A&P Quiz 10 (Ch 28 pt 3)
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
94 Terms
Uterine Tubes
extend from area of the ovary to the uterus, aka fallopian tubes and oviduct, at the superior border of the broad ligament, open directly into the peritoneal cavity, receives the secondary oocyte after ovulation
Mesosalpinx
portion of the broad ligament directly associated with the uterine tube
4 Regions of Uterine Tubes
infundibulum
ampulla
isthmus
uterine (intramural) part
Infundibulum
expanded region of uterine tubes near opening (ovary)
Fimbriae
long thin process surrounding the opening of the infundibulum, lined with ciliated mucous membrane to help move oocytes into uterine tube
Ampulla
portion of the uterine tube near the infundibulum, widest longest part of the tube, location where fertilization usually occurs
Isthmus
portion of the uterine tubes nearest the uterus, narrower with thicker walls
Uterine (Intramural) Part
portion of uterine tubes that passes through the uterine wall and ends in a very small uterine opening
3 Layers of Uterine Tube Wall
serosa
muscular layer
mucosa
Serosa of Uterine Tube Wall
outer layer formed by the visceral peritoneum
Muscular Layer of Uterine Tube Wall
middle layer of longitudinal and circular smooth muscle cells
Mucosa Layer of Uterine Tube Wall
inner layer consisting of mucous membrane and simple ciliated columnar epithelium, arranged into numerous longitudinal folds, provide nutrients for the oocyte or developing embryo, cilia help move small amounts of fluid and the oocyte or embryo through
Uterus
size and shape of a medium sized pear, 7.5 cm long and 5 cm wide
4 External Regions of Uterus
fundus
body
isthmus
cervix
Fundus
larger rounded superior part of uterus
Body
main part in the middle of the uterus
Isthmus
slight constriction at the junction between the body and the cervix of the uterus
Cervix
narrowed inferior part of the uterus, lined with columnar epithelium
3 Internal Regions of the Uterus
uterine cavity
cervical canal
uterine ostium
Uterine Ostium
internal region of the uterus that opens into the vagina
Anteverted
tipped slightly anteriorly, describes the normal state of the uterus
4 Uterine Supports
broad ligament
round ligament
uterosacral ligament
skeletal muscle of the pelvic floor
Broad Ligament
supports uterus, peritoneal fold extending from the lateral margins of the uterus to the wall of the pelvis, surrounds and supports the ovaries and the uterine tubes
Round Ligaments
supports uterus, extends from the uterus through the inguinal canals to the labia majora
Uterosacral Ligaments
supports uterus, attach the lateral wall of the uterus to the sacrum
3 Layers of Uterine Wall
perimetrium
myometrium
endometrium
Perimetrium
serous layer, visceral peritoneum covering the uterus
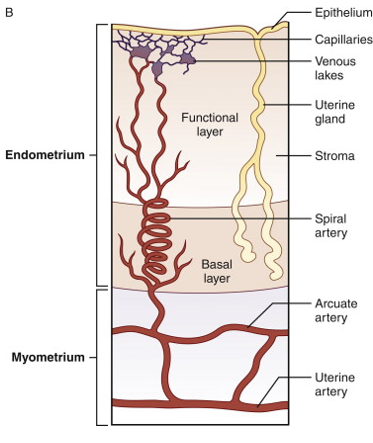
Myometrium
muscular middle layer of uterine wall, composed of thick layer of smooth muscle, accounts for bulk of uterine wall, thickest layer of smooth muscle in the body, less smooth muscle and more dense connective tissue in the wall of the cervix
Endometrium
inner layer of uterine wall, mucous membrane composed of simple columnar epithelium and connective tissue (lamina propria)
4 Things Found in Endometrium
spiral glands
basal layer
functional layer
spiral arteries
Spiral Glands
in endometrium of uterus, simple tubular glands scattered in the lamina propria and opening through the epithelium into the uterine cavity
Basal Layer
in endometrium of uterus, deepest part of the lamina propria continuous with the myometrium
Functional Layer
in endometrium of uterus, thicker layer consisting of most of the lamina propria and endothelium lining the uterine cavity
Spiral Arteries
in endometrium of uterus, small vessels of the lamina propria that supply the functional layer that are important in the cycle changes
Uterine Wall Diagram
Cervical Mucous Glands
found in the lining of the cervical canal, secrete mucous that fills the cervical canal and act as a barrier to substances from entering the uterus, around ovulation the mucus consistency changes to make it easier for sperm to enter the uterus
Vagina
female organ of copulation, receives penis during intercourse, allows menstrual flow and childbirth, 10 cm long
3 Features of Vagina
columns
rugae
fornix
Columns
longitudinal ridges extending the length of the anterior and posterior vaginal walls
Rugae
several transverse ridges extend between the anterior and posterior columns of the vagina
Fornix
superior domed part of the vagina that is attaches to the sides of the cervix
2 Layers of Vaginal Wall
outer muscular layer
inner mucous membrane
Outer Muscular Layer
smooth muscle that allows the vagina to increase in size, accommodate penis during intercourse, stretch greatly during childbirth
Inner Mucous Membrane
moist stratified squamous epithelium forming a protective surface
Vaginal Wall
two layers, lubricating fluid passes through the epithelium into the vagina, increases during intercourse
Hymen
thin mucous membrane covering the vaginal opening (orifice), can completely close vaginal opening but must be removed to allow menstrual flow, usually perforated by one or several holes
Altered States of Hymen
can be enlarged during first sexual intercourse, can be perforated by activities such as strenuous physical exercise
Vulva (Pudendum)
female external genitalia, consists of 4 regions
4 Regions of Vulva
vestibule
labia minora
clitoris
prepuce
Vestibule
region of vulva, space into which the vagina (posterior) and urethra (anterior) open
Labia Minora
region of vulva, long thin longitudinal skin folds that form the border on each side of the vestibule
Clitoris (simple)
region of vulva, small erectile structure at the anterior margin of the vestibule
Prepuce
region of vulva, fold of skin covering the clitoris where the labia majora unite
Clitoris
less than 2 cm in length, consists of a shaft and distal glands, contains numerous sensory receptors to initiate and intensify levels of sexual sensation
Corpora Cavernosa
two erectile tissue structures of the clitoris, expansion in diameter allows for better contact between clitoris and prepuce for stimulation
Crus of the Clitoris
formed by expansion bases of the corpora cavernosa that attach to the pelvic bones
Bulb of the Vestibule
erectile tissue lies deep to and on the lateral margins of the vestibular floor of either side of the vaginal orifice, expansion causes narrowing of the vaginal orifice allowing for increased contact of vagina and penis during intercourse
Female External Genital Glands
secrete fluid into the vestibule to prevent drying
2 Glands of Female External Genitalia
greater vestibular glands
lesser vestibular (paraurethral) glands
Greater Vestibular Glands
ducts on either side of the vestibule between the vaginal opening and the labia minora
Lesser Vestibular (Paraurethral) Glands
small mucous glands located near the clitoris and urethral opening
Labia Majora
two prominent round folds of skin, lateral to the labia minora, composed of subcutaneous adipose tissue, untie anteriorly to form the mons pubis over the pubic symphysis, lateral surface (and mons pubis) are covered with coarse hair, medial surfaces covered with numerous sebaceous and sweat glands
Pudendal Cleft
space between two labia majora, usually closed as the labia majora are in contact
Perineum
divided into two triangles by superficial and deep transverse perineal muscles
2 Triangles of Perineum
urogenital
anal
Urogenital Triangle
region of perineum that contains external genitalia
Anal Triangle
region of perineum that contains anal opening
Clinical Perineum
region between the vagina and anus, can be torn during childbirth
Episiotomy
incision in the clinical perineum
4 Regions of Breast
nipple
areola
areolar glands
suspensory (cooper) ligaments
Nipple
region of breast, raised external structure surrounded by the areola, highly sensitive to tactile stimulation, contains smooth muscle cells that contract causing the nipples to become erect in response to stimulation (touch, cold, sexual arousal)
Areola
region of breast, pigmented region
Areolar Glands
region of breast, just below the surface of the areola that create slightly bumpy surface, rudimentary mammary glands, secretions lubricate and protect the nipple and areola during nursing
Suspensory (Cooper) Ligaments
region of breast, support and hold the breast in place, extend from fascia over the pectoralis major muscles to the skin over the mammary glands to prevent excessive sagging
Breast Before Puberty
general structure is similar in both males and females, have rudimentary glandular system of mainly ducts and few alveoli
Breast During Puberty
female breast enlarges under influence of estrogen and progesterone
Gynecomastia
enlargement of male breasts
Mammary Glands
organs of milk production, located within breasts, modified sweat glands, 15-20 glandular lobes covered in adipose tissue, form conical mass with nipple at the apex, lobes are divided into lobules supplied by smaller ducts
Lactiferous Duct
one in each lobe of the mammary glands, opens on the surface of the nipple
Lactiferous Sinus
enlarged region of the lactiferous duct just deep to the surface that accumulate milk during lactation
Alveoli
secretory sacs at the ends of small ducts in mammary glands
Myoepithelial Cells
surround alveoli in mammary glands and contract to expel milk
In Nonlactating Glands
only duct system is present
Regulation of Female Reproduction
under hormonal and nervous control, hormones regulate development of female reproductive organs and their normal function
8 Hormones of Female Reproduction
estrogen
progesterone
gnrh
fsh
lh
prolactin
ncg
oxytocin
Estrogen Derivatives
includes estradiol, estrone, estriol
GnRH in Female Reproduction
stimulates production of fsh and lh
LH in Female Reproduction
causes follicles to complete maturation and undergo ovulation, causes ovulated follicle to become the corpus luteum
FSH in Female Reproduction
causes follicles to begin development
Prolactin in Female Reproduction
stimulates milk secretion following childbirth
Estrogen in Female Reproduction
causes proliferation of endometrial cells
causes development of mammary glands
development of secondary sexual characteristics
positive feedback before ovulation that increases lh and fsh secretion
negative feedback after ovulation that decreases lh and fsh secretion
Progesterone in Female Reproduction
causes hypertrophy of endometrial cells and secretion of fluid from uterine glands, helps maintain pregnancy
causes development of mammary glands
has negative feedback effect after ovulation that decreases lh and fsh secretion
causes development of secondary sexual characteristics
Oxytocin in Female Reproduction
causes contraction of uterine smooth muscle during intercourse and childbirth, causes contraction of myoepithelial cells in breast resulting in milk letdown
Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) in Female Reproduction
maintains corpus luteum and increase its rate of progesterone secretion during the first trimester of pregnancy, increases testosterone production in testes of male fetuses