Topic 9 - Chemistry of the atmosphere
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Describe the composition of the atmosphere today.
The proportion of gases in the air has not changed much in 200 million years
The composition of the atmosphere today is:
About four-fifths (approximately 80%) nitrogen
about one fifth (approximately 20%) oxygen
small proportions of other gases including carbon dioxide, water vapour and trace quantities of the noble gases, argon
Explain the Earth’s early atmosphere.
Theories on the development of Earth’s atmosphere have altered and developed over time as instrumental analysis has improved
The surface of the early Earth was molten for millions of years with no atmosphere
As cooling slowly occurred, the molten surface began to slowly solidify into land masses
Volcanoes formed on the land masses
During the first billion years of the Earth’s existence there was intense volcanic activity that released gases that formed the early atmosphere and water vapour that condensed to form the oceans. At the start of this period the Earth’s atmosphere may have been like the atmospheres of Mars and Venus today, consisting of mainly carbon dioxide with little or no oxygen gas.
Volcanoes also produced nitrogen which gradually built up in the atmosphere and there may have been small proportions of methane and ammonia.
When the oceans formed carbon dioxide dissolved in the water and carbonates were precipitated producing sediments, reducing the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Why is evidence for the Earth’s early atmosphere limited?
Evidence for the early atmosphere is limited because it was 4.6 billion years ago.
Explain how the levels of oxygen in the atmosphere increased.
Algae and plants produced the oxygen that is now in the atmosphere by photosynthesis, which can be represented by the equation:
Algae first produced oxygen about 2.7 billion years ago and soon after this oxygen appeared in the atmosphere. Over the next billion years plants evolved and the percentage of oxygen gradually increased to a level that enabled animals to evolve.
Explain how the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere decreased.
When the water vapour in Earth’s early atmosphere condensed, large amounts of CO2 dissolved in the oceans
Carbonates were precipitated during this process which later formed sediments on the seabed
Green plants and algae began to evolve and absorbed considerable amounts of carbon dioxide during photosynthesis
Animals fed on the plants which transferred carbon to their tissues including bones and shells and when these organisms died, their remains formed sedimentary rocks
Dead organisms turn into fossil fuels, such as crude oil, natural gas and coal which 'locked up' the carbon
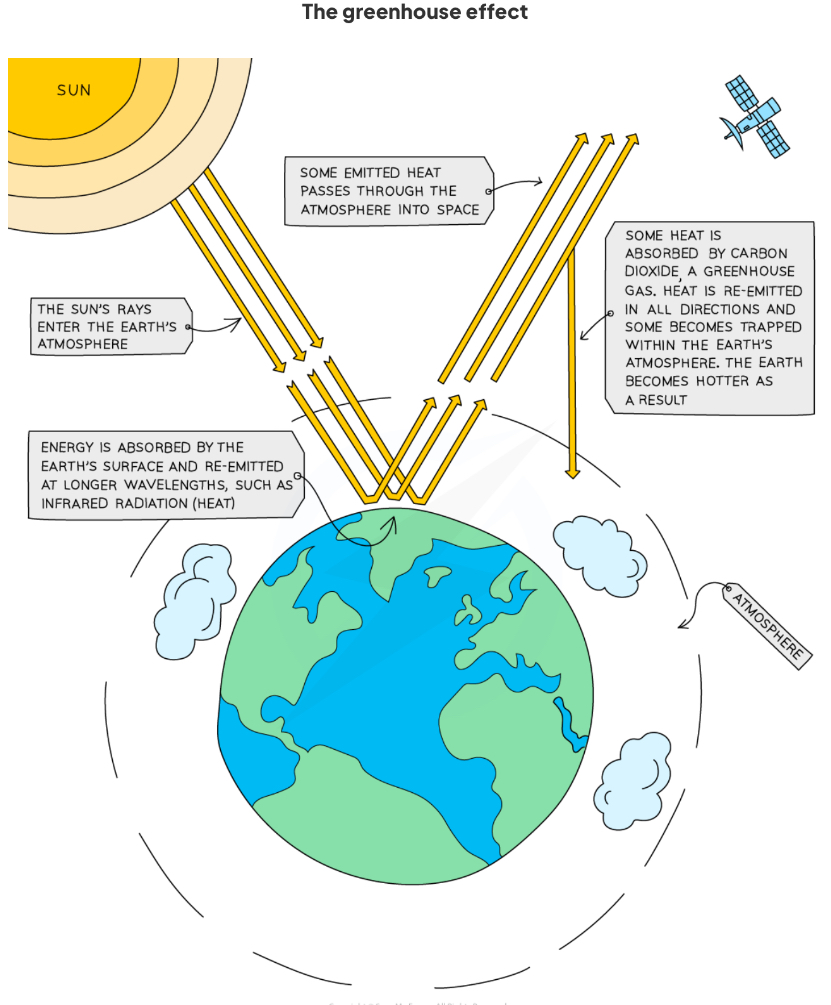
Explain the greenhouse effect.
Greenhouse gases maintain the temperatures on Earth high enough to support life
This is known as the greenhouse effect
Short wavelength radiation (ultraviolet radiation) is emitted from the sun
When it strikes the earth's surface, some of it is absorbed and some is re-emitted from the surface of the Earth as long wavelength radiation (infrared radiation)
Much of the radiation is trapped inside the Earth’s atmosphere by greenhouse gases which can absorb and store the energy
Increasing levels of carbon dioxide and methane, although present in only small amounts, are causing significant upset to the Earth’s natural conditions by trapping extra heat energy
Describe two human activities that increase the amounts of each of the greenhouse gases carbon dioxide and methane.
Methane levels are increasing due to:
More waste being sent to landfill sites due to an increasing human population
Increased levels of farming
Carbon dioxide levels are increasing due to:
The increased demand for energy resulting in more fossil fuels being burned
methane + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
Deforestation- fewer trees means less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by photosynthesis
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Define climate change.
Climate change is when there is a long term shift in worldwide weather patterns and conditions
Why is there doubt if human activity has cause climate change?
Advances in science and technology mean current levels of CO2 and global temperatures can be determined with a high degree of accuracy
Historical data is much less accurate due to the lack of accurate instrumentation and methods
Fewer locations would also have been measured due to the lack of satellites and transport
There are some methods to estimate past climate conditions, which include:
Analysis of the fossil record and tree rings
Analysis of gas bubbles trapped in ice from hundreds of thousands of years ago
Unfortunately, these methods, while providing at least some data, are not as precise as modern day techniques nor do they provide data which is representative on a global scale
The complexity of the Earth’s climate and contributing factors make it a difficult task to produce a working model that clearly shows the link between global warming and greenhouse gases
This and other difficulties have led to hype and speculation in the media in recent times in which some scientists have cast doubts on human activity and climate change
However, academic surveys have shown that about 97% of climate scientists do believe human activity is causing climate change
Describe four potential effects of global climate change.
Rising Sea Levels
The melting of the polar ice caps and glaciers is leading to rising sea levels
This results in destructive erosion to coastal regions, flooding of wetlands and habitat destruction for birds, fish and plants
Low lying cities are likely to see increased flooding and permanent loss of usable land without expensive barrier systems
Increased soil salinity is also a consequence of rising sea levels
Frequent and intense droughts
Some regions are seeing devastating droughts leading to crop failure and collapse of agricultural production
Food production is greatly compromised leading to hardship and starvation
Storms
The intensity of storms is increasing
Warmer ocean surfaces mean more moisture is entering the atmosphere so storms and hurricanes are more energetic and destructive
Extreme heat waves and rainfall
Extreme weather events are becoming more frequent resulting in great loss of life and destruction of infrastructure and ecosystems
Changing rainfall patterns are leading to uneven distribution of freshwater supplies
Lack of reliable freshwater supplies results in economic and political instability as neighbouring countries compete for dwindling resources
Define carbon footprint.
The carbon footprint is the total amount of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases emitted over the full life cycle of a product, service or event.
Describe actions to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide and methane.
The carbon footprint can be reduced by reducing emissions of carbon dioxide and methane
CO2 emissions can be reduced by using renewable energy supplies such as solar or wind energy instead of burning fossil fuels
Governments and global organisations are slowly switching to greener and sustainable sources of energy and often offer financial incentives to companies in an effort to convince them to “go green”
Apart from using renewable energy sources other ways individuals can reduce their carbon footprint include:
Cutting out unnecessary journeys
Using public transport rather than private cars
Reducing consumption of meat
Buying locally sourced foods to reduce food miles (the distance food travels from production to consumption)
Carbon off-setting: paying for reforestation projects to compensate for carbon emissions from flying for example
Switching to electric vehicles
Recycling and re-using materials to prevent them being sent to landfill
Give reasons why actions to reduce emissions of carbon dioxide and methane may be limited.
Alternative technologies are not good enough
Governments tend to be slow to act on these issues as they fear a negative impact on their economies
On an individual level, there is also resistance as it is difficult to convince people to change their ways
There is a lack of investment schemes for companies to help them to modernise their facilities
Ultimately, many people believe that reducing the global carbon footprint will be too expensive and not enough to tackle climate change, so climate mitigation strategies should be adopted hand in hand with carbon footprint reduction
Describe how carbon monoxide is produced by burning fuels.
Most fuels contain carbon and this produces carbon monoxide on incomplete combustion.
Describe how soot (carbon particles) is produced by burning fuels.
Most fuels contain carbon and this produces carbon monoxide on incomplete combustion.
Describe how carbon dioxide is produced by burning fuels.
Most fuels contain carbon and this produces carbon dioxide on complete combustion.
Describe how sulfur dioxide is produced by burning fuels.
Fossil fuels are often contaminated with small amounts of sulfur impurities
When these contaminated fossil fuels are combusted, the sulfur in the fuels get oxidised to sulfur dioxide
S (s) + O2 (g) → SO2 (g)
Sulfur dioxide is a major atmospheric pollutant
Describe how oxides of nitrogen are produced by burning fuels.
Although nitrogen is not present in fossil fuels, nitrogen oxides are a product of the combustion of fuels in car engines
The oxides are mostly a mixture of nitrogen monoxide and nitrogen dioxide
Nitrogen is normally an unreactive gas, but high temperatures inside combustion engines can make nitrogen in the air react with oxygen to produce oxides of nitrogen
Describe the properties and effects of carbon monoxide.
toxic because it combines with haemoglobin in the blood reducing the ability of the blood to carry oxygen
colourless and has no smell so hard to detect
Describe the properties and effects of carbon dioxide.
greenhouse gas, thought to be causing global warming and climate change
Describe the properties and effects of carbon particulates (soot).
pollute the air and blacken buildings
cause global dimming which reduces amount of sunlight reaching Earth’s surface
can damage lungs and cause respiratory problems
Describe the properties and effects of sulfur dioxide.
causes acid rain which damages plants and buildings
causes respiratory problems for humans
Describe the properties and effects of nitrogen oxides.
causes acid rain which damages plants and buildings
causes respiratory problems for humans