W12 Tissue integrity
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
U never want a wound too wet (exudate or water) ot too dry. Meds b4 wound care
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the 4 factors that can effect skin intergrity? Please provide examples
Age → dec in skin elasticity
Health status → immobility can lead to skin breakdown
Nutrition → vit.c and protien promotes healing
Hydration → promotes healing
A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has a surgical incision and a puncture wound from a fall. Which of the following correctly classifies these wounds?
a. Surgical incision – unintentional; puncture wound – intentional
b. Surgical incision – intentional; puncture wound – unintentional
c. Surgical incision – contaminated; puncture wound – clean
d. Surgical incision – unintentional; puncture wound – unintentional
b. Surgical incision – intentional; puncture wound – unintentional
A nurse is caring for a client who has a surgical incision closed with sutures and another client who has a venous ulcer on the lower leg. Which of the following best classifies these wounds?
a. Surgical incision – chronic; venous ulcer – acute
b. Surgical incision – contaminated; venous ulcer – clean
c. Surgical incision – acute; venous ulcer – chronic
d. Surgical incision – partial-thickness; venous ulcer – full-thickness
c. Surgical incision – acute; venous ulcer – chronic
What are the phases of wound healing and what the characteristics of each phase?
Hemostatsis and inflammatory
- Bleeding stops (vasoconstriction + clot formation)
- WBCs (neutrophils/macrophages) clean the wound
- Signs of inflammation: redness, swelling, warmth, pain
Proliferation
- Granulation tissue forms (new capillaries + fibroblasts)
- Collagen strengthens wound
- Re-epithelialization begins (skin cells migrate to cover wound)
Maturation/Remodeling
- Stronger collagen replaces earlier tissue
- Scar forms and wound contracts
- Final strengthening and restoration of skin integrity
Why does these factor effect wound healing
Desiccation
Maceration
infection
Necrosis
Desiccation
- No grandulated tissue will form since cells die from dehydration
Maceration
- Overhydration can lead to molecular breakdowns of cells (Grand cayon) and bacteria love wet dark places.
- This incules urine, feces , and sweat
Infection
- Cells can’t heal if there being attack by bacteria
Necrosis (Slough and eschar)
- Occupies space and prevents granulated tissue formation
What are some wound complications? (5)
Please explain why these are wound complications
Infection
- Cells can’t heal if there being attack by bacteria
Hemorrhage
- To much bleeding to form a blood clot and start the healing process
Fistula Formation
- Caused by maceration; a tunnel connecting two areas of the body
Dehiscence
-Inscions line opens up
Evisceration
-Inscions line opens up and organs are spilling out
A nurse walks into a patient’s room and finds that the client’s abdominal surgical wound has opened, and internal organs are protruding. Which of the following actions should the nurse NOT do?
a. The nurse covers the organs with a sterile moistened gauze.
b. The nurse calls for help.
c. The nurse stops the client from consuming any food or fluids
d. The nurse attempts to push the protruding organs back into the abdominal cavity.
d. The nurse attempts to push the protruding organs back into the abdominal cavity.
A nurse is caring for a client 14 days after abdominal surgery. The provider has ordered the removal of surgical staples. The client refuses, stating, "They don’t hurt, and I’d rather leave them in just to be safe." Which of the following responses by the nurse is most appropriate?
a. "Keeping them in longer won’t cause any harm."
b. "It’s your choice, but we can remove them at your next visit."
c. "Leaving staples in too long can cause the skin to grow over them, making removal more painful and increasing the risk of infection."
d. "Staples are only removed if they fall out on their own or look infected."
c. "Leaving staples in too long can cause the skin to grow over them, making removal more painful and increasing the risk of infection."
How long should the steri-strips be on the inscion line? Why is this important
1.5 - 2 in
This is important because it allows the steri-strips to grinp the skin tight
Differnce between pressure and shearing?
Pressure → Compressing blood vessels
Friction/ shearing forces → Tearing or injuring blood vessels
What are the 6 things nesscary to document in pressure ulcer assessment?
Record length(↕︎︎), width, depth
Describe the condition of the wound tissue
Beefy red, yellow, black %
Note any pain
Note tunneling or undermining
Clock format
Note surrounding tissue
Discolaration
Describe the drainage (amount/type)
Serous (clear) - Sanguineous (bloody) - Serosanguineous - Purulent (green.yellow, brown pus)
Define undermining
the tissue under the edges of a wound becomes eroded, resulting in a pocket or space beneath the skin
Define these terms that pertain to amount of drainage
None
Scant
small
Monderate
Large
None - Competely dry dressing and wound bed
Scant → Competely dry dressing and moist wound bed
small → Dressing is 25% wet / wound be is wet
Monderate → Dressing is 50% wet / wound be is wet
Large → Dressing is 75-100% wet / wound be is wet
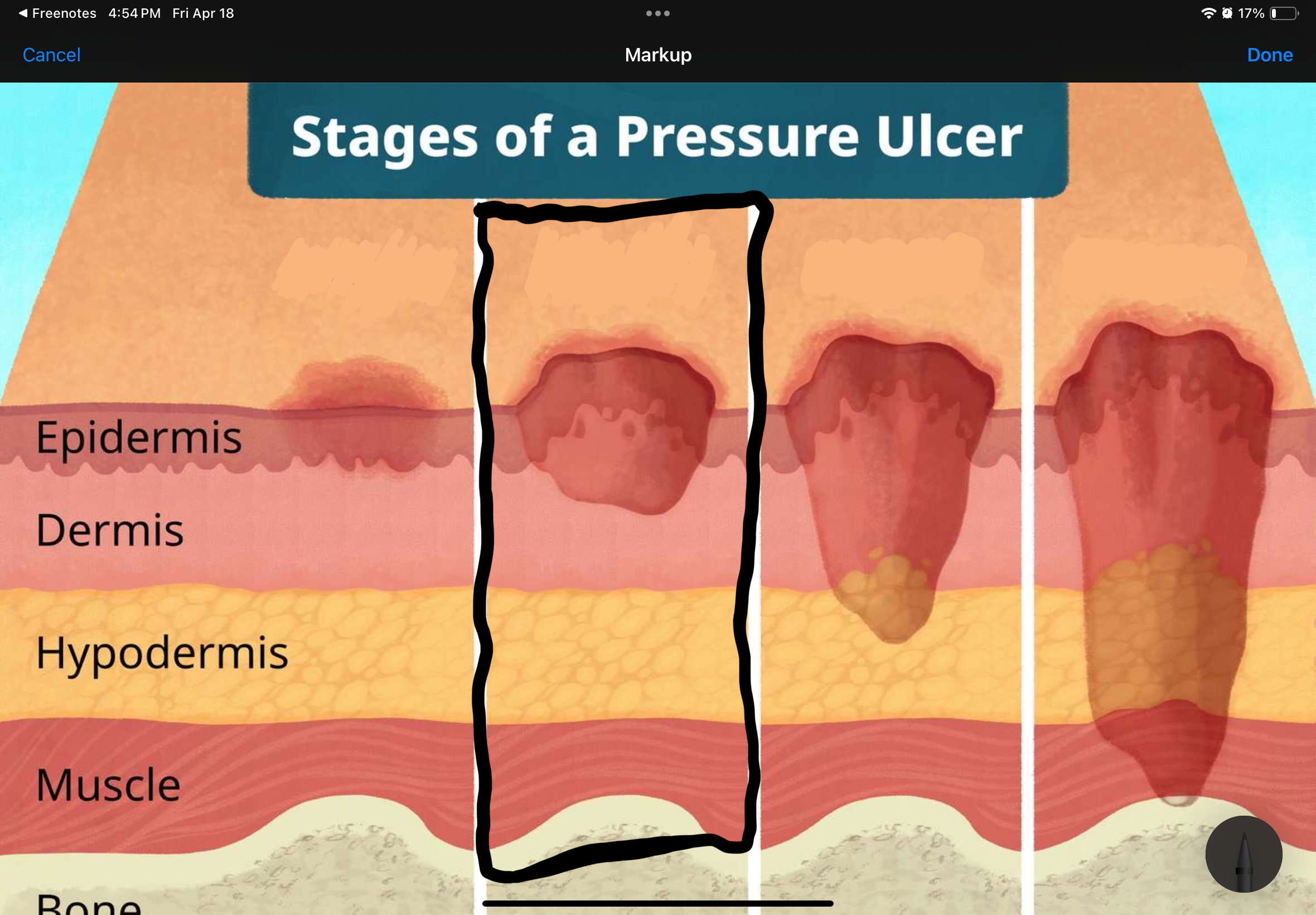
Name and describe the stage of this pressure uncler
Stage II: partial-thickness skin loss; superficial ulcer
involving epidermis or dermis
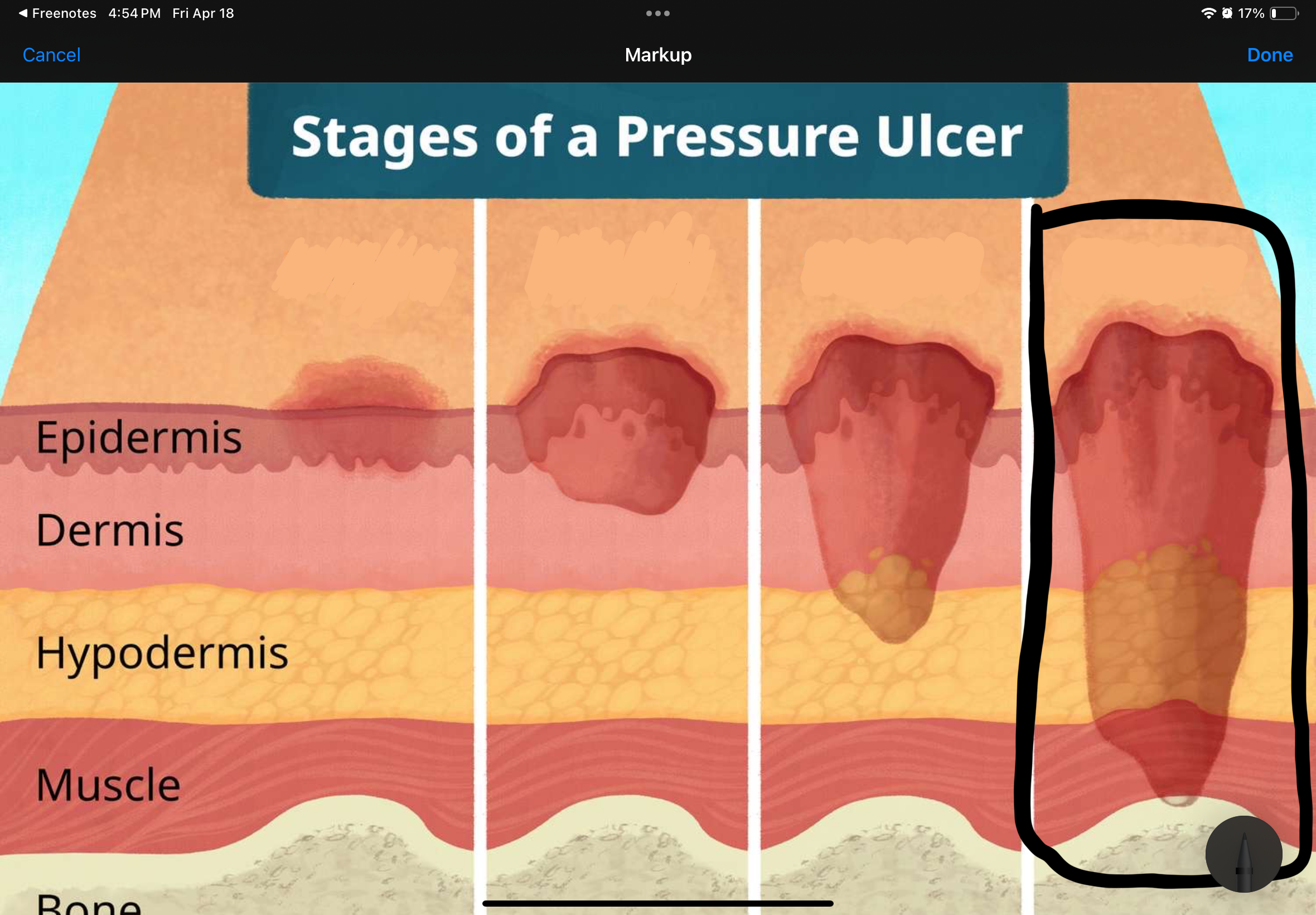
Name and describe the stage of this pressure uncler
Stage IV: full-thickness skin loss with extensive destruction; damage to muscle/bone
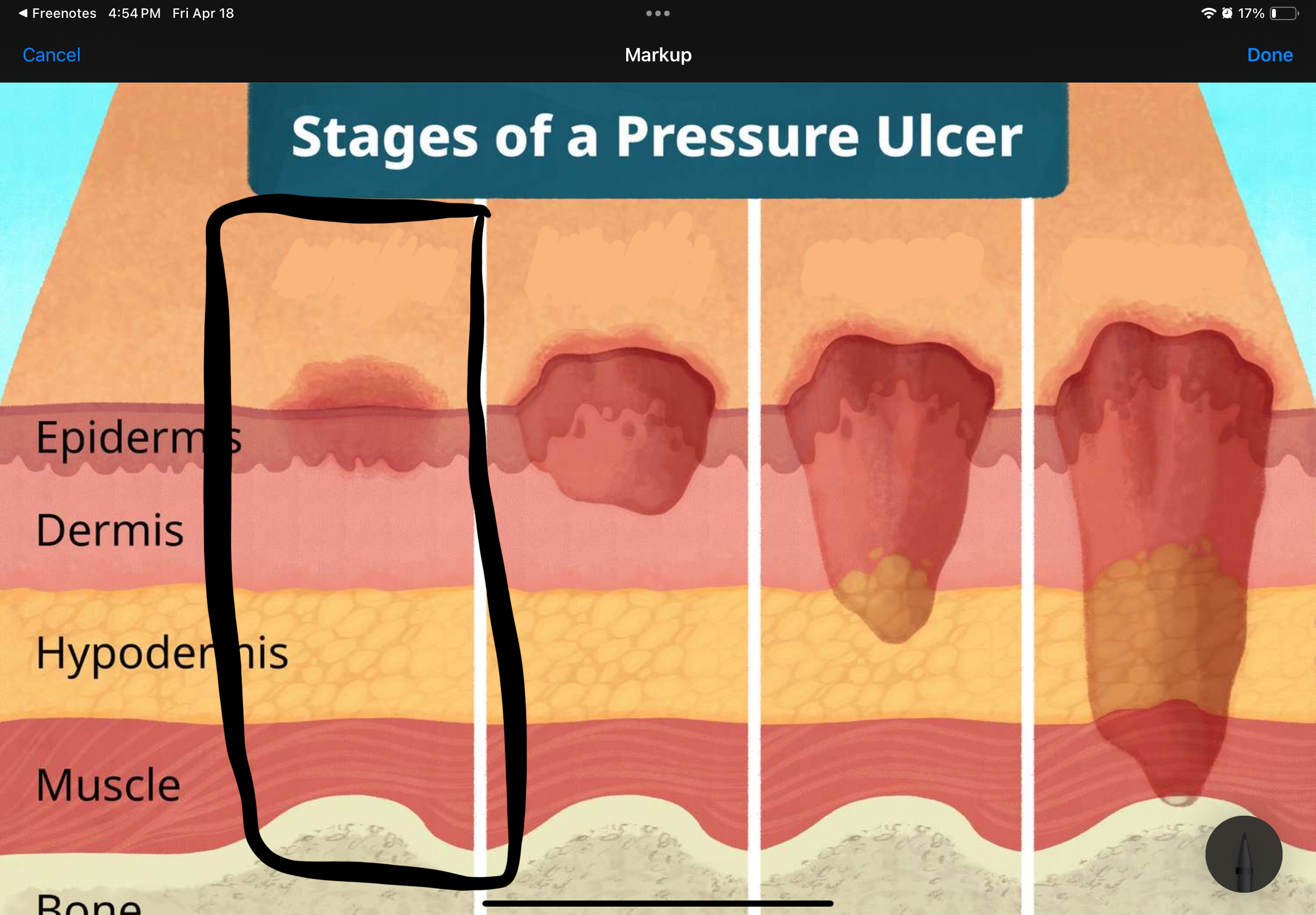
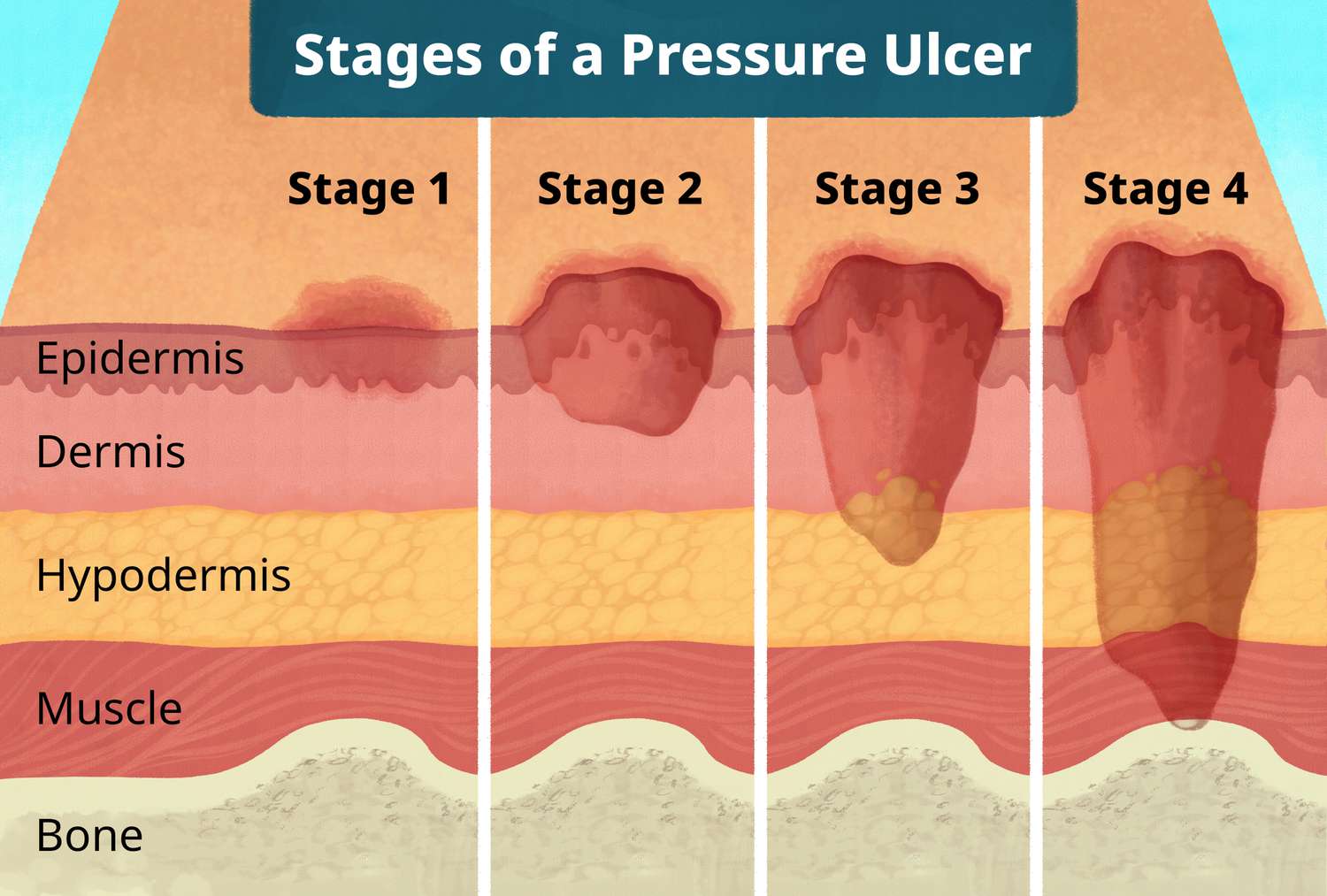
Name and describe the stage of this pressure uncler
Stage I: persistent (nonblanchable) redness
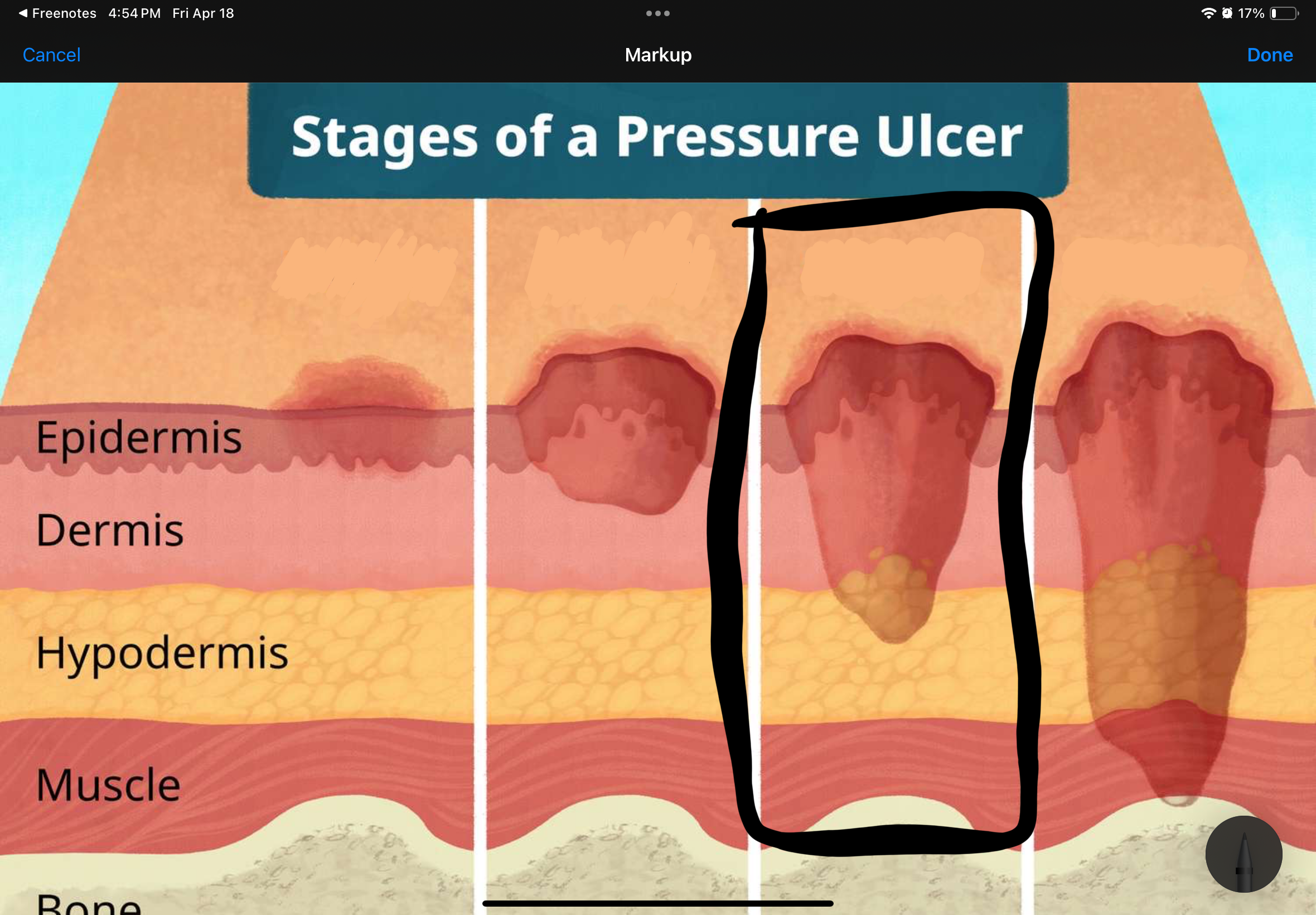
Name and describe the stage of this pressure uncler
Stage III: full-thickness skin loss; involving subcutaneous tissue
What makes a wound unstageable?
When Escar or slough covers the wound bed
what are the 4 ways to remove necrotic tissue? Please provide examples of each
Autolytic debridement
- Bodies' enzymes breaking down the necrotic tissue
Mechanical debridement
- Wet to dry dressing
- Maggots
- Saline irrigation
Enzymatic debridement
- Ointment
- Cream
Sharp debridement
- Scalpel
What are the 7 Wound Dressings/Treatments
Gauze dressing (can be it impreg w/ Petrolatum, Saline, Hydrogel)
Hydrogels (add moisture)
Anglintaes (take away moisture )
Transparent Flims
Antimicrobials
Enzymatic Debriders
Non-Stick Pads
Which system is at a higher risk for infection, open or closed? Why and please provide examples
Open since it open to the environment
- Penrose
Closed
- Jackson-Pratt drain
- Hemovac drain
What situiation would a nurse use a open or closed system?
Open → little to no fluid leak
Closed → Large amount of fluid leak
Inc HR, Blood sugar, Temp, and WBC, Change in mental status, and N&V are signs of …. and explain why
Infection
Inc HR → The body tries to circulate immune cells faster.
Inc BS → Stress hormones (like cortisol) raise glucose for quick energy.
Inc Temp → The body raises its core temp to inhibit bacterial growth.
Inc WBC → More white blood cells are produced to attack invading pathogens.
Change in mental status (confusion/lethgary) → The body is overworking itself.
N&V → inflammation affects the gastrointestinal system.