Species Diversity: Biodiversity
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
SBI3U (Secours) ~ Hyperdoc #1 + cladograms
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Biodiversity
the natural diversity or variation of living organisms
Sustainable Development
development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own
3 main levels of biodiversity
Specific Diversity
Genetic Diversity
Ecosystem Diversity
Specific Diversity
variety that exists in the different species found in a given area
Genetic Diversity
variety that exists at the level of alleles, entire genes, or chromosomal structure within species
Ecosystem Diversity
variety that exists in physical environments and biotic communities in an ecosystem
Around ______ species are discovered every year
10 000
Ecoservices
the benefits that sustainable ecosystems provide to the organisms that live in them are linked to ecosystem diversity
ex: pollination, pest control, waste management
Anthropocene
term that describes a geological period during which humans caused the majority of planetary changes
⇨ believed to be the next great extinction
LUCA
“Last universal common ancestor”, the original unicellular ancestor that all living things evolved from
Macroevolution
large-scale evolution that can lead to the appearance of new species
3 domains of life
Eubacteria
Archaea
Eukarya
Species biodiversity
Biodiversity is linked to the # of species on Earth
more unique species = less competition
individuals adapt to specific ecological niches
Why is biodiversity in danger?
climate change and human impacts on the environment such as noise and pollution
Why is it difficult to accurately describe a species?
☆ Individuals of different species can be very similar
ex: DNA of orcas shows that they are 3 distinct species
☆ Individuals of the same species can be variable
ex: male vs female, or different stages of life
Phylogeny
the history of the evolution of a species and their relationships
Why is phylogeny useful?
It helps determine common ancestors, or which organisms are most related to each other
Phylogenetic System
classifies organisms on the basis of ancestral relations
Phenetic System
classifies organisms on the basis of morphological similarity (form/shape)
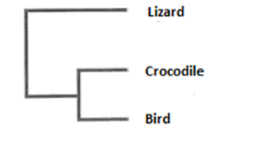
Name the type of system of classification
phylogenetic
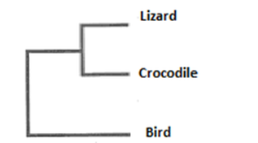
Name the type of system of classification
phenetic system
Taxonomy
a branch of biology which aims to identify, name, and classify species according to their natural characteristics
Carl Linnaeus
the father of taxonomy
created the first classification system
grouped organisms based on homologous characteristics (similarities from common ancestors)
grouped species into levels, called taxa
Taxa
a group that refers to organisms
⇨ ex: the order Rodents, or the phylum Chordata
The 8 taxa
Domain
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
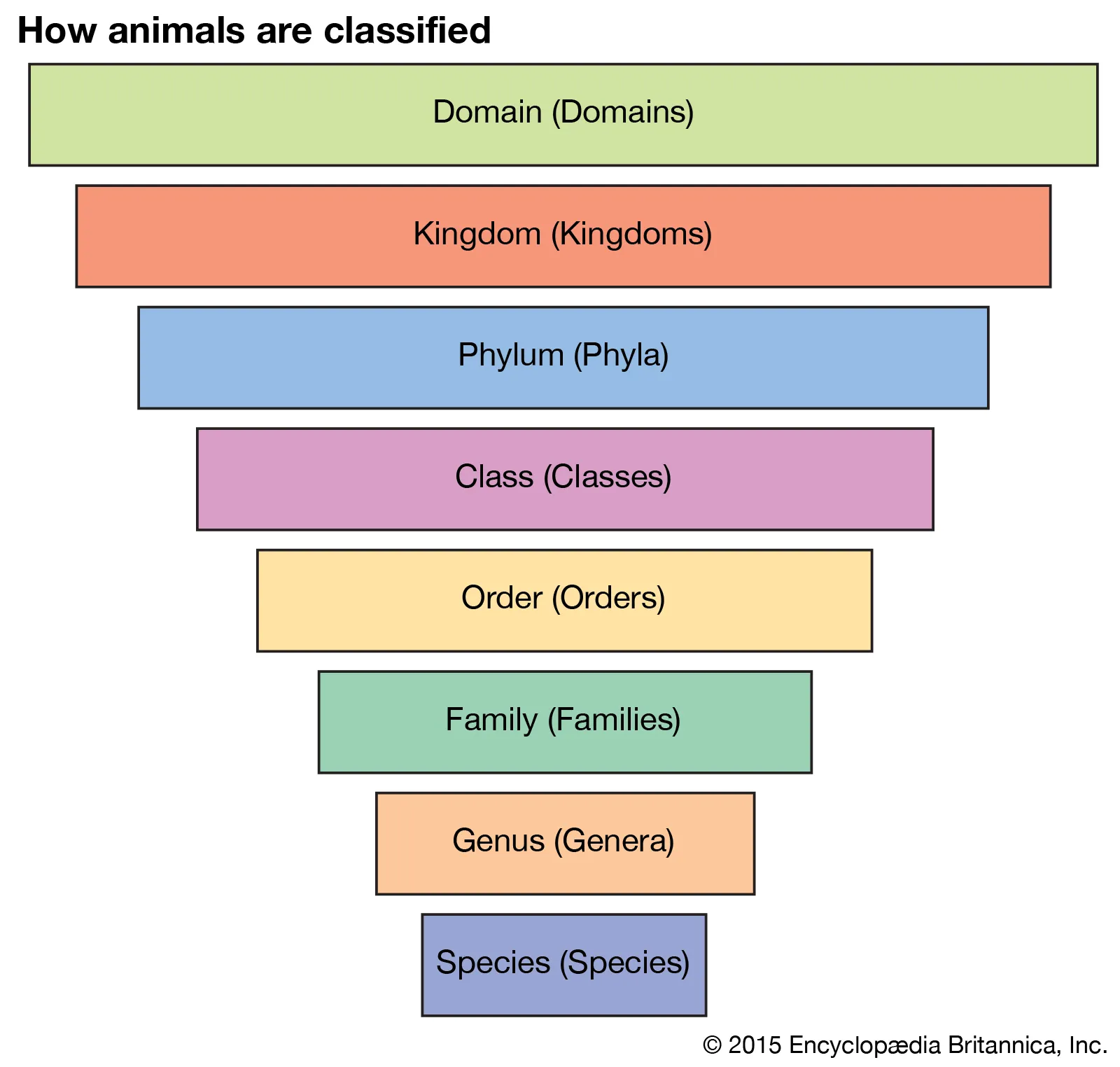
🐆 Example of the 8 taxa: LEOPARD (Panthera pardus)
D: Eukarya
K: Animalia
P: Chordata
C: Mammalia
O: Carnivora
F: Felidae
G: Panthera
S: Pardus
The 6 kingdoms of life
Animals (Animalia)
Plants (Plantae)
Fungi
Protists (Protista)
Archaea
Bacteria (Eubacteria)
Binomial Nomenclature
A system of naming plants & animals where each species is given an italicized name consisting of 2 terms:
genus (capitalized)
species
Biological names show relationships, so species with the _____ genus name are _____ related
same, closely
Dichotomous Key
an identification tool which consists of a series of binary choices which guide towards the identification of organisms
Autotroph vs Heterotroph
An autotroph is an organism that produces its own food, while a hetertroph consumes other organisms
Why doesn’t the Protista kingdom represent a phylogenic group?
they are a paraphyletic group, meaning they exclude certain eukaryotic organisms that share a common ancestor with them, and are spread across several eukaryotic supergroups.
Cladistics
classification based on common ancestry
Cladograms
diagrams that are constructed using morphological evidence, classification based on derived traits
species are placed in order that they descended from common ancestor
☆ a type of phylogenetic tree
Derived trait
a characteristic that evolved within one group but not another
☆ represented on a cladogram as hash marks or dots
Closely related species share more ______ _____
derived traits
Ancestral/Primitive trait
a characteristic that evolved in a common ancestor
Clade
a group of species that shares a common ancestor
☆ will form a triangle shape on the cladogram
Why are cladograms useful?
by looking at the shared, derived characteristics, we can use them to infer evolutionary relationships
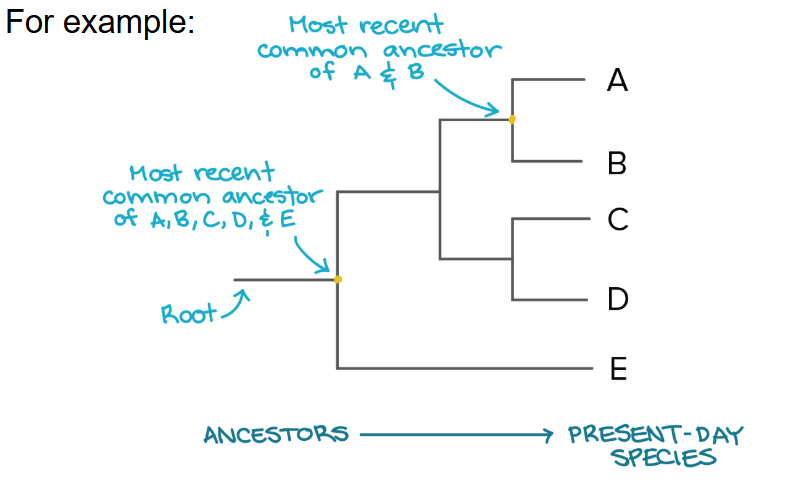
At each branch point lies the ____ ______ common ancestor of all the groups descended from that branch point
most recent
The y-axis of a cladogram represents ____
time
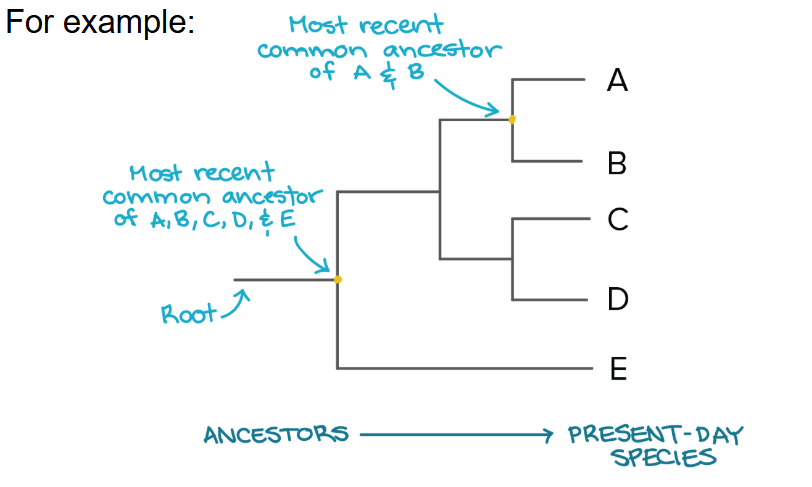
If one species’ line is ______ than the rest on a cladogram, that species is _____
shorter, extinct
when looking at an organism on a cladogram, the organisms to the ____ of it are more related to it than the ones on the _____
right, left
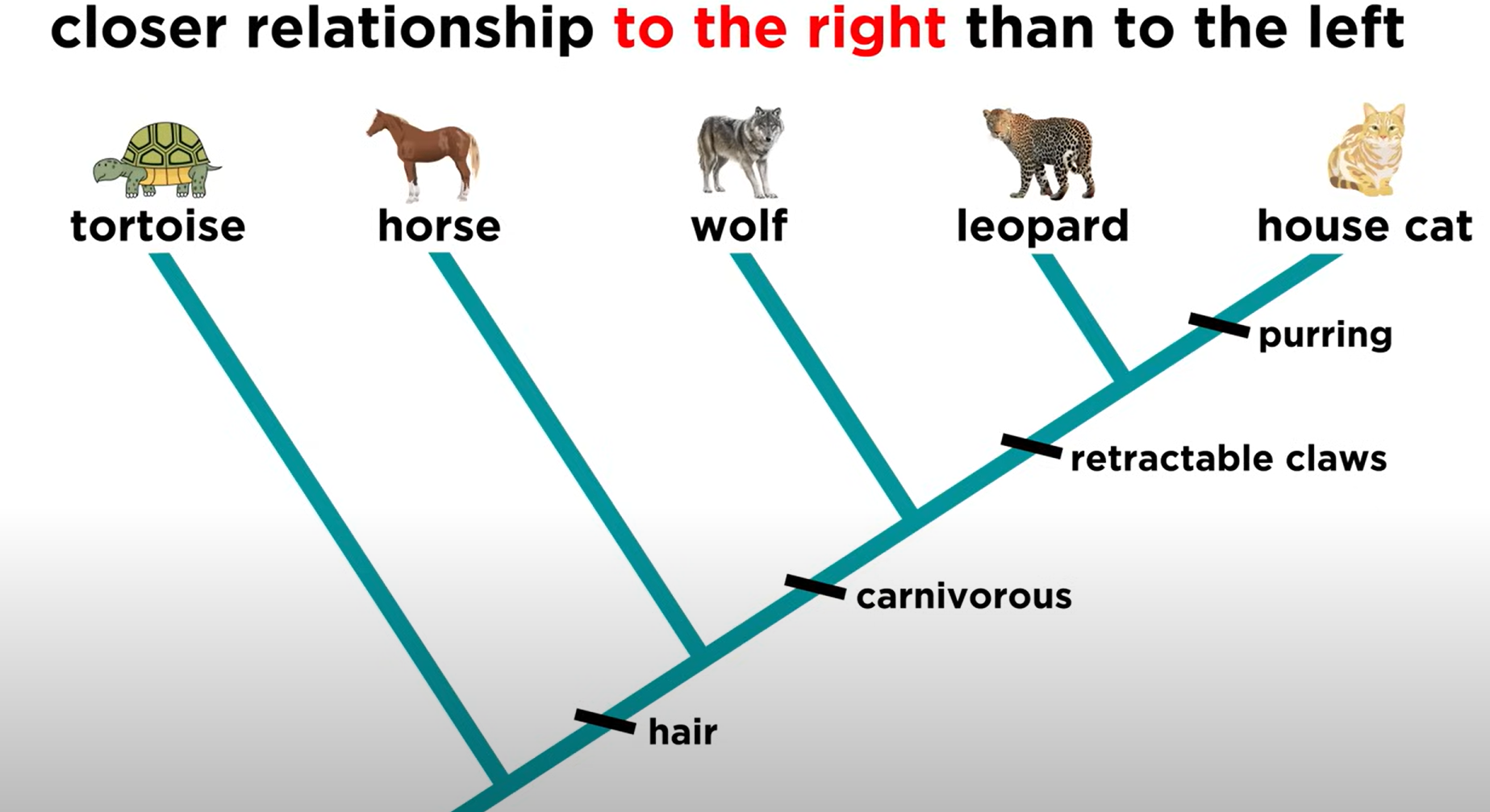
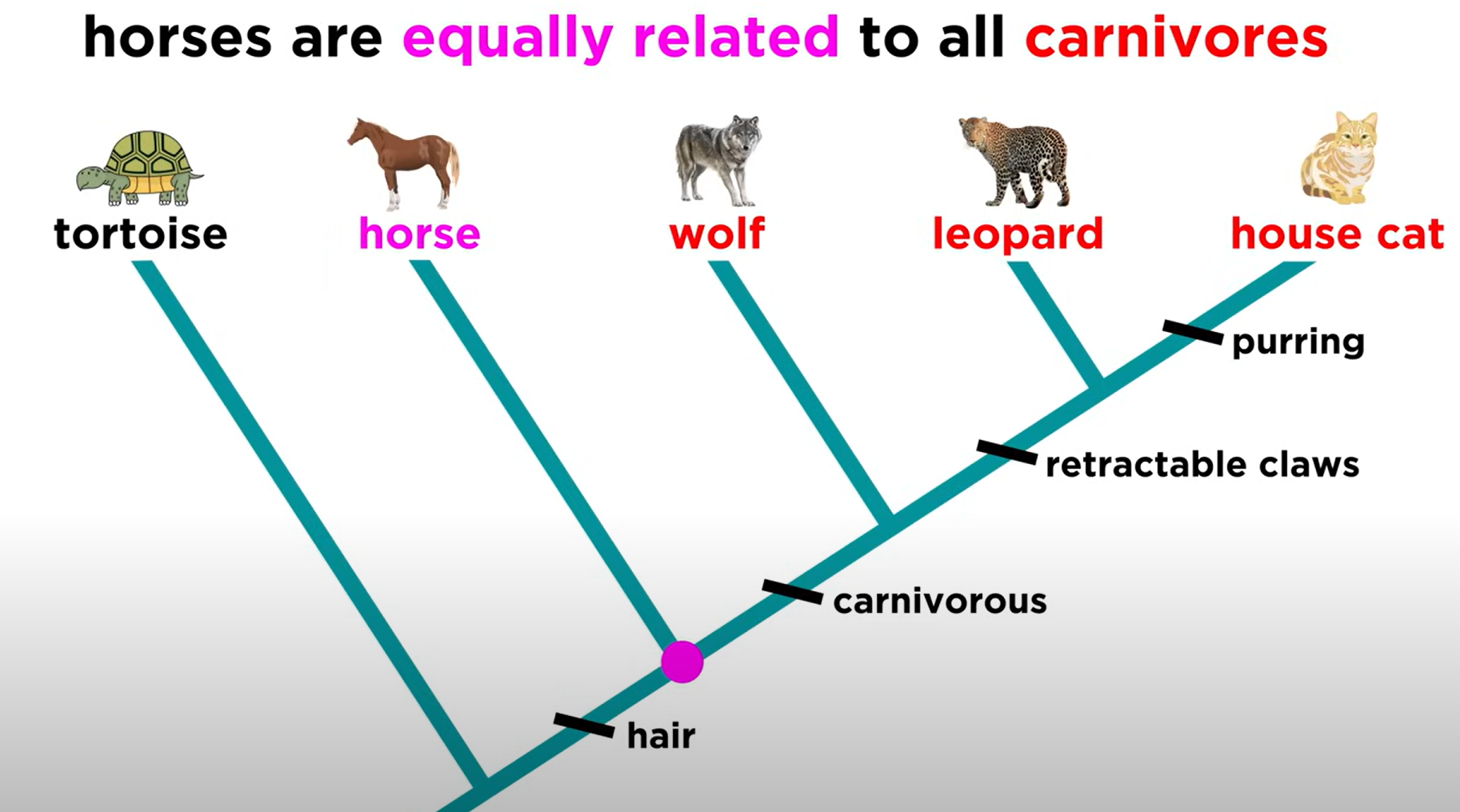
when looking at an organism on a cladogram, all organisms to the ____ of it are ____ as related to it
right, equally
🐸 provide an example of an adaptation that has made a particular species successful (multiple possible answers)
Tree frogs secrete a wax so they can stay in direct sunshine, unlike other frogs