Molecular genetics - Nucleic acids
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
DNA
deoxyribonucleic acid
what are nucleic acids?
chains of monomers called nucleotides joined by condensation reactions (polymerisation) (polymers)
what do viruses use as genetic material
RNA
What are the components of DNA?
a phosphate group
a nitrogenous base
phosphate group (phosphorus and oxygen) (attached to the 5 carbon)
What bond do nucleotide units use
and where is it between
Convalent bonds between the phosphate group of the 5’ C of one sugar and the hydroxyl group of the 3' C of the next sugar.
phosphodiester linkages
what are purines and what is their structure
they have two rings in their structure
guanine
adenine
what are pyrimidines and what is their structure?
they have one ring in their structure
thymine
cytosine
uracil
what base does RNA have that DNA doesn’t have
uracil instead of thymine
what is the structure of an RNA
Rna is composed of a ribose sugar, which means it has OH at the 2’ position.
covalent bonds form between nucleotides of RNA to make a strand
bonds between phosphate group of one 5’c and hydroxyl group on 3’C of another
what is the structure of dna nucleotides together called
doulbe helix
DNA polymer
what bonds are between the complementary bases?
hydrogen bonds to stabilize
adenine and thymine
guanine and cytosine
what term describes the direction of DNA strands?
antiparallel
is RNA double or single stranded?
SINGLE!!!
what is evidence of the common ancestor?
DNA is conserved in all forms of life
what does complementary base pairing allow for?
DNA retaining its sequence in replication stage of cell division
it ensures that the same protein is produced every time a gene is expressed
why does DNA replication occur in a 5’ to 3’ direction?
because DNA polymerase which catalyzes this reaction can only attached to the 3’ hydroxyl group
how do purines and pyrimidines stabilize the double helix
their lengths balance each other out so the pair is always the same length (always 3 rings length)
if mismatching occurs in replication it can be detected bc the pair is the wrong length
what is the name of the strand of DNA that links nucleosomes
linker DNA
what are nucleosomes
units of eukaryotic chromatin supercoiled to from chromosomes
DNA wrapped around 8 histone proteins and a special h1 protein
necessary form chromosomes to be properly sorted in mitosis and meisois
wen can DNA be accessed? (nucleosomes)
when the DNA is uncoiled and histones are moved out of the so that the DNA can be copied or transcribed
what did the hershey chase experiment conclude?
that dna was the genetic material and not protein
explain the hershey chase experiment
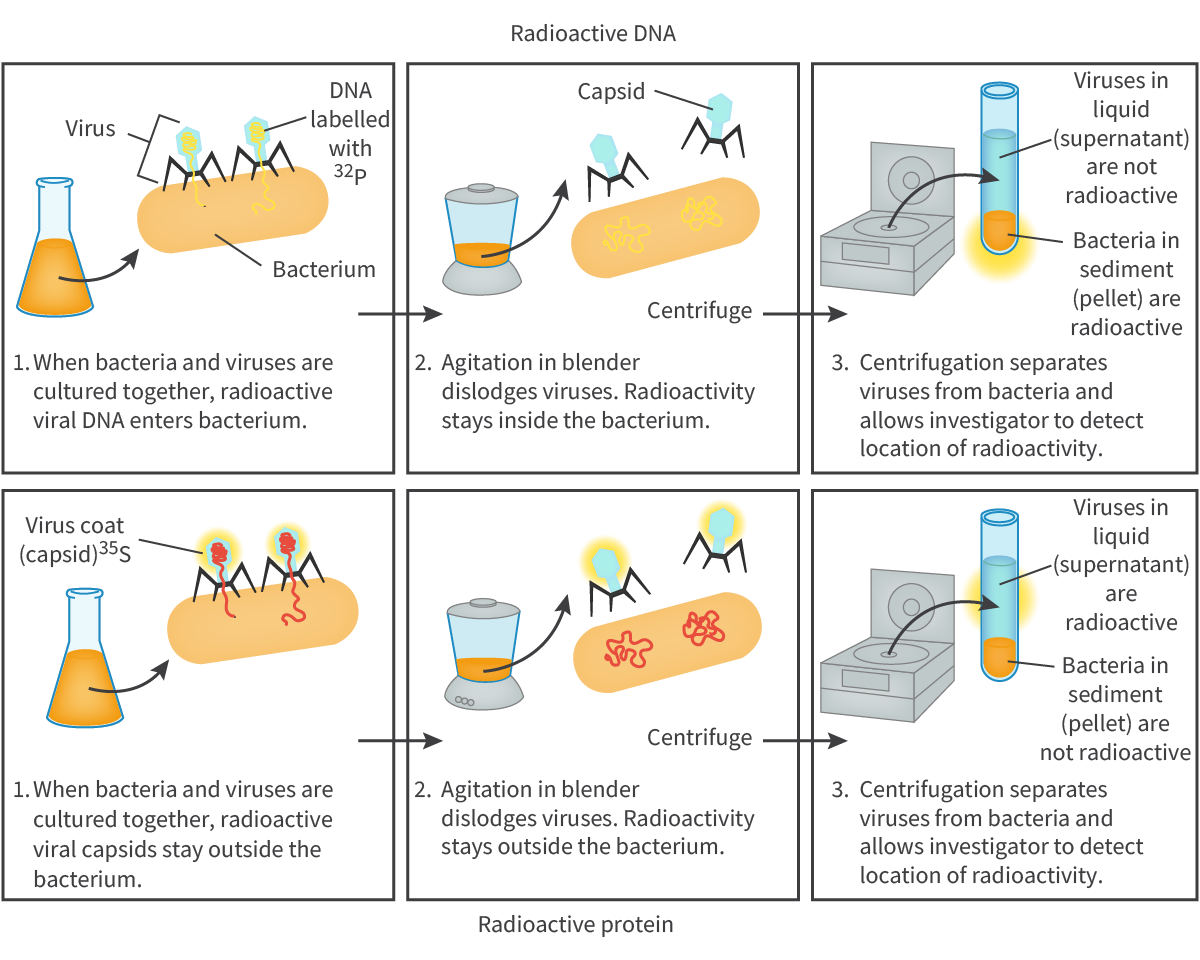
T2 bacteriophage used which inserts its genetic material (DNA) into bacterial cells but it’s protein coat stays on the outside
they labelled the protein with radioactive sulfur and the DNA with radioactive phosphorus
bacteriophages w radioactive phosphorus that infected other bacteria transmitted their radio-activeness
bacteriophages with radioactive sulfur had their virus coats removed by a blender and no bacteria was infected
Chargaff’s Rule
found that amounts of complementary base pairs were equal to each other
used paper chromatography to seperate the DNA and measure concentrations
falsified the tetranucleotide hypothsis (thought that DNA was single stranded with all 4 nucleotides equal)
when are nucleosomes held loosley/tightly
loose: normal activity
tight: cell division
why is DNA attracted to histones
because DNA is negatively charged and histones are positively charged