Middle ear anatomy and physiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
consists of
-inner skin of TM
-closed middle ear space lined with mucous layer and surrounded by porous mastoid bone
-Eustachian tube close otherwise forced open
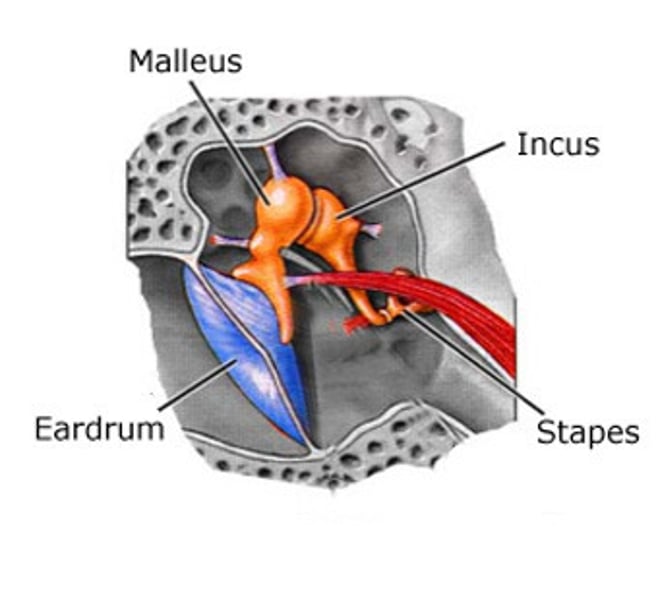
-middle ear ossicles: malleus, incus, stapes, ligaments
-two muscles: stapedius VII facial nerve, tensor tympani V trigeminal nerve
closed middle ear space is about
2cm3
Soft mastoid portion- houses outer ear canal, mastoid bone (air pockets)
Hard petrous portion- houses most of middle ear space and cochlea
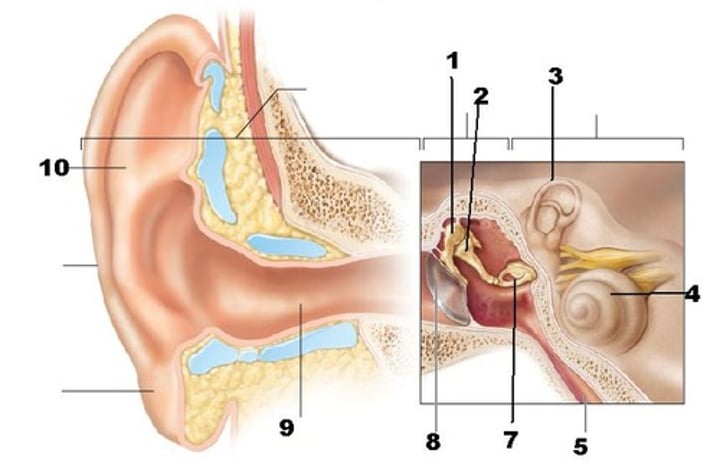
mucous membrane
lines entire space (including inside of TM and Eustachian tube)
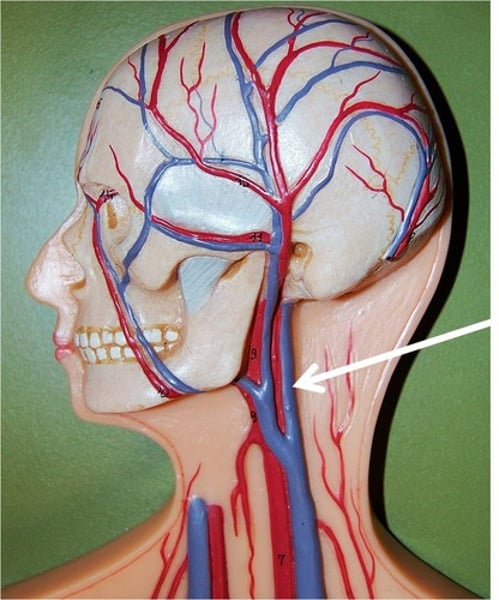
jugular vein
lies just below floor of middle ear space
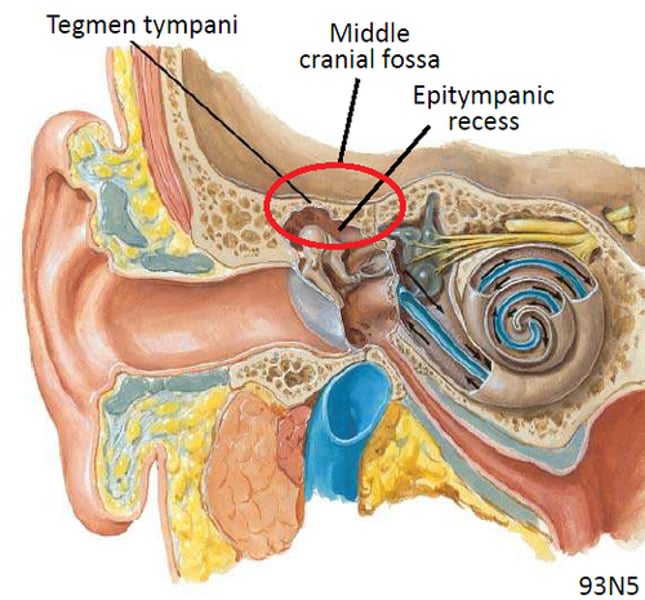
epitympanic recess
middle ear space just above TM and malleus
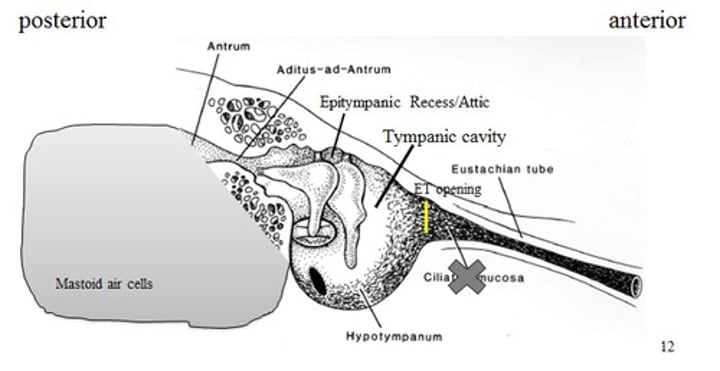
aditus ad antrum
area just above incus and stapes (more medial than epitympanic recess) mastoiditis begins here
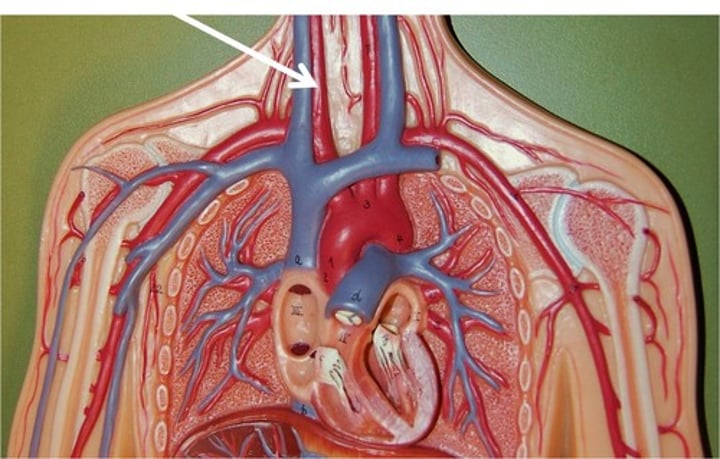
carotid artery
sits behind anterior wall (not in overhead)
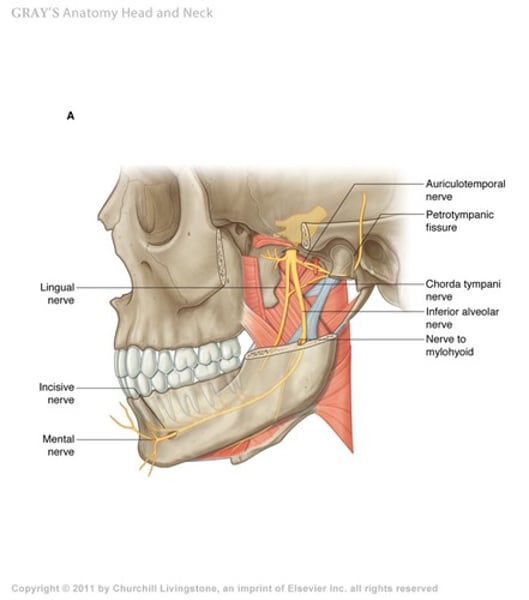
chorda tympani nerve
branch of VII facial nerve that passes through middle ear space
-can get in way of middle ear surgery
-carries taste info 2/3 one side of tongue
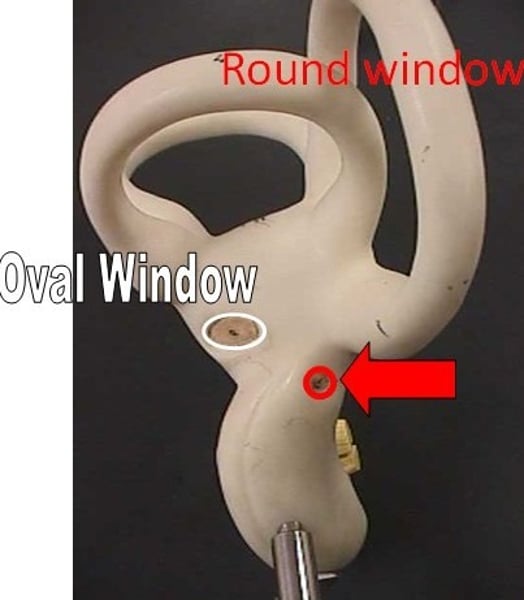
oval window
filled by footplate of stapes
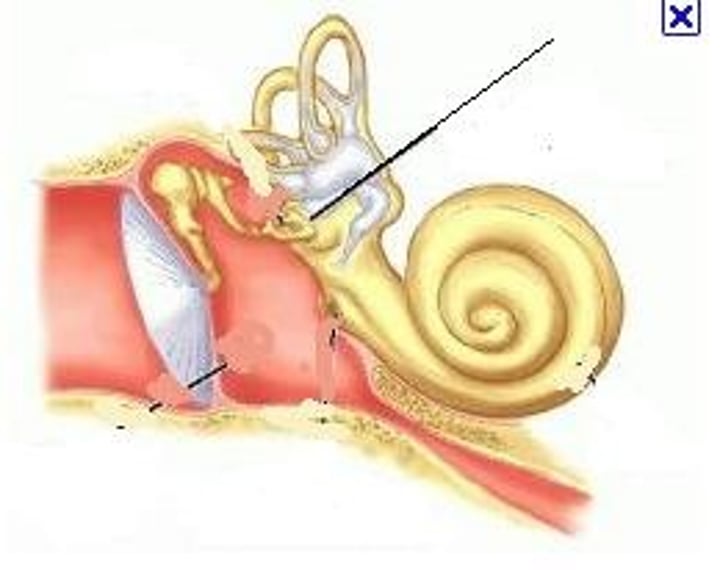
round window
covered by tough membrane
promontory
landmark bump between oval and round windows
Eustachian tube
connects middle ear to throat
cilia mucous lining move particles down
-closed unless swallowing, yawning, blowing nose
-opens once/min while awake and 1/5min when asleep
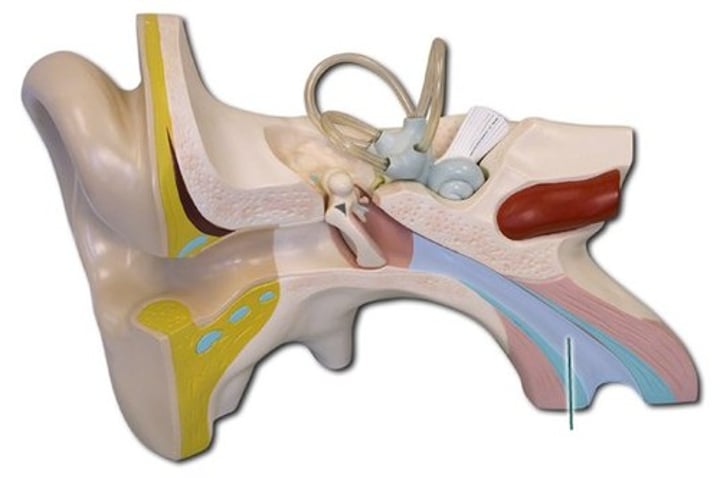
Air pressure must be
EVEN ON BOTH SIDES of TM for middle ear to work optimally middle ear mucous lining absorbs o2
-alleviates negative pressure
malleus
manubrium embedded in TM extends from umbo to top of TM
incus
long process and short process are the 2 main landmarks
stapes
head attached to incus
crura attached to footplate
footplate in oval window
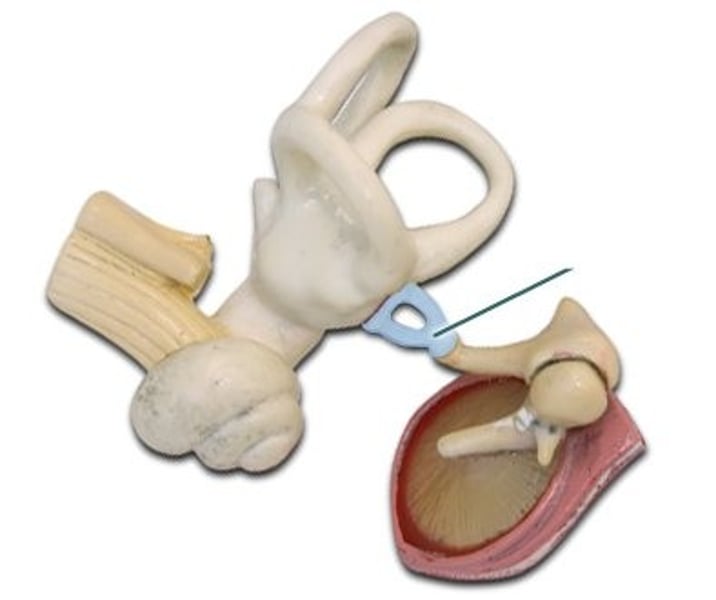
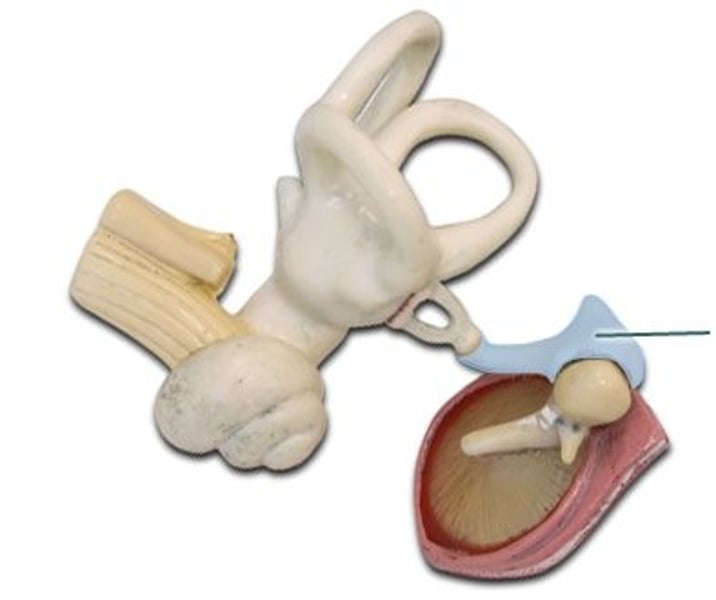
ligaments
extend from walls of middle ear space to hold ossicles in place
stapedius muscle
7mm long, goes from posterior wall of middle ear space to neck of stapes
-innervated by V11 facial nerve- STRONGEST 2 MUSCLES
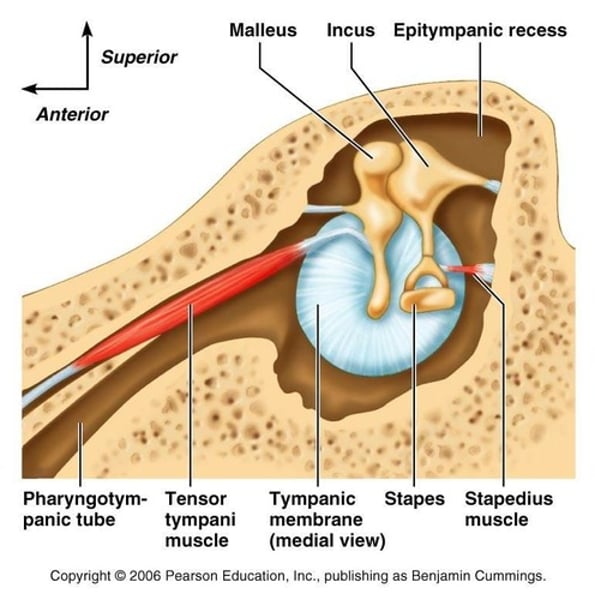
tensor tympani muscle
25mm long inserts into manubrium of malleus
innervated by weaker mostly sensory cranial nerve V or trigeminal
Physiology #1
air pressure has to be equal both sides of TM for middle ear to do job
-TRANSDUCES or changes vibration energy of sound into mechanical energy
ROCKING MOTION of footplate
Physiology #2
OVERCOMES IMPEDANCE MISMATCH
-as sound goes from AIR TO FLUID of cochlea
-EX swimming pool head under water CANT HEAR
AIR BORNE SOUND has to activate fluid filled cochlea
-or else loss of energy 99.9% (30-35dB)
Rinne tuning fork test
compares clients own HL by AC and BC
-what middle ear adds
normal ear should hear tone louder when fork is outer ear
1. area of TM (-) larger than footplate of stapes
17 times
17:1
2. leverage action
of ossicles increase force from TM to footplate by ratio
1.3:1
3. buckling action of TM
2:1
combine of increase SPL at oval window
is 44:1
17 x 1.3 x 2 = 44.1