Geology 104 Final -(SDSU)
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Hydrologic Cycle
Is the recycling of water among the 4 earth reservoirs:
- Atmosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Lithosphere
- Biosphere
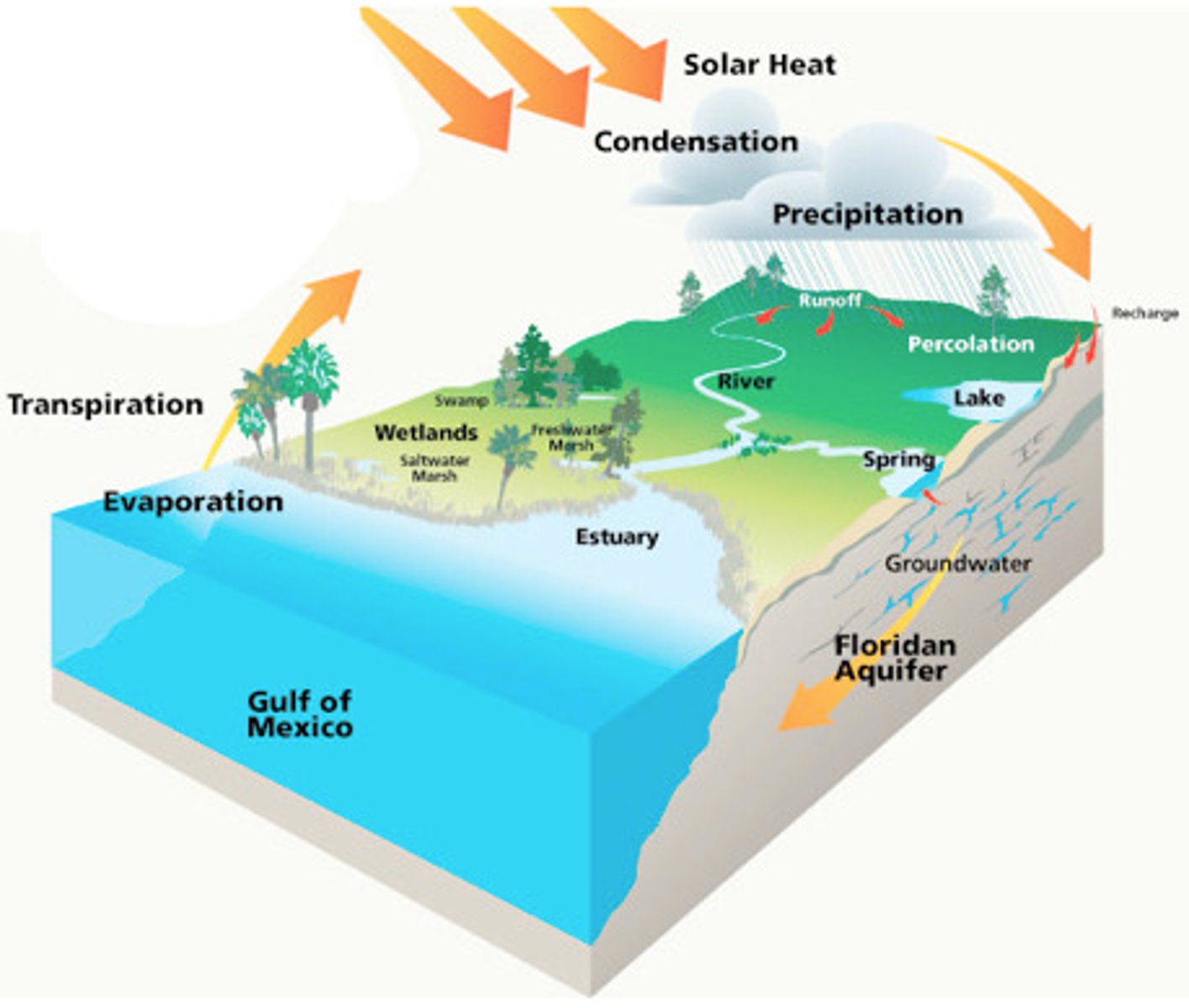
Phase change of Evaporation.
Evaporation: liquid to gas, heat is absorbed
Phase change of Condensation.
Condensation: gas to liquid, heat is released
What drives the weather?
- Sun
- Oceans
- Atmosphere
- Rotation of the earth
- Uneven solar absorption
Why is solar radiation strongest around equatorial regions?
Right angle
Solar Radiation
Strongest at the equator because it comes in at 90 degrees.
A) At Polar Regions-
Sun- low angle, large area, reflection- ice reflects solar radiation back to space. (Heat deficit: in these regions more heat is radiated back to space than is received in earth).
B) At Equatorial Regions-
Sun- high angle, small area, absorption of heat; oceans store heat. (Heat surplus: in these regions heat is retained in the atmosphere through the trapping of infrared radiation in the atmosphere; less heat is radiated back to space).
Composition (what gases make up the atmosphere?)
- N2 (Nitrogen) ~ 78%
- O2 (Oxygen) ~ 21%
- Ar (Argon) ~ 0.9%
- CO2 (Carbon Dioxide) ~ 0.04%
Temperature
Temperature decreases with altitude (height)
- Troposphere = all weather is created, "over turn" = air undergoes convection hot air rises (less dense), cold air sinks (more dense)
- Lowest part of the atmosphere at 12 km
- Jetliners fly in the troposphere to avoid weather
Density
How close together molecules/ atoms per 1 unit of volume
- warm air - less dense - rises into the atmosphere
- cold air - more dense - sinks to the earth's surface
Water Vapor
- warm air - humid, less dense, so air rises
- cold air - dry, denser, so air sinks
Pressure
- Low pressure (L)- light column of air (air rises); rainy/ cloudy weather, attract warm moist air, molecules are loosely packed and diverge (apart)
*Equatorial regions
- High pressure (H)- heavy column of air (air sinks); good weather, attracts cool/ dry air, molecules are tightly packed and converge (together)
*Subtropical regions
- Air goes from high to low to equalize weather
- Movement of air from H to L = winds (horizontal motion of air)
Air Pressure (how does it change with altitude?)
Pressure lowers as altitude increases, the column of air is going to be less; air molecules are fewer and are closer to the earth because of gravity
Convection Cell
*rises at the equator = high pressure system, less dense
Equator: (warm humid, no winds)
- Warm moist air - rises =
- Low air pressure; expands - cools =
- Condensation - clouds =
- Heat released
- Weather: rain, instability
* warm air rises; cool air sinks
Hadley Convection Cell
Is an atmospheric circulation pattern in the tropics that produces the easterlies (or trade winds)
- warm moist air rises up into the atmosphere at or near the equator, flows towards the poles (air cools) above the surface of the earth, returns to the earth's surface in the subtropics (30 degrees) and flows back towards the equator
- What latitudes? equatorial- subtropical, Deserts
(Sahara, Mojave)
What's going on at the equator?
- Warm moist air rises
- Low pressure air expands and cools down (cool air)
- Condenses into clouds as heat is being released into weather of clouds and rain
What's going on at 30 degrees North/ South?
(Top of Troposphere; subtropical)
- Cold, dry air- more dense - sinks - high pressure - air compresses and warms causing hot, dry weather
ex. San Diego: high pressure (no moisture),
between 30 - 60 degrees
Prevailing Winds
Originate at the subtropical high (~30 degrees northeast)
- Trade (Easterlies), east to west: Flow east towards the equator
- Westerlies, west to east: Flow west towards the poles
* Air that circulates north/ south of the equator is cold and dry
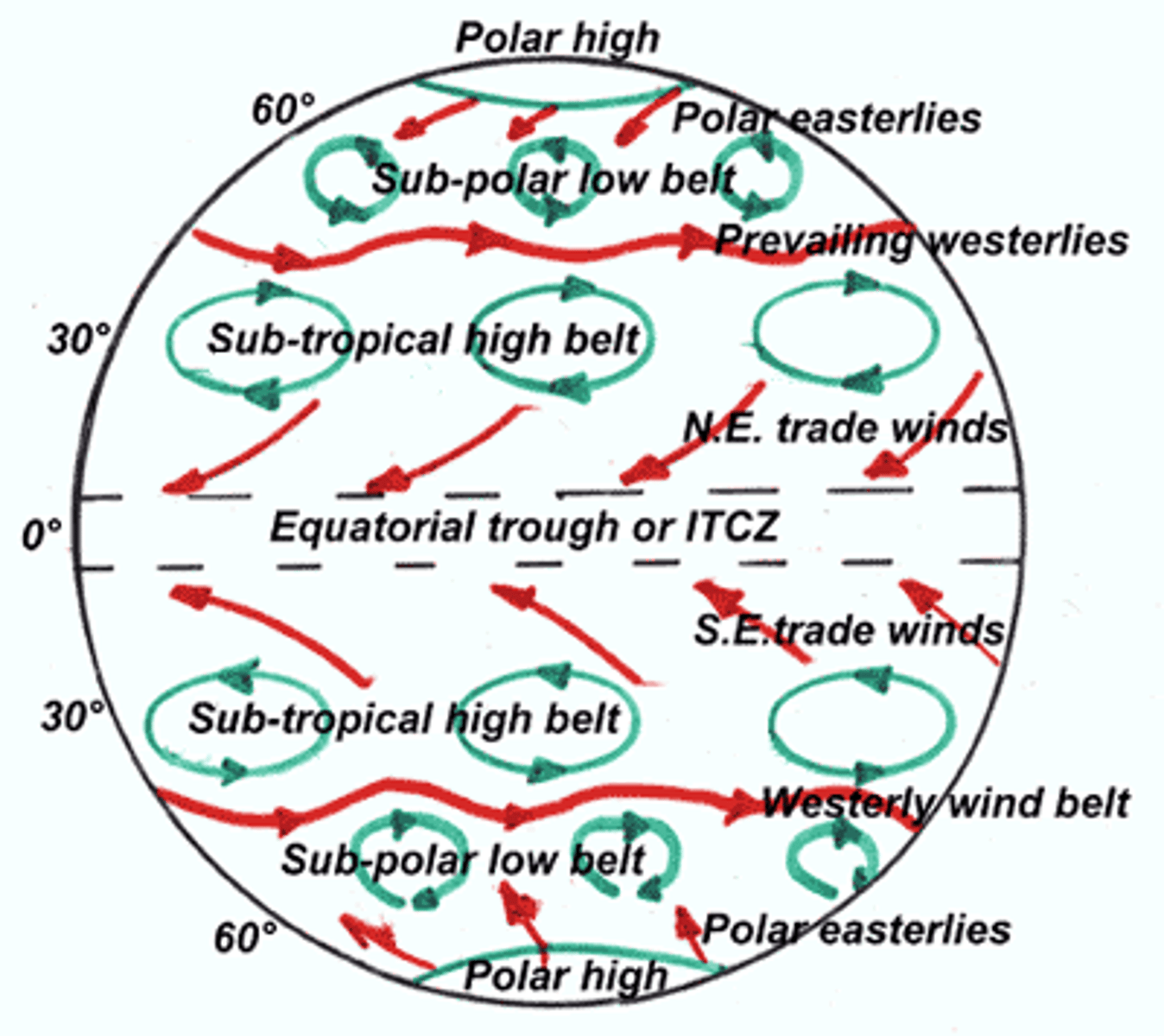
What helped Christopher Columbus travel to and from the Americas?
Easterlies to (sailed south), Westerlies from (sailed north)
The Coriolis Effect
Earth's rotation moves objects to the right in the northern hemisphere; veers to the right.
* at the equator, minimum (no movement)
* at the poles, maximum
Global Air Circulation
Trade winds = east to west; Gulf Stream - north (west of a continent, east of ocean basin)
Westerlie winds = west to east, CA Current - south (east of continent, west of ocean basin)
Cyclones (Hurricanes)
Spinning low pressure systems; rising, rotates counter- clockwise
- clouds, rain thunderstorms
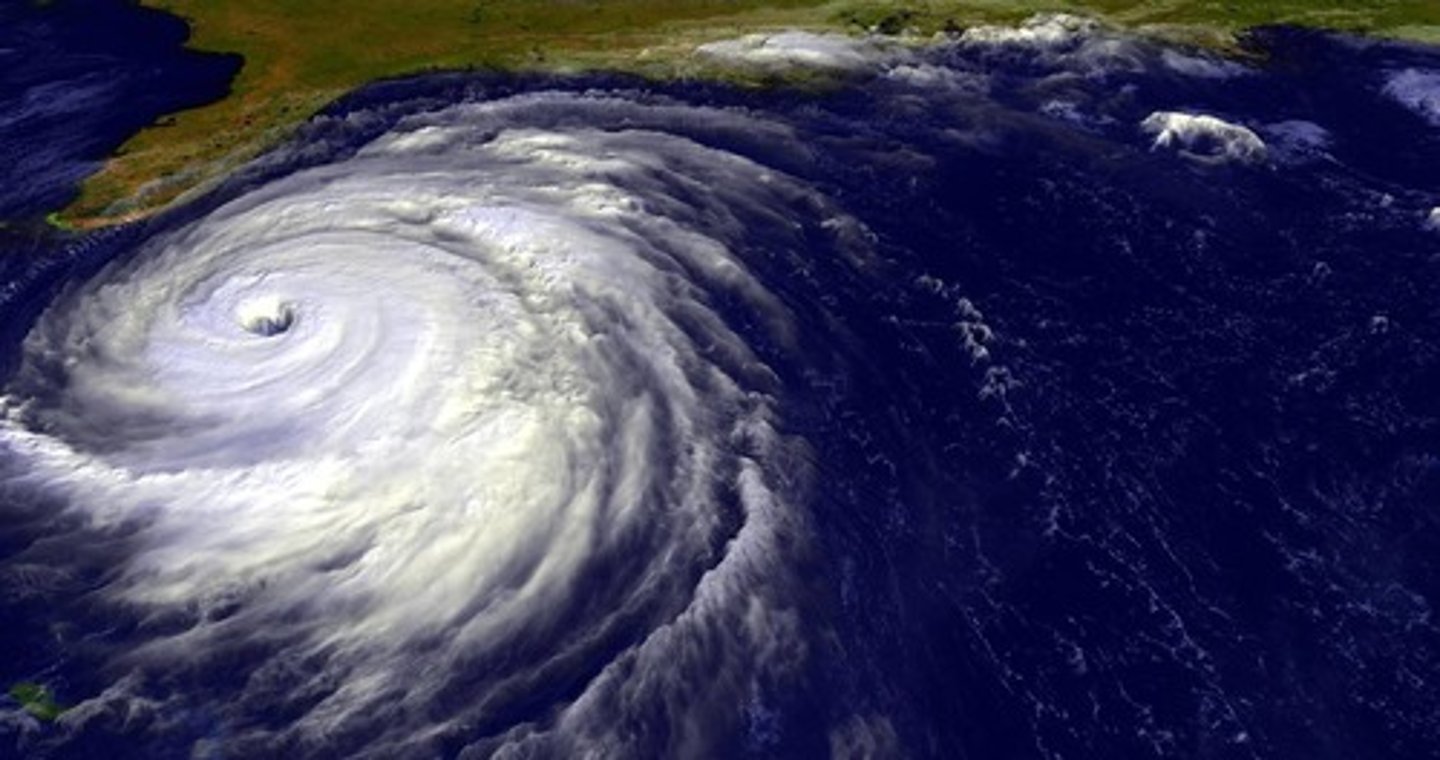

Anticyclones
Spinning high pressure systems; sinking, clockwise
- dry, look outside dry air!
California
* The Santa Ana Winds:
High pressure system (dry) from the high deserts flowing west; the air is sinking to the earth's surface heating up and diverging
Note: The California Firestorms, 2003, 2007 (wildfires), smoke goes to the oceans; land to sea (blew east to west)
Rainfall in California.
Mountains at the coast; Air that is moist goes up (rises) = low pressure system
- Along the many mountains of the state because the air is lifted against them, and condensation then occurs as the air cools
It rains the least in the south...
Orographic Lifting
Marine air moving against mountains; moist air moves up the windward (ocean) side of the mountain... the air cools, forms clouds, and rains, leaving the leeward (desert) side dry.
Windward (west)
Wet, ocean, rain on the west (forests)
Leeward (east)
Dry, desert
Rain shadow desert
on the east side of the mountains, due to clouds being unable to go over the top of mountains, they do not receive rainfall
ex. Death Valley- cold, dry air sinks- compressed heats up [kinetic energy]
Average Annual Percipitation
- Northern CA at the coast, higher latitude
- Mountains, Sierra Nevada
- No rain in the Mojave or Colorado desert
(subtropical latitudes- air is sinking = high pressure system; rain shadow desert)
Desert
An area that receives less than 10 inches of rain per year.
Life in deserts? Yes!
Hottest deserts on earth? at subtropical latitudes, right around 30 degrees where air sinks = high pressure system = dry climate
ex. Atacama desert, Chile
Coldest? South pole- continent with the ice sheet
Death Valley
Hottest, Driest, Lowest place on earth!
*Deepest area: 85 m below sea level = 280 ft (tectonically controlled- strike-slip fault)
- Faults on either side of the mountains
- Rifting apart, by faults (not a plate boundary)
High Temperature: 57 degrees celsius (134 degrees Fahrenheit)
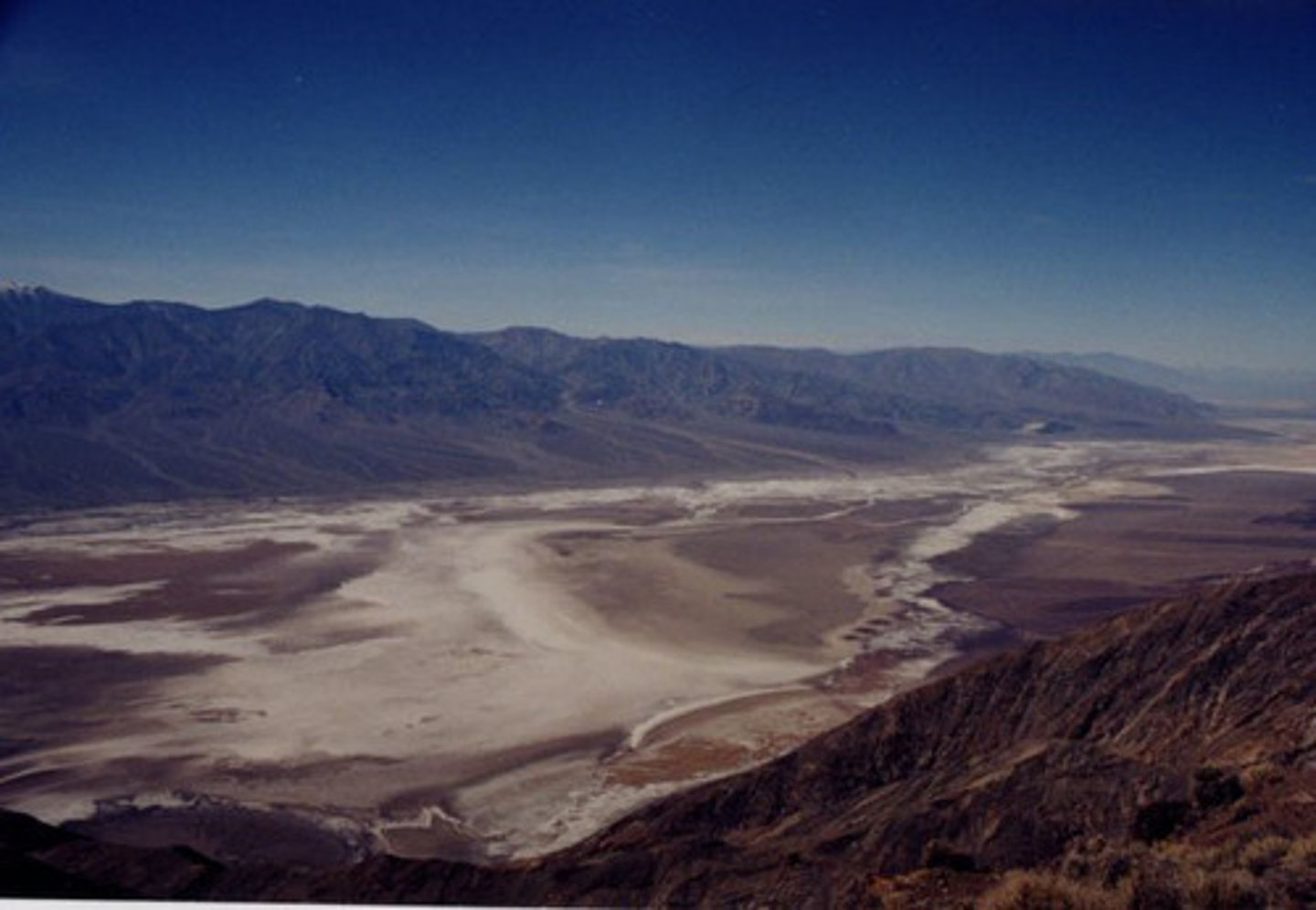

Death's Valley Famous Landmarks
- Telescope Peak, vertical range
- Artists Palette Formation
- Mesquite Sand Dunes (sandstone from mountains)
- Salt Flats, sodium chloride
- Devil's Golf Course, salt pinnacles
- Racetrack Playa- ice push
5 Main Types of Deserts: Subtropical
High pressure systems (30 degrees)
air sinking/ heating
Ex. Sahara
5 Main Types of Deserts: Continental
Interior of continents
Climate = harsher when farther from the ocean (moderate climate)
No heat capacity, very dry
Ex. Gobi- Mongolia *high desert
5 Main Types of Deserts: Rain shadow
Leeward side of mountains (dry side to the east)
Moist air gets blocked by the mountains
Ex. Mojave, Joshua Tree
5 Main Types of Deserts: Coastal
Dry winds, cold currents, no moisture *CA current
Ex. Atacama, Chile (Lamas)
Peruvian Current, South America
5 Main Types of Deserts: Polar
Cold, dry air
Ex. Antartica, Canada, Siberia
Penguins: sea birds, swim!!
Hurricanes
Is a tropical cyclone, meaning it is a storm forming at the tropical regions and spinning very fast counter-clockwise = low pressure system (air is rising)
*Based on winds and warm water
(26 degrees celsius = 78 degrees fahrenheit)
- Northern Hemisphere: counter-clockwise
- Southern Hemisphere: clockwise
Most hurricanes: Atlantic (east), Gulf Stream provides a source of warm water)
* Do not cross equator- no wind, no Coriolis
Source of power: Very powerful- heat energy absorbed (ocean surface, evaporation) and released (condensation)
Ex. Tropical cyclone Ita, Australia, 2014
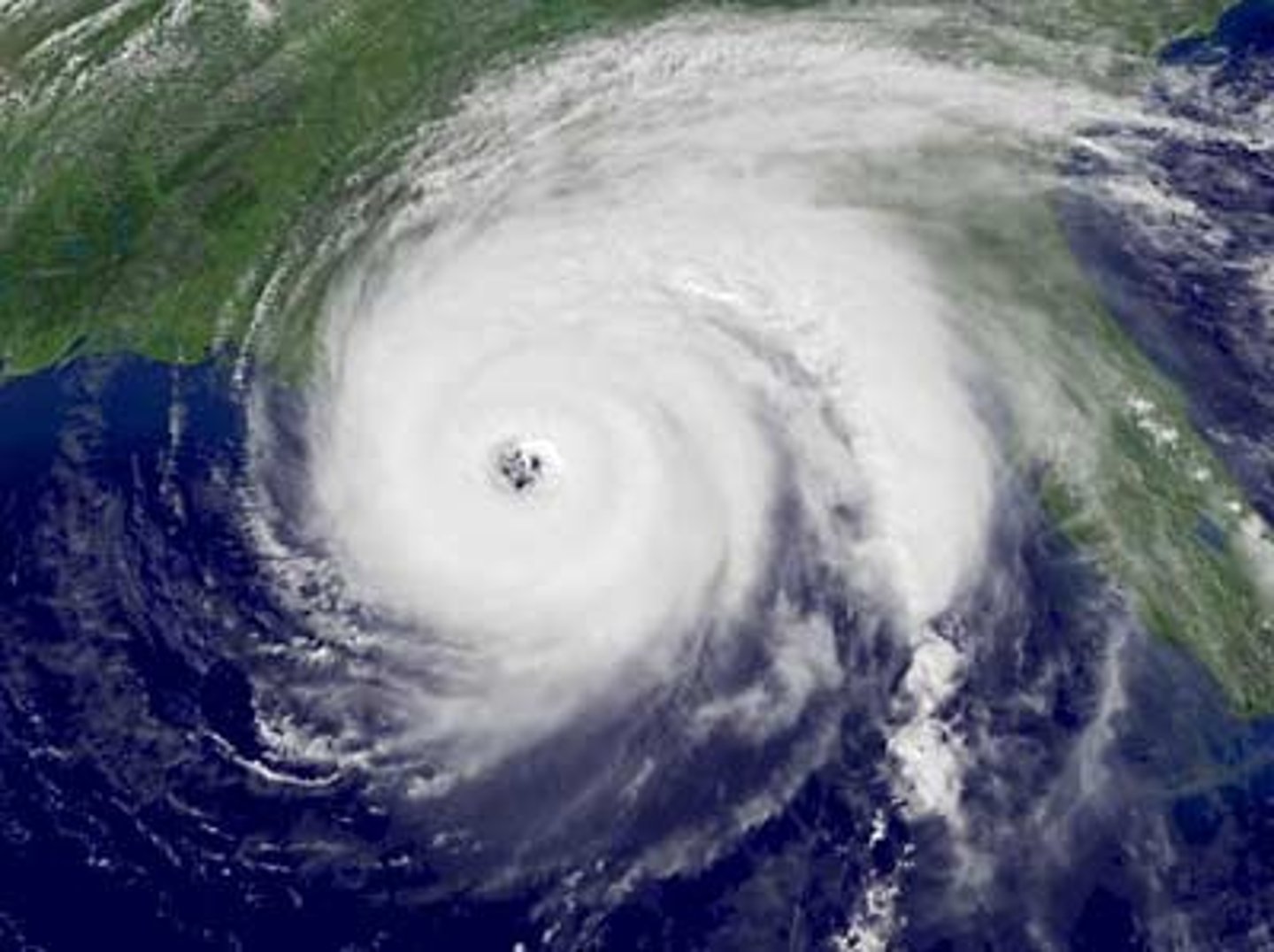

Hurricane Season
Late Summer and Fall:
- Depend on warm seas = fuel
- Summer solstice, June
- Oceans = high heat capacity (long time to heat, long time to cool)
- Oceans absorb heat; release their energy
USA Eastern Seaboard
Gulf Stream = warm, humid
Storms move east to west = easterly winds
Why do hurricanes dissipate on land?
Cut off heat source; goes from warm to cool
Storm Surge
Waves go inland; rise sea level above the tides, caused by strong winds (from hurricane) that push water to shore = flooding
Why would such large waves form?
Lots of energy, fast winds
Ex. Hurricane Sandy, 2012
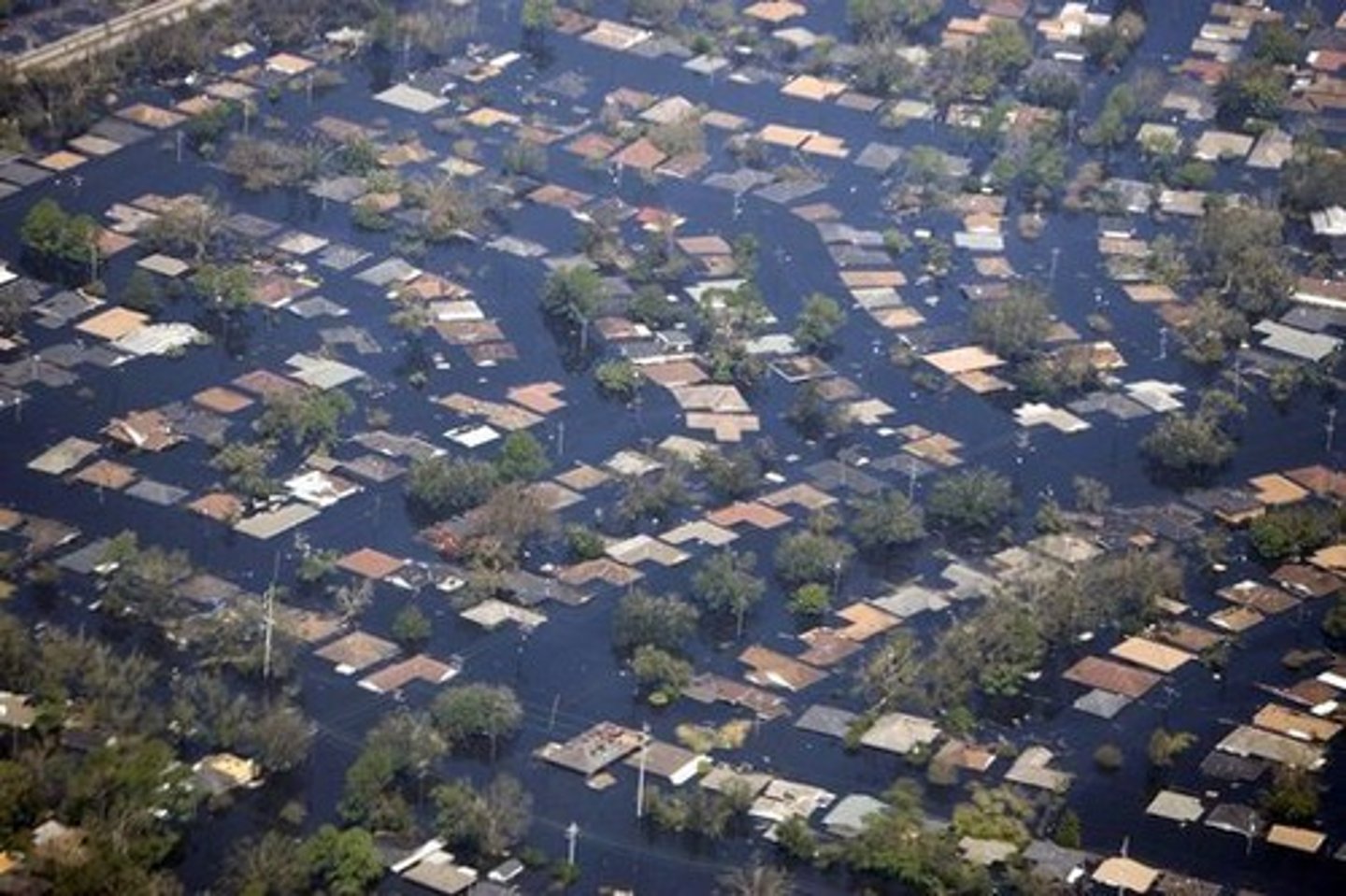
Hurricane Katrina
*Counter-clockwise
Devastating to New Orleans?
The city is on very high flat ground, therefore exposed to high sea; passive margin (no tectonics, broad shelf)
*Is on a delta; Mississippi river below sea level- sea level rising, city sinking (by 4 - 5 meters)

World Climates
Is weather the same as climate? No!
Weather
State of the atmosphere in a given place and time
*SD= high pressure
- What you see outside; 75 degrees and sunny
Climate
Average weather conditions in a region
*SD= warm/ dry = mediterranean mid latitude
- Snow in the northeast in January
Humid Tropical
Warm, rainy - vertical movement of air; low pressure (air is rising)
- equator (warm = less dense)
Dry
Hot, low rain - high pressure system (air is sinking)
Humid Mid-Latitudes, Mild
Temperature; mild winters,dry summers (moderated by ocean)
Ex. Mediterranean
Humid Mid-Latitudes, Severe
Cold severe winters
- Continental interiors
Ex. North America, Siberia, Northern Europe
Polar
Cold, dry
Mediterranean Climate
West coasts
California, Southern Europe
Humid Tropical Climate
Iquitos Peru (No seasons)
- Rain
Dry Climate
Tindouf, Algeria
Exmouth, Australia- 30 degrees latitude; subtropical
- No rainfall
- Temperature = 100+ degrees Fahrenheit
Mid-Latitude Mild: Mediterranean Climate
San Francisco, Ca
Portugal
Mid- Latitude Severe Climate
Duluth, Minnesota
Siberia, Russia
* Rain, cold
Polar Climate
Barrow, Alaska
Greenland
* Tundra, frozen (cold)
* No rain
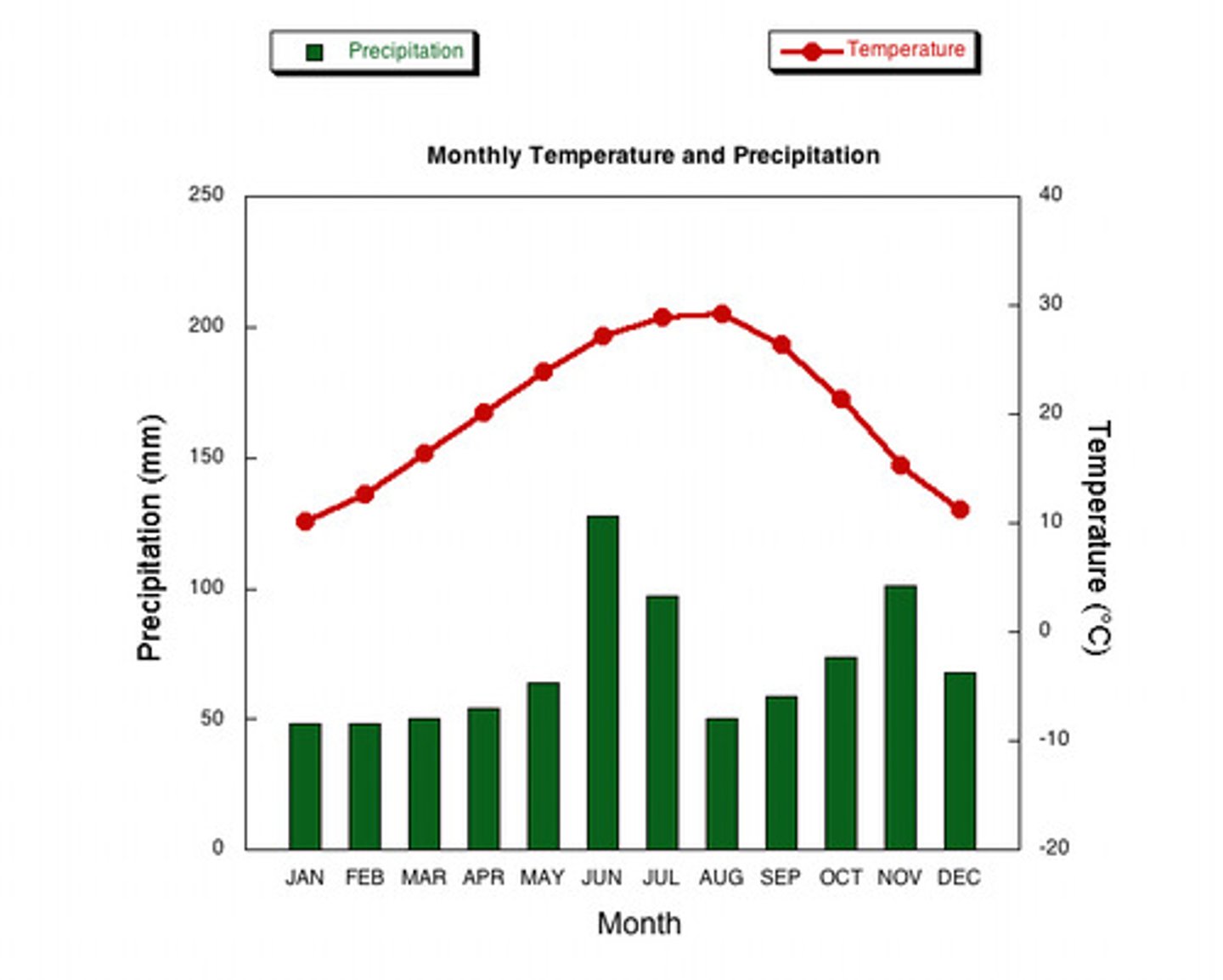
Climograph
Shows climate (average climate conditions)
x-axis - precipitation; rain fall (bar graph, blue)
y-axis - temperature (line graph, red)
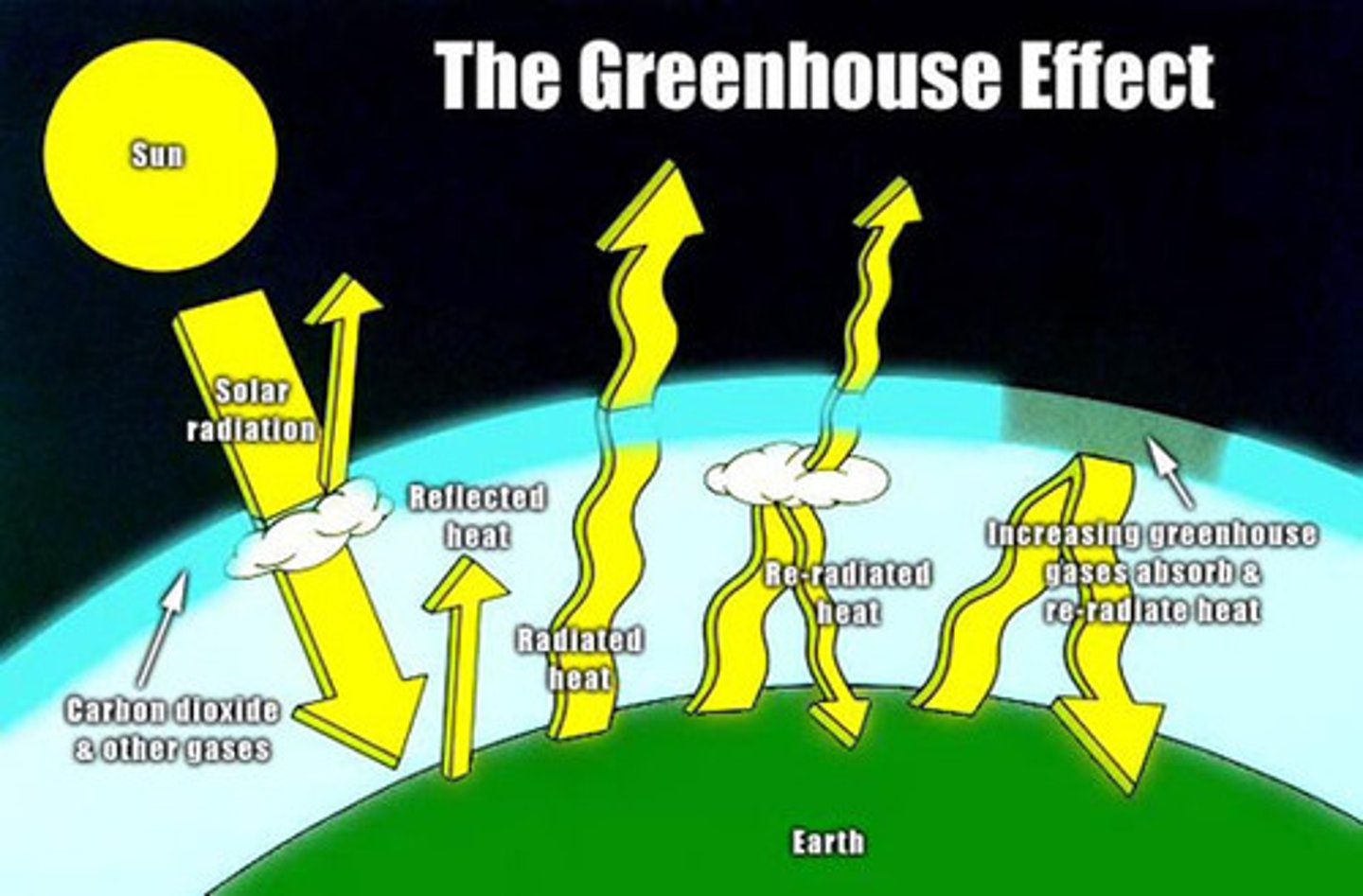
The Greenhouse Effect
The earth radiates infrared radiation; the atmosphere blocks this radiation because greenhouse gases don't let it escape into space. It therefore, re-radiates back to earth's surface keeping it warm.
*Life! plants
Most abundant greenhouse gases.
H2O- Water Vapor
CO2- Carbon Dioxide
CH4- Methae
N2O- Nitrous Oxide
O3- Ozone; Stratosphere- warmer
- Absorb infrared radiation
Temperature Record
Increased in last 100 years (positive slope)
* Temperature increased by 0.85 degrees celsius (130 years) = 33.53 degrees fahrenheit
Carbon Dioxide Record
CO2 increased by 40%, Human Activities (by 35%)
- oceans absorb a lot of heat and CO2 (+70%)
Greenhouse warming
Increase in heat- oceans and atmosphere = ice melts
note: warmer in the northern hemisphere, ice retreats of glaciers
- melting ice
- sea level rise; 1 m per year
- severe weather
- hurricanes
- drought (interior of continent)
- extinctions of organisms *polar bear
Muir Glacier, Alaska
1941- glaciers were advancing; downstream, growing faster than melting
2014 - glaciers are retreating; upstream, melting in the Summer
CO2 emissions by country (populous nations)
Rich-Poor
-China
-US
-Europe
-India
What is going on in the arctic?
Absorption/ Reflection, no sea ice (platform on the ocean; North Pole, Arctic)
If the ice melts, the ocean will heat up faster; oceans are warming as ice melts
Ex. Greenland melting faster than anticipated
- melt ponds; water on top of ice = not stable; sink below the ice and lubricates the ice sheet below it; accelerates the transport of ice to the ocean.
- water is denser; ice is less dense = sinks
Last 2 million years.
Glaciations and Inter-glaciations
*Trend is to cool
* 20 ice ages followed by increasing warmth
Movement of Antarctica?
65 million years ago
Dinosaurs
Triassic, Jurassic, Cretaceous
* Antarctica to the pole = colder
Last 60 million years.
Overall temperature trend is cooling
Today
Rapid warming
Manmade (burning of fossil fuels: oil, coal, natural gas)
Evidence of Climate Change: Climate Proxy's
- Deep sea sediments/ fossils - climate
- Rock evidence
- Ice cores - trapped gases
- Tree rings - determine age
Why was the climate so warm in Mesozoic?
Volcanic activity = greenhouse gases (H2O, CO2)
Tectonic Activity
250- 65 million years: warmer climates
Intense volcanoes, Mantle super plumes
- CO2 much higher
- Temp. ~ 10 degrees celsius higher