Forces Quiz
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Dynamics
what causes motion
force
any push or pull on an object
Volume
space taken by an object
Mass: (in kg)
Gravity - every object with mass / always attractive
inertia - tendency to avoid change
amount of matter
Not constant
Universal
Weight: (in N)
How much you are pulled down
Scaler
Force of gravity
W = m x -9.8 (acceleration due to gravity)
Force (push/pull)
Contact-
Spring force: contracting & extending of an object that returns to its original shape
Applied force: acting on an object(ex: pushing a box)
air resistance:
friction: opposes motion as the object slides past each other
Normal force: right angle, perpendicular, "normal", 90 degrees from the ground, comes from any surface
Tension: forces is applied through another object, tension must be the same
Tensile strain: how much something is pulled before it tears
Non-Contact -
Gravity
Magnetism: opposite attract; like-charge repel
an object in free-fall
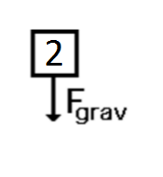
A metal cylinder hanging from a string, at rest
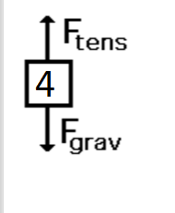
A bucket being lifted by a rope at constant velocity.
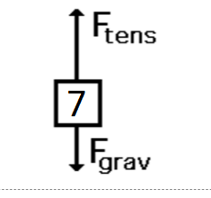
A person standing, at rest.
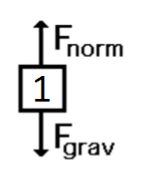
A person in an elevator moving upward at constant velocity.
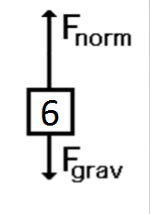
A metal cart slowing down while rolling to the right.
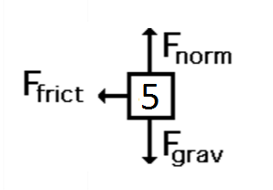
A box pushed by a person at constant velocity across a rough surface.
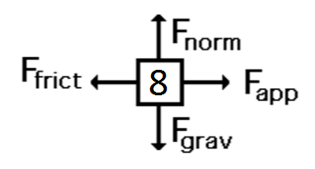
An elevator carries a person upwards at a constant velocity. What is the direction of the net force on the person?
zero
An elevator carries a person upwards at a constant velocity. How does the normal force on the person compare to the force of gravity?
normal force is equal to the force of gravity (no acceleration)
An elevator starts from rest and accelerates as it carries a person upwards. What is the direction of the net force on the person?
upward (same direction as acceleration)
An elevator starts from rest and accelerates as it carries a person upwards. How does the normal force on the person compare to the force of gravity?
normal force is greater than the force of gravity
An elevator slows to a stop as it carries a person upwards. What is the direction of the net force on the person?
downward (the direction of the acceleration)
An elevator slows to a stop as it carries a person upwards. How does the normal force on the person compare to the force of gravity?
normal force is less than the force of gravity
An elevator starts from rest and accelerates as it carries a person downwards. What is the direction of the net force on the person?
downwards
An elevator starts from rest and accelerates as it carries a person downwards. How does the normal force on the person compare to the force of gravity?
The normal force on the person is less than the force of gravity.
An elevator slows to a stop as it carries a person downwards. What is the direction of the net force on the person?
downward (The upward force from the floor is less than the downward force of gravity, resulting in a net downward force that causes the elevator to decelerate.)
An elevator slows to a stop as it carries a person downwards. How does the normal force on the person compare to the force of gravity?
The normal force on the person is less than the force of gravity.
An object is moving through outer space. There are no forces on the object. This object will…
continue to move in a straight line at a constant speed.
A chair is being pushed North across the floor at a constant velocity. The direction of the net force on the chair is __________.
zero
An apple is at rest on a table. According to Newton's first law, there are no forces on the object. True or False?
false
A passenger standing in a moving bus, facing forward, suddenly falls forward. This can be an indication which of the following?
A passenger standing in a moving bus, facing forward, suddenly falls forward because the bus is slowing down or decelerating.
A 25 kg brick is at rest on the ground. What is the net force on the brick?
0 N
A 25 kg brick is lifted off the ground at a constant velocity of 0.5 m/s. What is the force of gravity on the block?
245 N (25kg x 9.8)
A 25 kg brick is lifted off the ground at a constant velocity of 0.5 m/s. What is the net force on the block?
0 N
A 25 kg brick is lifted off the ground at a constant velocity of 0.5 m/s. How much force is the block being lifted with?
245 N (25kg x 9.8m/s)
If a net force of 200 N is applied to an object with mass 25 kg, what acceleration is produced?
8m/s squared (200N / 25kg)
A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration a. If a net force of 2F is applied to the same mass, then the acceleration will be:
2a
A net force F accelerates a mass m with an acceleration a. If the same net force is applied to an object with mass 2m, then the acceleration will be:
1/2a
kinetic friction
an object moving across a surface experiences a kinetic friction force, in the direction opposite of the object’s motion
static friction
an object at rest on a surface experiences a static friction, which is the friction force that balances forces parallel to the surface.