Excretion - Chp 31 nf
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Excretion
the elimination of metabolic waste from the body
Describe excretion in plants
stomata and lenticels excrete substances
during the day oxygen + water vapour are excreted
during the night carbon dioxide is excreted
What role do excretory organs play in homeostasis?
regulating body temperature
controlling osmosis
controlling the balance of body fluids
removing waste products
What are the excretory organs of the body + their functions?
Skin - excretes water and salts, regulates temperature
Lungs - excrete water vapour and CO2
Kidneys - excrete urea, water and salts
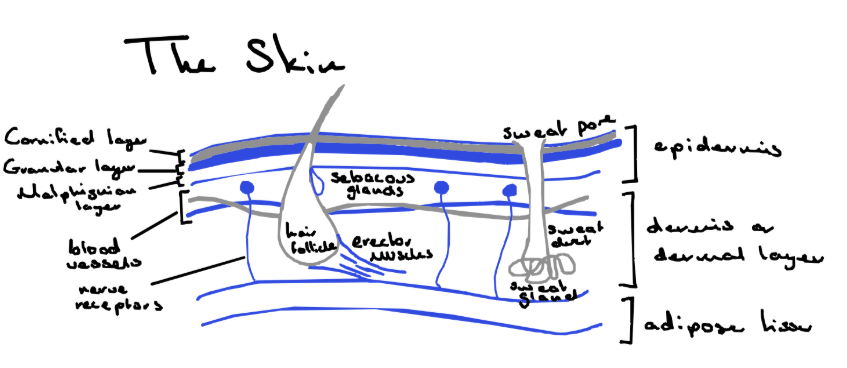
Diagram of the skin
Ectotherms
lose or gain heat from their external environment
Endotherms
generate heat from their own metabolic reactions
How does the skin regulate temperature?
When we are cold
piloerection - the erector muscle attached to each hair follicle contracts pulling the hair upright, this traps a layer of warm air close to the skin
vasoconstriction - blood vessels in the skin move away from the surface to preserve heat
When we are hot
hair lies flat on the skin, allowing heat to escape
vasodilation - The blood vessels expand to move towards the surface of the skin and get rid of excess heat
sweat - evaporation in a cooling process that takes away the excess heat from the skin
How does skin protect the body?
Melanin is a brown pigment produced in the cells in the Malpighian layer of the epidermis – this protects from harmful effects of the sun’s rays.
Keratin is a protein that is produced in the cells of the Granular layer of the epidermis – this creates a waterproof barrier.
Collagen is a strengthening protein found in the cells of the Dermis – this protects against damage day to day due to its elastic properties.
Sebum is produced in the sebaceous glands alongside every hair follicle – this protects the hair from damage and stops the skin from cracking and drying up.
What are additional functions of the skin?
produces vitamin D in the presence of sunlight
acts as a food and energy store in the adipose tissue
sensory organ
Overview of the urinary system:
consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, a urethra and associated blood vessels
filtration occurs in the outer cortex of the kidney, resulting the small substances both waste and useful are forced out of the blood
reabsorption occurs in teh cortex and medulla, allowing useful materials (glucose and amino acids) are taken back into the blood
secretion occurs in the cortex, and substances such as potassium and hydrogen ions are secreted into the cortex which helps control the blood pH
once all three processes are complete waste products are collected in the pelvic region and brough into the ureter to go to the bladder for storage
What is the bladder?
the bladder is a muscular organ that is not under voluntary control
we have control over the sphincter muscle
urine is sterile before it leaves the body, once it leaves it is subject to bacterial entities
What are the functions of the kidney?
The kidney has 3 functions:
Excretion
Osmoregulation - maintains a balance of salt and water
pH Control
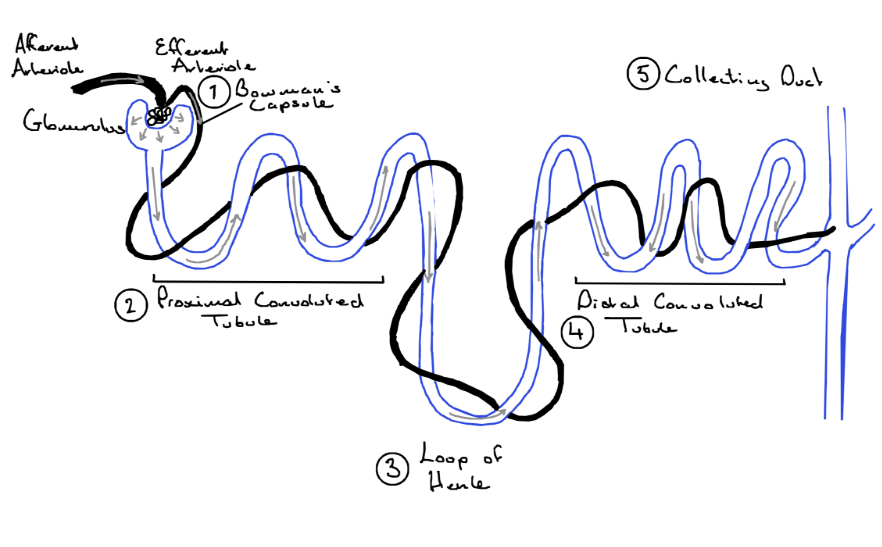
Diagram of the Nephron
What is the name of the blood vessels that supplies the kidneys with blood?
renal arteries
Describe the blood supply to the Nephron:
renal artery divides into arterioles
the afferent arteriole enters the nephron
it divides further to form a cluster capillaries - the glomerulus
the glomerulus is located in Bowman’s capsule
blood leaves the glomerulus through the efferent arteriole
it divides further into capillaries that surround the rest of the nephron
capillaries join up to from venules which leave the kidney via the renal vein
Describe the process of filtration:
blood containing waste enters the glomerulus via the afferent arteriole
due to high pressure, substances like glucose, amino acids, urea, salts and water are forced out of the glomerulus into the nephron
this liquid is glomerular filtrate
bigger substances like rbcs, wbcs, and platelets do not enter glomerular filtrate
How is the glomerulus adapted for efficient filtration?
pressure in the glomerulus is higher than normal blood pressure
there is increased pressure leading into the afferent arteriole
this leads to ultrafiltration
there is a large surface area
walls of the glomerular capillaries are more porous than regular capillaries
Describe the process of reabsorption:
Stage 1 - The Proximal Convoluted Tubule
the majority of water salts and usefule substances are reabsorbed
water is reabsorbed by osmosis
salts and other substances are reabsorbed by diffusion and active transport
Stage 2 - Descending Limb of the Loop of Henle
more permeable to water
water is reabsorbed
Stage 3 - Ascending Limb of the Loop of Henle
more permeable to salt
salt moves out from the nephron into the medulla of the kidney
by diffusion at bottom of the ascending limb
by active transport at the top of the ascending limb
the increase in salt concentration helps remove water from the descending limb and collecting duct
Stage 4 - The Distal Convoluted Tubule
precisely controls the concentration of water and salt, and pH levels
Stage 5 - The Collecting Duct
permeable to water, allows a small amount to be reabsorbed
liquid passing through is urine, and it moves through the ureters into the bladder
How is the proximal convoluted tubule adapted for its purpose?
it’s long
it is one cell thick/thin
it has numerous infoldings to increase surface area
high concentration of mitochondria provide energy for active transport
Describe Secretion
Hydrogen ions and potassium ions are secreted in the distal tubule to maintain blood pH
What is the difference between glomerular filtrate and urine?
glomerular filtrate has more water than urine
glomerular filtrate has useful substances like glucose and amino acids - urine does not
What does ADH stand for + what is another name for it?
ADH - Anti-Diuretic hormone
Vasopressin