NSU- Anesthesia ECG Quiz 6
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Conduction block
Any obstruction or delay of the flow of electricity along the normal conduction pathways
Sinus node exit block, AV blocks, and bundle branch blocks
What are the three main types of conduction blocks?
1st degree AV block
Characterized by a delay in conduction at the AV node or sometimes at the bundle of His
-diagnosed by prolonged PR interval >0.2s
-early sign of degenerative disease of conduction system
1st degree AV block
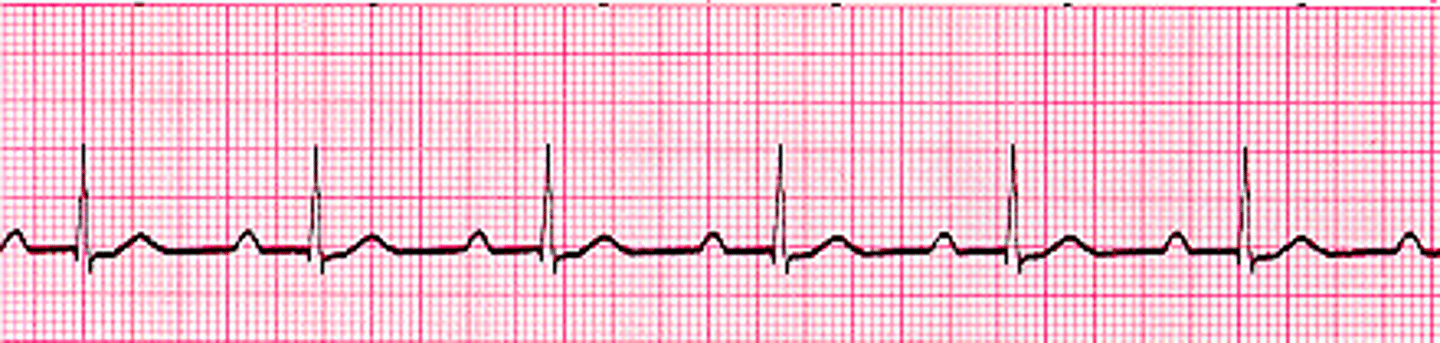
2nd degree AV block
Characterized by dropped ventricular beats
-consistent distance from P to P wave because sinus node is firing normally
-2 types: Mobitz type I and II
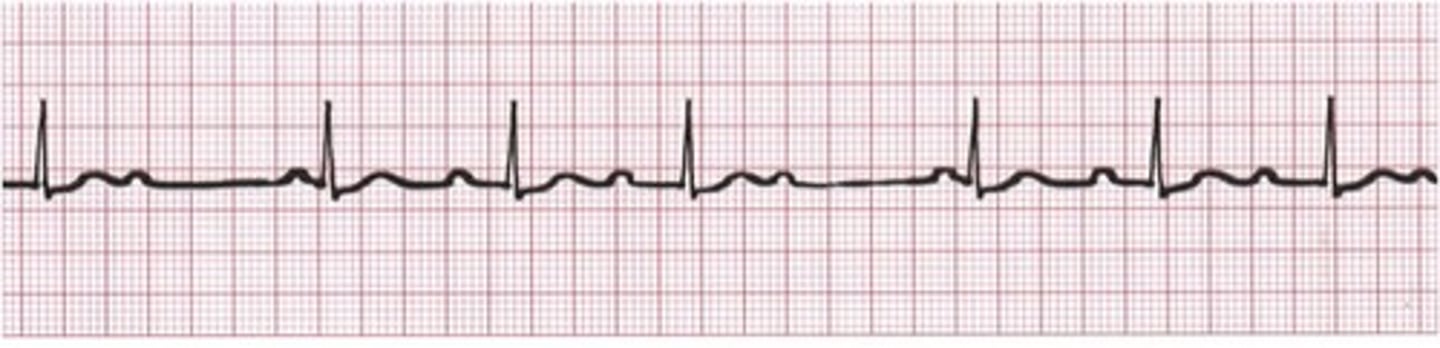
2nd degree AV block: Mobitz type I Wenckebach block
Characterized by variable block within the AV node, increasing with each impulse
-each successive atrial impulse encounters a longer and longer delay in the AV node until one impulse fails to make it through
-progressive lengthening of PR interval until one QRS is dropped
2nd degree AV block: Mobitz type I Wenckebach block
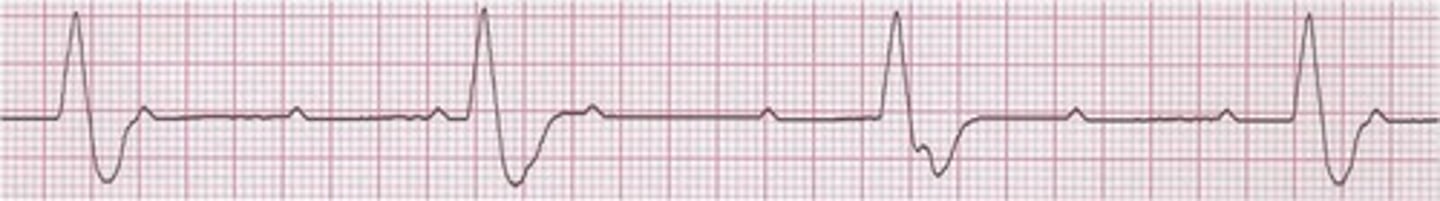
2nd degree AV block: Mobitz type II
Due to a block below the AV node at the Bundle of His
-serious - pacemaker is indicated
-greater risk of evolving to complete heart block
-no progressive lengthening of PR interval
-presence of dropped QRS without progressive lengthening of PR interval
2nd degree AV block: Mobitz type II
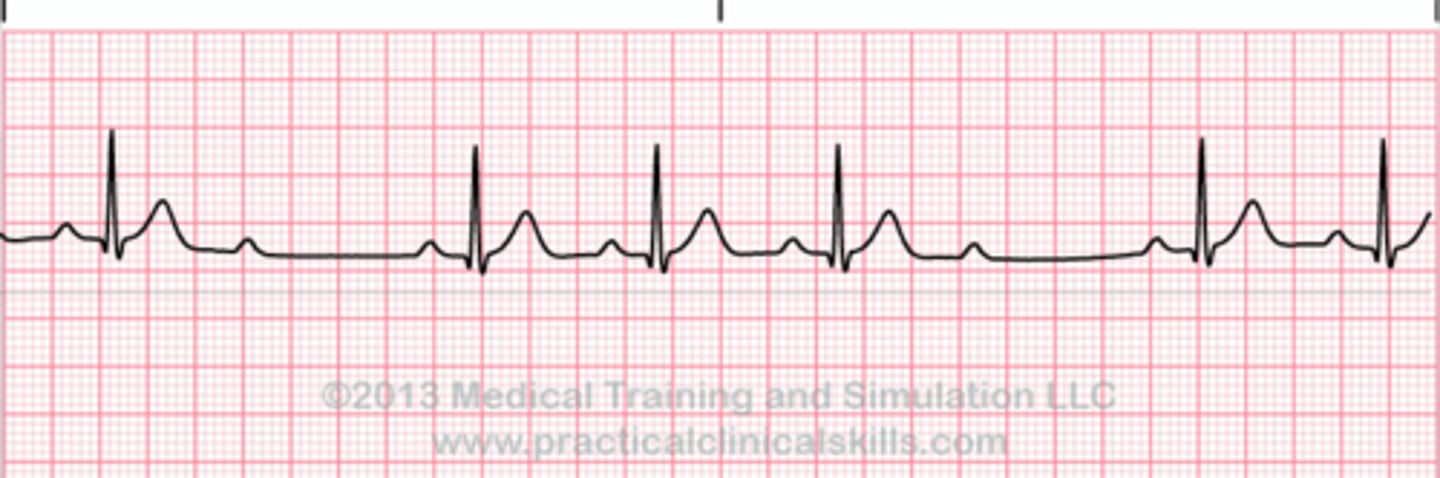
3rd degree AV block: Complete heart block
No atrial impulses are conducted to the ventricles
-atria and ventricles are driven by separate pacemakers (AV dissociation)
-presence of AV dissociation and ventricular rate < Sinus/ atrial node
3rd degree AV block: Complete heart block
First degree
If the R is far from the P, then you have a _____________
Wenckebach
Loner, longer, longer, drop! Then you have a _______
Mobitz II
If some Ps dont get through, then you have _______
Third degree
If Ps and Qs dont agree, then you have a ________
Bundle branch blocks
Conduction block of current flow in either the right or left bundle branches or both
-diagnosed by looking at width, axis, and configuration of the QRS complexes
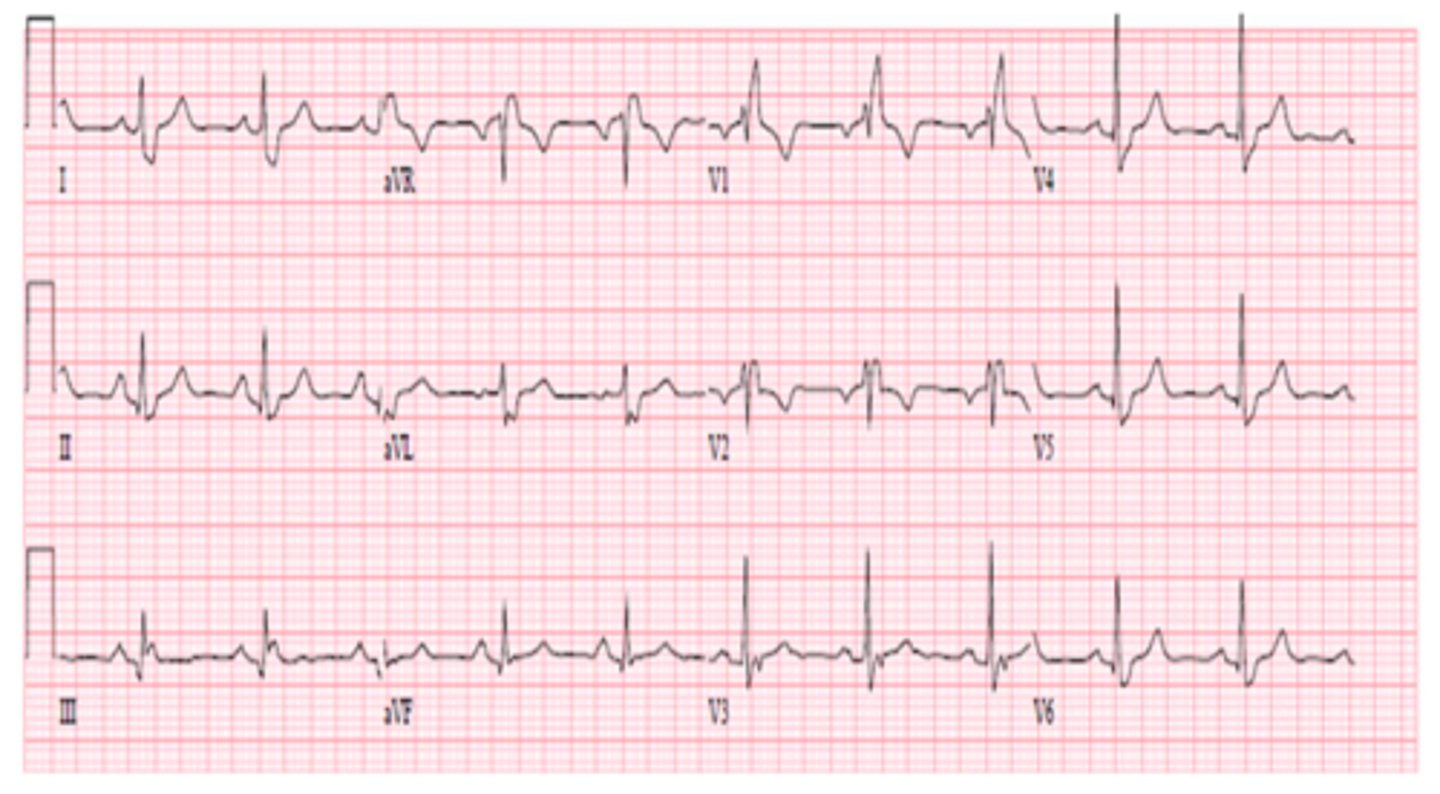
Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
-slower depolarization of RV--> wide QRS
-characteristic RSR' (rabbit ears) in V1 and V2
-R' is due to the delayed RV depolarization
-Late RV depolarization causes reciprocal wide/ deep S waves (looks like W) in L lateral leads
Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
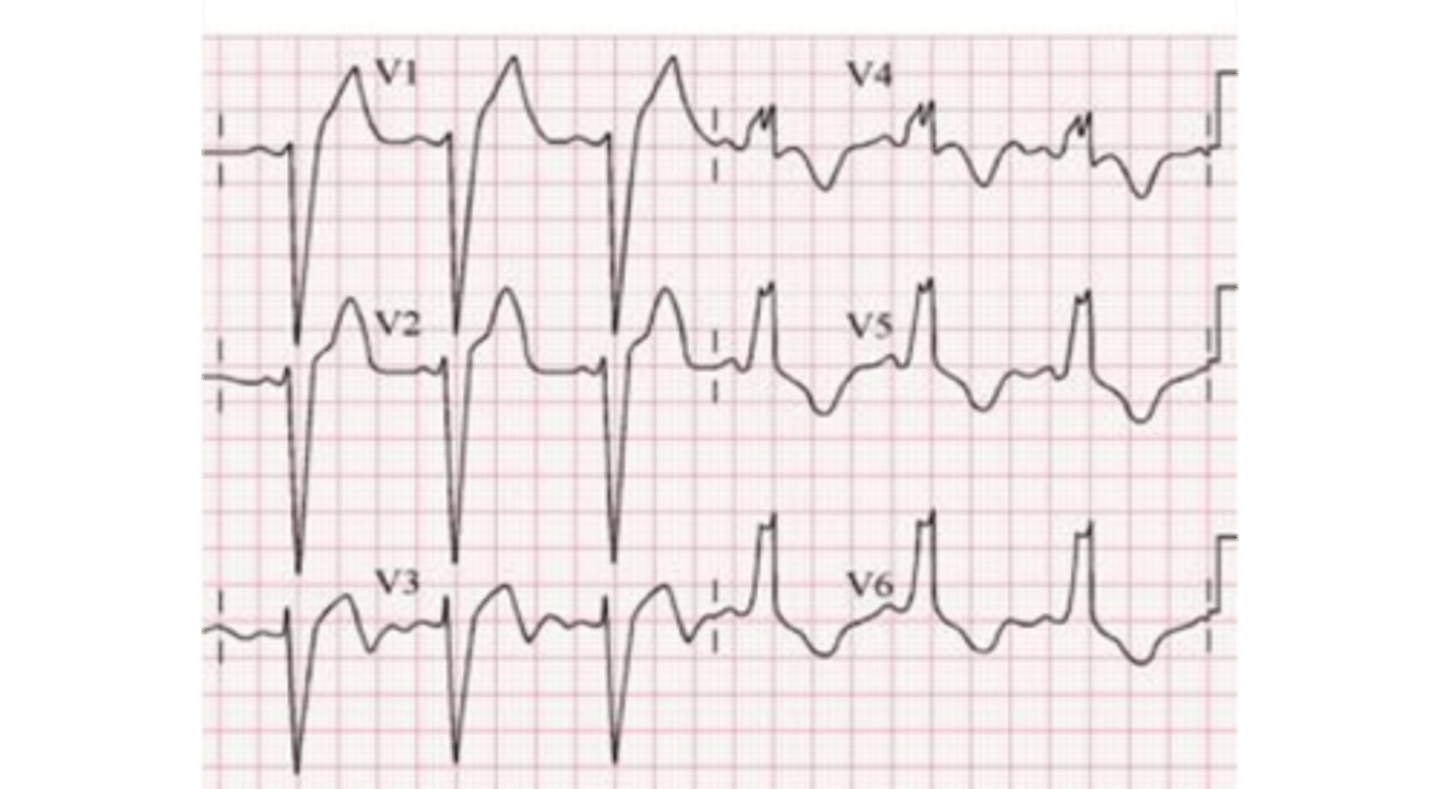
Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
-delayed depolarization of LV--> wide QRS
-wide/ notched R waves in lateral leads
-looks like an M
-NO Q WAVES
-reciprocal wide/ deep S waves in V1 and V2
Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
Left bundle branch block (LBBB)
W in V1 and M in V6
Right bundle branch block (RBBB)
M in V1 and W in V6
Hemiblock (incomplete LBBB)
DOES NOT PROLONG THE QRS
-only causes axis deviation
-only diagnosed in the absence of other causes of axis deviation
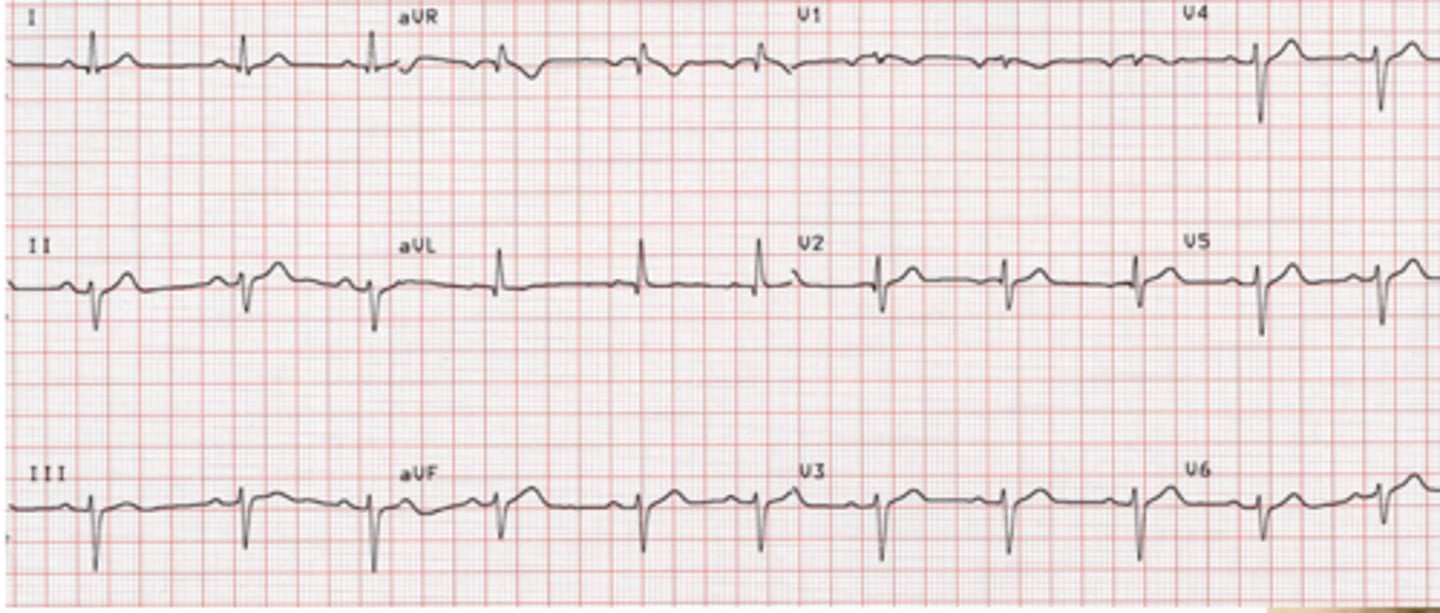
Left anterior hemiblock
-all current goes down the posterior fascicle
-left axis deviation between -30 and -90 degrees (without other causes of LAD)
-Tall R waves in the L lateral leads
-Deep S waves in inferior leads
Left anterior hemiblock
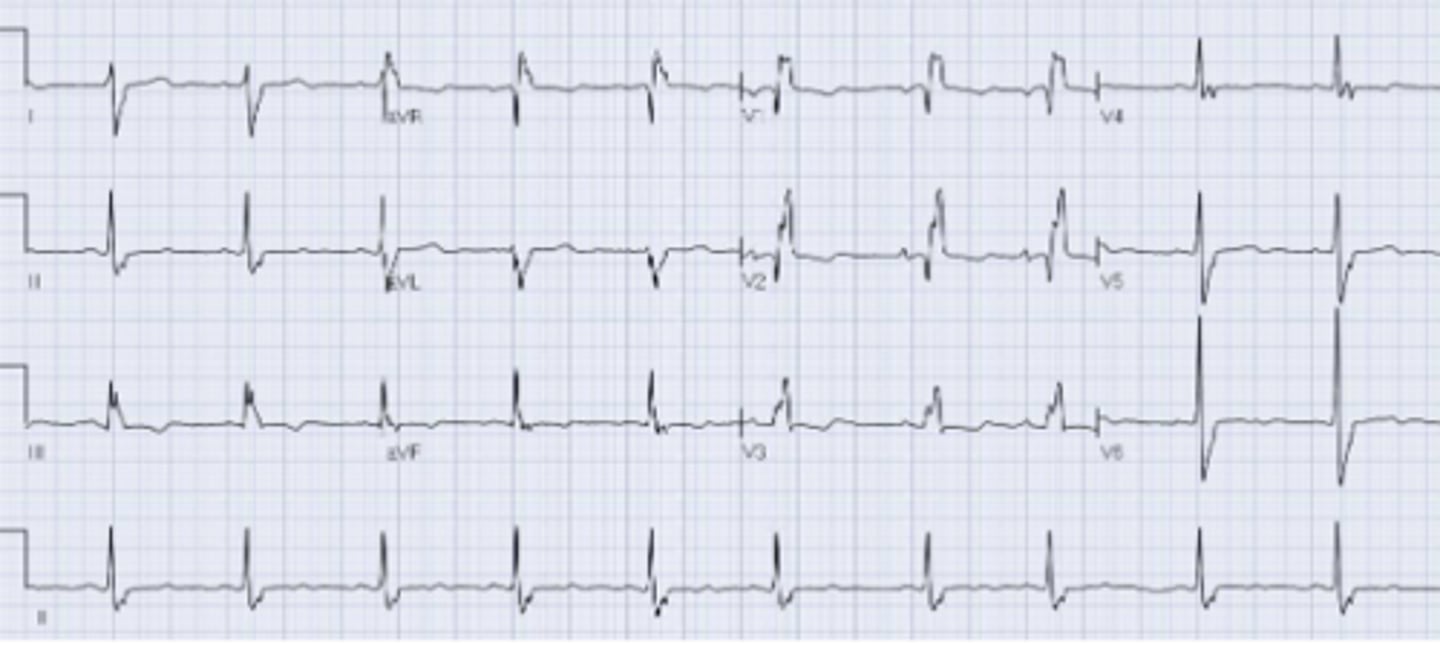
Left posterior hemiblock
-all current goes down the anterior fascicle
-right axis deviation +90 to +180 degrees (without other causes of RAD)
-Deep A waves in the L lateral leads
-Tall R waves in the inferior leads
Left posterior hemiblock
RBBB + anterior hemiblock
-wide QRS
-RSR' in V1 and V2
-LAD -30 to -90
RBBB + posterior hemiblock
-wide QRS
-RSR' V1 and V2
-RAD
Pacemakers
Used for:
-3rd degree AV block
-development of combinations of AV block and BBB during MI
-recurrent ventricular tachycardias
Demand pacemakers
Most popular, fires when HR falls below a set threshold
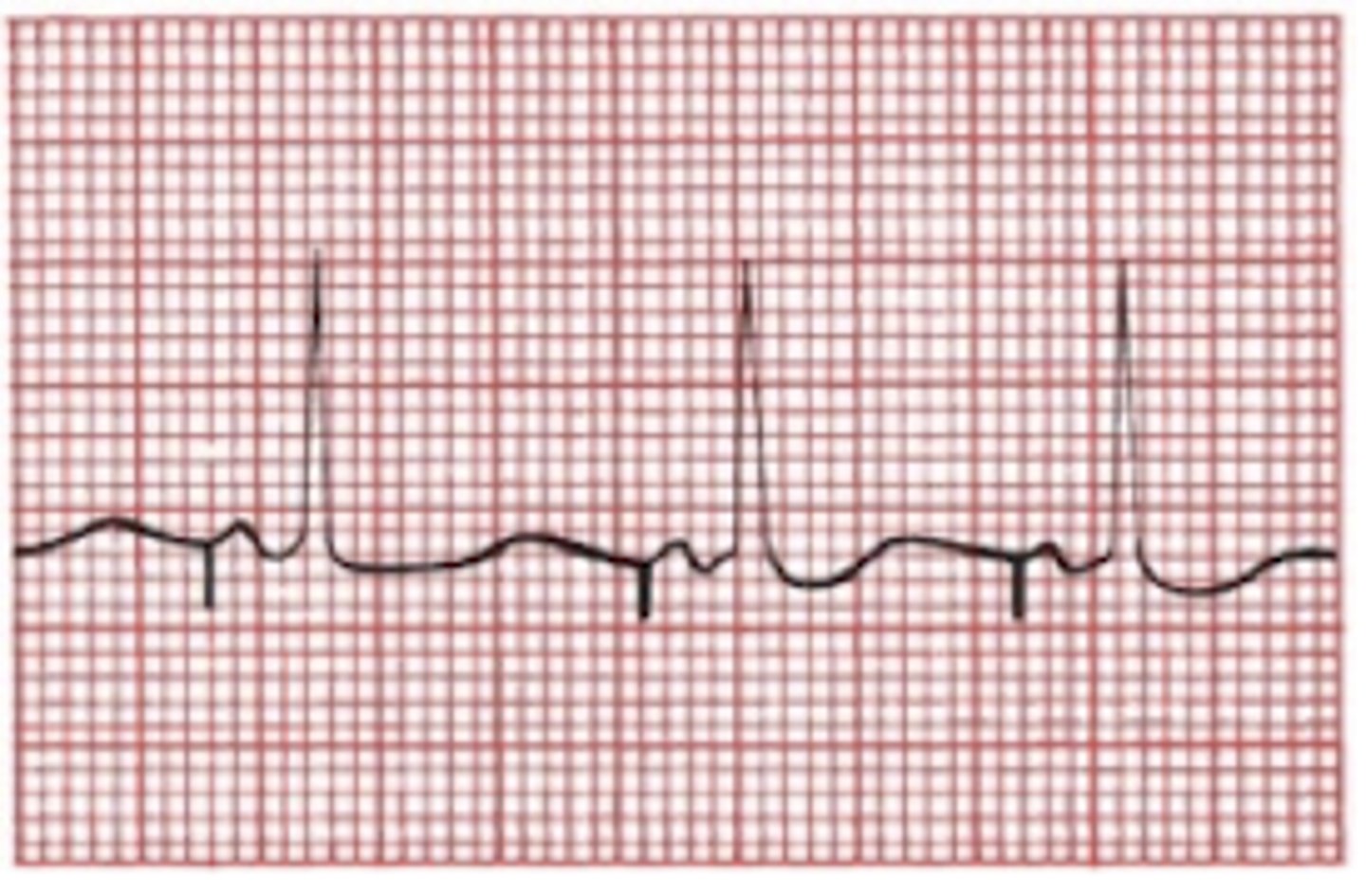
Pacemaker electrode placed in single chamber, right atrium
-spike followed by a P wave, normal PRI, normal QRS
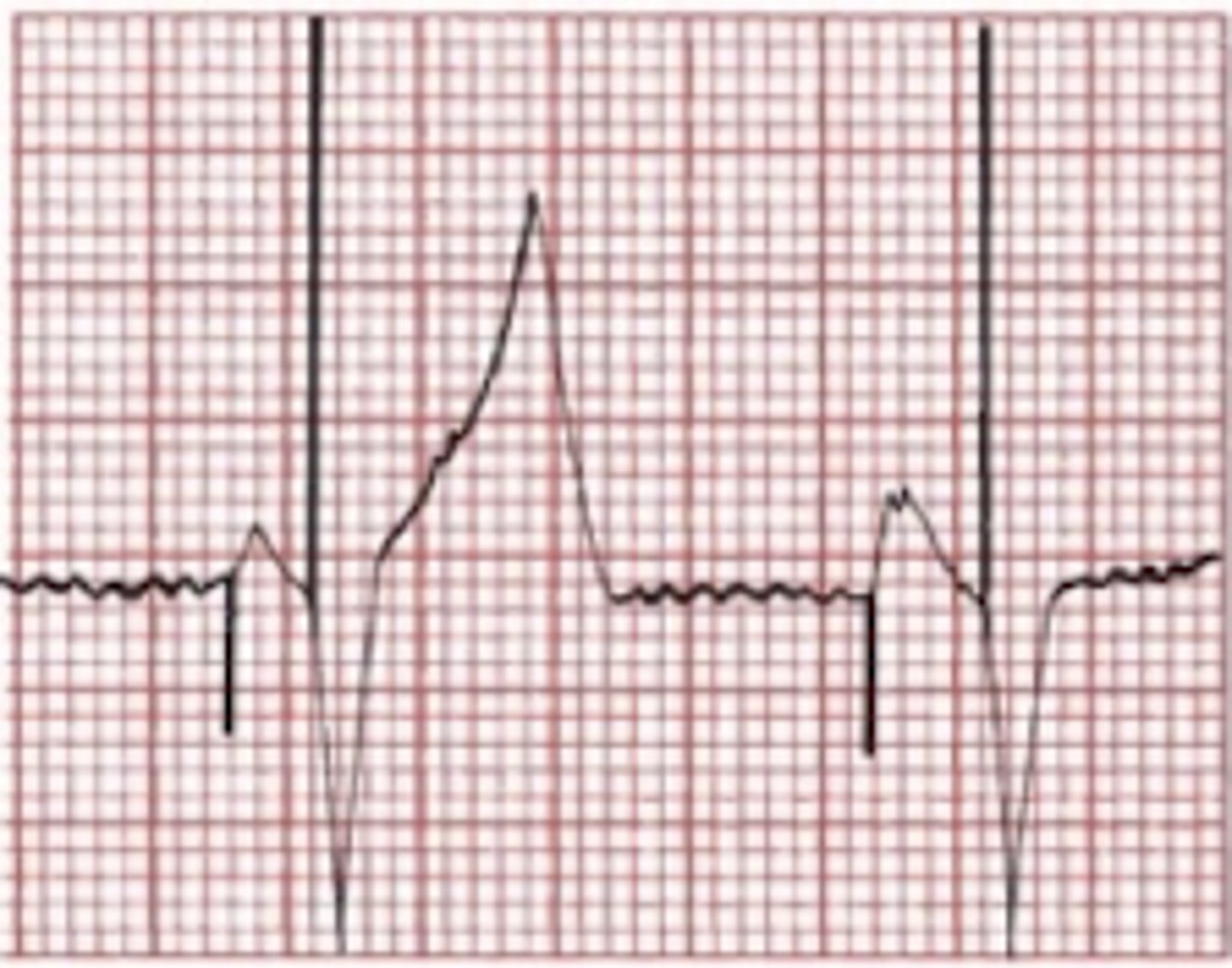
Pacemaker electrodes placed in two chambers, right atrium and ventricle
-spike followed by P wave
-spike followed by wide/ bizarre QRS like LBBB
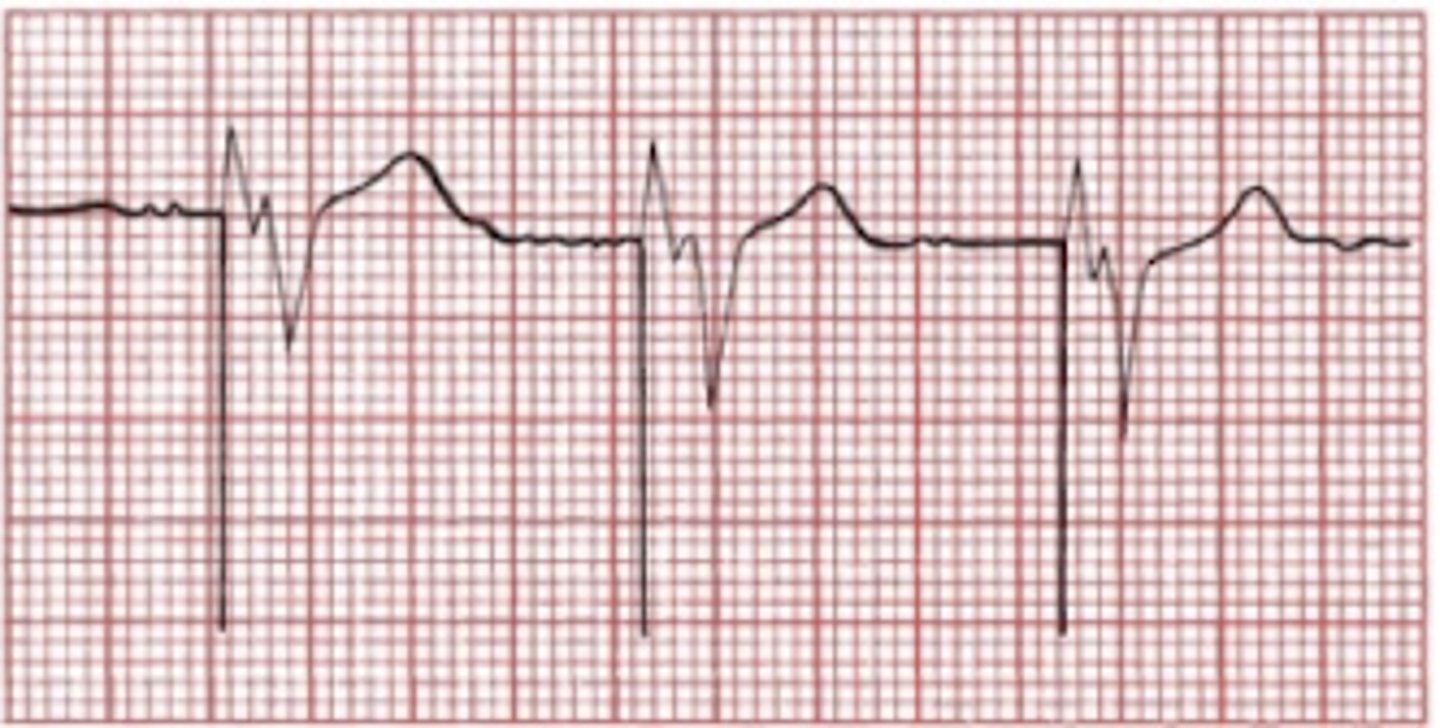
Pacemaker electrode placed in single chamber, right ventricle
-no P wave
-spike followed by wide/ bizarre QRS like LBBB
Risks of pacemakers
-infection/ bleeding
-inducing Vtach or Vfib
-precipitating heart failure
Biventricular pacemakers
Can improve EF and reduce symptoms of heart failure
-used for patients with reduced LV function and/or native LBBB
Bundle branch blocks
Wide QRSs