GCSE WJEC Biology- response and regulation of the body
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
negative feedback → blood glucose level rises
pancreas releases insulin into blood → body cells absorb more glusoce + liver absorbs glucose and stores it as glycogen → blood gucose level declines
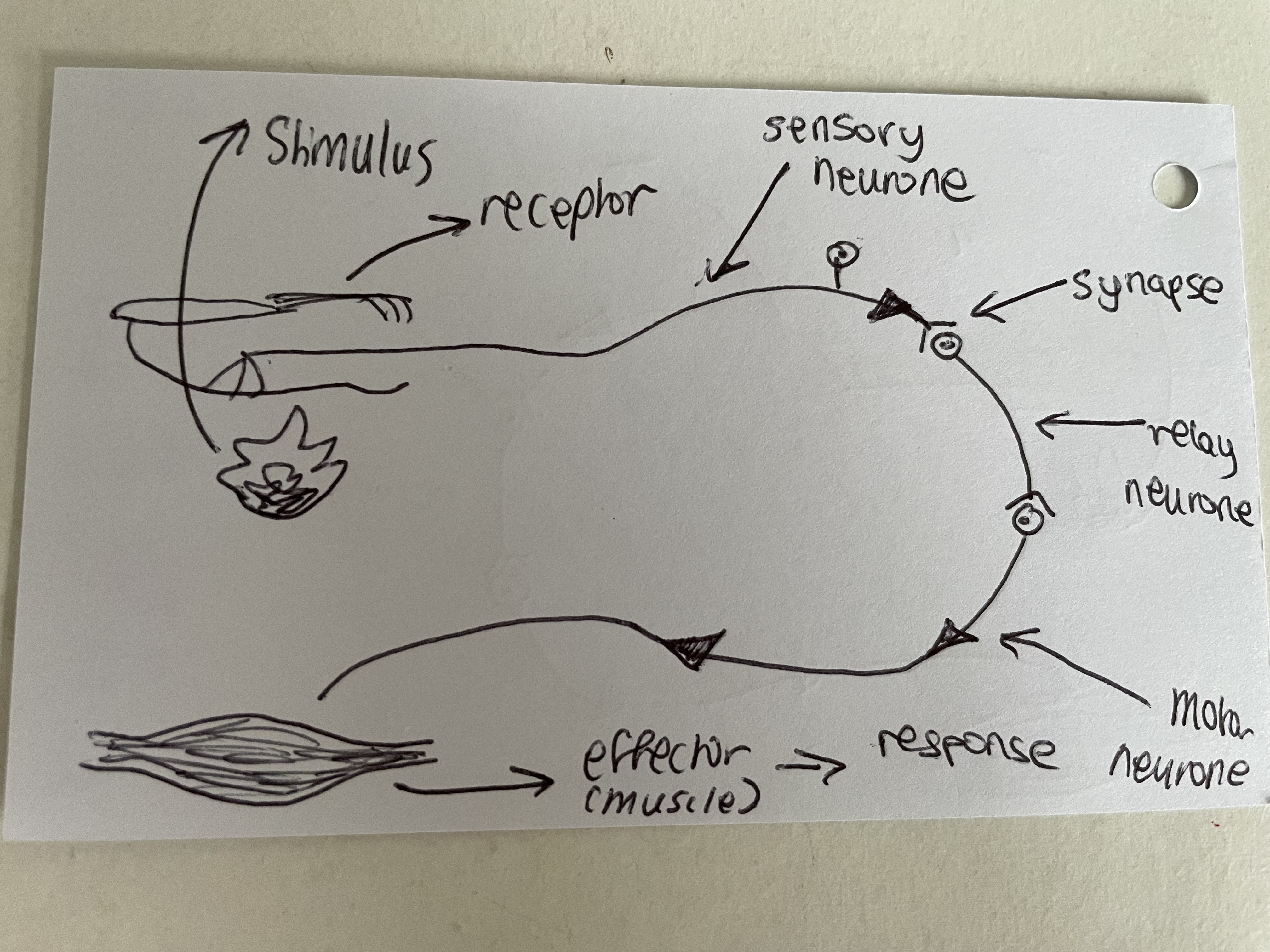
sense organ
groups of nerves
stimuli
specific changes in the environment
type 1 diabetes cause
body not producing insulin
type 2 diabetes cause
body cells not properly responding to insulin that’s produced
properties of reflex actions
fast
automatic
protective
stimuli examples
light + sound + touch + temp + chemicals
hormones
chemical messengers carried by blood control many body functions
negative feedback → blood glucose level falls
pancreas release glucagon travels to liver → converts glycogen to glucose → blood glucose level rises and returns to optimum
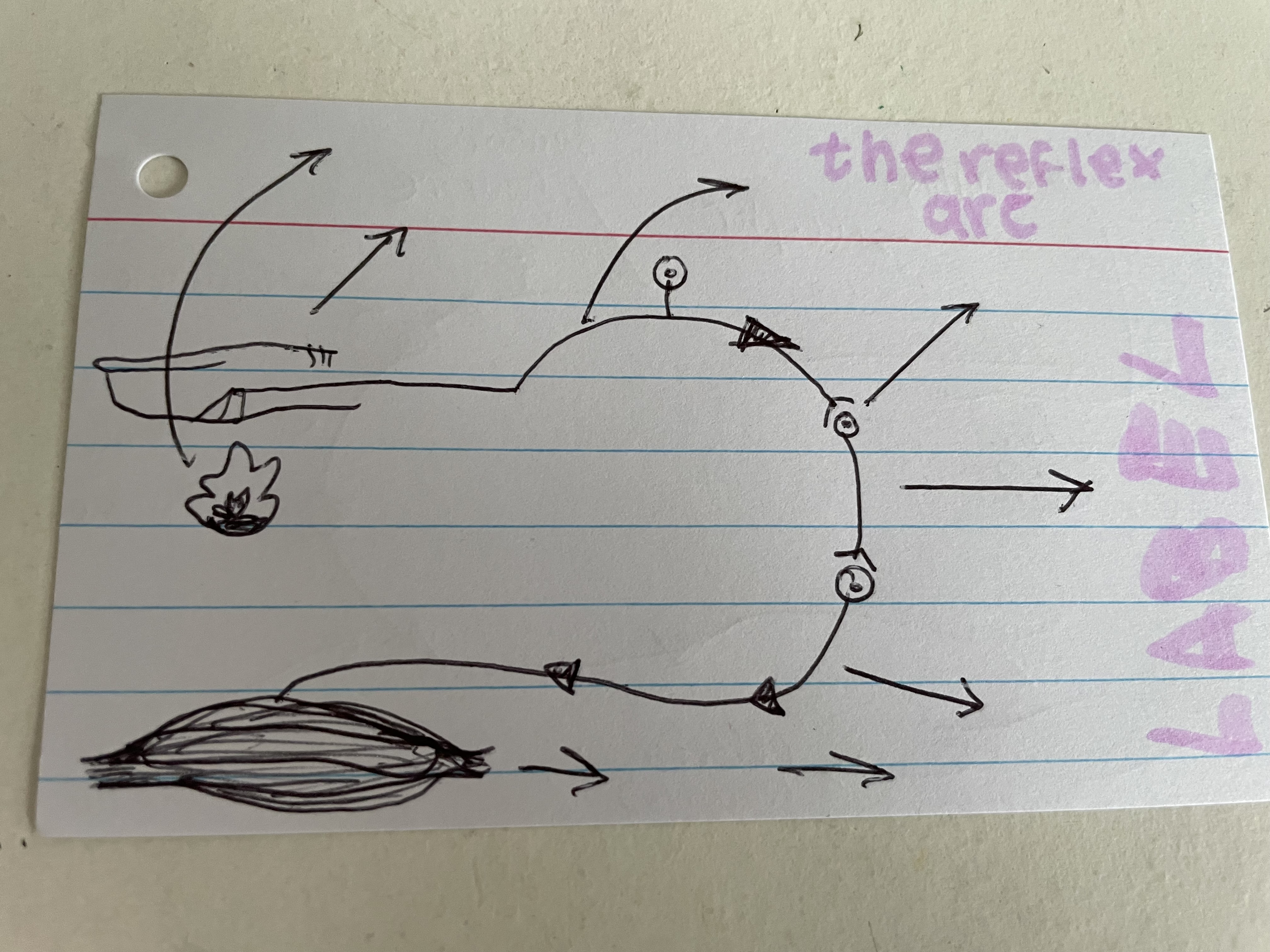
sense organs send information along specialised cells called … to the … in the form of …
sense organs send information along specialised cells called NEURONES to the CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM in the form of ELECTRICAL IMPULSES
synapse
point where 2 neurones meet + transfer information
response
reaction to a stimulus
effector (muscles/ glands)
carries out the response
effector/ motor neurone
carries nerve impulses to the effector- muscle
relay neurone
transfers a nerve impulse to the effector neurone
sensory neurone
carries nerve impulses to central nervous system
receptor
recieves the stimulus
central nervous system
brain + spinal cord
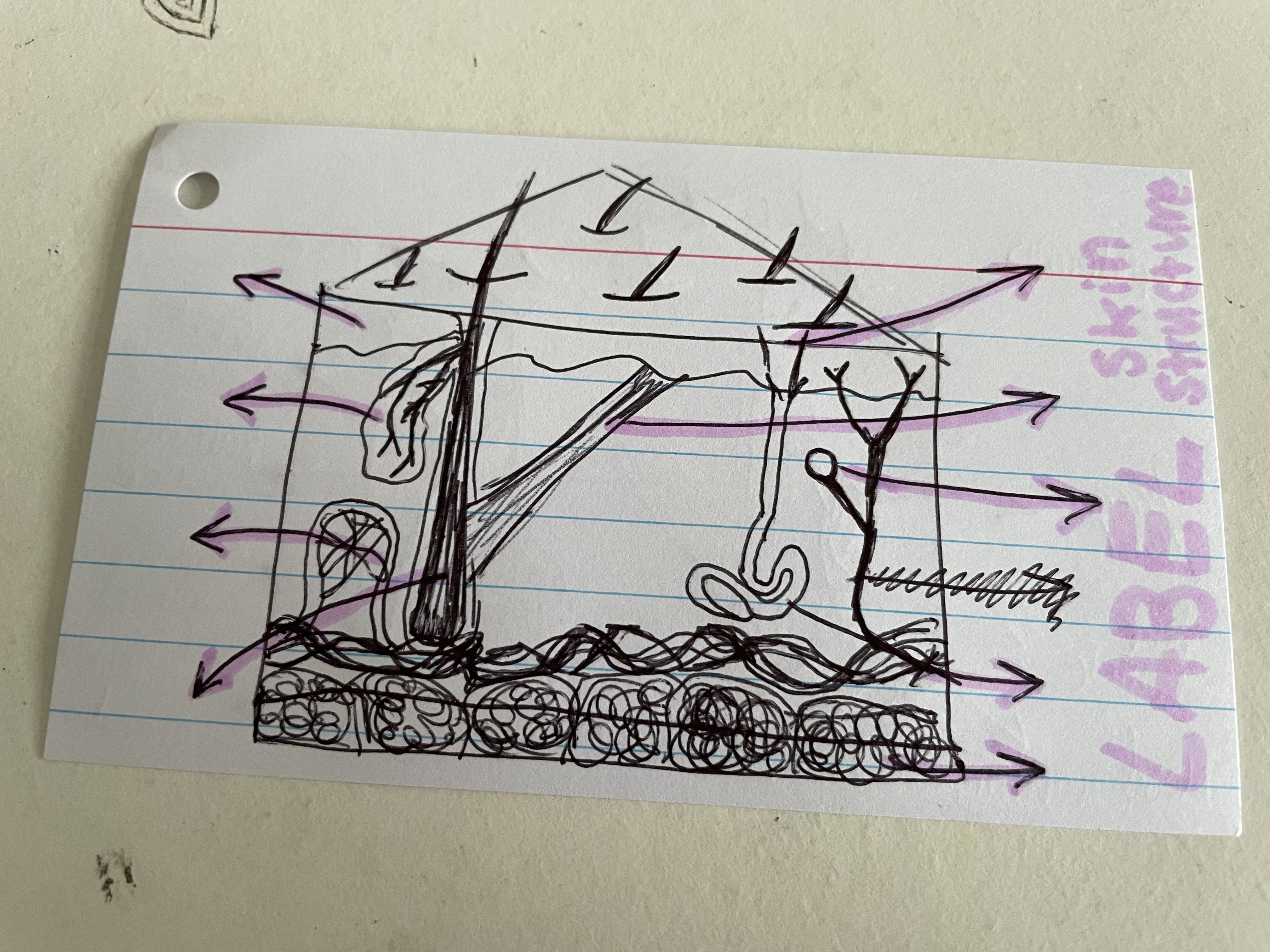
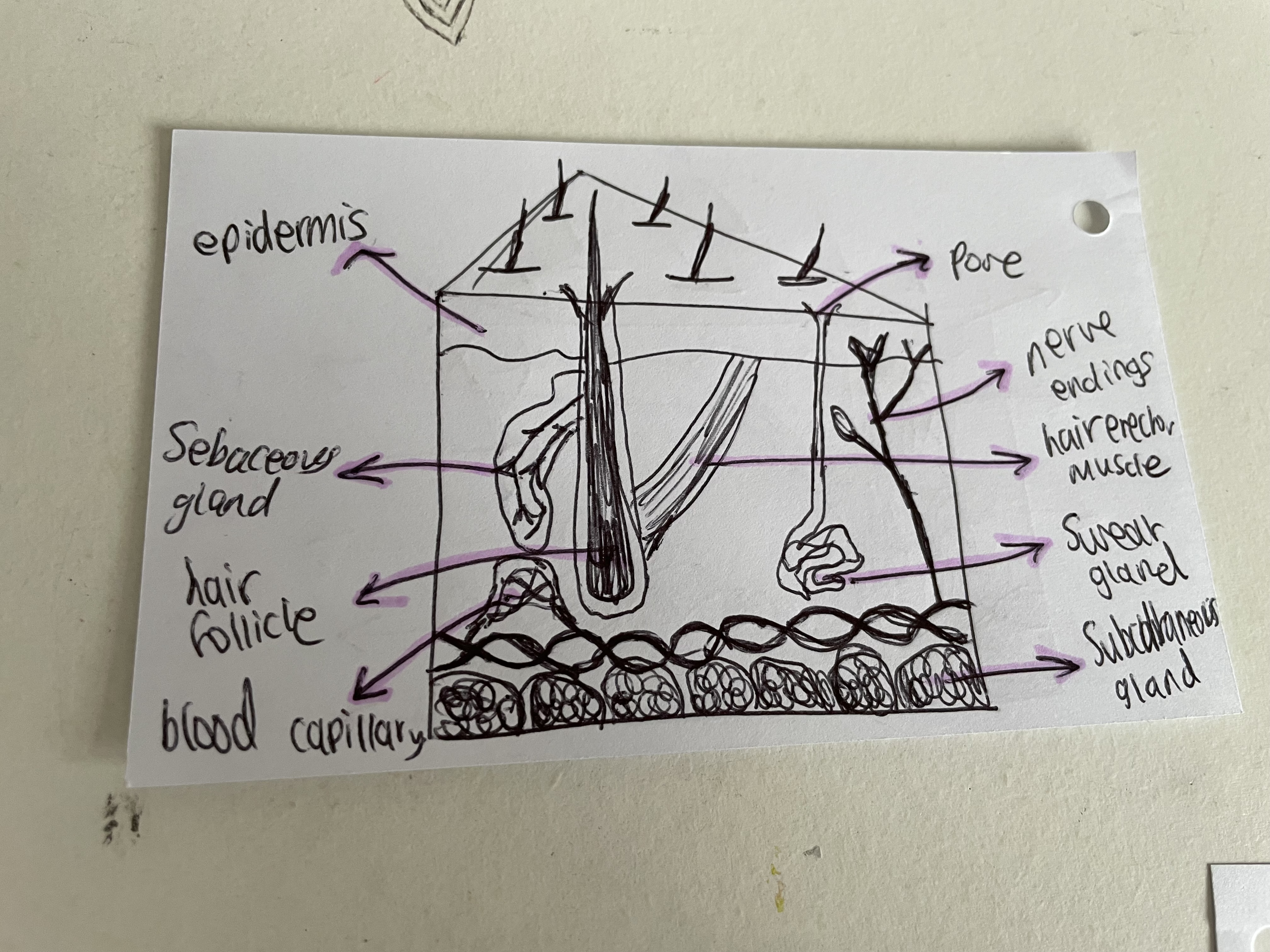
sweat gland
produces sweat to cool body when too hot
hair erector muscle
raises hair/ fur when body too cold
nerve endings
sensitive to different stimuli
pore
to let sweat get to surface of the skin
homeostasis
keeping internal environment constant no matter the external environment
sweat production in hot conditions
sweat pours onto skin surface evaporating taking excess heat from skin → cooler blood circulates and cools body (opposite in cold)
shivering in cold conditions
muscle contraction requires energy from respiration → releases heat to warm body (opposite in heat)
vasodilation in hot conditions
blood capillaries close to surface open up allowing more blood near surface → heat lost by radiation (opposite in cold- vasoconstriction)
erector muscle in cold conditions
contracts pulling hair upwards → traps a layer of air- insulates the skin (opposite in heat)
epidermis
layer of dead cells that protects the body
sebaceous gland
produces oily substance making hair + skin waterproof + reduces germ growth
blood capillary
carry blood and heat to surface of skin
hair follicle
a tube in the skin where a hair grows
subcutaneous gland
contains cells full of fat + oil to keep the body warm
insulin
REDUCES blood glucose levels when too high
controlling type 1 diabetes
control carbs eaten + inject insulin regularly
controlling type 2 diabetes
control carbs eaten + take tablets to reduce glucose level in blood
glucose is needed for
respiration
glucagon
INCREASES blood lucose levels when too low
alcohol effects
slows your reaction times + damages kidneys + liver


why glucose levels fall in a diabetic person
done exercise/ not eaten enough
negative feedback
a change from optimal internal conditions resulting in the body responding and restoring optimal conditions
factors controlled to maintain optimal conditions
temp + glucose + ph