AP U.S History Unit 2: The New Republic Republic
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What were the Articles of Confederation
A lose confederation between the 13 independent states tied together by shared common problems
What were the problems of the Articles of Confederation
No executive branch
No judicial branch
Each state had a single vote - population had no effect
To pass, all bills needed to have 9/13 states to agree
To ammend the articles, it required all 13 states to agree
Congress couldn’t regulate commerce - tariffs were placed between states
Couldn’t enforce tax collection properly - no way of actually raising revenue, they had to ask the states for money
Why were the articles of confederation purposely weak
because the Americans were fearful of a return to British despotism, therefore that is why no executive branch was included, and why congress couldn’t levy taxes
What was an advantage of the articles of confederation
it kept the idea of union alive through the early life of the American republic, and was a stepping stone towards the constitution
What was the old Northwest
Land acquired by congress following their victory in the revolutionary war
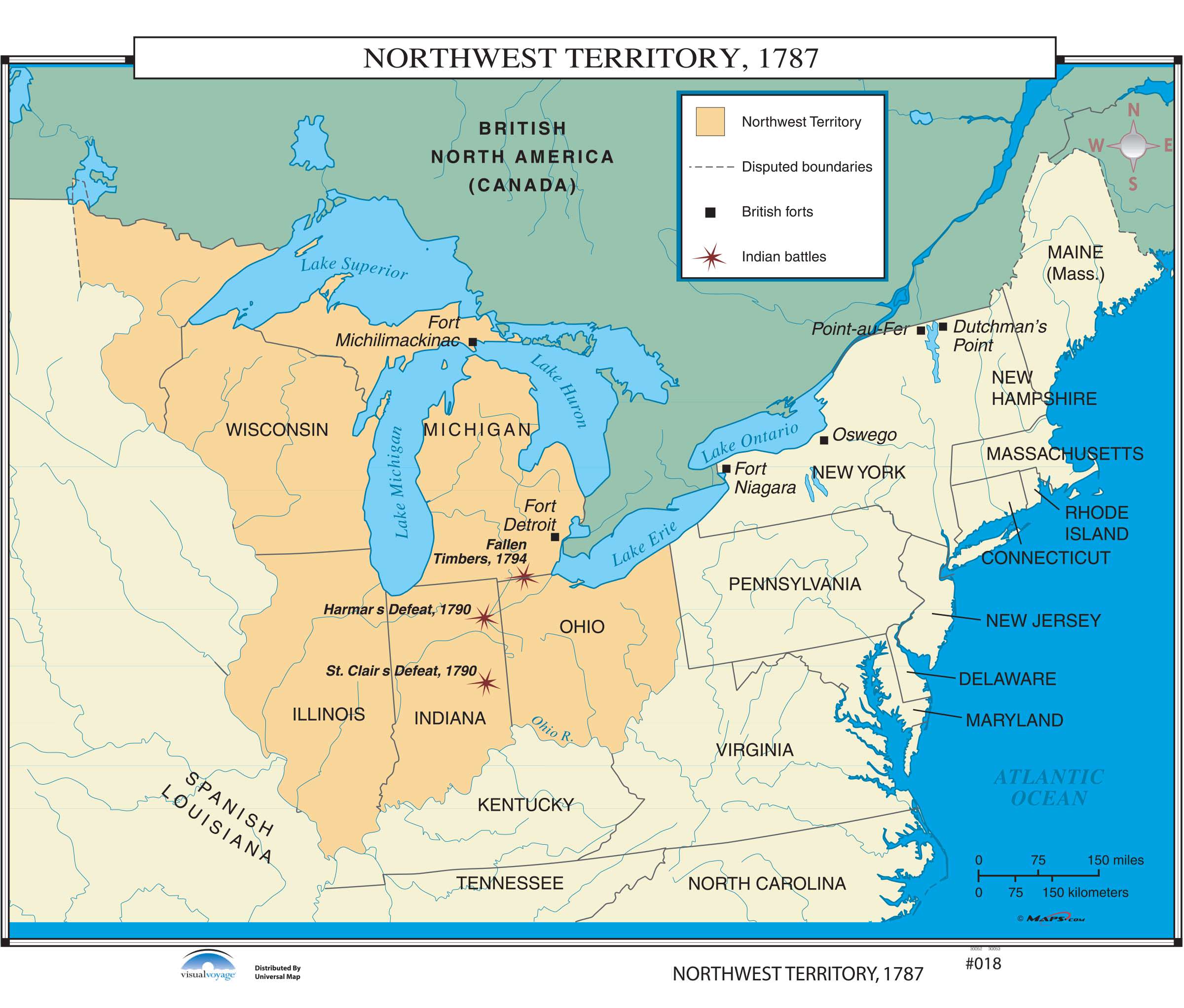
What was the land ordinace of 1785
Areas of the old Northwest should be sold to help pay off the national debt
What was the Northwest ordinace of 1787
With land being sold to settlers it established that an area of land would come under the “tutelage” of the federal government" and once it hit 60,000 settlers it would be admitted as a state with equal rights
Banned slavery in the new states in this region
How was Britain still hostile to America even after losing the revolutionary war
Refused to send an ambassador to America
Refused to repeal the navigation acts - this made sure that American trade would default and go through British shipping channels
Closed the British West Indies to American traders
Supported Indian revolts against Americans
Kept soldiers along the Northern frontier
maintain trade with the Indians
Could have been due to America not honouring fair treatment of loyalists and not paying their pre-revolutionary debts
How was Spain hostile to America following the end of the revolutionary war
1784 - closed American commerce along the missisippi
Schemed with Indians to frustrate American pioneers and settlers which led to a lack of order in certain regions and undermined American power
How was France hostile to America following the end of the revolutionary war
Demanded payment for supporting the Americans in the revolutionary war
What was a consequence of America being independent of Britain
Didn’t have protection from the royal navy, therefore major raiding by north African pirates took place on American merchant ships
What was the economic crisis in the United States following their victory in the revolutionary war
They were going broke, losing credit, and states were charging taxes on good from other states
What was Shay’s rebellion and its significance
A rebellion led by disgruntled veterans in Western Massachusetts, who were angry at their loss of land and economic disparity
Significance: While ultimately crushed easily, it alarmed many who were in elite, they viewed the weak articles of confederation allowing a rebellion to take place, and that the idea of liberty could wet the appitite of the peasents, leading to their downfall
Significance: Conservatives then upplayed the severity of the situation, stating that it affected the union as a whole, to make congress amend the articles
Significance: All believed in ammendments to the articles, viewed as weak
Conservatives: Worried for their wealthy positions in society
Revolutionaries: Better maintain the ideas of the revolution
Poor: protection of their liberties
What was the scenario leading up to the constitutional convention
Problems over commerce was the main problem that parked this congress
Virginia called a meeting at Annepolis but no one came - Hamilton stated that a meeting should be held the following year in Phillidelphia to strengthen the articles
55 delegates were elected to represent 12 states - Rhode Island sent no delegate
Washington presided over the congress - Jefferson in France, Adams in England
What type of men were at the constituional congress
Wealthy men, from rich backgrounds
What did the delegates hope to achieve at the constitutional congress
They hoped to transform the revolutionary ideas into a strong central authority
Sought to protect Americans abroad - Dey of Algeria
Wanted control over commerical treaties - hostility of British merchants
Avoid anarchy and uprising - Shay’s rebellion
What was the Virginia plan and New Jersey plan
Virginia plan: The house in the bicameral legislature should be based upon population - represented large state interests
New Jersey plan: Equal representation of states in a unicameral legislature - represented smaller state interests
What was the Great Compromise
Represenatation based on population was conceded to the larger states in the form of the house of representatives while equal representation with two delegates per state was conceded to the smaller states in the form of the senate
Why was the constitution short
Because it was born out of the Anglo-American common law - this made it unnesecary to be specific about every detail
What was the executive branch
Outlined in article 2 of the constitution it established a robust but legally refrained president - has the power to veto any law put forth from congress and can approve budgets
What was the electoral college compromise
A compromise on electing the president, this meant he was elected indirectly as the electoral college was based upon the states share of electors and population
What was the Three-fifths compromise
The south wanted slaves to be considered in representation (helping their influence) while the north did not want this (diminish their influence) - therefore they came to the agreement that slaves would represent 3/5 of a person
What was the slave trade compromise
The slave trade was allowed to continue to operate and the importation of slaves was allowed up until 1807, when the central government could ban the practice
What were three things that conservative delegates kept in mind when at the convention
Money and the protection of private property
Favoured a stronger government with three branches to keep their interests safe
Government by anarchy and mob rule could result without a strong central government
How was conservatism present in the constitution
Judges to be appointed for life by the president - prevents political pressure and ensures they rule by the constitution
The president elected indriectly - less chance of mob rule
Senators chosen indriectly by state legislators
Direct vote only permitted in the house
What did the constitution guarantee
Limited government and social contract - the authority of the people was the ultimate guarantee of authority
Why would it be difficult for the constitution to be rattifed and how did the constitutional convention overcome this difficulty
According to the old articles of confedertion to make an ammendment to the articles all 13 states had to agree, however the convention stipulated that once 9/13 states had agreed to the constitution it would be put into law
How did the states vote on whether to ratify the constitution or not
Special conventions were elected and organised to debate and ratify the constitution - therefore leadfrogging state governments and going more to the people
Who were the antifederalists
They opposed a strong central government
They consisted of:
State rights devotees
Backcounty dwellers
Debtors
Poorest classes
Who were the federalists
Supported a strong central government
Consisted of:
Wealthy
Educated
Had the support of the influential
What were the main concerns of the anti-federalists in relation to the constitution
They were worried that states rights were being submerged
They were also alarmed at the lack of an explicit bill of rights
What was the intital views of many states in regards to the constitution and why did they change
Many states orignally held anti-federalists views however, with promises by the central government ot ammend the constitution and add a bill of rights many states ratified the document
Which four states were slow to ratify the constitution and why did the finally end up ratifying it
New York - heated division between the federalists and anti-federalists however, with the publication of the federalist papers, it convinced many of the advantages of a strong federal government
Virginia - Heated division and debate between the two groups, orignally very anti-federalist but realising they couldn’t prosper without ratification led to Virginia ratifying it
Rhode Island - only ratified it after realising it could prosper economically without ratifying it
North Carolina - only ratified it after realising it could prosper economically without ratifying it
How did the ratifcation of the constitution both represent a conservative triumph and the continuation of republican and revolutionary ideals
The minority conservatives had overthrown the articles and erected safeguards against mobs while the republican gains of the revolutions persisted
Through checks and balances and limited government the constitution reconciled liberty with order
How did the federalists redefine popular sovreignty
Every branch of the new government represented the people
What were some equality movements occuring at the same time as the ratification of the constitution
States reduced property holding requirments for voting
1784 indentured servants in America were freed
Employers were called boss instead of master - shift in view
Hereditary societies were riddiculed
What occured with the relationship between the church and the state during this period
They became increasingly secularised: Virginia statue for religious freedoms (1784) - guaranteed relgious freedoms in Virginia
What was occuring with slavery in the northern states
Slavery was outlawed in some of the northern states while some instituted a phased elimination of the practice
Why was the domestic slave trade growing during this period
With the rise of cotton and the banning of the international slave trade
What was the relationship between emancipated African-Americans and whites
They were heavily discriminated against and laws emerged against interaccial marraige
Why was slavery allowed to continue to exist
Because the main concern of the union was preserving it, and the issues of slavery could have divided it
Did the political rights of women change
no
What was the idea of civic virtue and republican motherhood
Civic virtue: democracy depended on the unselfish commitment of each citizen to the public good
Republican motherhood - elevated women to a newly prestigious role as the special keepers of the national concienecss which took hold due to the civic virtue of mothers toward the children - this led to better educational oppurutnites emerging for women in hopes of them cultivating a better mind for their son
With settlers expanding across the appalachian mountains what new states were admitted to the union
Vermont, Kentuckey, Ohio, and Tenessee
With the election of a president in 1789, who was elected and what did he set up
George Washington was uniaminously elected president and set up a cabinet which included: secretary of state, treasury, and war
What were the first 10 ammendments to the constitution (the bill of rights)
Freedom of religion, press, speech, assembly, and petition
Right to bear arms
No one can be forced to house soldiers during peace time
No unreasonable searches and seizures
The right to due process
Right to a public and speedy trial
Right to a jury
No cruel and excessive punishments
The rights protected in the bill of rights aren’t the only rights protected
Reserves rights not explicitly stated in the constitution for the states
Who wrote the bill of rights
James Maddison
What was the Judiciary act of 1789
Organized the supreme court with one chief justice and five associates, as well as establishing federal district and cirucit courts as well as the office of the attorney general
What was Hamiltons goal and what was his aim?
To fix the economic troubles of the new union, in doing so he wanted to shape fiscal policy to favour the wealthy who would in turn lend the government money and political support, therefore supporting the federal government
How did Hamilton plan to secure the loans he needed from the wealthy
He needed to bolster the national credit but couldn’t secure the nessecary debts due to the lack of public confidence in the government so he asked congress to fund his endavour in two ways: Funding at par, and Assumption
What was Funding at par
The federal government would pay off the debts at face value and accumilate interest
What was assumption
Hamilton wanted the federal government to shoulder more debt so he convinced congress to take on the deby incurred by states during the revolutionary war which would help him accumilate more credit as he would take on state creditors
What was the reaction of states to Hamiltons economic policy
Many states liked this but to states like Virginia (which had payed of their debt) it was seen as further enchaining the states to the union - a compromise was reached - capital in the south for support from Jefferson to pass the bill
Why did Hamilton implement customs duties and excise taxes
Hamilton believed the more creditors to whom the government owed money to the more people there would be with a personal stake in the sucess of his ambitions
What were the tarrif laws implemented by Hamitlon
Sought to raise revenue by implementing a 8% tariff on dutiable imports - it was also meant to protect agricultural industries which congress was very concenred about - Hamilton viewed industry and manufacturing as the future and needed to be protected but congress ignored him
What was the excise tax implented by Hamilton
Mainly on whiskey in the back counties
Why did Hamilton want a national bank and what form would it take
He wanted a national bank similair to England in which a private institution where the government would be a major stockholder and the federal treasury would get surplus money
Federal funds would stay in circulation stimulating businesses
The bank would also print a stable national currency
Why did Jefferson oppose Hamiltons national bank
He viewed it as more encroachment on states rights and the continued binding of the federal government to the state government as well as the fact that Jefferson believed that the federal government didn’t have the authority to set up a national bank as it wasn’t explicitly stated in the constituion
How was Hamilton able to circumvent Jeffersons claim that the constitution didn’t enable the creation of a national bank
Hamilton responded by drawing on the nessecary and proper clause in the constitution that the government was granted explicit power over collecting taxes and trade, therefore by implied powers congress could establish a national bank to better carry out its goals
What was the Whiskey Rebellion
In response to Hamiltons excise tax on whiskey a group of rebels emerged in the backcounties, however, when Washington raised an army put down the rebellion they dispersed and Washington granted amnistey to those captured
What emerged in reaction to Hamiltonian policy
Political parties, the federalists began to form and in opposition the Democratic-Republicans led by Jefferson and Maddison who were worried about the ever growing power of the federal government
What was the popular reaction to the outbreak of the French revolution
It was met with excitment as it was viewed as an extension of the American revolution
What was the view of conservatives as the revolution became more and more bloody
The conservative federalists grew ever more worried and viewed the Jeffersonian masses as a threat
What was the neutrality procclomation (1793)
Washington delcared neutrality in the conflict between Britain and France due to his belief that the united states was millitarily, economically, and politically weak and needed time to further consolidate its power before asserting its self on the global stage
What affect did this procolmoation have on Jeffersonians
It alienated many of them
How was conflict with Britain almost a thing
Britain didn’t want to exit the lucrative fur trade therefore still maintained forts in positions which had been sceded to the united states, a violation of the peace treaty
Britain supplied weapons to Indian tribes (Miami confederation) they hoped to check the ambitions of the Americans - led to American conflicts with the Indians but following the Battle of Fallen Timbers Britain abandoned their allies
Britain seized American merchant ships and sailors and forced them to work on British ships - this was done by Britain to secure the Atlantic because American trade with the French West Indies undermined British advantage over France
What was the Treaty of Greenville
Following the conflict with the miami confederation the Americans secured vast amounts of the old northwest in reutrn for monetary compensation, right to hunt, and recognition of their sovreignty
Why did the Federalists still want to avoid war
Hamilton needed trade with Britain to bolster his economic plan
What was the Jay treaty
A treaty that secured peace with Britain but also saw major concessions made to keep the peace
Britain promised to evacuate the forts on American soil
Britain agreed to pay for the ships it had seized
Britain demanded that pre-revolutionary debts be paid
What was the reaction to the Jay treaty
It enraged the Jeffersonians as it was seen as bending to the will of Britain
It also infurated southerners who had to pay up on debts while the northern federalists recieved compensation for their seized merchant ships
What was the Pickney treaty (1795)
Fears of Anglo-American alliance led to Spanish concessions
Free navigation of the Missisippi
The right to depost at New Orleans and Florida
What was the significance of Washingtons farewell adress
Stepped down from office following his second term - set a precedent
Warned against long term alliances which could divide the nation
With Hamiltons growing unpopularity who was chosen to replace him as the Federalist candidate in the ensuing election
John Adams
Who were the High federalists
Led by Hamilton they undermined the power of Adams and favoured war with France
What was the X,Y,Z affair
In hopes of avoiding conflict with France Adams sent three representatives to meet with the French foreign minister, after arriving in France the french spokesman demanded three things
Uneutral loan of 32 million dollars
A personal bribe of 250,000 dollars
What was the significance of the X,Y,Z affair
It was viewed as an outrage in America and sent war hysteria throughout the nation, helped push along war preperations - the navy was expanded, new army authorised (not raised)
What was the Quasi War
Undeclared war with France which saw mainly conflict between France and America at sea
Even with the new found popularity following the X,Y,Z affair what did John Adams still want
He still wanted peace with France and recieved the new French foreign minister - the High federalists were outraged but the Jeffersonians gave Adams praise
What was the convention of 1800
Talleyrand wanted peace
It annuled the 22 year treaty between France and America
United states agreed to pay damages made by American ships
Avoided conflict with France and paved the way for the Louisiana purchase
What were the Alien Acts
It rased the residence requirments for aliens who desired to become citizens from 5 to 14 years
It also allowed the president to deport dangeours foreigners during peace and deport or imprison during wartime
What were the Sedition acts
Targeted freedom of speech and the press
Anyone who impeded the policies of the government or falsely defamed its officals would be liable to fine and imprisonment - many Jeffersonian editors were indicted - ten brought to trial and convicted
Why didn’t the supreme court strike the sedition act down as unconstitutional
Because it was filled with federalists who supported the policies of their party
What was Jefferson and Maddisons response to the Alien and Sedition Acts
To draft the Kentuckey (Jefferson) and Virginia (Maddison) resolution
What was the Kentuckey resolution and by extent the Virginia resolution
Invoking the compact theory - the idea that in creating a federal government the 13 states had entered into a compact regarding its juristiction, therefore the states could be the final judges of whether the federal government had overstepped its original authority - Jefferson argued that the federal government had overstepped its boundaries and in regards to the alien and sedition acts all 13 states could nullify the law (resurectted a idea of the articles of confederation)
What was the popular reaction to the Kentuckey and Virginia resolutions
Largely rejected and condemned but was born out of a worry that democracy was being eroded, Jefferson sought to oppose the federalists
Who were the federalists: their beliefs and make up
Advocated for a strong central government
Crush revolts
Subordinate sovreignty of states
Promote foreign trade
Support private enterprise
Federalists contained:
Merchants
Manufactuers
Shippers
Upper class
Tories
Who were the Democratic-Republicans: their beliefs and make up
Advocated for a weak central government
The best governance was the one that governed least
Power should be retained by the states
People could keep an eye on their public servants
Strict interpretation of the constitution
Democratic-Republicans contained
Agrarians
Agricultural south and southwest
Lower class
Southern Plantations
Immigrants
What was the difference between foreign policy between the Federalists and Democratic republicans
Federalists - Wanted to go outward and trade with the world
Democratic-Republicans - wanted to focus inward on the nations problems
What was Jeffersons belief in government
He believed in government for all people but not by all people, he didn’t believe in landless and illiterate people participating in government - like slavery