Planning Law in Ontario: Key Sections, Policies, and Procedures
1/308
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
309 Terms
What is the main law guiding planning decisions in Ontario?
The Planning Act
What does the Canadian Constitution Section 91 outline?
Federal powers, including temperance (criminal law)
What does the Canadian Constitution Section 92 outline?
Provincial powers, including property and civil rights
What is the purpose of the Provincial Policy Statement 2024?
To guide land-use planning and development in Ontario
What is the role of the Ontario Land Tribunal?
To provide exclusive jurisdiction for planning matters and determine questions of law and fact
What is an Official Plan in the context of the Planning Act?
A document that outlines a municipality's vision for land use and development
What must an Official Plan conform to?
Provincial Policy Statement and Provincial Plans
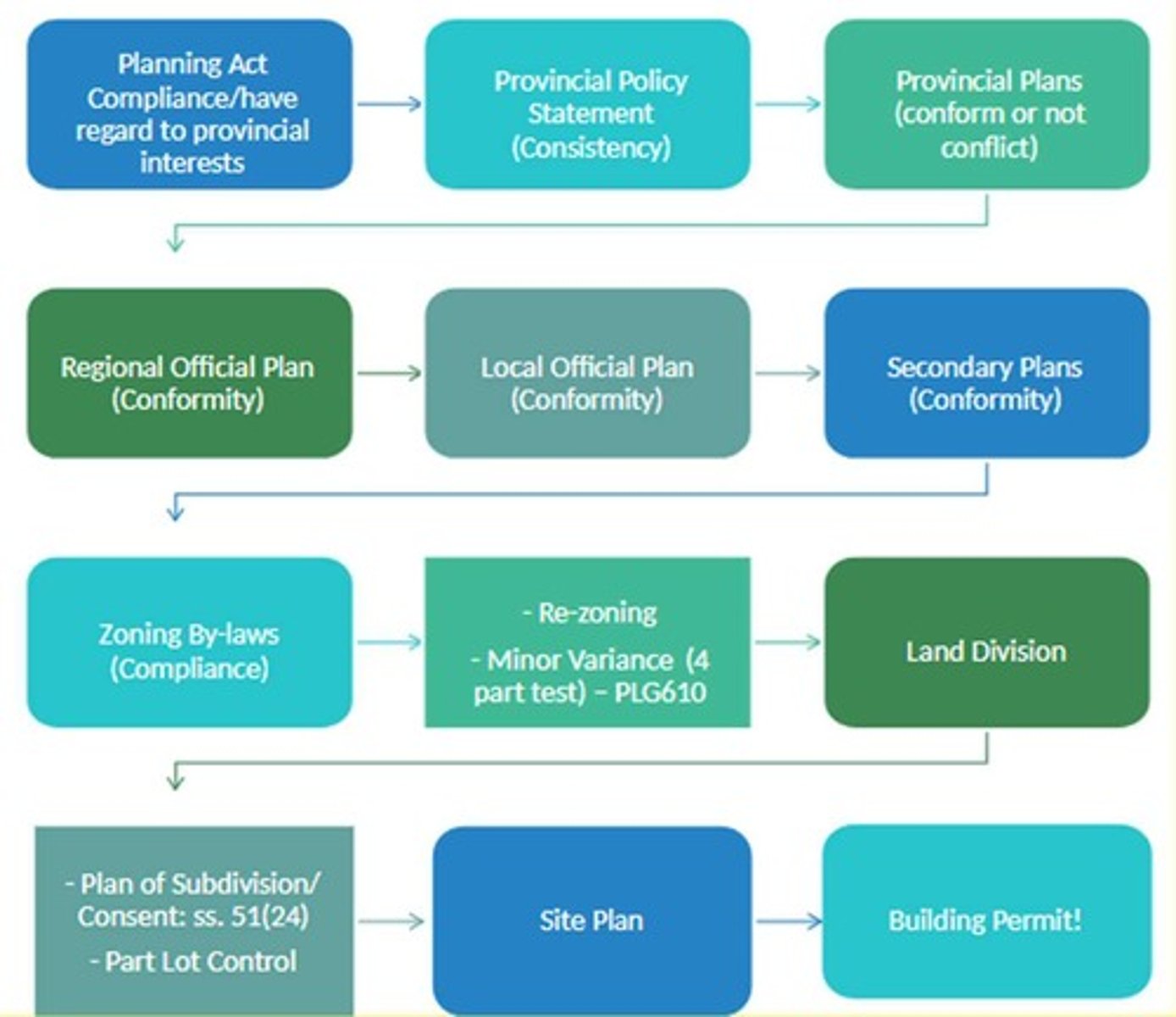
What is the hierarchy of planning instruments in Ontario?
1. PPS 2024 2. Provincial Plans 3. Official Plans 4. Zoning bylaws
What is the significance of Section 35 of the Canadian Constitution?
It enshrines treaty rights
What is the role of municipalities in land-use planning?
They implement provincial planning through the Planning Act and planning tools
What does the term 'creatures of the Province' refer to?
Municipalities, as they derive their powers from the provincial government
What is the purpose of the Municipal Act 2001?
To outline the powers and responsibilities of municipalities in Ontario
What sections of the Planning Act deal with the approval of Official Plans?
Sections 17 and 16
What is required for an Official Plan to come into force?
It must be adopted by the municipality and approved by the Minister
What is the significance of case law in planning decisions?
It provides precedents and guidance for interpreting planning laws
What are the responsibilities of the Minister under the Planning Act?
To ensure provincial interests are considered in planning decisions
What is the purpose of the Aggregate Resource Act?
To regulate the extraction of aggregate resources in Ontario
What does the Construction Act govern?
It governs construction-related matters, including contracts and liens
What is the role of the Ontario Land Tribunal in appeals?
To hear and decide appeals related to planning decisions
What is the importance of submitting comments to the Ministry before approval?
It allows stakeholders to express their views before decisions are made
What does 'public interest' mean in the context of land-use planning?
Balancing community needs with private rights
What are the key components of the Provincial Policy Statement 2024?
Building homes, settlement areas, rural areas, employment areas, natural heritage, and cultural heritage
What is the purpose of case management conferences in the Ontario Land Tribunal?
To manage the progress of appeals and ensure efficient hearings
What is the significance of the term 'binding provincial policy framework'?
It establishes mandatory guidelines for planning decisions
What is the process for adopting an Official Plan according to the Planning Act?
Municipalities must follow specific procedures outlined in Section 17
What does the term 'zoning bylaws' refer to?
Regulations that govern land use and development within a municipality
What is the role of the council in the planning process?
To make decisions on planning matters and adopt Official Plans
What controls land-use planning in Ontario?
The Province controls land-use planning.
What are municipalities considered in relation to the Province?
Municipalities are 'creatures of the Province' and only have powers granted by it.
What does the Provincial Policy Statement (PPS) require?
Municipal decisions must be consistent with the PPS.
What is the purpose of the Official Plan?
To set the municipality's long-term vision for land use.
What do zoning by-laws regulate?
Zoning by-laws set detailed regulations on land uses, heights, and setbacks.
What is the role of the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT)?
The OLT hears appeals of planning decisions and is governed by the Ontario Land Tribunal Act, 2021.
What is 'stare decisis' in case law?
Stare decisis refers to the principle that precedents must be followed.
What does 'ratio decidendi' mean?
Ratio decidendi is the binding reason for a court's decision.
What is 'obiter dicta'?
Obiter dicta are non-binding comments made by a judge.
What does 'intra vires' mean?
Intra vires means within the jurisdiction of the enabling legislation.
What does 'ultra vires' mean?
Ultra vires means outside the jurisdiction of the enabling legislation.
What is the appeal path for planning decisions in Ontario?
Municipal Council → OLT → Divisional Court (on questions of law).
What is the significance of the Constitution Act, 1867?
It defines the division of law-making power between federal and provincial governments.
What is the primary focus of the Planning Act?
To govern official plans, zoning, subdivisions, consents, variances, and site plan control.
What are the core planning principles in Ontario?
Public interest, consistency and conformity, fairness and transparency, finality vs flexibility, and rule of law.
What is the current planning issue regarding housing in Ontario?
The Province aims to add 1.5 million new homes while balancing growth with environmental protection.
What are Minister's Zoning Orders (MZOs)?
MZOs are tools used to fast-track development and growth.
What is the purpose of the Development Charges Act?
To manage growth and fund public infrastructure related to new developments.
What does the term 'public interest' refer to in planning law?
The balance between private land use and community needs.
What is the role of the Municipal Act, 2001?
It outlines the powers and responsibilities of municipalities in Ontario.
What is the significance of the Planning Act's regulations?
They provide detailed rules for official plans and zoning by-laws.
What is the relationship between the PPS and municipal decisions?
Municipal decisions must align with the values set by the PPS.
What is the purpose of site-specific tools in planning?
To manage specific developments through subdivision control and site plan approvals.
What does 'mandatory language' in legislation indicate?
It indicates requirements that must be followed, using terms like 'shall' or 'must'.
What does 'discretionary language' in legislation indicate?
It indicates options that may be exercised, using terms like 'may'.
What are the implications of climate change on planning regulations?
Regulations require that development be sustainable and resilient to climate impacts.
What does the Federal Parliament handle?
Matters of national interest.
What do Provincial Legislatures handle?
Matters of local concern.
Which document outlines the division of powers in Canada?
The Constitution Act, 1867.
What sections of the Constitution Act, 1867 define federal and provincial powers?
Sections 91 and 92.
What is the intent of Sections 91 and 92?
To establish exclusive jurisdiction for each level of government.
What is 'co-operative federalism'?
A model where federal and provincial governments work together and share responsibilities.
What is the purpose of the Peace, Order, and Good Government (POGG) clause?
To allow the federal government to legislate on matters not specifically defined in Section 92.
What are some key areas of federal powers?
Criminal law, trade and commerce, banking, navigation, and immigration.
What powers do provinces govern?
Local matters such as property rights, administration of justice, education, and healthcare.
What is the significance of Section 92A?
It expanded provincial control over natural resources in 1982.
What is the relationship between federal and provincial laws in case of conflict?
Federal law prevails under the doctrine of federal paramountcy.
What are municipalities considered under the Constitution?
They are 'creatures of the province' and derive their powers from provincial legislation.
What are the three main ways to challenge legislation?
Validity, applicability, and operability.
What does the doctrine of 'Pith and Substance' determine?
The true nature of a law to identify which level of government has authority.
What is the purpose of the 'Interjurisdictional Immunity' doctrine?
To protect the core powers of one jurisdiction from intrusion by another.
What is the effect of the federal paramountcy doctrine?
Federal law prevails in conflicts, rendering provincial law inoperative to the extent of the conflict.
What is required for a municipality to enact a by-law?
The municipality must have statutory authority under provincial law.
What happens if a municipal by-law conflicts with federal law?
The by-law is rendered inoperative to the extent of the conflict.
What is the significance of the 'Double Aspect' doctrine?
It allows both levels of government to legislate on the same subject without conflict.
What is meant by 'Impossibility of Dual Compliance'?
A test for conflict where it is impossible to obey both federal and provincial laws simultaneously.
What does 'Frustration of Federal Purpose' refer to?
A test for conflict where provincial law undermines the goal of federal law.
What is the role of the courts in reviewing municipal decisions?
To assess statutory authority and constitutional validity of municipal by-laws.
What is the historical significance of the case Hodge v The Queen (1883)?
It established principles for characterizing laws under the Pith and Substance doctrine.
What is an example of a federal power that cannot be legislated by provinces?
The enactment of the Criminal Code.
How do provinces regulate workplace safety?
Through their own legislation, such as the Occupational Health and Safety Act.
What is the purpose of the Municipal Act, 2011 in Ontario?
To provide the framework for municipal governance and powers.
What is the significance of concurrent jurisdiction in Canadian law?
It allows both federal and provincial governments to legislate on certain matters.
What is the impact of the Greenhouse Gas Pollution Pricing Act?
It was recently analyzed under the Pith and Substance doctrine for its jurisdictional implications.
What barred Mississauga from requiring the GTAA and Nav Canada to obtain building permits for Pearson Airport?
Parliament's exclusive jurisdiction over aeronautics, federal undertakings, and federal Crown property.
In Canada Post Corporation v Hamilton, why was Hamilton's road-permit by-law inoperative against Canada Post?
It frustrated the CPCA and Mail Receptacles Regulations that give Canada Post exclusive authority to locate community mailboxes.
What powers do municipalities have regarding pesticide use according to 114957 Canada Ltee v Hudson?
Municipalities may use 'general welfare' powers to restrict non-essential pesticide use if dual compliance with federal and provincial regimes is possible.
What was ruled unconstitutional in Rogers Communications INC. v. Chateauguay?
Measures that impair Parliament's core power over radiocommunication, including siting of cell towers.
What did the City of Burlington v Burlington Airpark INC. case establish about municipal by-laws?
A municipal by-law regulating the quality of fill is intra vires and applies to airport lands if it does not impair federal aeronautics powers.
What section of the Constitution recognizes Indigenous treaty rights?
Section 35.
What does Indigenous interest in land represent?
An independent legal interest that burdens the Crown's underlying title and gives rise to the duty to consult.
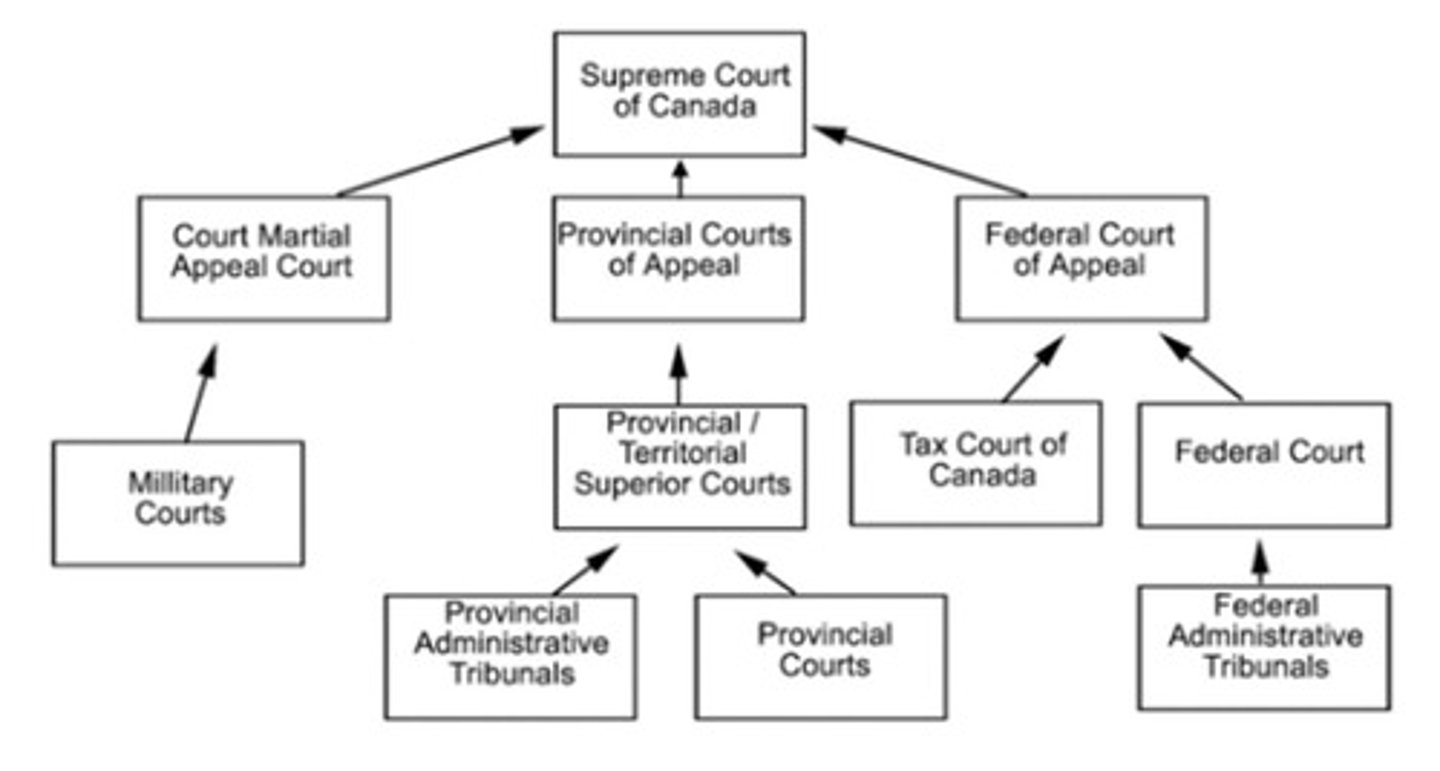
How many levels of court are there in Ontario?
Four levels: Ontario Court of Justice, Superior Court, Ontario Court of Appeal, and Supreme Court of Canada.
What is the primary legislation governing municipalities in Ontario?
The Municipal Act, 2001.
What role do municipal councils play in planning decisions?
They adopt by-laws and process development applications.
What is the Ontario Land Tribunal (OLT) responsible for?
Hearing and deciding appeals under the Planning Act.
What must planning decisions be consistent with according to the PPS 2024?
They must be consistent with the Provincial Planning Statement and conform to provincial plans.
What are some matters of provincial interest outlined in the Planning Act, Section 2?
Protection of natural features, agricultural land, housing, public health and safety, and climate change mitigation.
What is the purpose of the Planning Act as stated in Section 1.1?
To promote sustainable economic development in a healthy natural environment and to provide a land use planning system led by provincial policy.
What does the Greenbelt Plan aim to protect?
Prime agricultural land and natural heritage.
What is required for a by-law to be valid according to the Spraytech case?
Dual compliance with federal and provincial regimes.
What is the guiding principle for the Ontario Land Tribunal?
Fair, just, and expedited resolutions of appeals.
What does the term 'intra vires' mean in the context of municipal by-laws?
Within the powers or authority granted to municipalities.
What is the significance of the duty to consult in relation to Indigenous land rights?
It arises from the recognition of Indigenous interests in land and the Crown's fiduciary duties.