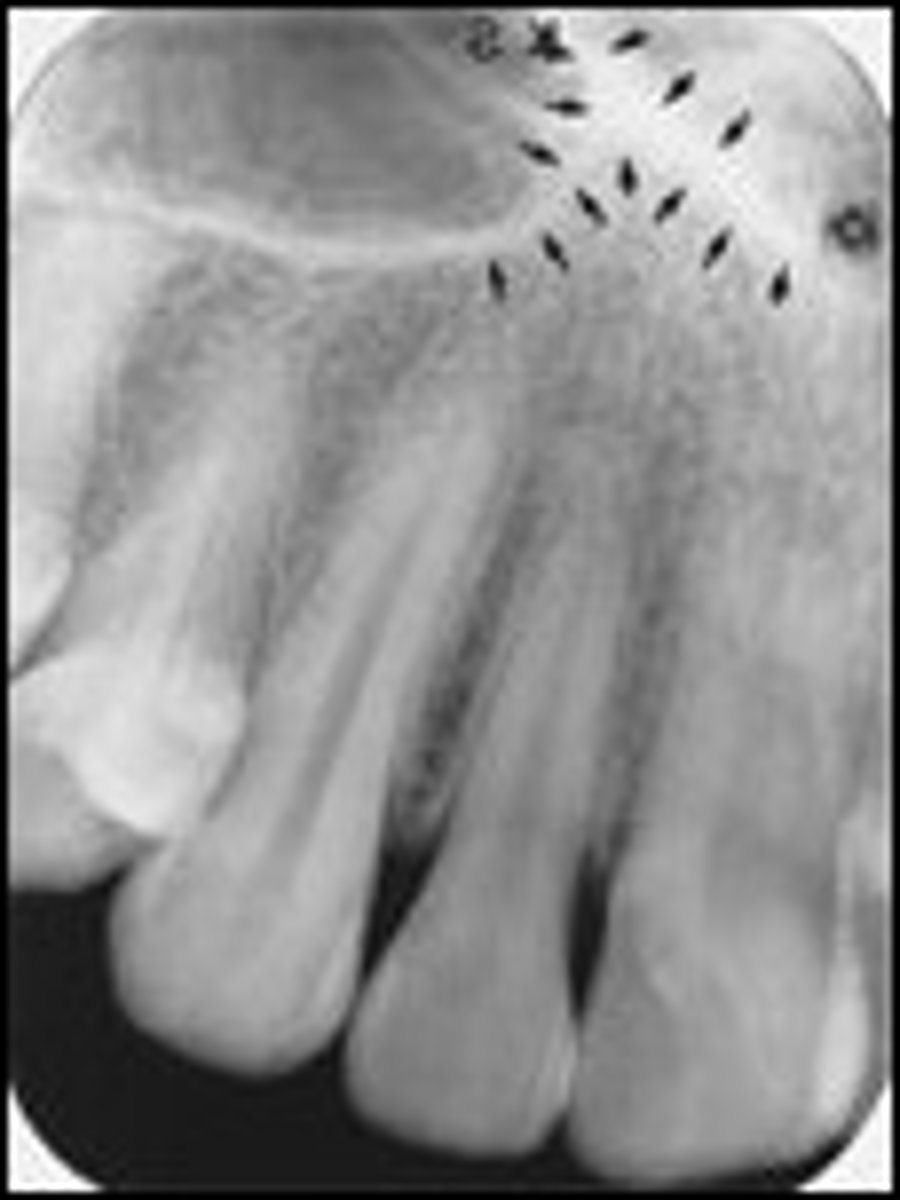
Maxillary sinus
-Hollow spaces in bone superior to molar and premolar.
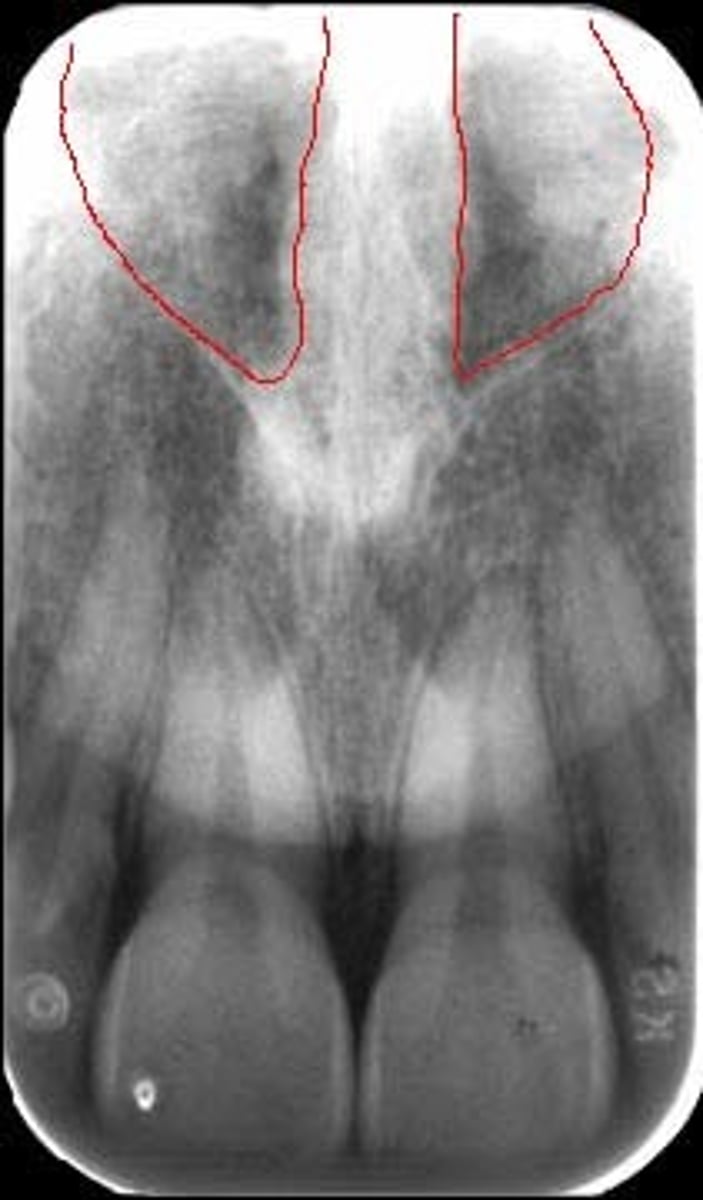
Inverted Y
-Junction where the nasal fossa and the maxillary sinus.
-Most commonly superior to the maxillary canine apex.
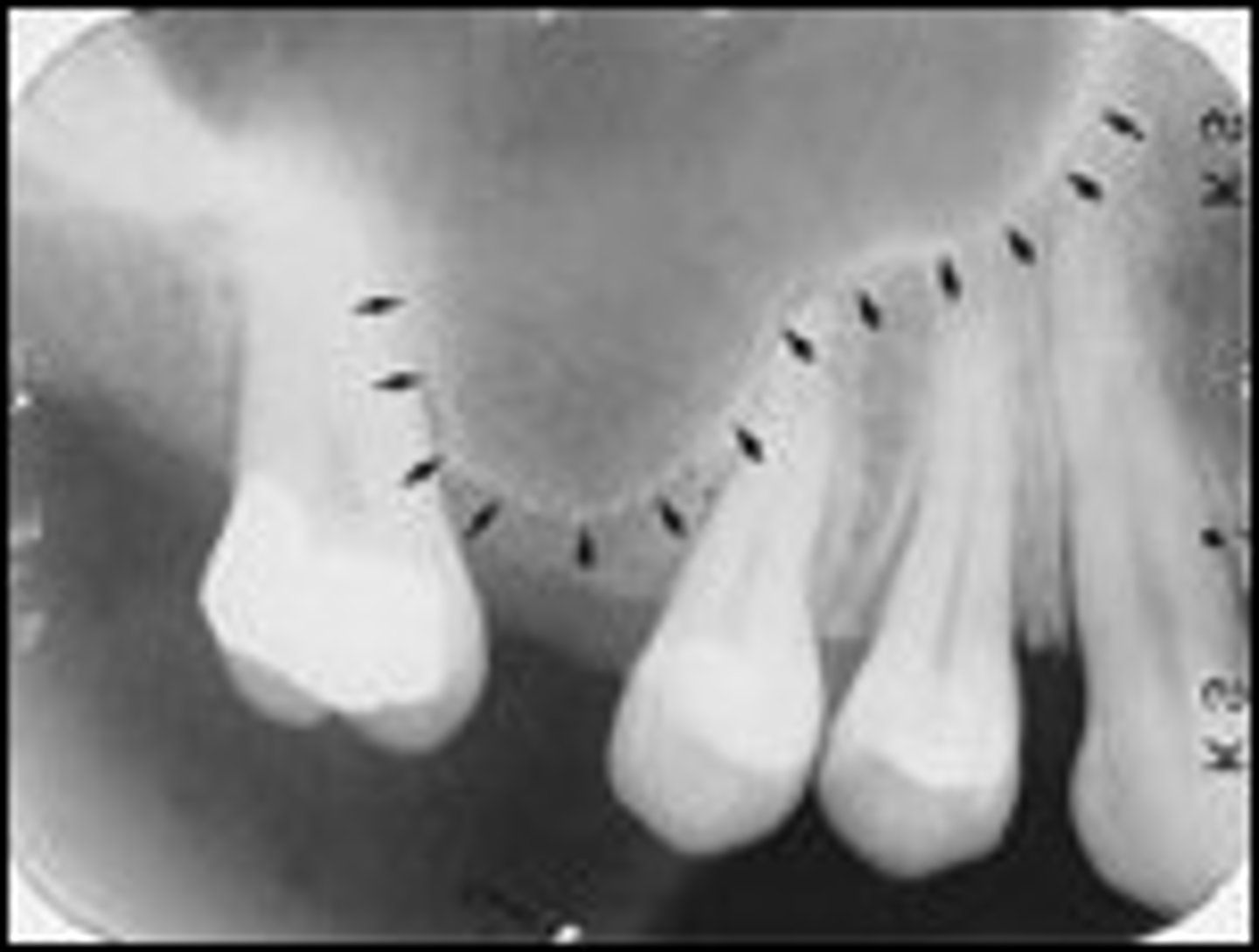
Maxillary Tuberosity
-Distal portion of the alveolar process.
-Rounded, radiopaque elevation distal to third molar regions.
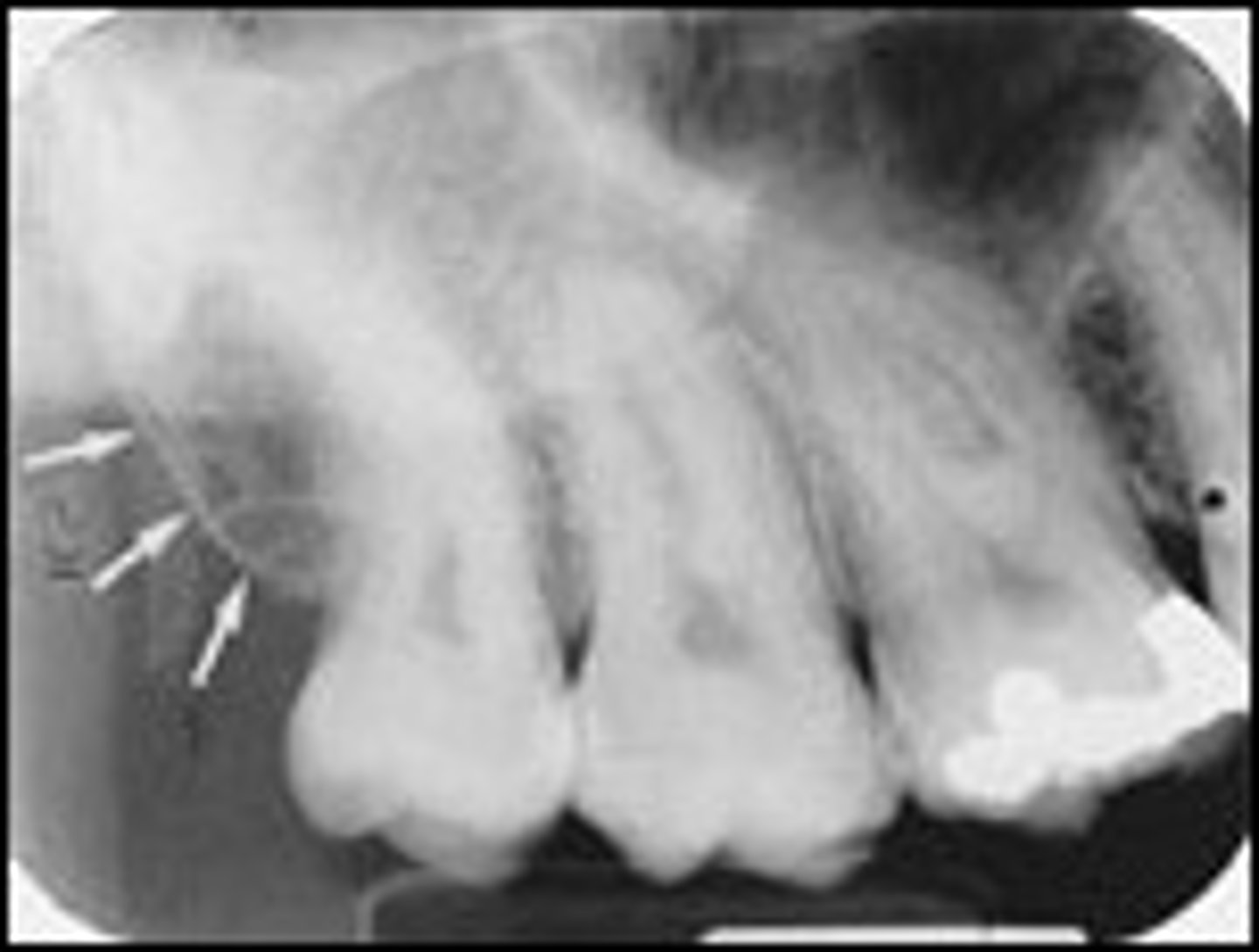
Hamulus
-Extension of medial pterygoid plate of sphenoid bone. Radiopaque hook-like protrusion posterior to maxillary tuberosity.
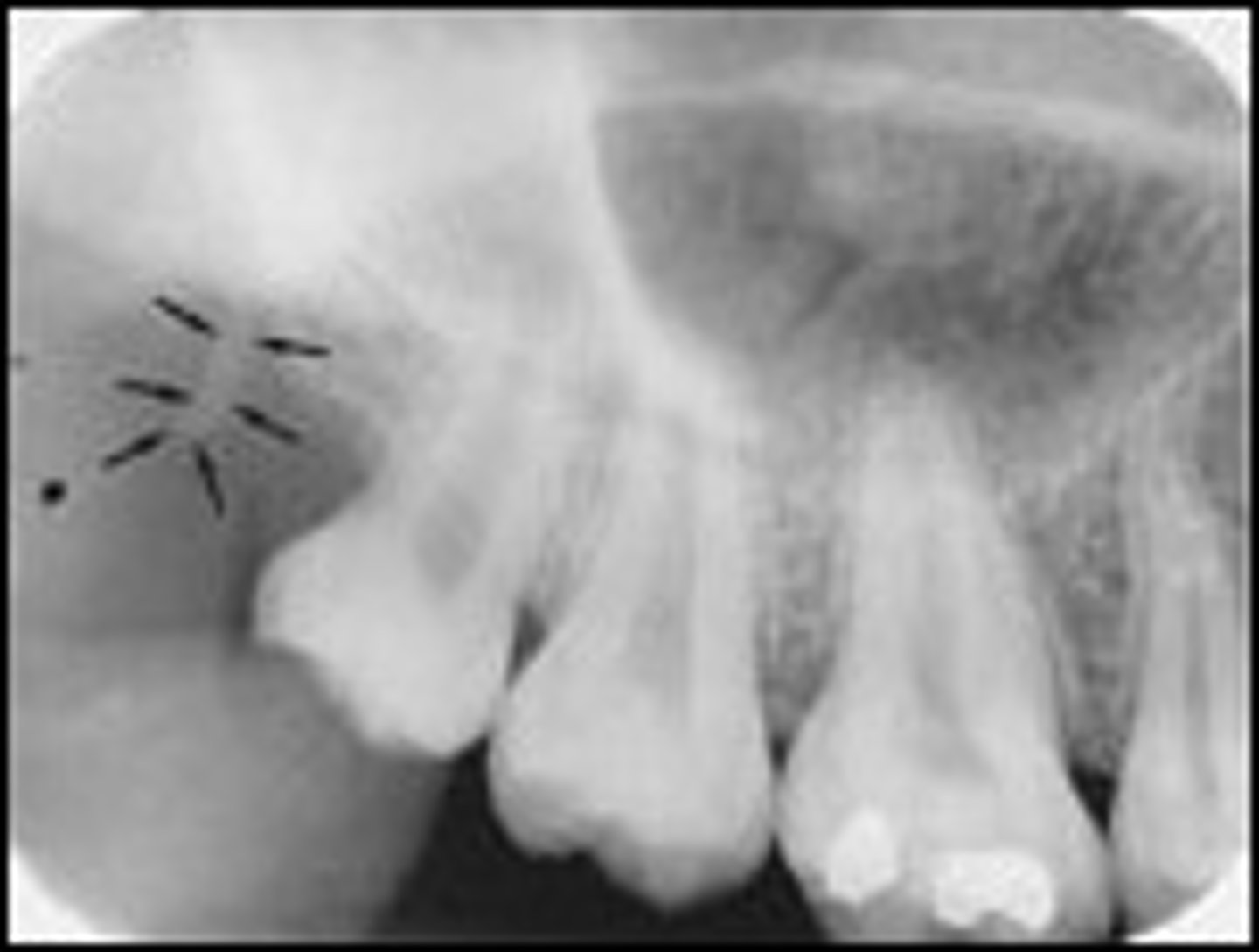
Zygomatic process
-Slender profusion of the temporal bone that serves to strengthen the zygomatic arch.
-U-shaped radiopaque band superior to molar apices.
Coronoid Process
-Anterior portion of ramus.
-Radiopaque triangular projection usually superimposed over maxillary tuberosity.
Genial tubercles
-Four bony spines used for muscle attachment of the genioglossus and geniohyoid muscles.
-Circular rap opacities inferior to central incisor apices.
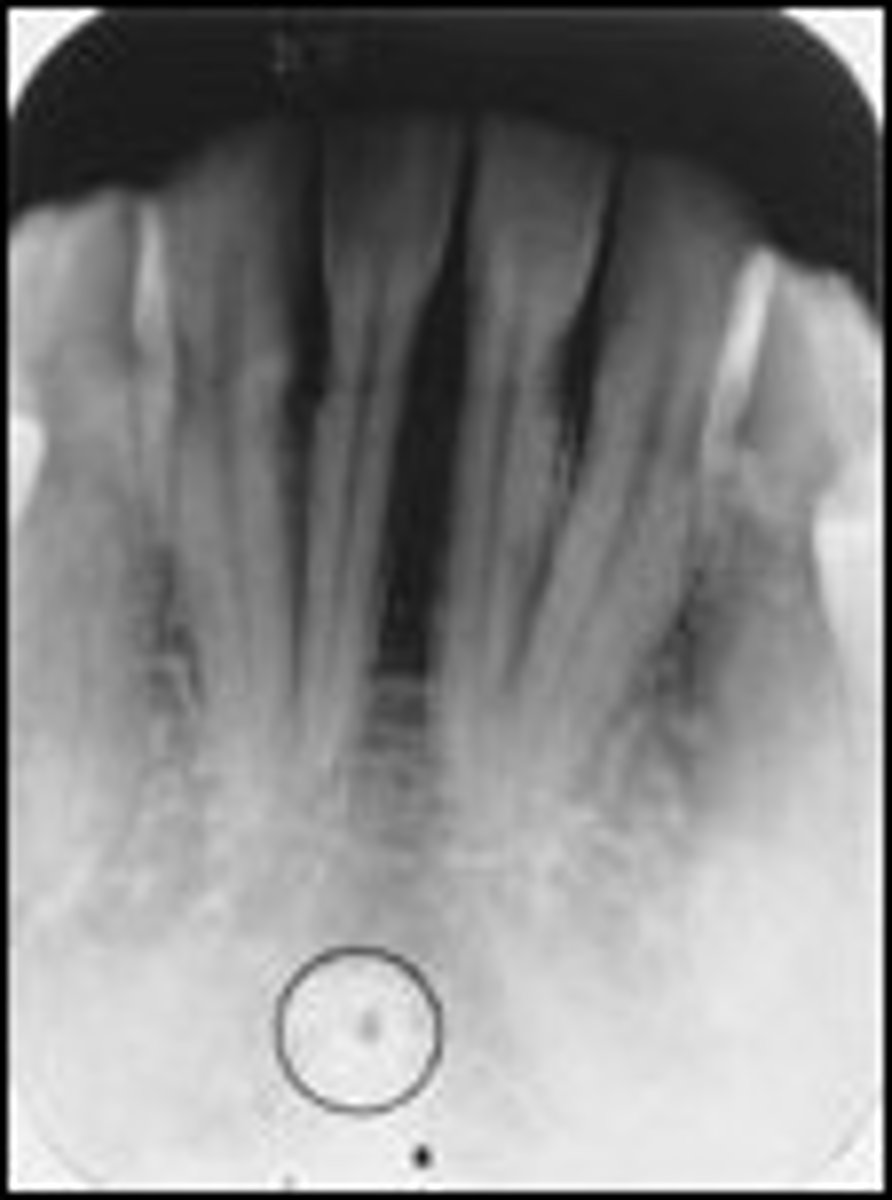
Lingual foramen
-Exit for incisive vessel branches.
-Radiolucent circle inside the radiopaque genial tubercles on the mandibular anteriors.
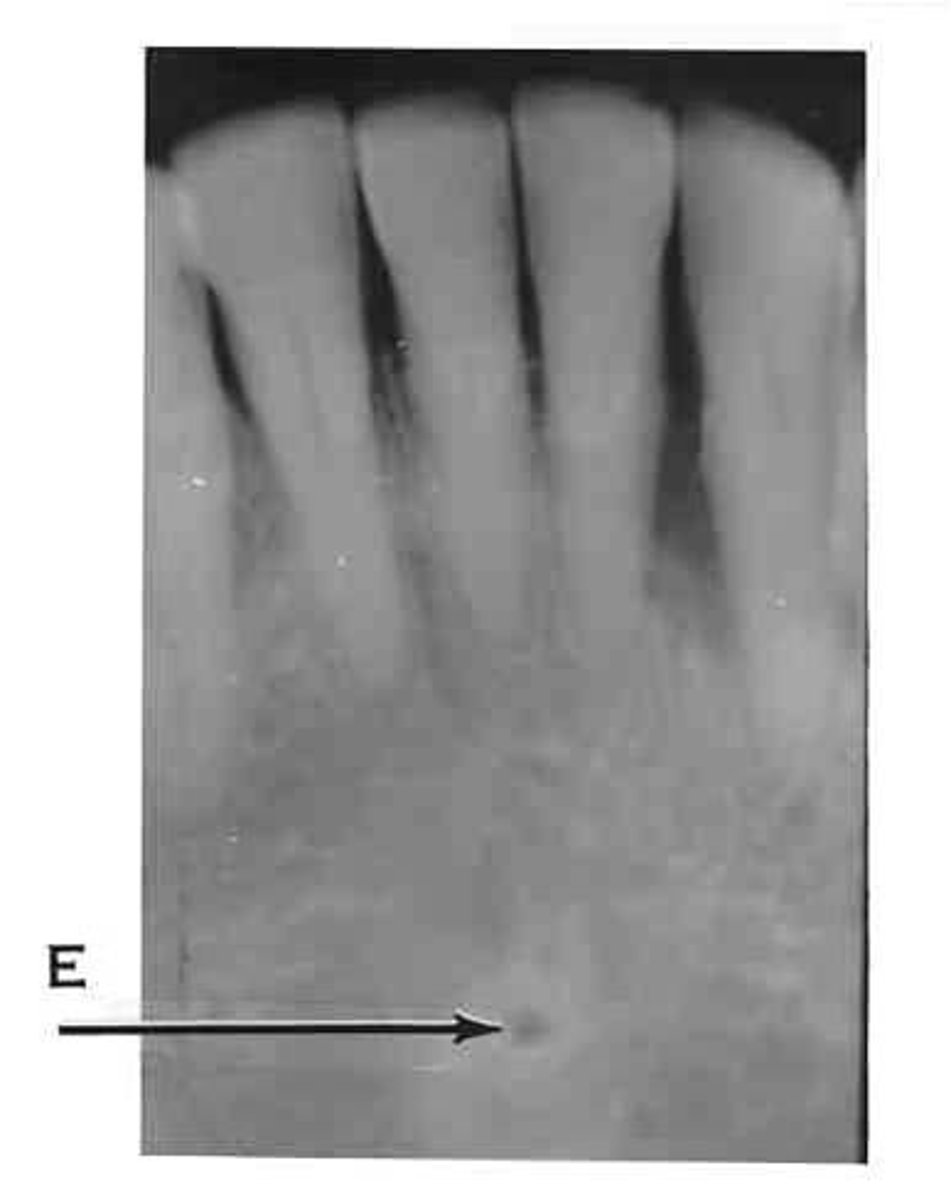
Mental Foramen
-Opening for mental nerve and vessels inferior to mandibular premolar apices.
-Round radiolucent area sometimes mistaken for periodical disease.
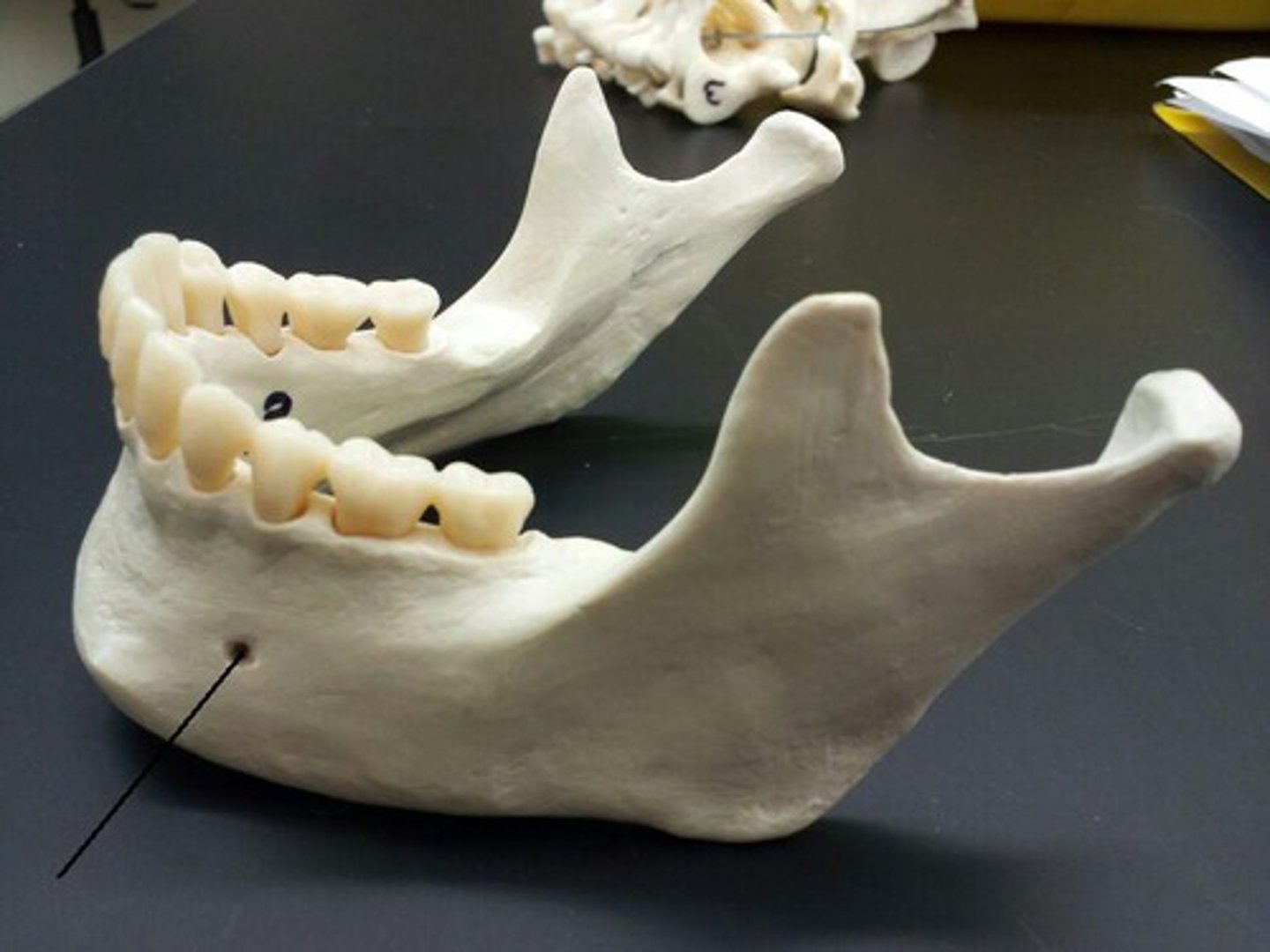
Mental ridge
-Ridge of bone located on the anterior surface of the mandible.
-Bilateral radiopaque lines, starting inferior to premolar apices and extending anteriorly to the midline.
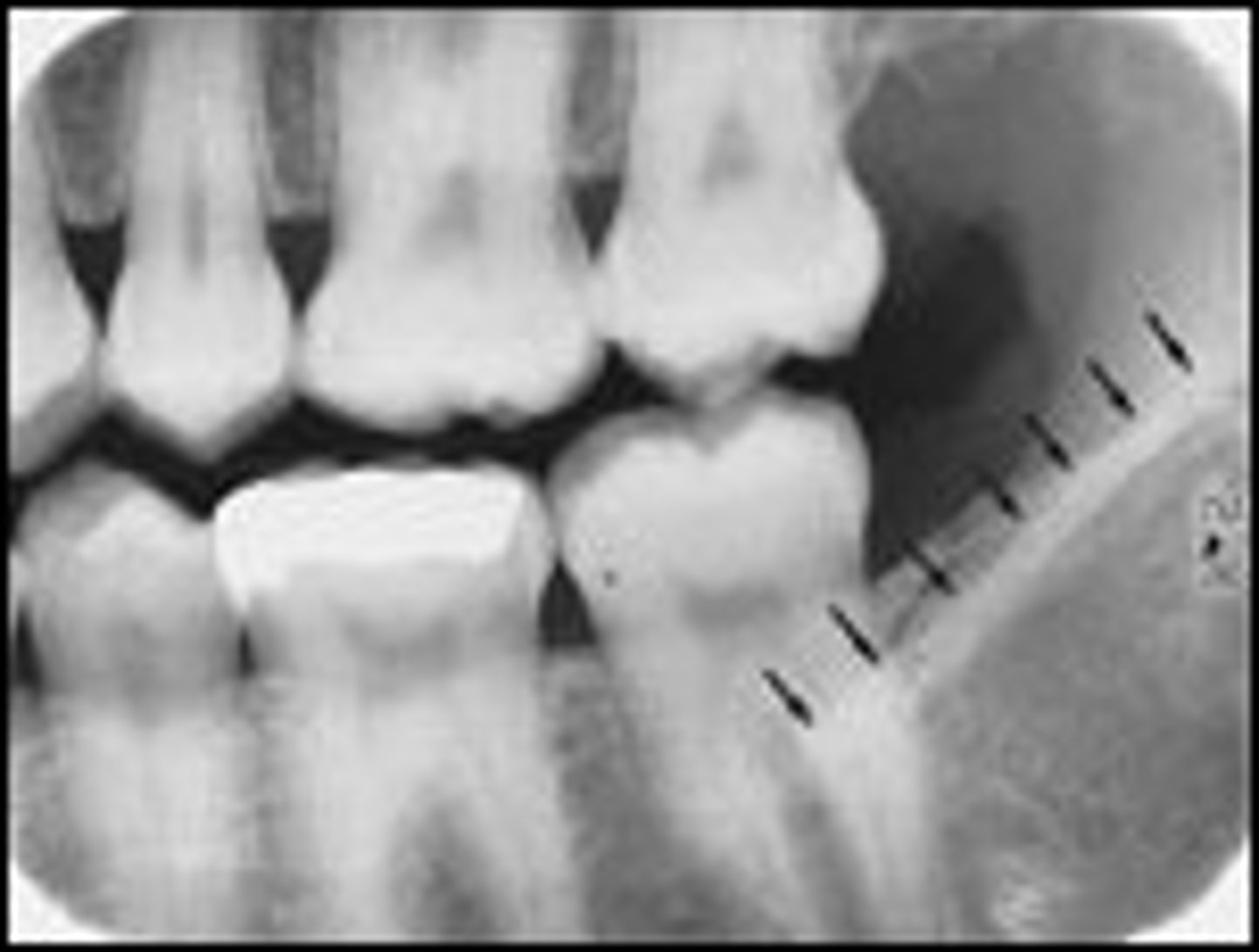
External oblique ridge
-Linear area of bone on external surface of mandible.
-Radiopaque line running anterior from the ramus across the molars.
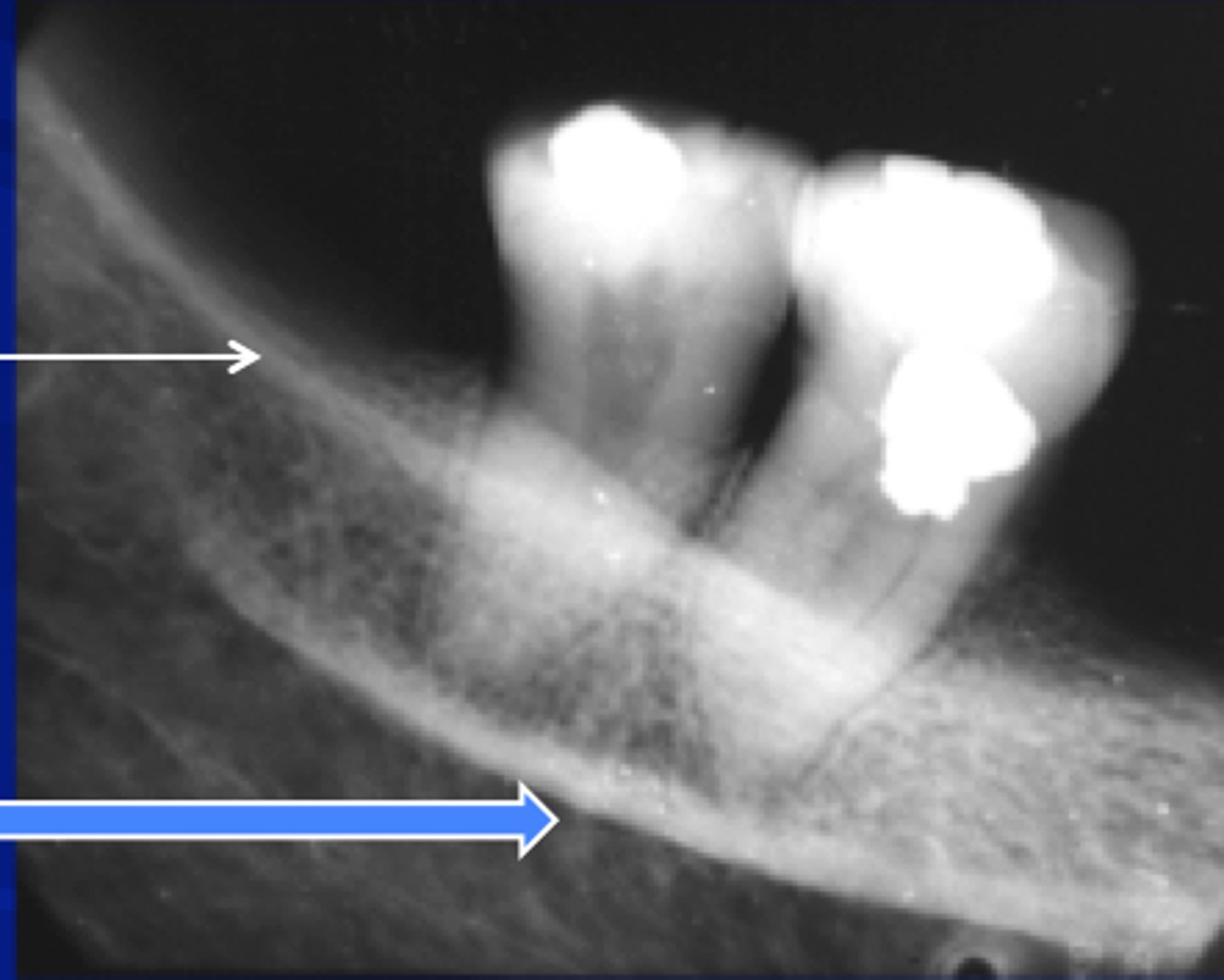
Internal oblique ridge (mylohyoid)
-Elevated long area on the internal surface of mandible.
-Radiopaque line running along the premolar and molar apices.
-Usually positioned below the external oblique ridge on radiographs.
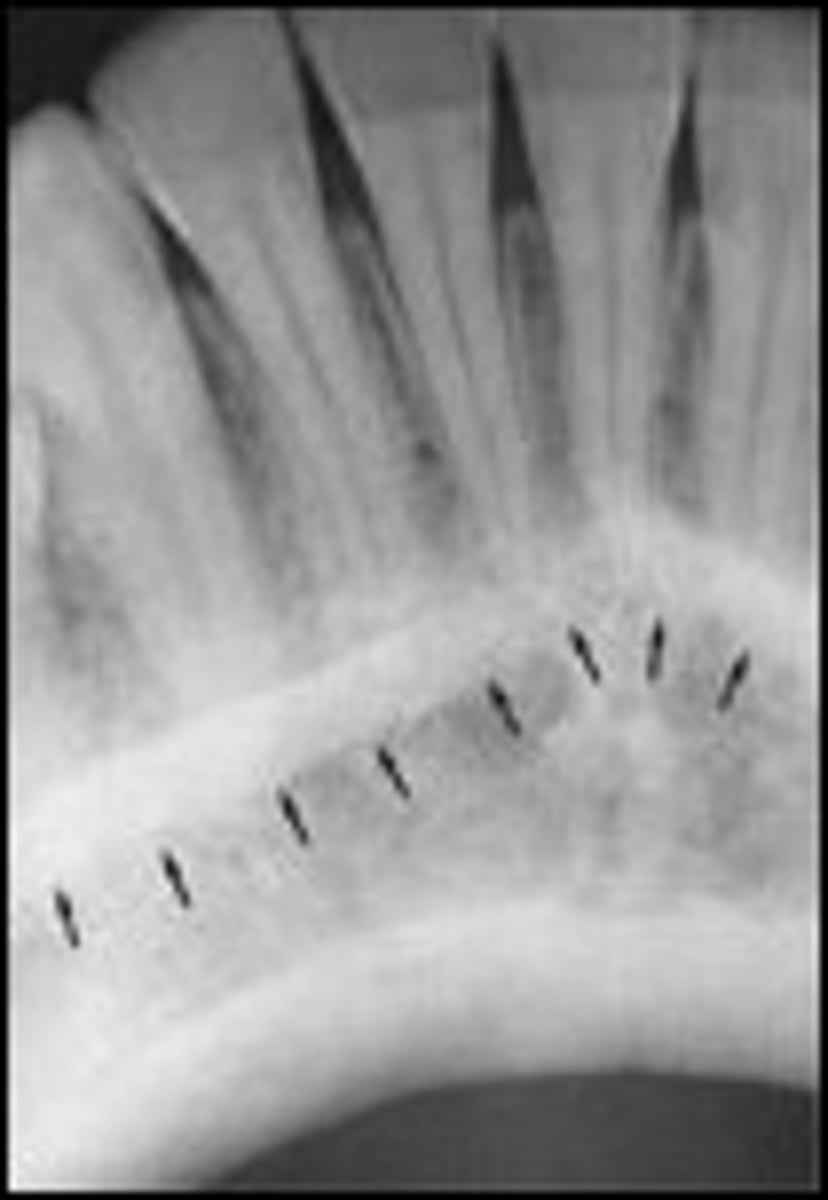
Nutrient canals
-Veritcal thin radiolucent lines near the teeth, may be mistaken for bone fractures.
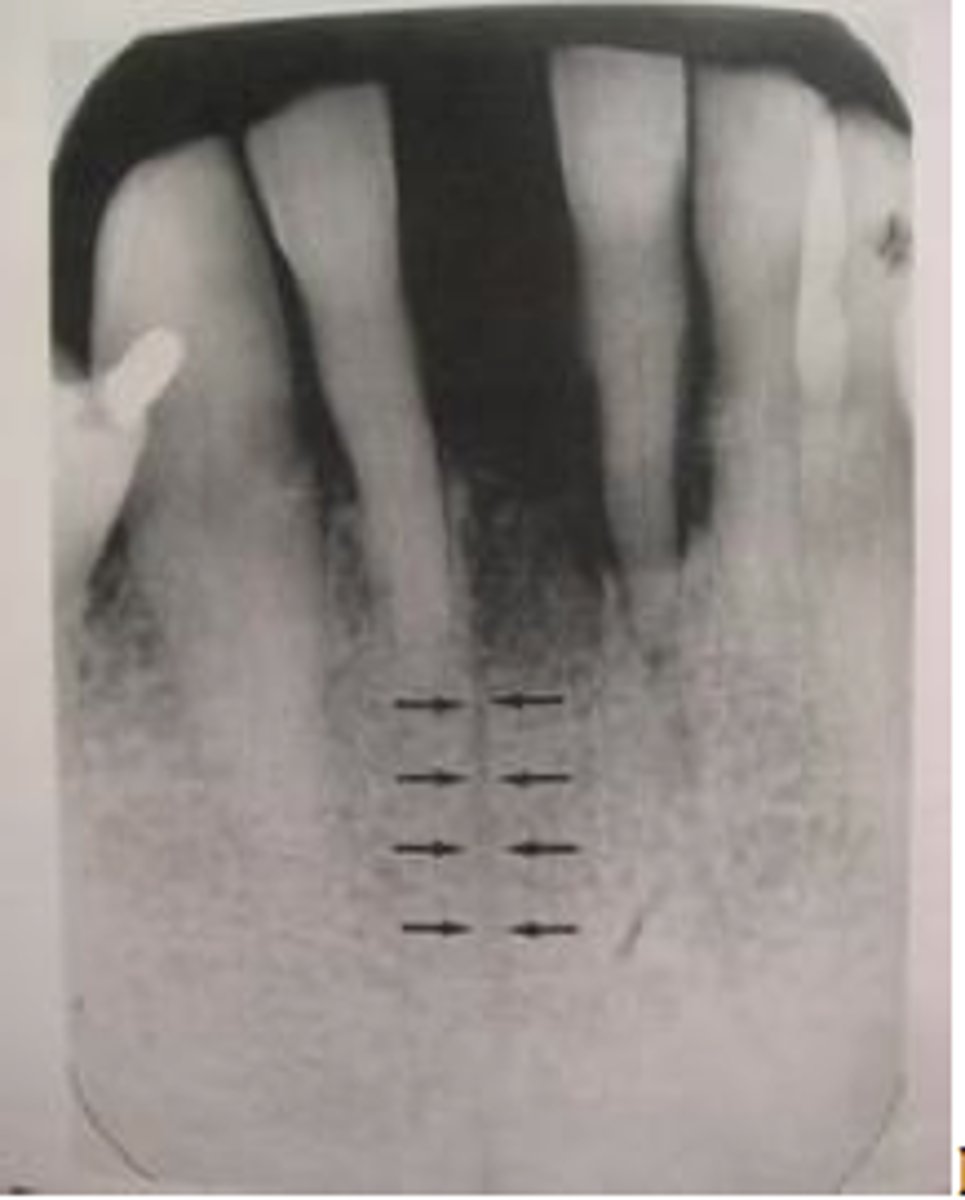
Mandibular canal
-Radiolucent horizontal band outlined with a thin line of cortical bone.
-Inferior alveolar nerve and arteries pass inside the canal. Stretches from the mandibular foramen to the mental foramen.
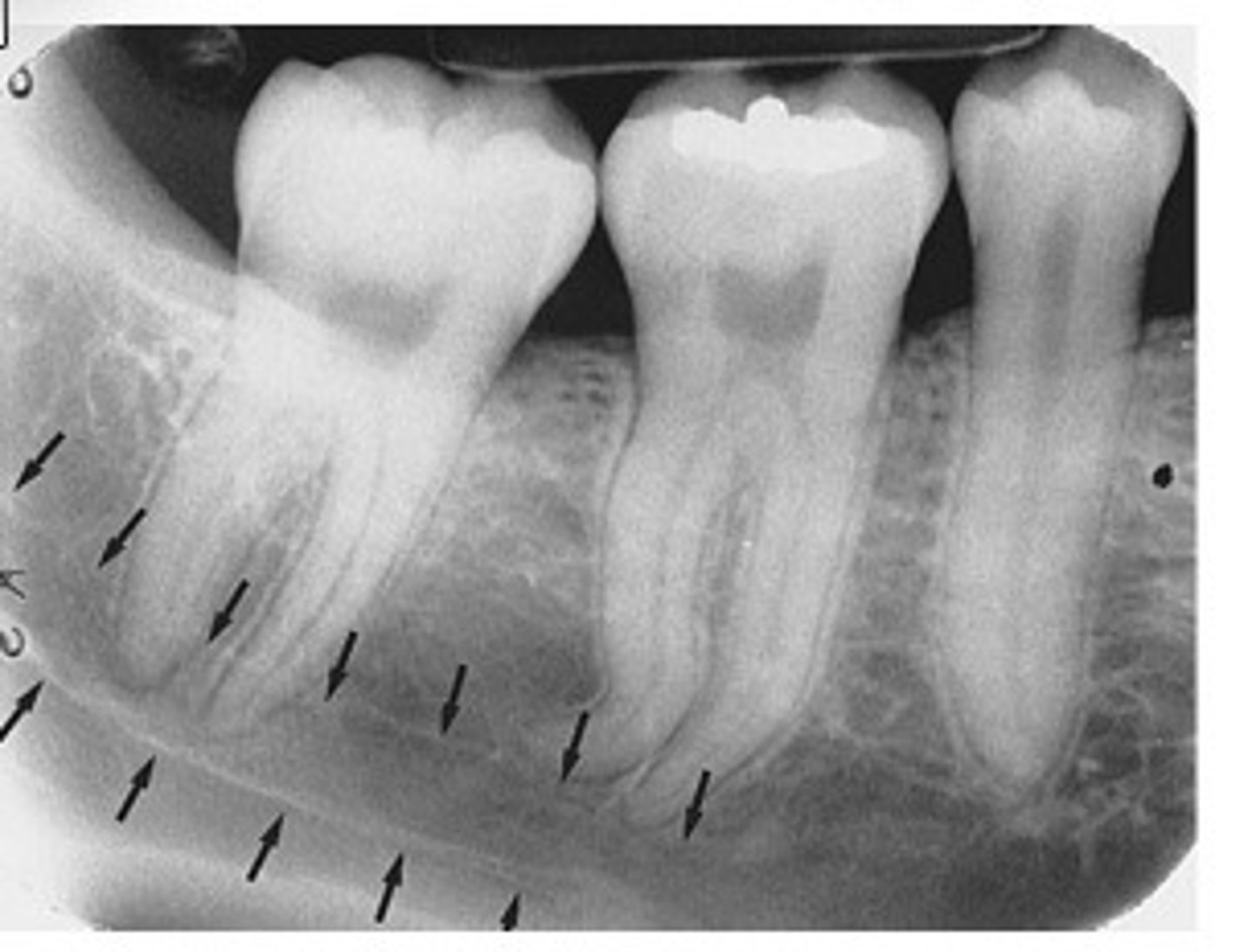
Panoramic exposure
-Useful for evaluating impacted teeth, eruption patterns, TMJ problems, etc.
-Usually not clear and detailed enough to assess caries and periodontal disease.
Periapical (PA)
-Captures the crown, CEJ, root, and surrounding areas.
-Used mainly for diagnosis of periodontal disease, pathology, endodontic therapy, and implants.
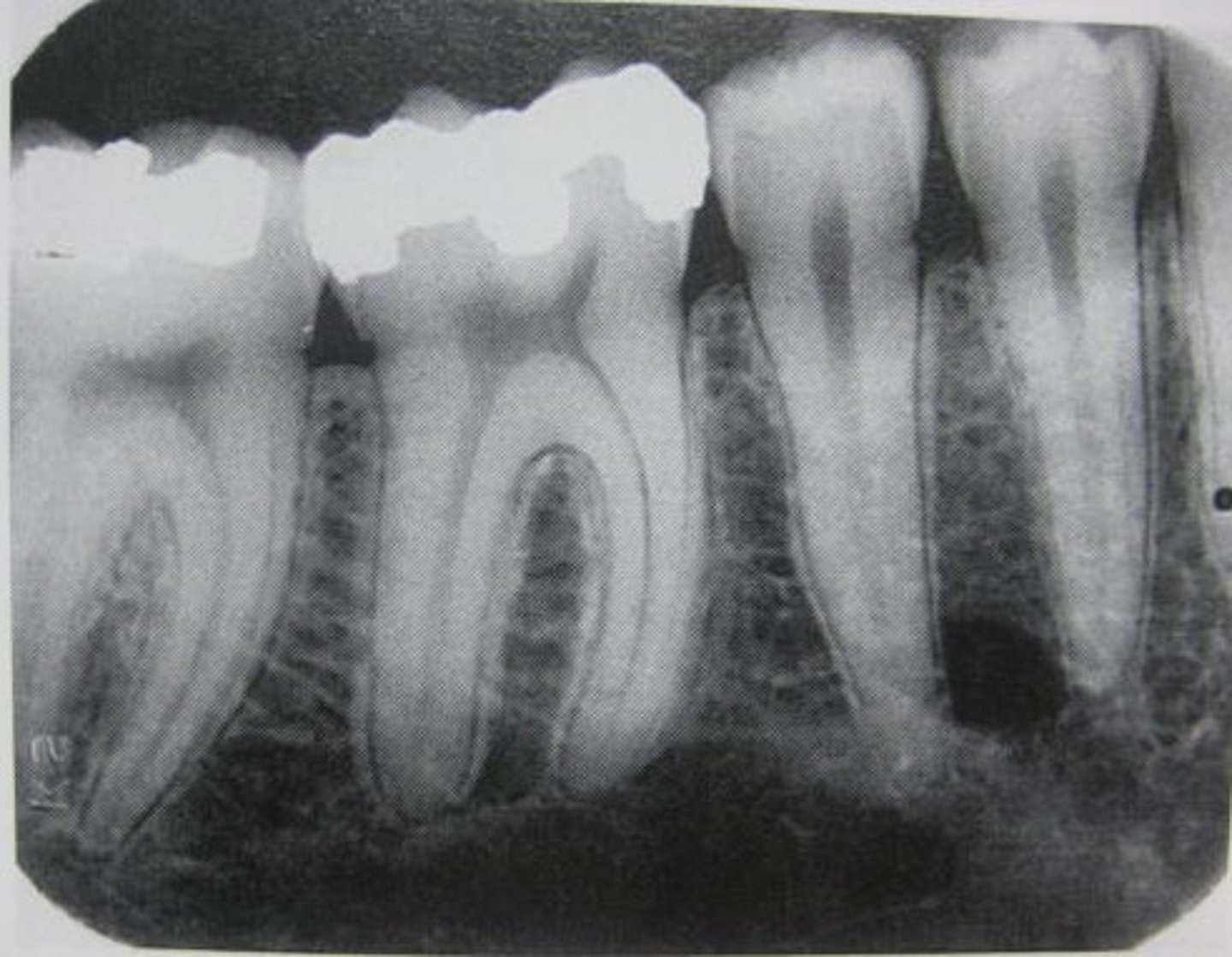
Bitewing (BW)
-Captures crowns, contacts, and height of alveolar bone.
-Used mainly for the diagnosis of dental caries (interproximally)
-Vertical bitewings can detect early periodontal disease because the bone level is visible.
Occlusal
-Captures bone surrounding the teeth, floor of the mouth, sialolith (stone), supernumerary teeth, etc.
Full-mouth series (FMX)
-Represent the entire dentition using a combination of PAs and BWs.
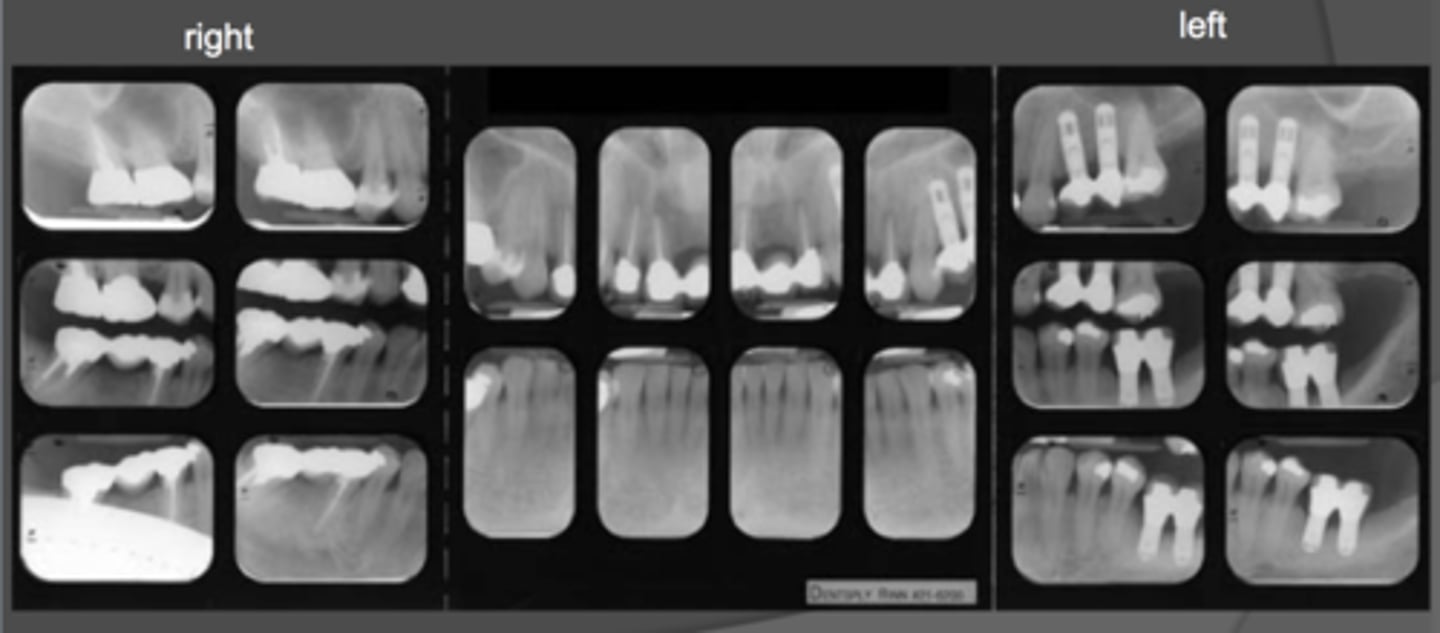
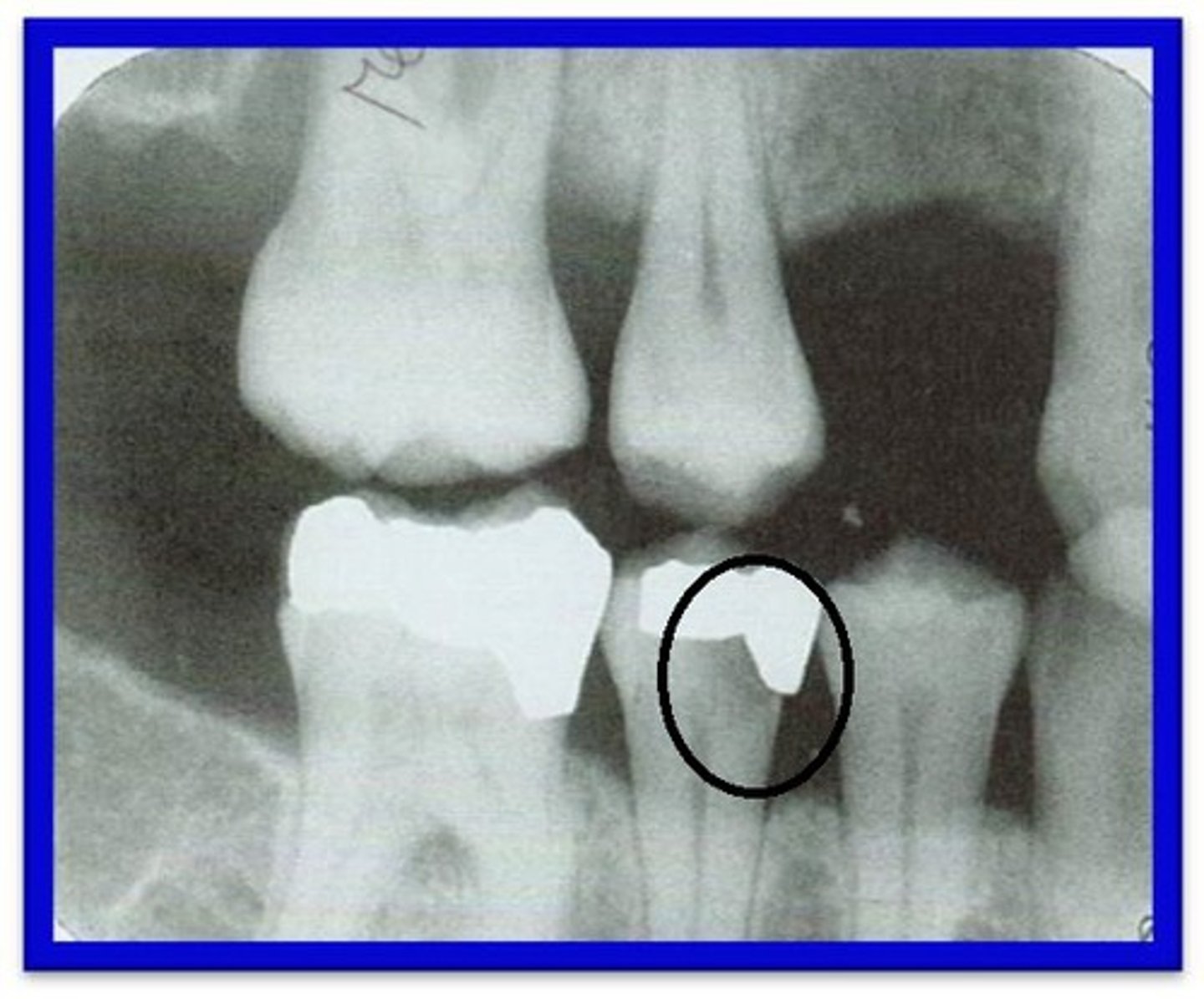
Incipient caries
Lesion that extends less than halfway through the enamel.
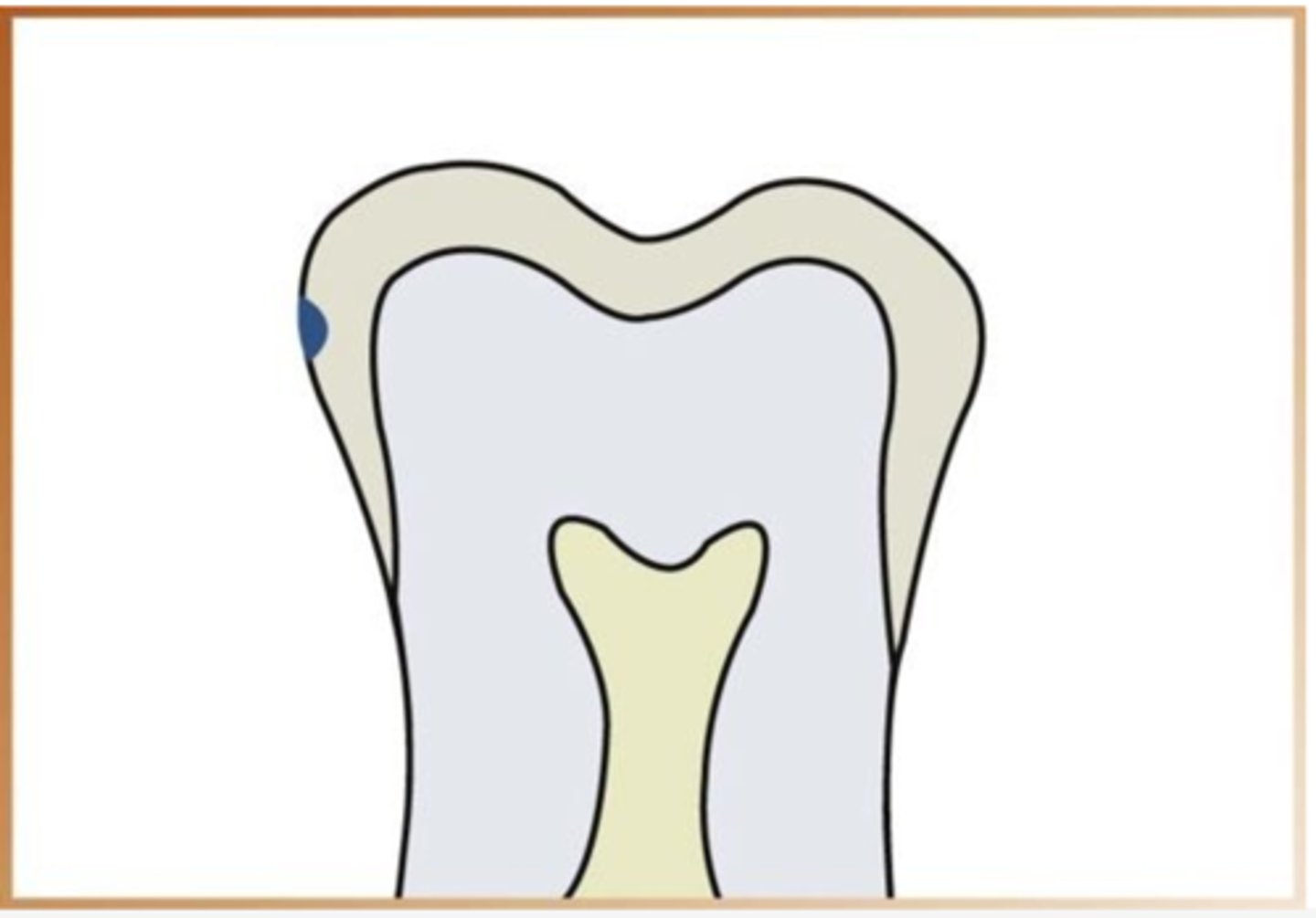
Moderate carious lesion
Lesion that extends more than halfway through the enamel but does not involve the DEJ.
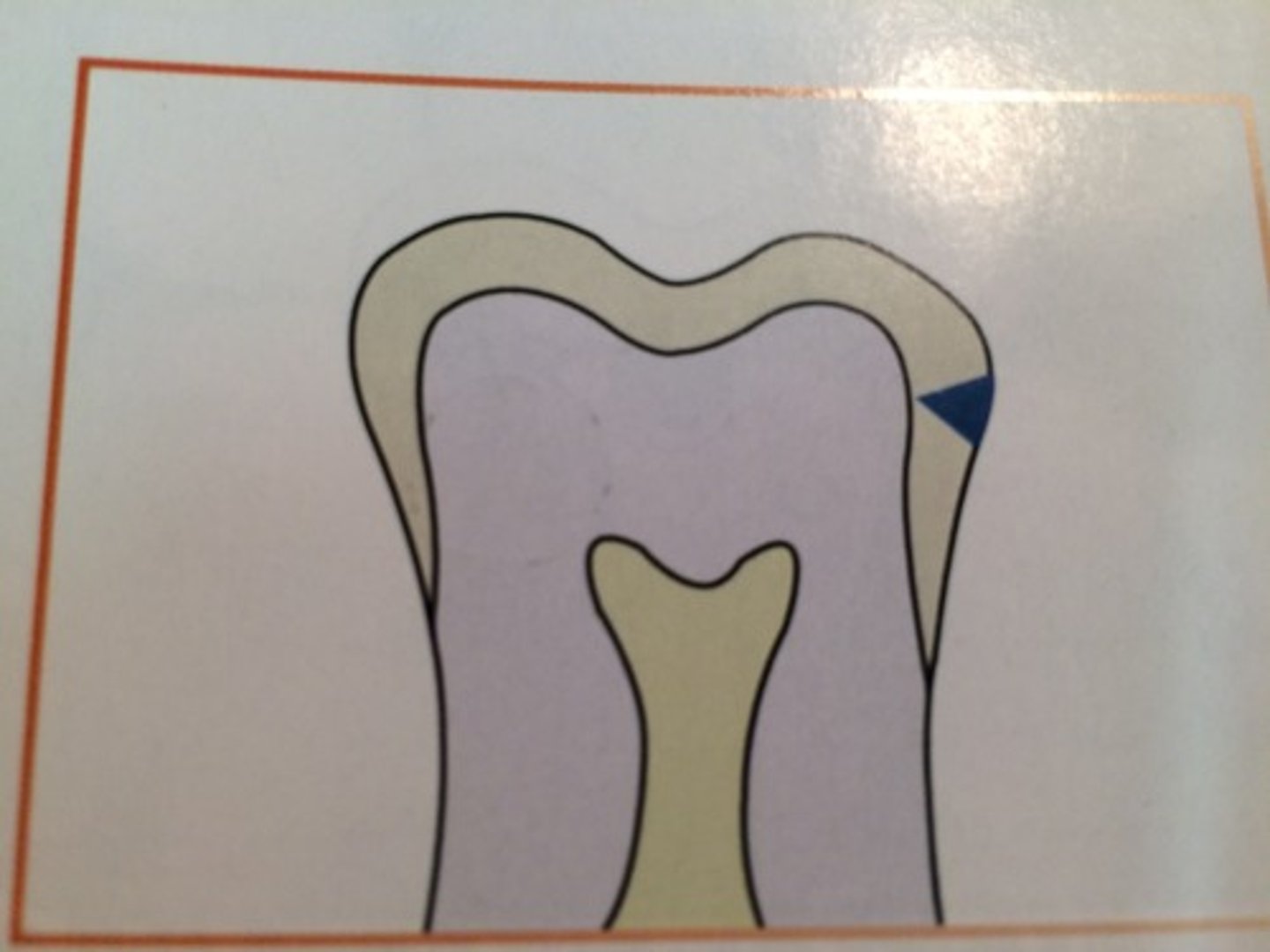
Advanced carious lesion
Lesion that extends to or through the DEJ but does not extend more than half the distance to the pulp.
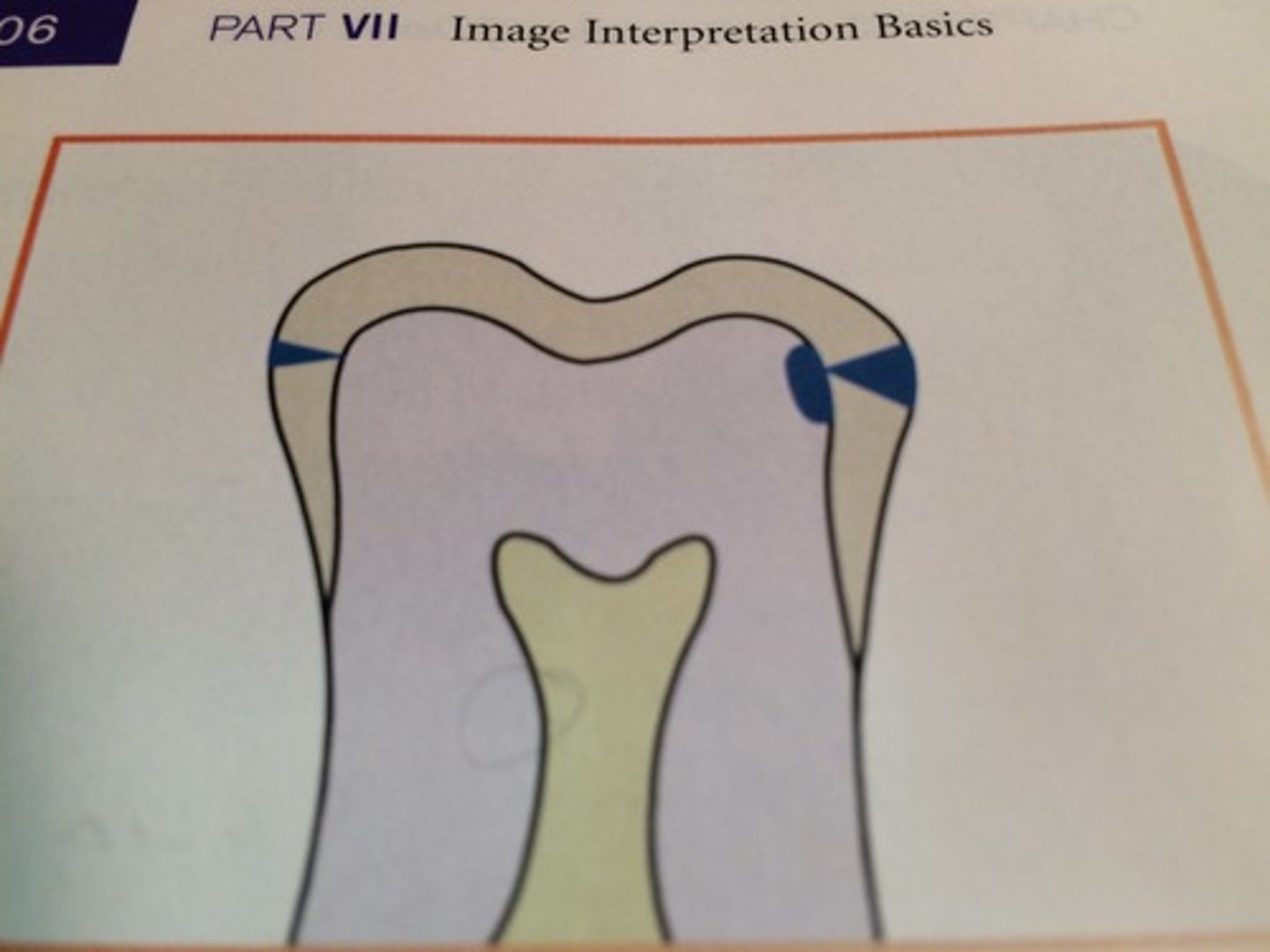
Severe carious lesion
Lesion that extends through enamel, through dentin, and more than half the distance to the pulp.
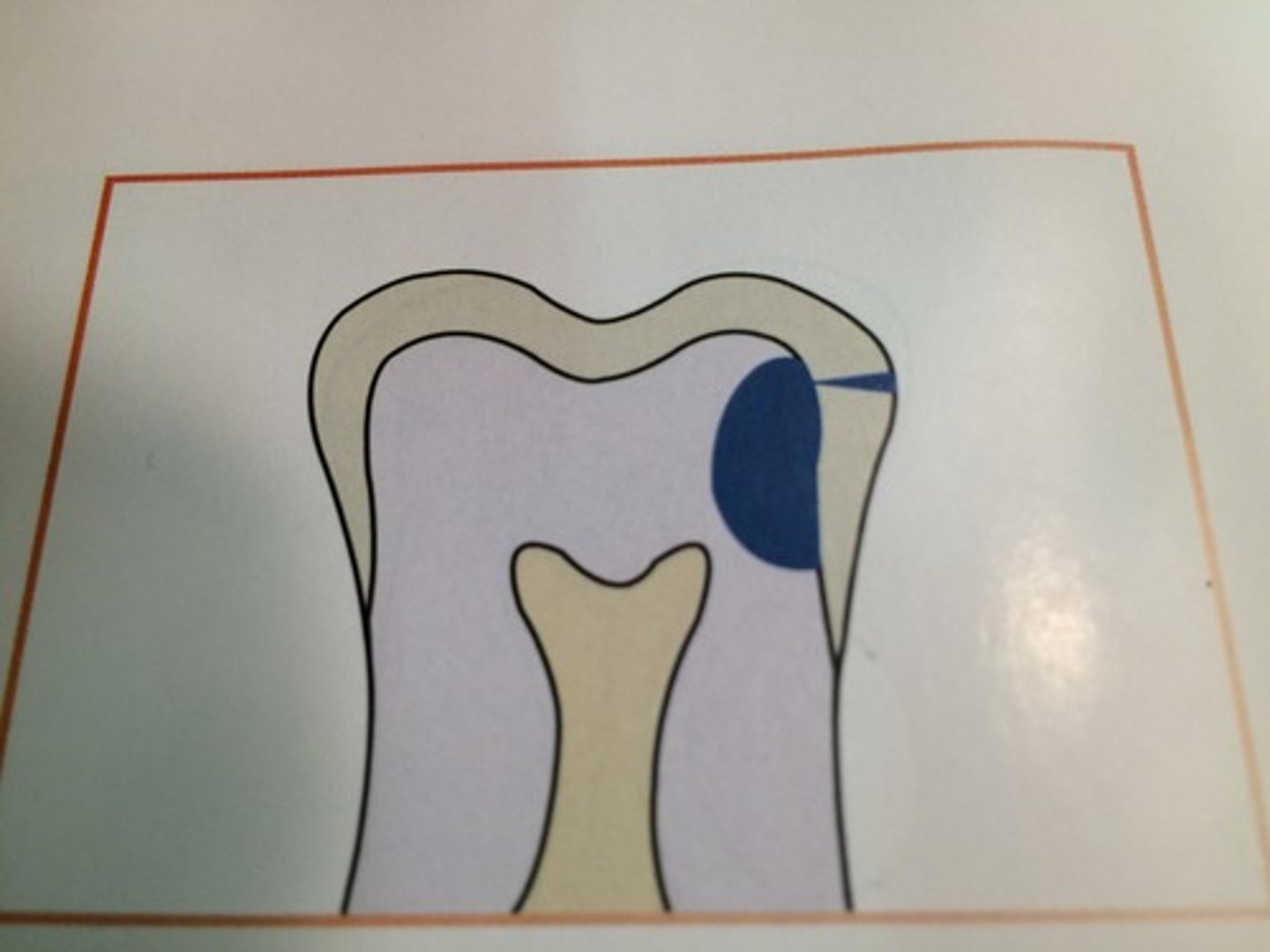
Recurrent caries
Appear under restorations