4.9 Barriers to Development
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
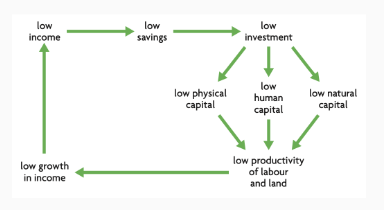
Poverty Cycle
List of economic barriers
Economic inequality
Lack of infrastructure or tech access
Low levels of human capital (health or education)
Dependence on primary commodity production
Lack of access to international markets
Informal economy
Capital flight
Indebtedness
Geography (landlocked or tropical climate and disease)
List of political and social barriers
Weak legal system
Ineffective taxation
Weak banking system
Weak property rights
Gender inequality
Lack of good governance
Unequal political power
Limited access to infrastructure and technology
Misallocation of resources - provided infrastructure is inappropriate given the needs of the population
Access to infrastructure is also limited in terms of access to the poor
Limited resources in developing or purchasing technology to improve efficiency and production capacity
Improved tech can also increase production, but may lead to unemployment due to capital deepening.
Low levels of human capital
Barrier to education
Lack of funding and lack of quality materials
Inability to pay
Gender or racial discrimination
Barrier to healthcare
Lack of funding and lack of access to medical services
Poor sanitation/hygiene and access to clean water
Insufficient medical facilities
Dependency on primary sector production
Inelastic and price volatility
Benefit developing countries when prices are high, but may wreck developing countries when prices fall.
Limited access to international markets
Due to limited infrastructure or geography
Developing countries’ currency may be non-convertible
Barrier to entry: protectionist measures in a developed country
Informal economy
Workers lack social protection, workers rights, and decent working conditions.
Government does not gain tax revenue
Lower HDI scores and high levels of informal employment
Capital flight
Large scale transfer of privately owned capital to other countries, caused by economic or political instability, which may cause depreciation due to higher supply.
High levels of indebtedness
Exacerbated by volatility in primary commodity prices, global financial crisis, and the fact that debt is usually issued in USD
Dollar dominated debt:
buy dollar using currency (that is usually valued less)
Trade resources (give up national debt)
Geography
Landlocked countries
Poor transportation infrastructure
Tropical climate and endemic diseases
Reduce labor productivity and agricultural production
Tropical diseases negatively affect human capital (health)
Weak legal system and property rights
Applies justice equally
If people do not have ownership or protection of property, they are not incentivized to produce!
Ineffective taxation structures
Loss of tax revenues prevents the government from investing in human capital and infrastructure.
High levels of tax evasion and corruption
Dependence on indirect taxation
Banking system
Incentive to save and source of credit or loans for individuals and businesses
Hindrance: poor individuals do not have collateral to collect credit
Foreign banks in developing countries only cater to large businesses focused on profit.
Gender inequality
Results in unequal participation in labor force and access to health care.
Benefits of empowerment of women:
improves family health
contribute to production and pass on their skills to their children
Improved standards of living due to greater income
Lower birth rates, education, and population growth
Lack of good governance
Corruption (abuse of public office for private gain)
Bribery
Embezzlement
Extortion
Fraud
Patronage
Influence peddling
Nepotism
Lack of accountability of government
Government spends a lot of large scale projects
Negatively affects growth and development
Reduce efficacy of legal system ad increases costs and prices
Environmental damage and poor worker safety
Damages trust in institutions and governments
Disincentivizes FDI