Gravitational Fields
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ADD GRAV FIELDS IS1 NOTES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Examples of natural satellites:
Moon, Earth, Sun
How do natural satellites stay in orbit?
As the satellite is launched into space, it will constantly be attracted to the Earth
If the Earth and satellite fall at the same rate, the satellite will orbit
Equation for orbital speed:
v = sqrt(GM/r)
Low Earth orbit satellites
Satellites with a low distance from the Earth
r is low, implying that orbital speed is high
Uses of low Earth orbit satellites:
Observation and remote sensing
Geostationary satellites
Far away from the Earth
Appear to be stationary on Earth (in one fixed position)
Must be above the equator, rotate in the same direction and have a time period of 24 hours
Uses for geostationary satellites:
Communications, weather, television
Gravitational Potential
The work done per unit mass to move an object from infinity to that point
Gravitational Potential equation
Vg = -Gm/r as r → ∞, Vg → 0
Gravitational Potential energy
The work done to move a mass from infinity to a point in a gravitational field
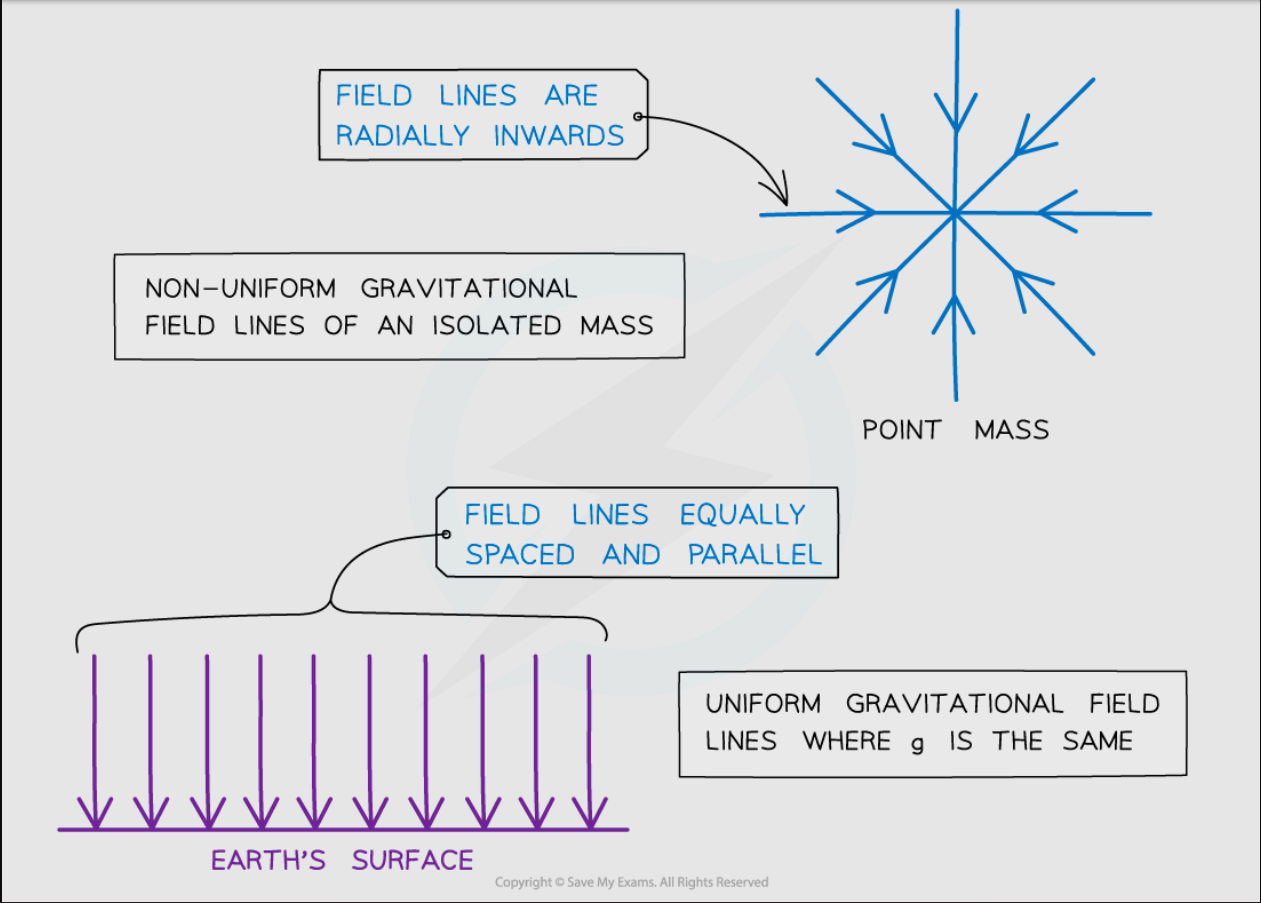
Uniform grav. field vs radial grav. field
A uniform grav. field is an approximation for where field lines are parallel, but radial grav. field lines point towards a central mass
Change in Gravitational Potential energy equation
ΔE = mΔVg
In radial fields, E = -GMm/r
The area of a force-radius graph
The change in G.P.e
Escape velocity
The minimum speed an object needs to escape the gravitational field of a body
Escape velocity equation and derivation
Ek = Ep
½mv² = GMm/r
v = sqrt(2GM/r), where r is the distance from the surface of the body
Kepler’s Third Law derivation
Assume a circular planetary orbit
Centripetal force to keep the planet in orbit is provided by the Gravitational Force between the Sun and Planet
F = mv²/r = GMm/r²
r³=(GM/4π²)T²
Therefore, r³ ∝ T²
K3’s Law for linear velocity:
v² = GM/r
v = 2πr/T
How does gravitational potential vary between the Earth and Moon?
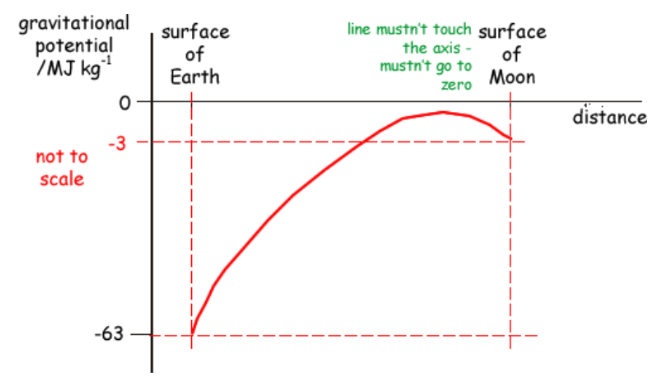
Change in gravitational potential formula + derrivation
Distance from r1 to r2
Vg1 = -GM/r1
Vg2 = -GM/r2
ΔVg = Vg2 - Vg1
= -GM/r1 + GM/r2
Total energy equation
Total energy = Ek + Ep
A satellite with mass 200kg has a velocity of 5.6 × 10³ ms^-1 and has a circular orbit of 1.28 × 10^7m around the Earth. Given the mass of the Earth is 6 × 10^24 kg, what is the potential energy of the satelite?
Ek = 1/2mv² = 3.14 × 10^9J
Ep = -GMm/r = -6.25 × 10^9J
T = Ek + Ep = -3.11 × 10^9J
Escape velocity is independent of:
Escape velocity is independent of mass
Gravitational field
A field created around any object with mass, extending to infinity but diminishing as distance from the centre of mass increases
Gravitational field strength
The gravitational force exerted per unit mass to a point within a gravitational field
Gravitational field lines
Lines of forced used to map gravitational field patterns around an object with mass
Radial field
A symmetrical field that diminishes with distance from its centre, eg a gravitational field around a sphere
Point mass
A mass with negligible volume
Uniform gravitational field
A gravitational field where the field lines are equidistant, parallel and the value of the gravitational field strength is constant
Newton’s law of gravitation
The force between two masses is directly proportional to the product of the masses
The force between two masses is direction proportional to the square of the separation between them
F = -GMm/r²