Male reproductive system- animal anatomy
1/119
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
120 Terms
Describe the spermatogenesis cycle by a factory system
“High speed manufacturing”- in the testes millions of sperm is produced.
“Finishing shops” - in the epididymis (head and body), the sperm becomes specialized and gain the ability to “swim”
“Warehouse and shipping”- in the epididymis tail this is where the sperm is stored between ejaculations
“Fine alterations and packaging”- in the accessory glands seminal fluid is created which provides nutrients to the sperm and is a median for sperm cells to travel
“Delivery system”- In the urethra the sperm cells leave here at ejaculation
what are the 3 parts of the epididymis
head, body, and tail
what is the function of the testes exocrine wise
to produce sperm
FITB: Testis ____ determines sperm count
size
how does testes size determine sperm count
because the larger the testes the higher the number of seminiferous tubules which is what makes the sperm
what is the function of the testes endocrine wise
to produce testosterone from the interstitial cells
what are the important structures in the cross section of the scrotum/ testes
seminiferous tubules, parietal layer. visceral layer, tunica albuginea, dartos muscle and epidermis
what is the epidermis on the scrotum
the outermost layer of skin
what is the dartos muscle in the scrotum
the muscle surrounding the scrotum that contracts and pulls the scrotum towards the body when it is cold
what is the parietal layer of the scrotum
the layer of cells around the scrotum that comes after the vaginal cavity
what is the visceral layer of the scrotum
the layer of cells in the scrotum that are found before the vaginal cavity
what is the tunica albuginea in the scrotum
the cavity where the lobule and mediastinum are suspended in inside the scrotum
what is the seminiferous tubules in the scrotum
the tubules inside the lobules of the scrotum where sperm is created
where does sperm creation occur
in the seminiferous tubules
what cells are responsible in the production of testosterone in response to LH
Leydig cells
what are the 4 goals of Spermatogenesis
provide males with a continual supply of male gametes through stem cell renewal, provide genetic diversity by meiosis, maximize reproduction by providing numerous amounts of sperm, and provide an immunologically privileged site where germ cells are not destroyed by the male’s immune system
where does spermatogenesis occur
in the seminiferous tubules
what is the purpose of Sertoli cells as for spermatogenesis
to provide nutrients to the growing sperm cells
FITB: Sperm cells starts off as an _____ shape
circular
Define Spermatogenesis
the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis.
what are the two stages of spermatogenesis
spermatocytogenesis and spermiogenesis
what are the two stages that occur in spermatocytogenesis
proliferation and meiosis
what occurs in the proliferation phase of spermatocytogenesis
the mitotic division of spermatogonia and stem cell renewal
what is the one phase called in spermiogenesis
differentiation
when does spermiogenesis occur
after meiosis 2 (the creation of spermatids)
What happens in the differentiation stage of spermiogenesis
they change from a spherical spermatid to specialized spermatozoan
what occurs in the meiotic phase of spermatocytogenesis
the meiotic division of spermatogonia into spermatocytes which created genetically diverse germ cells ( 1N spermatid)
what is spermiation
the phase after spermiogenesis where the spermatozoa penetrating the Sertoli cell gradually moves back out leaving behind the extra cytoplasm as a residual body and the rest remains at the base of the head ( proximal cytoplasmic body)
what is a residual body
the Sertoli cell and extra cytoplasm left behind after the spermatozoa moves out
what are the 4 sections of the spermatozoa
head, mid piece, principle piece, and end piece
what are the important parts of the head of the spermatozoa
plasma membrane, acrosome, equatorial segment, nuclear membrane, and nucleus
what does the acrosome part of spermatozoa do
it contains enzymes that once the sperm reaches be able to penetrate the cumulus cells
what happens in the equatorial segment of the spermatozoa
where the physical contact between sperm cell and oocyte occurs here
what is the purpose of the blue mitochondria in the middle piece of the spermatozoa
the gives the tail section energy to move
what does the annulus do in the middle piece of the spermatozoa
it acts as a diffusion barrier to ensure proper diffusion of energy for tail mobility
how does the sperm cells move through the seminiferous tubules
by natural movement of fluid
where does maturation/ puberty of sperm cells occur
in the epididymis
True or False: Puberty/ maturation of sperm is reached immediately following spermiation.
false: it occurs in the epididymis
What cause immature sperm to ejaculate
frequent ejaculations
What is the common characteristic of immature sperm cells
the presence of the proximal cytoplasmic droplet
what does it mean when the sperm has an proximal cytoplasmic droplet
the sperm cell is immature and the tail cannot move on its own
what does it mean when a sperm cell has a distal cytoplasmic droplet
the sperm cell is mature, and it can swim on its own
what is the hormonal control of spermatogenesis
The hypothalamus sends GnRH to the AP and the AP snds LH to the Leydig cells and sends FSH to the Sertoli cells
what are the two results when heat interrupts sperm production
abnormal shape of head( abnormal sperm) and decreased sperm count
how does a heat stressed bull/ heat stressed sperm increase embryonic mortality
the sperm will appear normal, eggs wills still be fertilized, and will result in high embryonic mortality
what temperature range should the testes be in relation to the body
the testes should be 2 to 4 degrees lower in temperature than the body
How is the dartos muscle related to temperature regulation in the testes
it pushes the testes tighter toward the body when cold and away by relaxation when hot
What type of nerves are in the scrotum
thermosensitive nerves
what does the nerves in the scrotum do
govern scrotal sweating and respiration
FITB: Respiration rate _______ with ______ scrotal temperature.
increases, increases
Explain the process in which the scrotal nerves cause the sweat glands to start or panting to start when an animal is hot
the nerves detect a change in temperature and sends a message to the hypothalamus which interprets the signal saying that it is hot, the hypothalamus sends a message to either the sweat glands which causes the skin to sweat or the signal goes to the respiratory muscles which causes them to contract and start panting
what are the three items in the testes that helps thermoregulation
the dartos muscle, cremaster muscle, and pampiniform plexus
How does the cremaster muscle help thermoregulation
it supports the testes by keeping them in place, pulls the testes up towards the body when it is cold, and also facilitates countercurrent heat exchange
how does the pampiniform plexus help thermoregulation
by hosting countercurrent heat exchange
what is the primary regulator of testicular heat regulation
the pampiniform plexus
why is the Pampiniform Plexus the most effective cool down for the testicles
it has testicular vein and artery network involved
how does countercurrent heat exchange occur in the testes
the heat from the arterial blood is transferred to the cooler venous blood
what is the most effective way to cool testicular temperature
countercurrent heat exchange
What type of cells are in the seminiferous tubules
Sertoli cells and germ cells
What is the Rete Testis
the collecting tubules network for sperm before they leave seminiferous tubules
what are the items in the tubular system of the male repro tract
seminiferous tubules, Rete Testis, Efferent ducts, Vas Deferens, and the Epididymis
What is the function of the Efferent Ducts
to help sperm move along
what is the function of the Vas Deferens
to transport sperm
what is another name for Vas Deferens
Ductus Deferens
what is the function of the Epididymis
to transport sperm from the testis to vas deferens, for maturation of the sperm cells, and store sperm cells
where does the majority of the sperm cells in the epididymis concentrate at
in the tail
where are the sperm cells stored in the epididymis
the tail
how long is the epididymis
about 70 yards
How does the sperm cells mature in the epididymis
the cytoplasmic droplet moves down and drops off as sperm matures
what are the 4 adjectives of the sperm found in the head of the epididymis
they are not motile, not fertile, has a proximal cytoplasmic droplet and has low disulfide crosslinking
What are the 5 adjectives of the sperm found in the body of the epididymis
they have some motility, have some fertility, has a translocating cytoplasmic droplet, has a moderate to high disulfide and can bind to an oocyte
what are 5 adjectives of the sperm found in the tail of the epididymis
they have normal motility, they are fertile, they have a distal cytoplasmic droplet, has high disulfide crosslinking and can bind oocytes
what does the development of the accessory glands depend on
testosterone
what are the 5 important accessory glands
vesicular glands/ seminal vesicle, prostate, ampulla, bulbourethral glands and colliculus seminalous
what is another word for the bulbourethral glands
cowpers gland
what is the bulbourethral gland responsible for
it is responsible for the gel that comes with swine sperm(a glue-like substance)
what happens in the colliculus seminalous
this is where the semen first made; sperm makes contact with the accessory fluid ( seminal plasma)
what is the accessory fluid in the accessory glands
seminal plasma/ fluid
what is the purpose of the accessory fluid
to provide nutrition to the sperm, transport sperm into the female tract and act as a protection/ buffer against female’s acidic vagina where sperm is deposited during natural service
In what animal is the bulbourethral gland large
in swine
what is the function of the penis
as a copulatory organ
what are the 3 parts of the penis
base, shaft, and glans
what is the base of the penis
the root
what is the main portion of the penis
the shaft
what is the glans of the penis
the specialized end with a heavy population of sensory nerves
what are the two types of penises
Fibroelastic penis and vascular penis
what types of animals have a fibroelastic penis
ram, bull, boar
what type of animal has a vascular penis
a stallion
what does a fibroelastic penis have
a sigmoid flexure
what does the sigmoid flexure of the penis do
it allows the penis to retract and give it an S-shape
what does the retractor penis muscle do
maintain the sigmoid flexure of the penis
what are the 6 important structures of the penis
Crura, Tunica Albuginea, Corpus Cavernosum, Corpus Spongiosum, urethra and erection canals
how does the crura contribute to the penis function
it has muscular wall that encloses arteries and when the animal becomes excited these arteries dilate which increases blood and is forced down into the penis by the crura
What does the tunica albuginea do
Separates the Corpus cavernosum and corpus spongiosum
what makes up a majority of the erectile tissue
Corpus cavernosum
What makes up the spongy erectile tissue of the penis
corpus spongiosum
what occurs in the erection canals of the penis
this is where blood flows to make erection occur
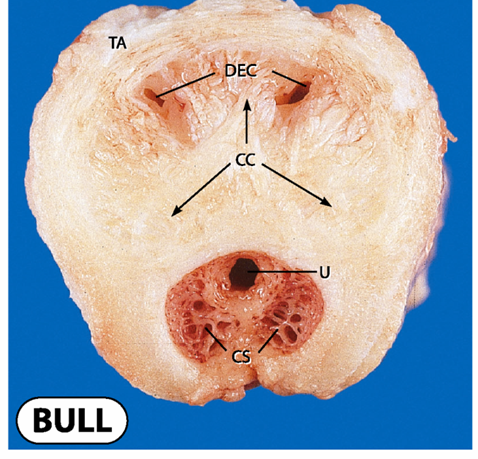
what is the Corpus cavernosum on this picture
the CC section
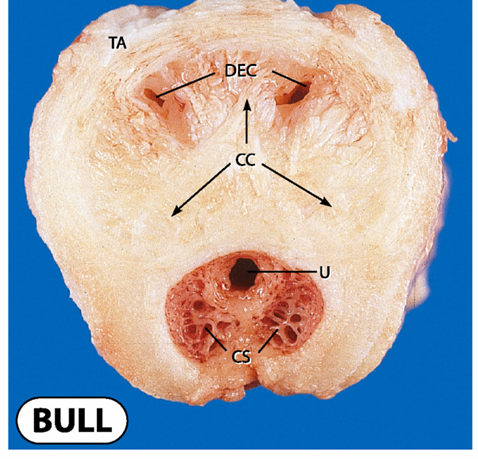
what is the Corpus spongiosum of this picture
the CS portion of the picture
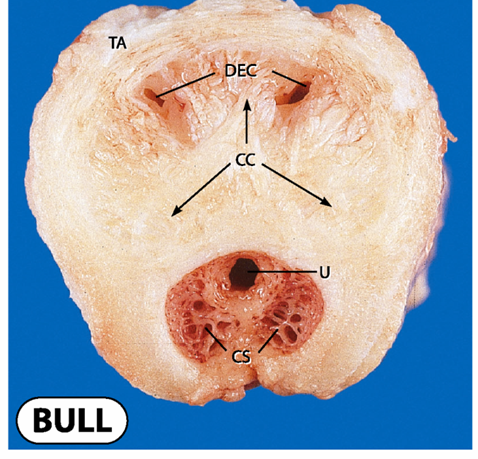
where is the erection canals in this picture
the DEC portion